Hidden
Persuasion
Media & Communication - Lecture week 5
Johannes de Boer
Last week
- Self-persuasion
- Promised land
- Attractiveness
- Decoy
This week
- Mere exposure
- Anthropomorphism
- Loss or gain
- God terms
Topics
What to learn?
- Information from the slides
- Discussed topics from the book "Hidden Persuasion"
- See Blackboard for PDF.
- Dutch translation of key topics available on Blackboard
Mere Exposure
The more we see it, the more we like it
- What do you think about Coca Cola?
- Write down 3 associations with this brand.

How it works
- Neutral or positive things are perceived as more positive when repeated.
- Caused by increased feeling of familiarity
- Valid for all visual stimuli (products and people)
- Flood exposure
- Works even if there is no existing connection
Definition
Note
- The first 10-20 exposures are most important
- Each additional exposure has a reduced impact
- Each additional exposure has a reduced impact
- Exposures should be brief
- With sufficient delay
- To prevent overexposure
Product Placement
I'm moving to Johannesburg!
Let's try!
You need a pen + paper

REMEMBER
Which face correspondents with which name
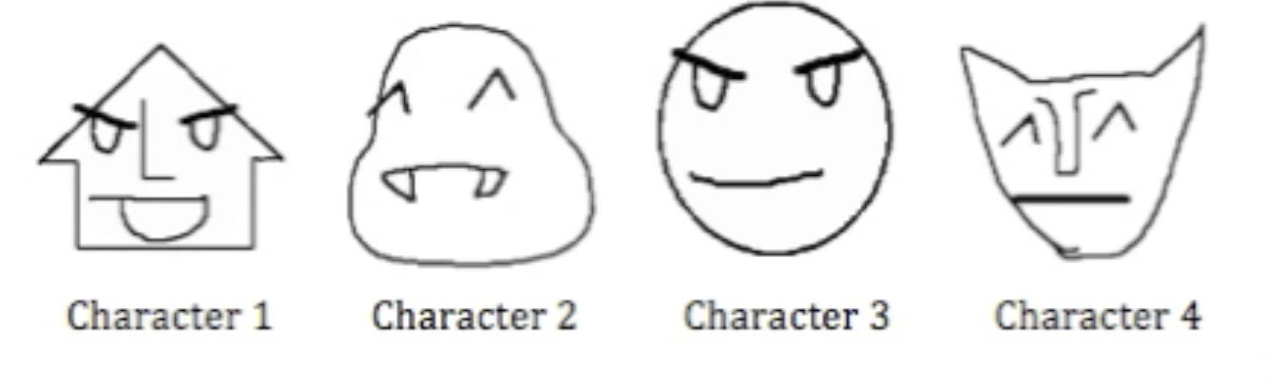
RECALL
Write down the name of each character

How many correct?

Draw your preferred characters
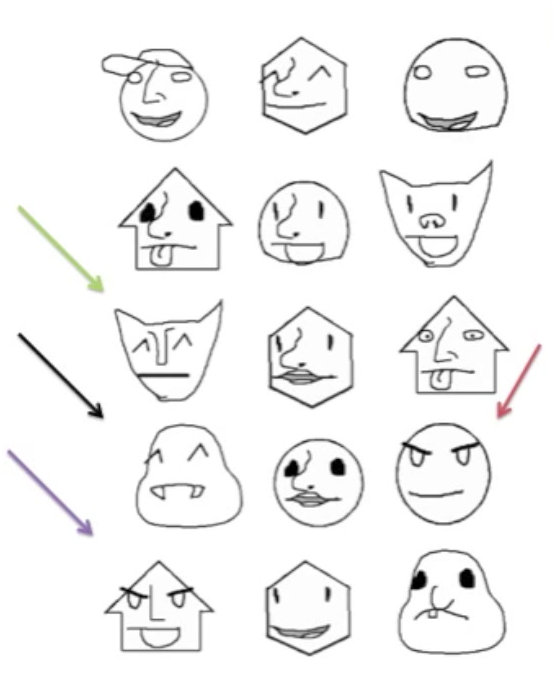
How many of these do you prefer?
Anthropomorphism
When a brand or product is seen as human-like,
people will like it more and feel closer to it.
What do you see?
- Scenario
- Characters
- Emotions

