Programación para iOS
Bibliografía
- Universidad de Stanford. (http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs193p/cgi-bin/index.php)
- Developer Center (http://developer.apple.com/iphone/library/navigation/index.html
https://github.com/jorgevila/ios-playground
Introducción
iOS
-
Gran curva de aprendizaje
-
Hay que aprender a utilizar Cocoa frameworks (UIKit, etc)
-
También iPhone frameworks
-
Un nuevo IDE: XCode y nuevas herramientas Interface Builder, StoryBoard, Instruments.
-
Lenguajes de programación: Objective C / Swift
-
Diseñar iconos y gráficos específicos para la aplicación.
iOS

Introducción iOS
- Versión reducida de distribución BSD sin shell
- Aplicaciones desarrolladas con Objective-C / Swift
- UI basada en UIKit (obj-C framework)
- Librerías disponibles: cocoa-touch (cocoa for mac)
Objective-C
- Capa desarrollada sobre C
- Utilizada principalmente sobre MAC OS X, iPhone OS, GNUStep Compiled with GCC 4.0 (with objective-C support)
- Desarrollada por NextStep
Entorno

y todo, sólo para Mac

Arquitectura
Cocoa Touch es la base inicial de cualquier proyecto, contiene el framework UIKit

Obj-C librería gráfica
Audio / Vídeo / Animaciones
Librerías para servicios básicos: red, SQL, etc
Librerías para gestión de memoria, threads
Está diseñado para no bajar de nivel en la pila si no es realmente necesario implementar un comportamiento realmente novedoso.
Guía de buenas prácticas
- Reducir complejidad
- Iconos / imágenes adaptadas a cada dispositivo
- Toda apliación debe guardar su estado
- No bloquear la música
- Tiempo se arranque mínimo

Se puede...
Acceder a la cámara
Obtener la posición
Eventos de acelerómetro y movimiento
Acceder al sonido
Guardar datos en el móvil: SQLite DB
Iniciar una llamada
Acceder a los contactos
Utilizar un WebView (HTML/JS)
Background tasks (>iOS7)
Notificaciones
Recursos: cámara
- Se utiliza el UIImagePickerController
- También para seleccionar imágenes de la galería
- Capturar vídeo

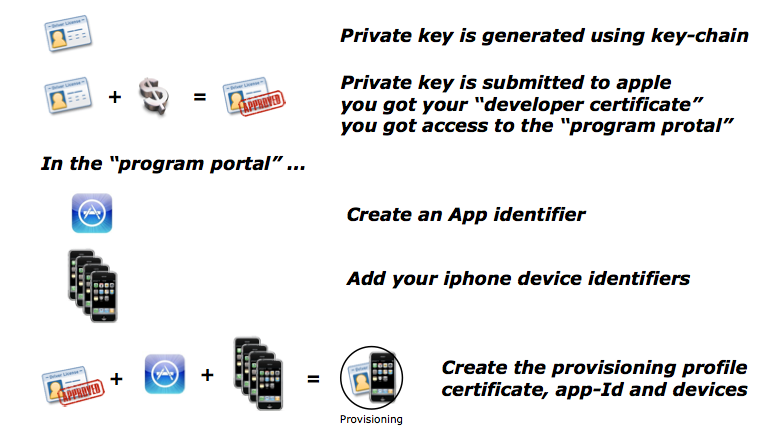
Introducción al esquema de Licencias, AppStore, etc.
Para publicar una App
- Desarrollar Apps es gratuito, publicarlas no.
- Modelos de licencia de desarrollo:
Pública: 99$ - 100 dispositivos TEST y ad-hoc
Privada: 299$ - Entidad de más de 500 empleados
Universitaria: Gratis – 200 dispositivos TEST

¿Y cuanto se puede ganar?
- Si es gratis, nadie saca nada (ni te cobran)
- Puedes poner anuncios con iAd (y sacar beneficio por click)
- Si es de pago el 30% para Apple y el 70% para el desarrollador (-IVA)
- Compras In-App

¿cómo publico una aplicación?
Se utiliza iTunes Connect:
- Establecer usuarios: Admin, técnico, finanzas, etc.
- Firmar Contrato.
- Proveer información de la aplicación: nombre, screenshots, palabras clave, rating, etc.
- Enviar …
- Y rezar para que la aprueben ;)
- en torno a un 10% de rechazos, por cualquier detalle
- Distribution guide
Antes habrá que probarla
Simulador: No es necesaria licencia.
Sistema de instalación Ad-Hoc (Test):
- Se utiliza el iPhone Provisioning Portal.
- Mediante certificados.
- Apple firma la aplicación y así se asegura que no se sobrepasa el número de dispositivos.


Text
Recapitulando: flujo de aplicación
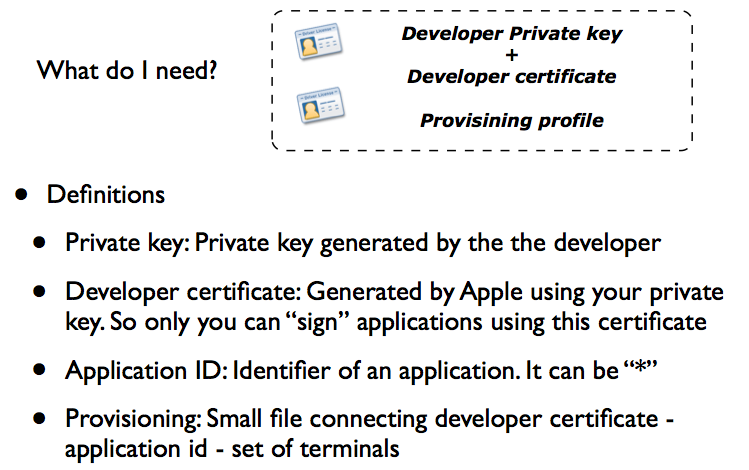
Recap: Qué necesito?
Referencia
Diseño


Estadísticas relevantes
- Lenguaje orientado a objetos
- Sintaxis -supuestamente- clara y simple
- Paso de mensajes entre objetos
- Casi todo definido en runtime
- Cocoa libraries -> GUI
Stepstone->NextStep->Apple
Primitive
Data types
int, short, long
float, double
char
BOOL = boolean (YES|NO)
Punteros
Como en C
&i -> dirección en memoria de la variable i
Puntero:
int *addressofi = &i;
Global y static
global variables definidas al principio del fichero
static variables con el keyword "static"
Conditionals
if / else if / else
for
while
break
continue
do-while
for in loop (Obj-C 2.0)
for(int i=0; i< 22; i++) {
printf(“Checking i=“@d\n”, i);
if(i+90 == i*i)
{
break;
}
}for(Item_Type *item in Collection_of_Items) {
//do whatever with the item
Nslog(@” Looking now at %@”, item);
// %@ converts anything to string
}Funciones
return_type functionName(type v1, type v2, ...)
{
// code of function
}
//Example:
void showMeInfo(int age)
{
printf("you are %d years old", age); // or NSLog()
}
/////////////////////// Function - Pass by reference
return_type functionName(type v1, type *v2, ….)
{
//code of function
}
//Example – call above
int v1 = 2;
int v2 = 3;
functionName(v1, &v2);Main
#import <whatever/what.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
//your code here*******
return 0;
}
}
Automatic Reference Counting %= automatic garbage collection de java
Se acabaron los memory leaks con @autoreleasepool
Text output
printf()
printf(“Hi Lynne”); //this is actual C code
NSLog()
NSLog(@”Hi Lynne”); //this is strictly Objective-C
r
Aquí empieza lo diferente

Objects

Clases: interfaz

Métodos
Java:
public void function(int x, int y, char z) {};
Object.function(x, y, z);
Objective C:
-(void) method:(int)x, (int)y, (char)z;
[Object function:x, y, z];
// aplicar function al objeto Object con los parámetros x,y,z
- (int) multiplyThis:(int) x ByThis:(int) y AndThis:(int) z;
Method name is multiplyThis:ByThis:AndThis
Métodos: +,-
Los métodos se declaran con + o -
+ -> "class method" , como métodos estáticos de java
- -> "instance methods", métodos públicos en una instancia de clase/objeto
Properties
Para declarar setter/getter de variables
// Person.h
@interface Person : NSObject{
//don’t need to declare the variables here
// ---they are done with @property}
@property float heightInMeters; //will create setter and getter method for this var
@property float weightInKilos; //will create setter and getter method for this var
- (float) bodyMassIndex; //instance method
@end
// Person.m
#import “Person.h”
@implementation Person
@synthesize heightInMeters, weightInKilos;
- (float) bodyMassIndex
{ return weightInKilos / (heightInMeters * heightInMeters); }
Properties
@property (nonatomic) <type> <property name>
@property (strong or weak) <type which is a pointer to an object> <property name>
@property (getter=<getter name>) ...
@property (readonly) ... & @property (readwrite) ...
@synthesize <prop name> = _<prop name> (only if you implement both setter and getter)
Clases: Implementación

