Webdevelopment (VAK)
ASP.NET Core Razor Pages
Program
-
Lesson 0 HTTP Protocol-
Request + Response + Simple Input Validation
-
-
Lesson 1 Razor Pages + Statemanagement
-
Lesson 2 Razor Pages Page Structure + Validation
-
Lesson 3 Database Interaction (Dapper)
-
Lesson 4 Ajax Requests + Other techniques - Note: Lesson 2 + Lesson3 will probably be switched
Material / Resources / Assignments
Recommended Software
-
.NET
Core6.x framework (SDK) - Jetbrains Rider (IDE) -- free for students
- Or other IDE: Visual Studio (Code)
Git Repository
-
git pull
- to get the latest updates
- some bug fixes/improvement
- second group of users (so expect some errors)
git clone https://github.com/NHLStenden/WebdevCourseRazorPages.git WebdevCourseRazorPages
cd WebdevCourseRazorPagesExecute the following command in the terminal:
My Material
Project Structure
- Project Structure
- Examples
- Exercises
- Readme.md
- Exercises.Tests (only Lesson1)
- Test are restrictive!
- To test the exercises
- If a test fails take a look a the test-code
- If you think there is an error in a test please contact me.
Examples
Run the project (Examples), click on an example
/Lesson1/GetRequest
Run the project (Examples), click on an example
Exercises & Test
README.md files contain exercises
Program the solutions in Lesson1Exercises, Assignment1.cshtml, etc..

Exercises:
Tests:
Run a Test
Demo in IDE
If a test fails (red)
- You made an error accordingly to the test
- Take a close look at the error message from the test
- Try to fix the error
- Reread the exercises
- I made a mistake (bug)
- please let me know
- You need help to solve the exercises
- fellow students
- werkcollege
Material
- Examples & Exercises
- Microsoft Learn: Create a web UI with ASP.NET Core
-
Razor Pages for ASP.NET Core - Full Course (.NET 6)
- Examples from learningprogramming.net
- Books:
- ASP.NET Core Razor Pages in Action (not printed yet, preview)
Werkcollege
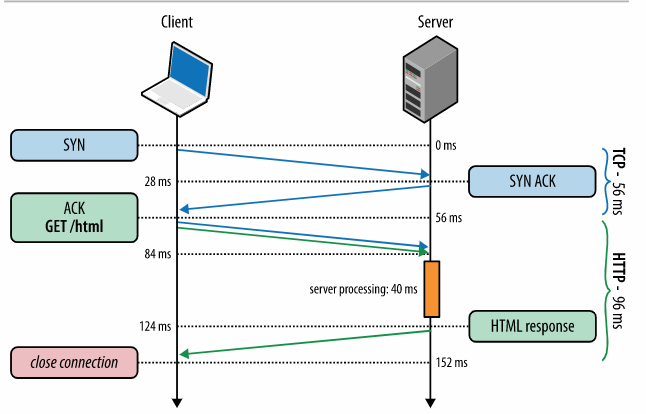
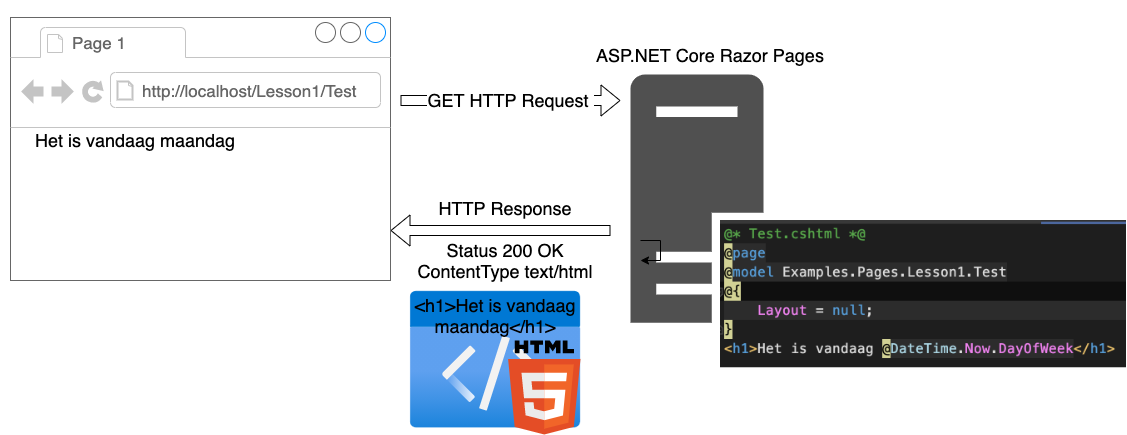
Lesson 0 - HTTP Protocol
- How the Client (browser) connects to a Server and Request a webpage with the HTTP Protocol.
- HTTP GET Request
- HTTP POST Request
- HTTP Response
- How we can interact with the HTTP Protocol, more precisely HttpRequest, HttpResponse.
Lesson 0 - HTTP Protocol
HTTP Protocol:
- The client sends an HTTP-Request to the server
- The server sends an HTTP-Response to the client
client
server
What is a Protocol?
- Analogy:
- If two people share the same language, they can communicate.
- A good example is buying bread at a local bakery.