Definition
The tendency to describe and visualise animals or non-living things using human characteristics.
Humans try to explain many events with Anthropo-morphism (forces of nature, behaviour of animals) by ascribing thoughts, needs, or intentionality to these events as if they were human.
Kids
We use it when we're little: stuffed animal, pets.
Feeling pity for Nemo
History

We keep using it.
Our brain continues to try to see things as human-like.
It makes us bond with objects. It makes it see more like us!
Growing old
Futuristic Anthropomorphism?
When did you use it
in your work?
Loss or gain
Should the glass be half full or half empty? Fearing loss increases risk-taking: expecting gains increases safety behaviour
Loss vs Gain Framing
"Healthy lifestyles" campaigns are often framed negative.
The effect is dependent on conscious processing of the image.
Everything else being equal: People opt for certainty.
Certainty effect
the certainty effect happens when people overweight outcomes that are considered certain relative to outcomes that are merely possible
- Li & Chapman (2009)
A
The FIRST Gamble is 61% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 39% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 63% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 37% chance of winning 0.
A
The FIRST Gamble is 98% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 2% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 100% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 0% chance of winning 0.

A
The FIRST Gamble is 61% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 39% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 63% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 37% chance of winning 0.

A
The FIRST Gamble is 98% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 2% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 100% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 0% chance of winning 0.

Both changes increased 37%
Certainty effect
happened
Situation 1 : both gambles risky
Most people prefer higher outcome
Situation 2 : Smaller outcome becomes certain
Most people prefer sure thing over risky option
Certainty effect
People are drawn to certainty, giving higher preference to options that have high levels of certainty.
Often leads to risk/loss aversion
Loss aversion
Loss aversion
People are 2x more sensitive for feelings of los, than to feelings of gain.
Once in a loss situation, we do everything to avoid it.
A loss or gain frame needs to be followed up by a clear "how-to" to move someone to act.
God terms
Some words are to intrinsically good,
it is hard to say 'no' to them
Terms people value
Equality
Freedom
Justice
Love
Wonderful
Happiness
Progress
Democracy
Terms people avoid association with
Terrorist
Inequality
Deterioration
Rivalry
Hypocrite
Sadness
Weakness
Incompetent
Let's try!
Note all God terms
(words with positive meaning)
in the speech by MLK.
God Terms Examples
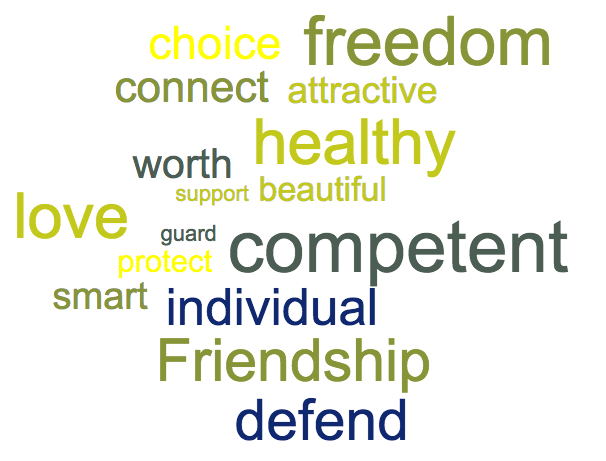
Many words have inherent positive or negative connotations.
They refer to desires,
needs, and fears.


Remarks
God terms & Devil terms play into our needs. Using these words triggers the respective needs in the target.
When God terms are popular for a while, the powers of their use deteriorates
(they can even turn into Devil terms!)
Thank you
Good luck - Prepare well!
MedCom-PT2
By Johannes de Boer
MedCom-PT2
- 449