Clases: instancia
ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] init];
ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] initWith* ];
NSString* myString = [[NSString alloc] init];
alloc -> reserva memoria e instancia el objeto.
init -> inicializa valores en el nuevo objeto.
Algunas clases crean un método específico de inicialización.
ClassName *object = [ClassName method_to_create];
NSString* myString = [NSString string];
Clases: instancia
A partir de otros objetos
NSString’s - (NSString *)stringByAppendingString:(NSString *)otherString;
NSString’s & NSArray’s - (id)mutableCopy;
NSArray’s - (NSString *)componentsJoinedByString:(NSString *)separator;
Using class methods to create objects
NSString’s + (id)stringWithFormat:(NSString *)format, ...
UIButton’s + (id)buttonWithType:(UIButtonType)buttonType;
NSMutableArray’s + (id)arrayWithCapacity:(int)count;
NSArray’s + (id)arrayWithObject:(id)anObject;
Destroying a class object = nil; // null
Clases: self
self == this
//some code inside a method of a class
//method class to getter for the variable heightInMeters
float h = [self heightInMeters];
//another example a method in a class that adds itself (object) to an array that is //passed
-(void) addYourselfToArrayLNSMutableArray *) theArray
{ [theArray addObject:self]; }
Mensajes

Mensajes

Memoria:
alloc - release

init - dealloc

init - dealloc

Ciclo de vida de un objeto

Ciclo de vida completo

Cada referencia a un objeto incrementa el contador en memoria, y no se libera mientras exista una referencia.
alloc - release

alloc - release
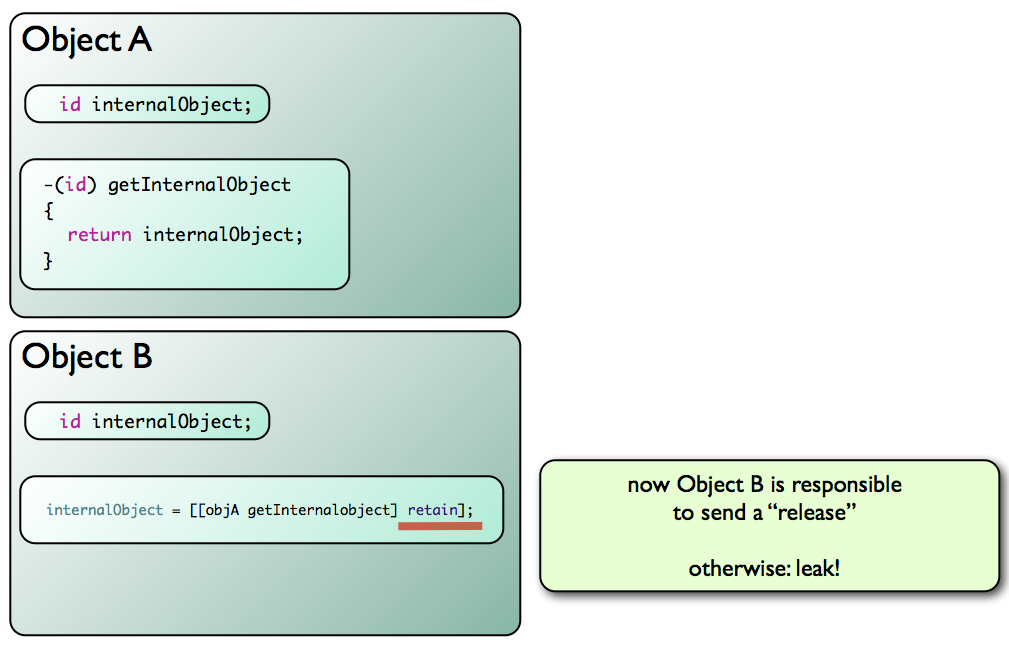
Memory Leak
- Si hacemos "alloc" o "retain" mantenemos una referencia al objeto, si no es "weak".
- Si mantienes un objeto, nadie puede liberarlo de memoria mientras no hagamos release
- Para todo "alloc" o "retain" debemos enviar un "release", o tenemos un memory leak
Introspección
Todo objeto que hereda de NSObject:
isKindOfClass: herencia
isMemberOfClass: tipo de clase de objeto, no herencia
Obtener una clase es un método de clase: if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {}
respondsToSelector: devuelve si un objeto responde a un método.
Directiva @selector() (SEL)
if ([obj respondsToSelector:@selector(shoot)]) { [obj shoot]; }
Arrays
- NSArray/NSMutableArray contiene un número fijo/variable de objetos
- El array mantiene siempre una referencia a sus elementos, de manera que evita que sean liberados de memoria
//Init the mutable array with an initial capacity of 5 elements
NSMutableArray* array = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithCapacity:5];
//Init a UIView element
UIView* myView = [[UIView alloc] init];
//Add the new view to the array
[array addObject:myView]; // myView has received here a "retain" message
//Release the object (no automatic deallocation because array keeps the ownership)
[myView release];
@[@“a”,@“b”] == [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:@“a”,@“b”,nil].
myArray[index] == [myArray objectAtIndex:index].setMethod

setMethod

copy - autorelease

DataTypes
NSInteger number;
NSUInteger unsignedNumber
NSString
Usado en iOS en vez de char* type
NSString *theMessage = @"hola";
NSUInteger charCount= [theMessage length];
if([string_1 isEqual: string_2]) { // equal strings }
NSInteger
Strings con @
@”Hello World”;
NSString *myString = @”Hello World”;
int len = [myString length];
int len = [@”Hello World” length];
NSString *myString = [[NSString alloc] initWithString:@”Hello World”];
int len = [myString length];
// Formatting output with NSLog
int a = 1;
float b = 33.22;
char c = ‘A’;
NSLog(@”Integer %d Float: %f Char: %c”, a, b, c);NSString inmutable
NSString es inmutable. Normalmente las funciones envían un mensaje a un NSString que devuelve un NSString nuevo.
self.display.text = [self.display.text stringByAppendingString:digit];
NSMutableString
Versión de NSString modificable para realizar modificaciones sin crear un nuevo objeto
Más tipos
- NSValue: wrapper para otros tipos como structs de C
- NSData: almacén de datos en binario
- NSDate: NSDateFormatter, NSDateComponents, ...
- NSNumber: wrapper para int, float, double, BOOL, enum. NSNumber *three = @3; *three = @(3)
NSArray
- array inmutable de punteros a objetos
- count = número de items
- objectAtIndex:i = item i del array (empezando en 0)
NSArray *thearray = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:o1,o2,o3,o4, nil];
//get element
[thearray objectAtIndex:0]; //element at index 0
//Example
NSDate *now = [NSDate date];
NSDate *tomorrow = [now dateByAddingTImeInterval:24.0*60.0*60.0]; //add a day
NSDate *yesterday = [now dateByAddingTimeInterval:-24.0*60.0*60.0]; //minus a day
//array of Dates
NSArray *dateList = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:now, tomorrow, yesterday];
//get elements in array
NSDate *first = [dateList objectAtIndex:0];
NSUInteger dateCount = [dateList count];
for(int i=0; i<dateCount; i++)
{ NSDAte *d = [dateList objectAtIndex:i];
NSLog(@” Date is %@”, d);
}
for(NSDate *d in dateList)
{ NSDAte *d = [dateList objectAtIndex:i];
NSLog(@” Date is %@”, d);
}
NSMutableArray
- array mutable de punteros a objetos
- count = número de items
- objectAtIndex:i = item i del array (empezando en 0)
- addObject:obj
- insertObject:obj
- removeObjectAtIndex:i
NSMutableArray *thearray = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:o1,o2,o3,o4, nil];
//get element
[thearray objectAtIndex:0]; //element at index 0otros
- NSDictionary: hash table
- NSMutableDictionary
- NSSet/NSMutableSet
- NSOrderedSet/NSMutableOrderedSet
+ (id)dictionaryWithObjects:(NSArray *)values forKeys:(NSArray *)keys;
+ (id)dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:(id)firstObject, ...;
//Creation example:
NSDictionary *base = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithInt:2], @“binary”,
[NSNumber numberWithInt:16], @“hexadecimal”, nil];
Can create with this syntax: @{ key1 : value1, key2 : value2, key3 : value3 }
NSDictionary *colors = @{ @“green” : [UIColor greenColor],
@“blue” : [UIColor blueColor],
@“red” : [UIColor redColor] };Property List
Colección de colecciones
Cualquiera de las clases NSArray, NSDictionary, NSNumber, NSString, NSDate, NSData
Se utiliza para ficheros de propiedades:
[plist writeToFile:(NSString *)path atomically:(BOOL)] //plist is NSArray or NSDictionary
NSUserDefaults
Almacenamiento de property lists en un NSDictionary, persistente entre ejecuciones de la aplicación.
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setArray:rvArray forKey:@“RecentlyViewed”];
// Write after batch of changes
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] synchronize];
UIKit
UIKit is the framework with all graphical elements for native iphone apps

UIViewController
UIViewController es el controlador para Navegación y Tabs

+UIKit

+UIKit
UIButton
UILabel
UIFont
UIColor
UITextView
UIColor
Objeto que representa un color.
Se puede inicializar con RGB, HSB, etc
Pueden tener un alpha:
UIColor *color = [otherColor colorWithAlphaComponent:0.3]).
Hay una lista de colores estándar:
[UIColor greenColor];
[UIColor lightTextColor].
UIFont
UIFont *font = [UIFont preferredFontForTextStyle:UIFontTextStyleBody];
UIFontDescriptor: + (UIFont *)fontWithDescriptor:(UIFontDescriptor *)descriptor size:(CGFloat)size;
Bold from UIFontTextStyleBody preferred font
UIFont *bodyFont = [UIFont preferredFontForTextStyle:UIFontTextStyleBody];
UIFontDescriptor *existingDescriptor = [bodyFont fontDescriptor];
UIFontDescriptorSymbolicTraits traits = existingDescriptor.symbolicTraits;
traits |= UIFontDescriptorTraitBold;
UIFontDescriptor *newDescriptor = [existingDescriptor fontDescriptorWithSymbolicTraits:traits];
UIFont *boldBodyFont = [UIFont fontWithFontDescriptor:newDescriptor size:0];NSAttributedString
Controla las características de una fuente en pantalla (color, outline, stroke, underline, etc).
NSAttributedString no es un NSString : - (NSString *)string;
NSMutableAttributedString
- (void)addAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes range:(NSRange)range;
- (void)setAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes range:(NSRange)range;
- (void)removeAttribute:(NSString *)attributeName range:(NSRange)range;
Ejemplos:
UIButton’s - (void)setAttributedTitle:(NSAttributedString *)title forState:...;
UILabel’s @property (nonatomic, strong) NSAttributedString *attributedText; UITextView’s @property (nonatomic, readonly) NSTextStorage *textStorage;
UILabel
Se puede utilizar a través de la propiedad text.
pero también:
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSAttributedString *attributedText;
Este atributo no es mutable, por lo que para modificarlo hay que utilizar una copia.
NSMutableAttributedString *labelText = [myLabel.attributedText mutableCopy]; [labelText setAttributes:...];
myLabel.attributedText = labelText;
UITextView
UILabel multi-línea, editable, scroll, etc. Texto y attributos utilizando NSMutableAttributedString
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSTextStorage *textStorage;
NSTextStorage hereda de NSMutableAttributedString.
iOS SDK
Capas

Cocoa Touch
Foundation
- Bases de datos / Colecciones
- Wrappers para servicios del sistema
UIKit
- Clases de interfaz gráfico
- Runtime de la aplicación
- Gestión de eventos
- APIs de hardware
Otros: Mapkit, Message
a bajo nivel
Media
- Soporte de imágenes y video
- Animación con OpenGL
- Acceso a fotos y videos del dispositivo
Core Services
- Localización (usa Core Location Framework)
- SQLite (base de datos ligera) (Interfaz en C)
Core OS
- Framework para trabajar con protocolos de red
- Core Location Framework
Patrones de diseño
Hay 6 patrones de diseño importantes
- Modelo-Vista-Controlador
- Target-Action
- Delegación
- Gestión de memoria
- Block objects
- Hilos y concurrencia
Los patrones no son más que maneras de hacer las cosas. Hay que adaptarse a ellos.
Delegación
Alternativa a hacer subclases (Objective-C NO es multiherencia)
En UIKit Framework se hace un uso intensivo
- UIApplicationDelegate
- UITableViewDelegate
- UITextFieldDelegate
Básicamente, una clase es asignada como 'delegada' para realizar algunas funciones de otra clase (Patrón de Decoración)
Ciclo de Vida

Ciclo de Vida

Ciclo de Vida

UIApplicationDelegate
Cada aplicación tiene un delegado que cumple este protocolo, para dotar de comportamiento a la aplicación
Métodos importantes:
•applicationDidFinishLaunching
•applicationWillTerminate
•applicationDidReceiveMemoryWarning
Target Action
Una acción (método) de un objeto (target) es invocada al realizar algún tipo de interacción (event)
En UIKit Framework la clase UIControl se encarga de encapsular estos tres elementos
En iOS una clase o subclase de UIControl puede realizar diferentes acciones en diferentes objetos en respuesta al mismo evento
MVC

MVC

Controlador
UIApplication
Gestiona el bucle de eventos y coordina otros aspectos del comportamiento de la aplicación. Notifica al objeto delegado cuando ocurren eventos en la aplicación
Objeto delegado
Inicializa la aplicación y presenta la ventana de la interfaz. Además se encarga de tratar los eventos de la aplicación, aviso de memoria, la aplicación va a terminar...
View Controllers objects (UIViewController)
Se encargan de la presentación de cada vista, y de gestionar la interacción del usuario con la interfaz, así como modificar el modelo de datos de la aplicación.
Vistas
UIWindow
Presentar las vistas y mandar los eventos de la interfaz al controlador.
Vistas, controles y capas
Dibujan la representación de los datos, controles y el patrón target-action.
Modelos de datos
Clases e información de la aplicación.
Example UIApplication
XCode

Modificación sintáctica: id <MyProtocol> obj, como el interfaz en Java
Protocol
@protocol Foo <xyz>
- (void)someMethod;
@optional
- (void)methodWithArgument:(BOOL)argument;
@required
// getter (only) is part of this protocol
@property (readonly) int readonlyProperty;
// getter and setter are both in the protocol
@property NSString *readwriteProperty;
- (int)methodThatReturnsSomething;
@end
// importing the header file that declares the Foo @protocol
#import “Foo.h”
@interface MyClass : NSObject <Foo>
// MyClass is saying it implements the Foo @protocol
// (do not have to declare Foo’s methods again here,
// it’s implicit that you implement it)
@end
- (void)giveMeFooObject:(id <Foo>)anObjectImplementingFoo;
@property (nonatomic, weak) id <Foo> myFooProperty; // properties too!
Comienza con el carácter ^
Es un conjunto de código ejecutable y referenciable como objeto
Block
[aDictionary enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id key, id value, BOOL *stop) {
NSLog(@“value for key %@ is %@”, key, value);
if ([@“ENOUGH” isEqualToString:key]) {
*stop = YES; }
}];View Controllers
¿Qué es un controlador?
Función:
- Carga la vista y los valores iniciales
- Recibe los eventos de la interfaz
- Gestiona la rotación: (BOOL) shouldAutorotateToInterfaceOrientation: (UIInterfaceOrientation) interfaceOrientation
- Libera los recursos relacionados con la vista
Clases

UIViewController
Puede contener:
- Variables de tipo del modelo de datos
- Variables 'outlets' (IBOutlet) para conectar con objetos de la vista
- Acciones 'outlets' (IBAction) para conectar con objetos de control de la vista
- Otros métodos auxiliares
Ciclo de vida de un controlador

- initWithNibName: Configuración no relacionadas con la vista
- viewDidLoad: Valores iniciales (relacionados con la vista)
- viewWillAppear: La vista va a aparecer
- viewWillDisappear: Guardar el estado
- viewDidUnload: Liberar recursos

ViewController LifeCycle
awakeFromNib -> Instanciado desde el storyboard
viewDidLoad -> IBOutlets creados
cuando se posicionan las vistas
viewWillLayoutSubviews: viewDidLayoutSubviews:
cuando aparece y desaparece el controlador
viewWillAppear: viewDidAppear:
cuando cambia la posición (rotación)
viewWillLayoutSubviews: viewDidLayoutSubviews:
si es por rotación, también se reciben
[will/did]Rotate[To/From]InterfaceOrientation
viewWillDisappear: viewDidDisappear:
en caso de falta de memoria -> didReceiveMemoryWarning
IBAction
Acción que se puede ejecutar en respuesta a un evento.
- (IBAction)exampleAction:(id)sender;
Se enlaza con una acción directamente en el interfaz
IBOutlet
Referencia a un elemento gráfico.
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *textField;
Composición
UINavigationController

Gestiona la barra de navegación (UINavigationBar)
- Botón 'Atrás'
- Título
- Otros controles
- Pila controllers (last-in,first-out)
UINavigationItem
Todos los controladores tienen una variable UINavigationItem
Personaliza la barra superior cuando el controlador está en el top de la pila (visible)
UIBarButtonItem *lftBoton = [UIBarButtonItem alloc];
[lftBoton initWithTitle:@”Dale!”
style: UIBarButtonItemStyleBordered
target:self action:@selector(metodoBoton:)];
self.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem =lftBoton;
[lftBoton release];
Estructura:
NSString *title; UIBarButtonItem *leftBarButtonItem, *rightBarButtonItem; UIView *titleView; NSString *backButtonTitle;

Example UINavigationViewController
Composición
UITabBarController

Gestiona la barra de pestañas (UITabBar)
- Vistas en un array
UITabBarItem
Todos los controladores tienen una variable UINavigationItem
Personaliza la barra superior cuando el controlador está en el top de la pila (visible)
UITabBarItem *item = [[UITabBarItem alloc]
initWithTabBarSystemItem:UITabBarSystemItemBookmarks tag:0];
self.tabBarItem = item;
[item release];
Estructura:
NSString *title; UIImage *image; NSString *badgeValue
Combinando controladores
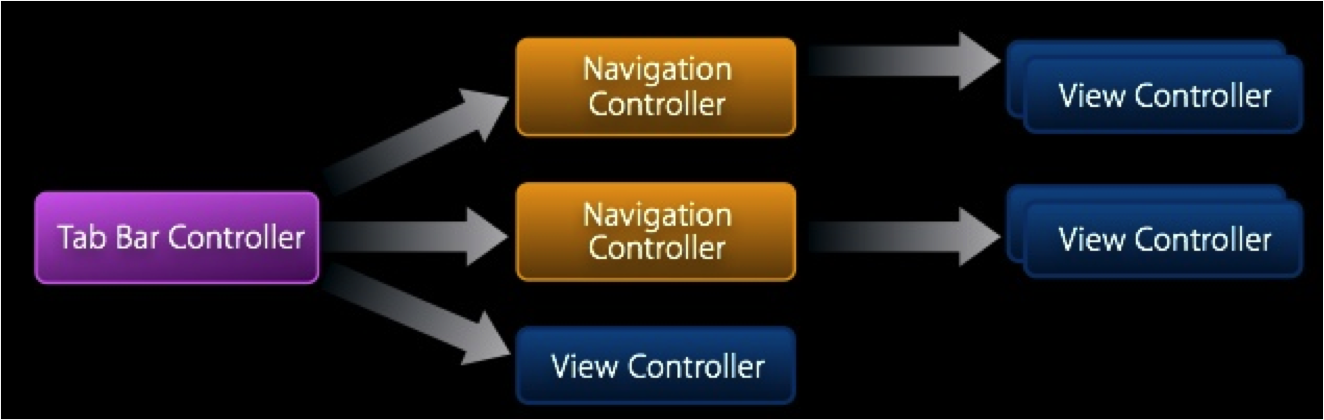
Navegación
Las escenas se conectan con segues, que represetan una transición entre dos view controllers.

Navegación

Tipos de Segue
Show/Push: se añade nuevo contenido a la pila
Show detail: añade nuevo contenido o reemplaza el existente.
Present modally: muestra un controlador modal como "hijo" del actual, que tiene la responsabilidad sobre el mismo
Popover presentation: se presenta un popover sobre una vista del view controller.
Custom: una transición realizando sobre UIStoryboardSegue.
Unwind: reverse navigation.
Navegación condicional
Se implementa en código utilizando:
- (void)performSegueWithIdentifier:(NSString *)segueId sender:(id)sender;
sender -> es el iniciador del evento
- (IBAction)rentEquipment
{
if (self.snowTraversingTalent == Skiing) {
[self performSegueWithIdentifier:@“AskAboutSkis” sender:self];
} else {
[self performSegueWithIdentifier:@“AskAboutSnowboard” sender:self];
} }
Segue por código
Se transmite la información que necesite al siguiente controlador, y se cede el control.
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@“DoSomething”]) {
if ([segue.destinationViewController isKindOfClass:[DoSomethingVC class]]) {
DoSomethingVC *doVC = (DoSomethingVC *)segue.destinationViewController;
doVC.neededInfo = ...; }
} }Se puede condicionar
Si se responde NO a este método, el segue no continuaría. Por ejemplo, para validación de datos.
- (BOOL)shouldPerformSegueWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier sender:(id)sender {
if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@“DoAParticularThing”]) {
return [self canDoAParticularThing] ? YES : NO;
}
}
Unwind segue
// Target viewcontroller
- (IBAction)myUnwindAction:(UIStoryboardSegue*)unwindSegue

Ejemplo Navegación
ViewController
Vistas modales
Permiten mostrar una nueva pantalla para coger información, presentar de forma distinta un contenido, etc.

Vistas modales
Mostrar un controlador de forma modal
[self presentModalViewController:viewController animated:YES];
Ocultar un controlador
[self dismissModalViewControllerAnimated:YES];
Modal ViewController
- (void)add:(id)sender {
// Create the root view controller for the navigation controller
// The new view controller configures a Cancel and Done button for the
// navigation bar.
RecipeAddViewController *addController = [[RecipeAddViewController alloc] init];
addController.modalPresentationStyle = UIModalPresentationFullScreen;
addController.transitionStyle = UIModalTransitionStyleCoverVertical;
[self presentViewController:addController animated:YES completion: nil];
}
Tablas

UITableView
UITableViewController
Protocolos
- UITableViewDataSource
- UITableViewDelegate (Apariencia y comportamiento)
Celdas (UITableViewCell)
Estilos


UITableViewController
Delegado de UITableViewDataSource y UITableViewDelegate, separando modelo y vista
UITableViewDelegate
–willDisplayCell:forRowAtIndexPath;
–willSelectRowAtIndexPath;
–didSelectRowAtIndexPath;
–accessoryTypeForRowWithIndexPath
– accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath
UITableViewDataSource
–numberOfSectionsInTableView;
–numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section; *
–cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;
–InsertSections, deleteSections, reloadSections
–insertRowsAtIndexPaths...
UITableView Protocols
delegate controla cómo se muestra la tabla
dataSource proporciona los datos de la table
UITableViewController
es automáticamente un UITableView delegate y dataSource
@property (nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView;
( == self.view en UITableViewController!)
UITableViewDataSource
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)sender
cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
}
typedef enum {
UITableViewCellStyleDefault,
UITableViewCellStyleValue1,
UITableViewCellStyleValue2,
UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle
} UITableViewCellStyle;Hay que definir un UITableViewCell
Salvo que trabajes en estático y no te importe el por defecto.
UITableViewDataSource
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)sender
cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
UITableViewCell *cell;
cell = [self.tableView
dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@“Flickr Photo Cell”
forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.textLabel.text = [self
getMyTitleForRow:indexPath.row
inSection:indexPath.section];
return cell;
}UITableViewDelegate
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)sender didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)path ! {!
// go do something based on information about my Model!
// corresponding to indexPath.row in indexPath.section
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)sender
accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
// Do something related to the row at indexPath,
// but not the primary action associated with touching the row
}UITableView Segue
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender
{
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [self.tableView indexPathForCell:sender];
// prepare segue.destinationController to display based on information
// about my Model corresponding to indexPath.row in indexPath.section
}El sender es un UITableViewCell
Datos
Sistema de Archivos
Cada aplicación tiene su propio conjunto de directorios
<Application Home>
MyApp.app
MyApp
MainWindow.nib
SomeImage.png
Documents
Library
Caches
Preferences
Sólo pueden escribir en su directorio Home
Sistema de Directorios
NSPathUtilities.h → Conjunto de categorías para trabajar con rutas del sistema de archivos de una aplicación
Buscando el directorio Documents:
NSString *documentDirectory;
NSArray *paths = NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains
(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
documentsDirectory = [paths objectAtIndex:0];
Accediendo al bundle
Accediendo al bundle de la aplicación
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
Obteniendo la ruta de un recurso en el bundle
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
[bundle pathForResource:@”image” ofType:@”jpg”];
Property Lists
Es una manera de representar jerarquías simples de datos
Sólo soporta arrays, diccionarios, strings, fechas, enteros, dobles y booleanos
Una property list es una clase (array o diccionario) que engloba uno o varios objetos soportados
Representada con XML o con un binario (más compacto)
Se usa para una cantidad menor de unos pocos cientos de KBs
Property Lists
Métodos para escribir
- (BOOL)writeToFile:(NSString *)aPath atomically:(BOOL)flag;
- (BOOL)writeToURL:(NSURL *)aURL atomically:(BOOL)flag;
Métodos para leer
- (id)initWithContentsOfFile:(NSString *)aPath;
- (id)initWithContentsOfURL:(NSURL *)aURL;
Ejemplo de lectura (en el caso de NSArray):
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"places" ofType:@"plist"];
NSArray *placesArray = [NSArray initWithContentsOfFile:path];
Integradas en la aplicación o en la aplicación Settings
Normalmente, si tienen poco uso, se utilizarían las settings.
Clase NSUserDefaults
–Método de clase → +(id)standardUserDefaults
–Es una Property List
Ejemplo de uso (insertar valor y recuperarlo)
NSUserDefaults *defaults = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
[defaults setObject:@”Pedro” forKey: @”name”];
NSString *nombre = [defaults stringForKey:@”name”];
Settings Bundle
Settings.bundle en tu aplicación sirve para añadir las preferencias a la aplicación Settings de iPhone/iPod/iPad
Muestra una pantalla con controles
Cada control tiene (al menos)
*Tipo (Type)
*Titulo (Title)
*Clave (Key)

XML
NSXMLParser - clase para parsear XML dirigido por eventos (como JAXP)
NSXMLParser *parser = [[NSXMLParser alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:url];
[parser setDelegate:self];
[parser setShouldProcessNamespaces:NO];
[parser setShouldReportNamespacePrefixes:NO];
[parser setShouldResolveExternalEntities:NO];
[parser parse]; //empieza a parsear
Iniciar un objeto NSXMLParser y asignarle un delegado
didStartElement → Guardar el tag y reservar memoria estructura
didEndElement → Guardar valores en la estructura
foundCharacters → Guardar valor del tag
JSON
NSJSONSerialization - clase para parsear JSON
NSMutableDictionary *returnedDict =
[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data
options:kNilOptions error:&error];
O utilizando una librería como JSONKit
NSData* jsonData = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:&response error:&err];
NSDictionary *resultsDictionary = [jsonData objectFromJSONData];
CoreData
Core Data no es un RDBMS, aunque utiliza SQLite por debajo.
Utiliza un NSManagedObjectContext, a partir de un UIManagerdDocument o el AppDelegate.
El modelo se crea como un Data Model en el XCode.

CoreData
Insert/Delete un objeto:
NSManagedObjectContext *context = aDocument.managedObjectContext;
NSManagedObject *photo =
[NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@“Photo”
inManagedObjectContext:context];
[context deleteObject:photo];Atributos:
- (id)valueForKey:(NSString *)key; !
- (void)setValue:(id)value forKey:(NSString *)key; !
El tipo es nil por defecto.
NSNumber para números, boolean; NSData para datos binarios, NSDate para fechas, NSSet para relaciones
CoreData
Queries: NSFetchRequest
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@“Photo”];
request.fetchBatchSize = 20;
request.fetchLimit = 100;
request.sortDescriptors = @[sortDescriptor];
request.predicate = ...;
NSArray *photographers = [context executeFetchRequest:request error:&error];NSPredicate:
NSString *serverName = @“flickr-5”;
NSPredicate *predicate =
[NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@“thumbnailURL contains %@”, serverName];
// unique a photo in the database
@“uniqueId = %@”, [flickrInfo objectForKey:@“id”]
// matches name case insensitively!
@“name contains[c] %@”, (NSString *)
// viewed is a Date attribute in the data mapping!
@“viewed > %@”, (NSDate *)
// Photo search (by photographer’s name)!
@“whoTook.name = %@”, (NSString *)
// Photographer search (not a Photo search)
@“any photos.title contains %@”, (NSString *) CoreData y UITableView
NSFetchedResultsController enlaza un NSFetchRequest con UITableViewController. Normalmente se utiliza una @property para referenciar el NSFetchedResultsController
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@“Photo”];
request.sortDescriptors = @[[NSSortDescriptor sortDescriptorWithKey:@“title” ...]];
request.predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@“whoTook.name = %@”, photogName];
NSFetchedResultsController *frc = [[NSFetchedResultsController alloc]
initWithFetchRequest:(NSFetchRequest *)request
managedObjectContext:(NSManagedObjectContext *)context
sectionNameKeyPath:(NSString *)keyThatSaysWhichSectionEachManagedObjectIsIn
cacheName:@“MyPhotoCache”]; // careful!
//UITableView
- (NSUInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)sender
{
return [[self.fetchedResultsController sections] count];
}
- (NSUInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)sender
numberOfRowsInSection:(NSUInteger)section
{
return [[[self.fetchedResultsController sections]
objectAtIndex:section] numberOfObjects];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)sender
cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
UITableViewCell *cell = ...;
NSManagedObject *managedObject = [self.fetchedResultsController objectAtIndexPath:indexPath];
}SQLite
Acceso a una Sqlite a bajo nivel.
#import <sqlite3.h>
sqlite3_open, sqlite3_prepare_v2, sqlite3_step
sqlite3_column_count, sqlite3_column_text
sqlite3_column_name, sqlite3_changes, sqlite3_last_insert_rowid, sqlite3_errmsg, sqlite3_finalize, sqlite3_close
Views and Gestures
Vistas
Una vista es una clase que hereda de UIView
Es parte de una jerarquía:
Una vista sólo tiene un padre - (UIView *)superview
Pero puede tener muchos hijos - (NSArray *)subviews
El orden importa (front-back)
UIWindow
UIView raíz de la jerarquía
En iOS sólo tenemos (normalmente) un UIWindow, no se trata de ventanas.
Vistas
Se construye gráficamente en Xcode, aunque se puede hacer por código.
- (void)addSubview:(UIView *)aView; // sent to aView’s (soon
- (void)removeFromSuperview; // sent to the view that is being removed
La raíz de nuestro modelo es: @property view
UIViewCo@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *view
Esta vista es el padre de nuestras vistas, la que sufre la rotación, se le añaden vistas hijo, etc.
Coordenadas
CGFloat
CGPoint: struct con 2 CGFloat (x,y)
CGPoint p = CGPointMake(34.5, 22.0);
CGSize: struct con 2 CGFloat (ancho, alto)
CGSize s = CGSizeMake(100.0, 200.0);
CGRect: struct con CGPoint origen y size
CGRect aRect = CGRectMake(45.0, 75.5, 300, 500);
Coordenadas
Pixels por punto en la pantalla
@property CGFloat contentScaleFactor
Espacio ocupado
@property CGRect bounds;
Centro
@property CGPoint center;
Límites de la vista padre:
@property CGRect frame;

Crear una vista
Normalmente se crean en el XCode, arrastrando una vista y modificándola en el Identity Inspector
También se puede crear por código:
CGRect labelRect = CGRectMake(20, 20, 50, 30);
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:labelRect];
label.text = @”Hello!”;
[self.view addSubview:label];Custom View
Para crear nuestras propias vistas o manejar los eventos de una forma diferente.
Extender UIView y sobreescribir el método:
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)aRect;
Se dibuja utilizando Core Graphics.
Actualizar mediante los métodos
- (void)setNeedsDisplay;
- (void)setNeedsDisplayInRect:(CGRect)aRect;
Transparencia
UIColor tiene la propiedad de alpha, que se puede modificar en el UIView backgrounnColor
@property BOOL opaque; debe de ser NO
@property CGFloat alpha en UIView modifica la transparencia de toda la vista.
@property (nonatomic) BOOL hidden; puede esconder completamente una vista
UILabel
Subview para dibujar text en una vista.
UILabel *scoreLabel = [ [UILabel alloc ]
initWithFrame:CGRectMake((self.bounds.size.width / 2), 0.0, 150.0, 43.0) ];
scoreLabel.textAlignment = UITextAlignmentCenter;
scoreLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
scoreLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
scoreLabel.font = [UIFont fontWithName:@"Arial Rounded MT Bold" size:(36.0)];
[self addSubview:scoreLabel];
scoreLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"%d", score];
//How much space will a piece of text will take up when drawn?
CGSize textSize = [text size];UIImageView
Crear una imagen a partir de un fichero de los recursos
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@“foo.jpg”];
De un fichero o de datos raw
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:(NSString *)fullPath];
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithData:(NSData *)imageData];
UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"image Name"]] ;
@property (nonatomic) UIViewContentMode contentMode;
Controla el refresco de la pantalla.
UIViewContentMode {Left,Right,Top,Right,BottomLeft,BottomRight,TopLeft,TopRight}
UIViewContentModeScale{ToFill,AspectFill,AspectFit} UIViewContentModeRedraw -> repintar con cada cambio de límites
Default: UIViewContentModeScaleToFill
Animaciones
Animaciones de propiedades de un UIView
frame
transform (translation, rotation, escale)
alpha (opacity)
Animación de apariencia (UI)
Animación dinámica (gravedad, fuerzas, alineamiento, etc)
UIView animation
Fade en 3 segundos sólo si se completa la animacion.
Animation class method in UIView
+ (void)animateWithDuration:(NSTimeInterval) duration
delay:(NSTimeInterval)delay
options:(UIViewAnimationOptions)options
animations:(void (^)(void))animations
completion:(void (^)(BOOL finished))completion;
[UIView animateWithDuration:3.0
delay:0.0
options:UIViewAnimationOptionBeginFromCurrentState
animations:^{ myView.alpha = 0.0; }
completion:^(BOOL fin) { if (fin) [myView removeFromSuperview]; }];UIView animation
UIViewAnimationOptions
BeginFromCurrentState
AllowUserInteraction
LayoutSubviews
Repeat
Autoreverse
OverrideInheritedDuration
OverrideInheritedCurve
AllowAnimatedContent
CurveEaseInEaseOut
CurveEaseIn
CurveLinear
UIView Transiciones
Reemplazar una vista
+ (void)transitionFromView:(UIView *)fromView
toView:(UIView *)toView
duration:(NSTimeInterval)duration
options:(UIViewAnimationOptions)options
completion:(void (^)(BOOL finished))completion;
Dinámicas
Pasos:
Crear un UIDynamicAnimator
Añadir UIDynamicBehaviors (gravedad, colisiones, etc)
Añadir UIDynamicItems (UIViews)
//Create a UIDynamicAnimator
UIDynamicAnimator *animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc]
initWithReferenceView:aView];
//If animating views, all views must be in a view hierarchy
// with reference view at the top.
//Create and add UIDynamicBehaviors
UIGravityBehavior *gravity = [[UIGravityBehavior alloc] init];
[animator addBehavior:gravity];
ICollisionBehavior *collider = [[UICollisionBehavior alloc] init];
[animator addBehavior:collider];UIDynamicItem
Añadir items a behaviors
id <UIDynamicItem> item1 = ...; id <UIDynamicItem> item2 = ...; [gravity addItem:item1]; [collider addItem:item1]; [gravity addItem:item2]; <UIDynamicItem> @protocol UIDynamicItem @property (readonly) CGRect bounds; @property (readwrite) CGPoint center; @property (readwrite) CGAffineTransform transform; @end
UIDynamicBehaviour
UIGravityBehavior: ángulo y magnitud
UICollisionBehavior: colisiones y límites
UIPushBehavior: aceleración en 2 modos [continuous, instantaneous]
UIAttachmentBehavior: alineamiento a un punto u otra vista.
UISnapBehavior: animación de estar pegado a un punto.
UIDynamicBehavior superclase para crear una composición
- (void)addChildBehavior:(UIDynamicBehavior *)behavior;
Autolayout
Definir las UIViews con reglas en vez de números. Muchas restricciones pueden afectar a las vistas:
- Rotación
- Tamaño de la pantalla
- Composición de controles
Normalmente se utiliza el XCode para configurarlo
Gestos
UIGestureRecognizer es la clase que reconoce los gestos. Es una clase abstracta, normalmente la implementación está contenida en el UIViewController o en el mismo UIView.
- (void)setPannableView:(UIView *)pannableView
{
_pannableView = pannableView;
UIPanGestureRecognizer *pangr =
[[UIPanGestureRecognizer alloc]
initWithTarget:pannableView //La propia vista como target
action:@selector(pan:)]; //Método a ejecutar en el target
[pannableView addGestureRecognizer:pangr]; //Activar el gesto en la vista
}UIGestureRecognizer
UIPanGestureRecognizer tiene 3 métodos:
- (CGPoint)translationInView:(UIView *)aView;
- (CGPoint)velocityInView:(UIView *)aView;
- (void)setTranslation:(CGPoint)translation inView:(UIView *)aView;
Estados:
@property: @property (readonly) UIGestureRecognizerState state;
{Possible, Recognized, Began, Failed,
Changed, Ended, Continuous, Cancelled}
Gestos: callback
- (void)pan:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)recognizer
{
if ((recognizer.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged) ||
(recognizer.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded)) {
CGPoint translation = [recognizer translationInView:self];
// move something in myself (I’m a UIView) by translation.x and translation.y
// for example, if I were a graph and my origin was set by an @property called origin
self.origin = CGPointMake(self.origin.x+translation.x, self.origin.y+translation.y);
[recognizer setTranslation:CGPointZero inView:self]; // Reset cumulative distance
 }
}Más gestos
UIPinchGestureRecognizer
@property CGFloat scale;
@property (readonly) CGFloat velocity;
UIRotationGestureRecognizer
@property CGFloat rotation;
@property (readonly) CGFloat velocity;
UISwipeGestureRecognizer
@property UISwipeGestureRecognizerDirection direction; @property NSUInteger numberOfTouchesRequired;
UITapGestureRecognizer
@property NSUInteger numberOfTapsRequired;
@property NSUInteger numberOfTouchesRequired;
UIScrollView
Dentro del XCode: un UIView se puede embeber en un Scroll View.

UIApplication
Objeto aplicación, diferente del Application Delegate que contiene información global.
UIApplication *myApplication =
[UIApplication sharedApplication];
Network Activity Indicator
Propiedad de UIApplication.
@property (nonatomic, getter=is...) networkActivityIndicatorVisible;
Cuando esta propiedad se pone a YES, aparece un spinner en la status bar indicando cuándo hay actividad en la red.
Modal, Text Fields, Alertas y Acciones
Modal View Controller
Se superpone a la pantalla actual, rompiendo la navegación -> Ventana modal.
Transiciones:
@property UIModalTransitionStyle modalTransitionStyle; UIModalTransitionStyleCoverVertical, UIModalTransitionStyleFlipHorizontal. UIModalTransitionStyleCrossDissolve, UIModalTransitionStylePartialCurl
Pantalla en iPad
@property UIModalPresentationStyle modalPresentationStyle;
UIModalPresentationFullScreen, UIModalPresentationPageSheet, UIModalPresentationFormSheet, UIModalPresentationCurrentContext
UITextField
UILabel pero editable. Interacción clave con el teclado.
- (BOOL)textFieldShouldEndEditing:(UITextField *)textField {
if (textField == SSN) { // SSN is an outlet
NSString *regEx = @"[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{4}";
NSRange r = [textField.text rangeOfString:regEx options:NSRegularExpressionSearch];
if (r.location == NSNotFound) {
UIAlertView *av = [[[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"Entry Error"
message:@"Enter social security number in 'NNN-NN-NNNN' format"
delegate:self cancelButtonTitle:@"OK" otherButtonTitles:nil] autorelease];
[av show];
return NO;
}
}
return YES;
}Teclado personalizado
@property(nonatomic) UIKeyboardType keyboardType
myTextField.keyboardType = UIKeyboardTypeASCIICapable;
UIKeyboardTypeDefault, UIKeyboardTypeASCIICapable, UIKeyboardTypeNumbersAndPunctuation, UIKeyboardTypeURL, UIKeyboardTypeNumberPad, UIKeyboardTypePhonePad, UIKeyboardTypeNamePhonePad, UIKeyboardTypeEmailAddress, UIKeyboardTypeDecimalPad, UIKeyboardTypeTwitter, UIKeyboardTypeWebSearch, UIKeyboardTypeAlphabet = UIKeyboardTypeASCIICapable
Popups: Action sheet
Menú de acciones de estilo iPhone.

Popups: Action sheet
Menú de acciones de estilo iPhone.
-(id)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title
delegate:(id <UIActionSheetDelegate>)delegate
cancelButtonTitle:(NSString *)cancelButtonTitle
destructiveButtonTitle:(NSString *)destructiveButtonTitle
otherButtonTitles:(NSString *)otherButtonTitles, ...;
- (void)addButtonWithTitle:(NSString *)buttonTitle;
//Displaying the Action Sheet!
UIActionSheet *actionSheet = [[UIActionSheet alloc] initWithTitle:...];
[actionSheet showInView:(UIView *)]; // centers the view on iPad
[actionSheet showFromRect:(CGRect) inView:(UIView *) animated:(BOOL)];
[actionSheet showFromBarButtonItem:(UIBarButtonItem *) animated:(BOOL)];Popups: Alert View


Popups: Alert View
-(id)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title
message:(NSString *)message
delegate:(id <UIActionSheetDelegate>)delegate
cancelButtonTitle:(NSString *)cancelButtonTitle
otherButtonTitles:(NSString *)otherButtonTitles, ...;
UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:...];
[alert show];
alert.alertViewStyle = UIAlertViewStyle{SecureText,PlainText,LoginAndPassword}Input; Popups: Alert View
UIAlertView *alert = [[[UIAlertView alloc]
initWithTitle:@"Username:"
message:@"Please enter your username:"
delegate:self cancelButtonTitle:@"Cancel"
otherButtonTitles:nil] autorelease];
alert.alertViewStyle = UIAlertViewStyleLoginAndPasswordInput;
alert.tag = 12;
[alert addButtonWithTitle:@"Go"];
[alert show];
}
- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView didDismissWithButtonIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex
{
if (alertView.tag == 12) {
if (buttonIndex == 1) {
UITextField *textfield = [alertView textFieldAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"username: %@", textfield.text);
}
}
}Deprecated en iOS 9
UIAlertController * alert= [UIAlertController
alertControllerWithTitle:@"Title"
message:@"Message"
preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert];
UIAlertAction* yesButton = [UIAlertAction
actionWithTitle:@"Yes, please"
style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault
handler:^(UIAlertAction * action)
{
//Handel your yes please button action here
[alert dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}];
UIAlertAction* noButton = [UIAlertAction
actionWithTitle:@"No, thanks"
style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault
handler:^(UIAlertAction * action)
{
[alert dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}];
[alert addAction:yesButton];
[alert addAction:noButton];
[self presentViewController:alert animated:YES completion:nil];UIAlertView is deprecated. Use UIAlertController with a preferredStyle of UIAlertControllerStyleAlert instead
Popover
UIPopoverController no es un UIViewController, contiene una referencia al controller.
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIViewController *contentViewController;
- (IBAction)presentPopover:(UIBarButtonItem *)item
{
if (!self.popover) {
self.popover = [[UIPopoverController alloc] initWithViewController:vc];
[self.popover presentPopoverFromBarButtonItem:item ...];
}
}
- (void)dismissPopoverAnimated:(BOOL)animated; también deprecated
UIModalPresentationPopover
avc.modalPresentationStyle = UIModalPresentationPopover;
avc.popoverPresentationController.sourceView = theButton;
[self presentViewController:avc animated:YES completion:nil];Universal Apps
Universal Applications
Es una única aplicación que corre tanto en iPhone como en iPad.
Se crea un nuevo storyboard para iPad/iPhone
BOOL iPad = ([[UIDevice currentDevice] userInterfaceIdiom] == UIUserInterfaceIdiomPad); !
UISplitViewController
Top-level controller para iPad. Con 2 view controller, master y detail.

Networking
Model Framework for Cocoa and Cocoa Touch
Mantle
Permite componer una capa model de abstracción sencilla.
Evitando tener que trabajar con
-hash
-isEqual:
NSCopying
NSCoding
Ejemplo.
Example: Book Model
@interface TGRBook : MTLModel
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *author;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *overview;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSArray *genres;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSDate *releaseDate;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSNumber *identifier;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *title;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSURL *coverURL;
@endEjemplo.
NSError *error = nil;
TGRBook *book = [TGRBook modelWithDictionary:@{
@"title" : @"The Sandman",
@"author" : @"Neil Gaiman",
@"genres" : @[@"Graphic Novels", @"Fantasy"], ...
} error:&error];
TGRBook *anotherBook = [book copy];
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:book toFile:@"my_file"];
TGRBook *b = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:@"my_file"];Simplemente heredando de MTLModel
El modelo puede estar representado en JSON
Our Book Model could have a JSON representation
{
...
"artistName": "Neil Gaiman, Sam Keith & Mike Dringenberg",
"description": "<p>NEW YORK TIMES bestselling author...",
"genres": ["Graphic Novels", "Books", "Comics & Graphic Novels"],
"releaseDate": "2012-08-21T07:00:00Z",
"trackId": 554016043,
"trackName": "The Sandman, Vol. 1: Preludes & Nocturnes (New Edition)", "artworkUrl100": "http://a4.mzstatic.com/us/r30/Publication/...",
...
}
This is how iTunes represents media (including books)Simplemente heredando de MTLModel
MTLJSONSerializing
@interface TGRBook : MTLModel <MTLJSONSerializing>
Hay que especificar:
Cómo mapear las propiedades con el path JSON
Como convertir el valor de JSON a property key.
MTLJSONSerializing
+ (NSDictionary *)JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey {
return @{
@"author" : @"artistName",
@"overview" : @"description",
@"identifier" : @"trackId",
@"title" : @"trackName",
@"coverURL" : @"artworkUrl100" };
}
MTLValueTransformer
+<key>JSONTransformer methods
Predefinidos:
MTLURLValueTransformerName MTLBooleanValueTransformerName
+ (NSValueTransformer *)releaseDateJSONTransformer {
return [MTLValueTransformer reversibleTransformerWithForwardBlock:^(NSString *str) {
return [self.dateFormatter dateFromString:str];
} reverseBlock:^(NSDate *date) {
return [self.dateFormatter stringFromDate:date];
}];
}
+ (NSValueTransformer *)coverURLJSONTransformer {
return [NSValueTransformer valueTransformerForName:MTLURLValueTransformerName];
}Mapping estructuras
@interface TGRUser : MTLModel <MTLJSONSerializing>
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) NSArray *purchasedBooks;
@property (copy, nonatomic, readonly) TGRBook *nowReading;
@end
+ (NSValueTransformer *)purchasedBooksJSONTransformer {
return [NSValueTransformer mtl_JSONArrayTransformerWithModelClass:TGRBook.class];
}
+ (NSValueTransformer *)nowReadingJSONTransformer {
return [NSValueTransformer mtl_JSONDictionaryTransformerWithModelClass:TGRBook.class];
}MTLJSONAdapter
TGRBook *book =
[MTLJSONAdapter modelOfClass:TGRBook.class
fromJSONDictionary:JSONDictionary
error:&error];
NSDictionary *dictionary =
[MTLJSONAdapter JSONDictionaryFromModel:book];Transformer reversible.
Puede convertir cualquier modelo que implemente <MTLJSONSerializing> en un NSDictionary y viceversa
MTLManaged
// MTLManagedObjectSerializing protocol
// Entity name
+ (NSString *)managedObjectEntityName {
return @"Book";
}
// Map
+ (NSDictionary *)managedObjectKeysByPropertyKey {
return @{
@"coverURL" : @"coverLink"
};
}
// Transformer
+ (NSValueTransformer *)coverURLEntityAttributeTransformer {
return [[NSValueTransformer valueTransformerForName:MTLURLValueTransformerName]
}
//MTLManagedObjectAdapter
NSManagedObject *managedBook =
[MTLManagedObjectAdapter managedObjectFromModel:book
insertingIntoContext:moc];
TGRBook *book = [MTLManagedObjectAdapter modelOfClass:TGRBook.class
fromManagedObject:object error:&error];Easy Networking Framework
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"https://itunes.apple.com"];
AFHTTPClient *client = [[AFHTTPClient alloc] initWithBaseURL:url]; !
[client getPath:@"search" parameters:@{
@"term" : @"the sandman",
@"entity" : @"ebook"
} success:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation *operation, id JSONResponse) {
NSLog(@"Search results: %@", JSONResponse);
} failure:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation *operation, NSError *error) {
...
}];Respuesta en JSON
{
"resultCount": 50, "results": [{
"artistId": 3603584,
"artistName": "Neil Gaiman, Sam Kieth & Mike Dringenberg",
"kind": "ebook",
"price": 1.99,
"description": "<p>The first issue of the first volume...",
"currency": "USD",
"genres": ["Graphic Novels", "Books", "Comics & Graphic Novels"],
"genreIds": ["10015", "38", "9026"],
"releaseDate": "2013-05-01T07:00:00Z",
"trackId": 642469670,
"trackName": "Sandman #1",
...+ Mantle
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"https://itunes.apple.com"];
AFHTTPClient *client = [[AFHTTPClient alloc] initWithBaseURL:url]; !
[client getPath:@"search"
parameters:@{
@"term" : @"Neil Gaiman",
@"entity" : @"ebook"
} success:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation *operation, NSDictionary *JSONResponse) {
NSArray *results = JSONResponse[@"results"];
NSValueTransformer *transformer;
transformer = [NSValueTransformer
mtl_JSONArrayTransformerWithModelClass:TGRBook.class];
NSArray *books = [transformer transformedValue:results];
NSLog(@"Books: %@", books);
} failure:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation *operation, NSError *error) {
...
}];El mapping puede ser costoso, debería hacerse fuera del thread principal de la UI
NSNotification
NSNotification
Notificaciones de eventos del MVC
[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]
Registrarse a eventos:
- (void)addObserver:(id)observer selector:(SEL)methodToInvokeIfSomethingHappens
name:(NSString *)name // name of station (a constant somewhere)
object:(id)sender; // whose changes you’re interested in (nil is anyone’s)
Notificación del evento:
- (void)methodToInvokeIfSomethingHappens:(NSNotification *)notification {
notification.name // the name passed above
notification.object // the object sending you the notification
notification.userInfo // notification-specific information about what happened }
Lista de notificaciones del sistema
// System/Library/Frameworks/UIKit.framework/Headers/UIApplication.h
UIKIT_EXTERN NSString *const UIApplicationDidEnterBackgroundNotification NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(4_0);
UIKIT_EXTERN NSString *const UIApplicationWillEnterForegroundNotification NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(4_0);
UIKIT_EXTERN NSString *const UIApplicationDidFinishLaunchingNotification;
UIKIT_EXTERN NSString *const UIApplicationDidBecomeActiveNotification;
UIKIT_EXTERN NSString *const UIApplicationWillResignActiveNotification;
Push Notification

Push Notification

Push Notification - Message
{
"aps":
{
"alert":
{
"action-loc-key": "Open",
"body": "Hello, world!"
},
"badge": 2
}
}Multithreading
Multithreading
"Asynchronous design approach"
Mecanismo basado en colas, donde se acumulan los bloques a ejecutar, que luego se ejecutan en el thread asociado
La cola principal es la que maneja la UI. Toda actividad en la UI debe realizarse en la cola principal. Actividad no relacionada con la UI que consuma mucho tiempo debería realizarse sin bloquear la cola principal.
Multithreading
Obtener la referencia a la cola principal
NSOperationQueue *mainQ = [NSOperationQueue mainQueue];
Ejecutar una acción en la cola principal.
NSObject method
- (void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aMethod
withObject:(id)obj
waitUntilDone:(BOOL)waitUntilDone;
Ejemplo de API asíncrona
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:
[NSURL urlWithString:@“http://...”]];
NSURLConfiguration *configuration = ...;
NSURLSession *session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:configuration
delegate:nil
delegateQueue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]];
NSURLSessionDownloadTask *task;
task = [session downloadTaskWithRequest:request
completionHandler:^(NSURL *localfile,
NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) {
/* UI tasks on mainQueue delegate */ }];
[task resume];Ejemplo de API asíncrona
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:
[NSURL urlWithString:@“http://...”]];
NSURLConfiguration *configuration = ...;
NSURLSession *session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:configuration];
// No delegateQueue
NSURLSessionDownloadTask *task;
task = [session downloadTaskWithRequest:request
completionHandler:^(NSURL *localfile,
NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) {
/* Non UI tasks */
/* Now UI tasks on main queue */
[self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(doUIthings)
withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO];
}];
[task resume];Biblioteca para la ejecución de código concurrente, on iOS y OSX multicore.
Proporciona colas thread-safe:
serial queues -> colas de ejecución de una tarea cada vez (FIFO)
concurrent queues -> comienzan FIFO, pero acaban sin garantía
Grand Central Dispatch
Background task
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0),^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:myURL];
myData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[self processTheData:myData];
});
});
// UI Update
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0),^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:myURL];
myData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
[self processTheData:myData];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// code that updates UI goes here
});
});Limitar las operaciones con NSOperationQueue
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSOperationQueue *queue;
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
self.queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init];
self.queue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 4;
}
[self.queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:myURL];
myData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
[self processTheData:myData];
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] addOperationWithBlock:{
// code that updates UI goes here
}];
}]; Delays - dispatch_after
- (void)showOrHideNavPrompt
{
NSUInteger count = [[PhotoManager sharedManager] photos].count;
double delayInSeconds = 1.0;
dispatch_time_t popTime =
dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(delayInSeconds * NSEC_PER_SEC)); // 1
dispatch_after(popTime, dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^(void){ // 2
if (!count) {
[self.navigationItem setPrompt:@"Add photos with faces to Googlyify them!"];
} else {
[self.navigationItem setPrompt:nil];
}
});
}Locks - dispatch_once
+ (instancetype)sharedManager
{
static PhotoManager *sharedPhotoManager = nil;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
sharedPhotoManager = [[PhotoManager alloc] init];
sharedPhotoManager->_photosArray = [NSMutableArray array];
});
return sharedPhotoManager;
}Permite hacer un singleton thread-safe
NSURL* url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://example.com"]; NSMutableURLRequest* urlRequest = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url]; [urlRequest addValue:@"application/json" forHTTPHeaderField:@"Accept"]; NSOperationQueue* queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init]; [NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:urlRequest queue:queue completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse* response, NSData* data, NSError* error) { if (data) { NSHTTPURLResponse* httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse*)response; // check status code and possibly MIME type (which shall start with "application/json"): NSRange range = [response.MIMEType rangeOfString:@"application/json"]; if (httpResponse.statusCode == 200 /* OK */ && range.length != 0) { NSError* error; id jsonObject = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:0 error:&error]; if (jsonObject) { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ // self.model = jsonObject; NSLog(@"jsonObject: %@", jsonObject); }); } else { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ //[self handleError:error]; NSLog(@"ERROR: %@", error); }); } } else { // status code indicates error, or didn't receive type of data requested NSString* desc = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"HTTP Request failed with status code: %d (%@)", (int)(httpResponse.statusCode), [NSHTTPURLResponse localizedStringForStatusCode:httpResponse.statusCode]]; NSError* error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@"HTTP Request" code:-1000 userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey: desc}]; dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ //[self handleError:error]; // execute on main thread! NSLog(@"ERROR: %@", error); }); } } else { // request failed - error contains info about the failure dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ //[self handleError:error]; // execute on main thread! NSLog(@"ERROR: %@", error); }); } }];
Core Motion
Sensores
API para acceder a los sensores del dispositivo
- acelerómetro
- giróscopo
- magnetómetro
Mediante la clase CMMotionManager. Acceso a un recurso global, por lo que es recomendable obtener sólo una instancia por aplicación para mantener el rendimiento.
Sensores
Primero hay que obtener la disponibilidad del hardware
@property (readonly) BOOL {accelerometer, gyro, magnetometer, deviceMotion}Available
Programar los sensores para obtener los datos
-(void)start {Accelerometer,Gyro,Magnetometer,DeviceMotion}Updates;
@property (readonly) BOOL {accelerometer,gyro,magnetometer,deviceMotion}Active;
- (void)stop{Accelerometer,Gyro,Magnetometer,DeviceMotion}Updates;
Sensores
Registrarse para recibir datos de acelerómetro:
- (void)startAccelerometerUpdatesToQueue:(NSOperationQueue *)queue withHandler:(CMAccelerometerHandler)handler;
queue == [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init]
Recibir datos de giróscopo:
- (void)startGyroUpdatesToQueue:(NSOperationQueue *)queue withHandler:(CMGyroHandler)handler;
Registrarse al campo magnético
- (void)startMagnetometerUpdatesToQueue:(NSOperationQueue *)queue withHandler:(CMMagnetometerHandler)handler;
typedef void (^CMMagnetometerHandler)(CMMagnetometerData *data, NSError *error)
Localization
Internacionalización - i18n
Registrar los idiomas. Los storyboards extraerán ficheros .strings para cada idioma.
Para strings en el código, utilizar genstrings *-m
NSString *NSLocalizedStringWithDefaultValue(NSString *key, NSString *table,
NSString *bundle, NSString *defaultValue,
NSString *comment);
Ejemplo: @“hello” -> NSLocalizedString(@“hello”, @“Greeting at start of application.”)
Bundles
Los recursos están contenidos en un bundle para cada idioma (es.lproj).
Dentro de estos directorios estarán los .string, imágenes, sonidos. Primero se busca el idioma top-level (default) y luego el locale específico.
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle bundleForClass:[self class]];
NSString *path = [bundle pathForResource:@“speedlimit”
ofType:@“jpg”];
Locale
NSLocale es diferente para cada idioma. Indica el idioma seleccionado por el usuario en los ajustes.
De esta manera, se pueden ajustar fechas y números según el idioma.
+ (NSString *)localizedStringFromNumber:(NSNumber *)number
numberStyle:(NSNumberFormatterStyle)style
NSNumberFormatter *formatter = [[NSNumberFormatter alloc] init];
[formatter setNumberStyle:NSNumberFormatterDecimalStyle];
NSNumber *parsedNumber = [formatter numberFromString:userInputtedString];
Ajustes
Ajustes

NSUserDefaults
Getter
if ([[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] boolForKey:@"CacheDataAggressively"]) {
// Do something
}
Setter
NSUserDefaults* defaults = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
[defaults setBool:YES forKey:@"CacheDataAggressively"];
[defaults setObject:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:(3600 * 24 * 7)]
forKey:@"CacheExpirationDate"]; // Set a 1-week expiration
Geolocalización
Core Location
Es un framework para manejar localización y direcciones, no tiene UI
CLLocation
@propertys: coordinate, altitude, horizontal/verticalAccuracy, timestamp, speed, course
Core Location
@property (readonly) CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate;
typedef {
CLLocationDegrees latitude; // a double
CLLocationDegreeslongitude; //adouble } CLLocationCoordinate2D;
}
@property (readonly) CLLocationDistance altitude; // meters A negative value means “below sea level.”
@property (readonly) CLLocationAccuracy horizontalAccuracy; // in meters
@property (readonly) CLLocationAccuracy verticalAccuracy; // in meters
kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation
kCLLocationAccuracyBest
kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters
kCLLocationAccuracyHundredMeters
kCLLocationAccuracyKilometer
kCLLocationAccuracyThreeKilometersDirección y velocidad
@property (readonly) CLLocationDirection course;
@property (readonly) NSDate *timestamp;
// in degrees, 0 is north, clockwise
@property (readonly) CLLocationSpeed speed; // in meters/second
Distance between CLLocations
- (CLLocationDistance)distanceFromLocation:(CLLocation *)otherLocation; // in meters
CLLocationManager
+ (CLAuthorizationStatus)authorizationStatus; // Authorized, Denied or Restricted (parental, enterprise)
+ (BOOL)locationServicesEnabled; // user has enabled (or not) location services for your application
+ (BOOL)significantLocationChangeMonitoringAvailable;
+ (BOOL)isMonitoringAvailableForClass:(Class)regionClass; //[CLBeacon/CLCircularRegionclass]
+ (BOOL)isRangingAvailable; // device can tell how far it is from beacons!
- Crear una instancia de CLLocationManager y configurar un delegado para notificaciones push
- Configurar el tipo de localización deseada y monitorizar (pull)
Push
// Error reporting
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didFailWithError:(NSError *)error;
kCLErrorLocationUnknown
kCLErrorDenied
kCLErrorHeadingFailure
@property CLLocationAccuracy desiredAccuracy;
@property CLLocationDistance distanceFilter; !
- (void)startUpdatingLocation;
- (void)stopUpdatingLocation;
// Recomendable asegurarse de pararlo si no se van a procesar.
//Notificación
(void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateLocations:(NSArray *)locations; // of CLLocation!
- (void)startMonitoringSignificantLocationChanges;
- (void)stopMonitoringSignificantLocationChanges;Beacons
CLLocationManager
- (void)startMonitoringForRegion:(CLRegion *)region;
// CLCircularRegion/CLBeaconRegion
- (void)stopMonitoringForRegion:(CLRegion *)region;
Detectando cuándo se entra en una región o cerca de otro dispositivo
Beacons
CLLocationManager’s delegate
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didEnterRegion:(CLRegion *)region;
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didExitRegion:(CLRegion *)region;
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager monitoringDidFailForRegion:(CLRegion *)region
withError:(NSError *)error;
Ejemplo
UPM Example
App, Icons, Splash
git checkout splash
- Creamos la aplicación como Single View
- Modificamos el icono
- Modificamos el Splash
- Podemos crear todos los iconos necesarios en http://makeappicon.com
- Se añaden en los assets
Login

git checkout splash
- Pantalla de Login
- Campos de texto:
- user
- password
- IBOutlet
- Botón de entrar
- Segue
- IBAction
- Alert View
Pantalla de alumno

git checkout alumno
- Foto del alumno
- Campos de texto:
- name
- Navigation Bar
- Navigation Bar Item
- Edit segue
Editar alumno

git checkout editar_alumno
- Foto del alumno
- UIImagePickerController
- Campos de texto:
- name
- Navigation Bar
- Navigation Bar Item: Guardar
- Navigation Bar Back
- Unwind segue
UIImagePickerController
Vista model para obtener referencias a las fotos y vídeos de la cámara y la galería.
Primero hay que probar qué capacidades hay disponibles:
+ (BOOL)isSourceTypeAvailable:(UIImagePickerControllerSourceType) sourceType;
UIImagePickerControllerSourceTypePhotoLibrary/Camera/SavedPhotosAlbum
+ (BOOL)isCameraDeviceAvailable:(UIImagePickerControllerCameraDevice) cameraDevice;
UIImagePickerControllerCameraDeviceFront| UIImagePickerControllerCameraDeviceRear
UIImagePickerController
- (IBAction)takePhoto:(UIButton *)sender {
UIImagePickerController *picker = [[UIImagePickerController alloc] init];
picker.delegate = self;
picker.allowsEditing = YES;
picker.sourceType = UIImagePickerControllerSourceTypeCamera;
[self presentViewController:picker animated:YES completion:NULL];
}
- (void)imagePickerController:(UIImagePickerController *)picker
didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo:(NSDictionary *)info
{
// extract image/movie data/metadata here, more on the next slide
UIImage *chosenImage = info[UIImagePickerControllerEditedImage];
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:...]; // or popover dismissal
}
// Also dismiss it when cancel happens!
- (void)imagePickerControllerDidCancel:(UIImagePickerController *)picker
{
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:...]; // or popover dismissal
}
Tab Bar

git checkout editar_alumno
- Creamos el TabBarController
- Tab Bar Items
- Iconos
- Títulos
- Enlaces
Table View

git checkout expediente
- Table View Controller
- Configuramos la celda
- Creamos el modelo estático
Web View

git checkout ayuda
- Creamos un nuevo Tab Bar item
- Añadimos un WebView
- Cargamos el HTML desde el mismo bundle.

git checkout settings
- Nuevo Settings Bundle
- Modificamos las propiedades.
Avisos - Pager

git checkout avisos
- UIPageViewController
- Modelo estático de avisos
- Modelo de página
Login - request

git checkout login_network
- Mantle + AFNNetworking
- JSON
- Ojo con el segue!
Expediente - request

git checkout login_network
- Mantle + AFNNetworking
- Modelo
- JSON array
- TableViewCell
Programación para iOS
By Jorge Vila Forcén
Programación para iOS
- 3,875