How to GET a webpage
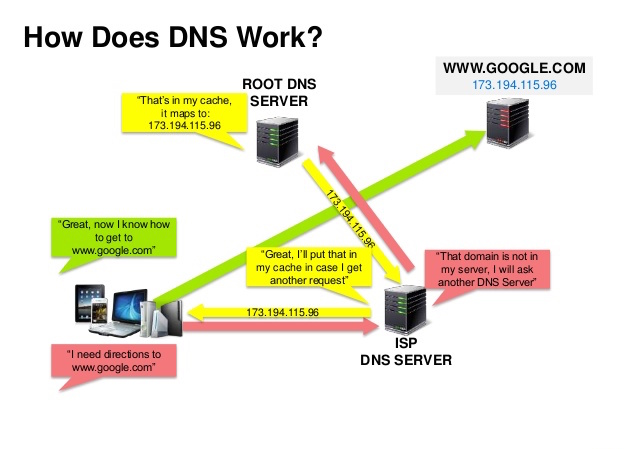
Domain Name Server
- What is the IP address of www.google.com
How to GET a webpage
- The Client (e.g. a browser) connects to a Server using the (TCP) connection (socket).
- First, we need the IP address (DNS Server)
- IP Protocol is a network protocol, i.e. how computers communicate
-
With the IP address, a TCP connection can be established (TCP three-way handshake)
- Socket == two-way connection of specific type (e.g. TCP)
- First, we need the IP address (DNS Server)
- When the connection is Established the Client Request a page with the HTTP Protocol
- GET Request
See the image on the previous slide for a graphical explanation.
DNS
Domain Name Server
- What is the IP address of www.google.com
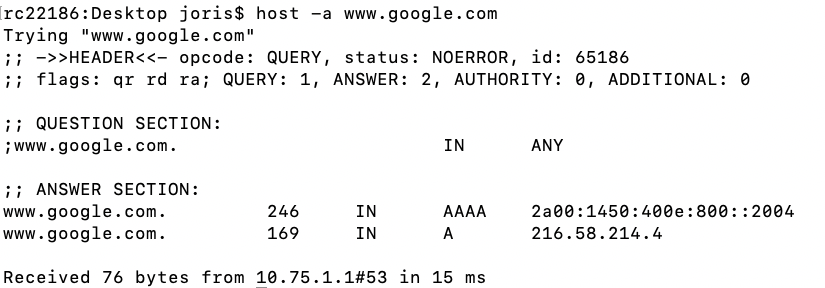
The IP4 Address of www.google.com. 216.58.214.4
Establish a connection
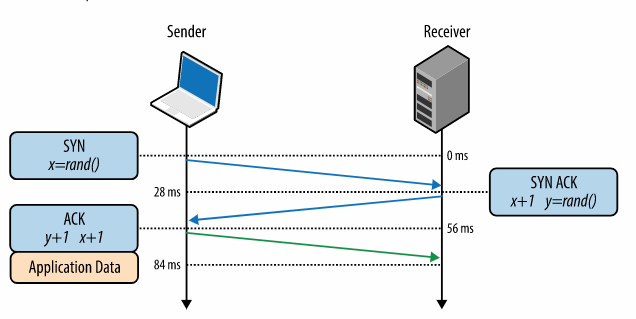
- To establish a TCP connection a Three-way handshake
- After the handshake is completed application data can flow.
- HTTP Protocol Messages
- After the handshake is completed application data can flow.
How to GET a webpage
Let send an HTTP GET Request
HTTP GET Message is used to retrieve a website
- Request
- Header
- Response
- Header
- Body (Content)
Demo in Postman and Chrome Development Tools
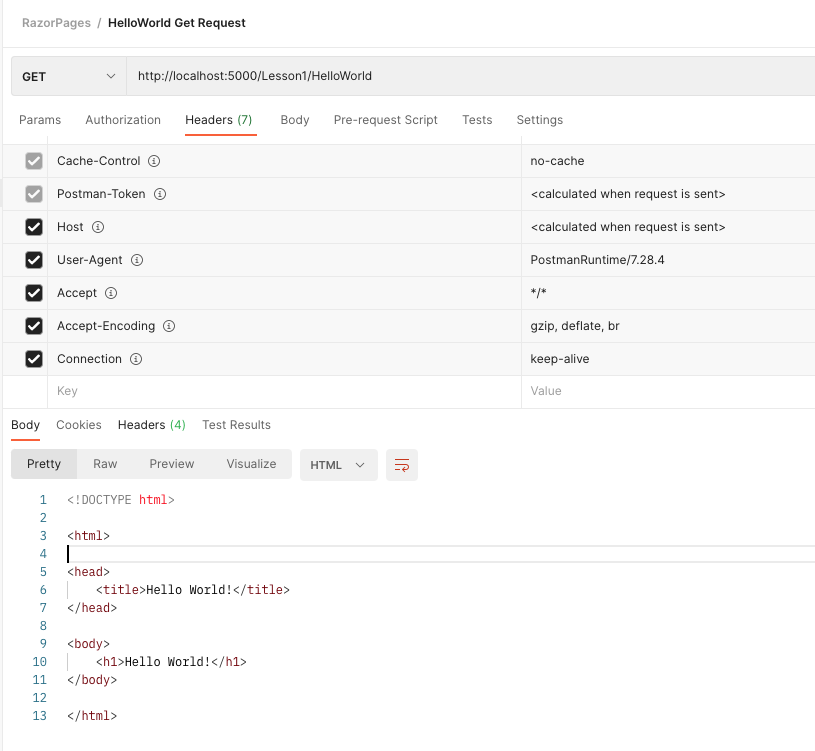
The HTTP Request
Method / HTTP-verb (GET, POST)
Path
Verion of HTTP Protocol
Headers
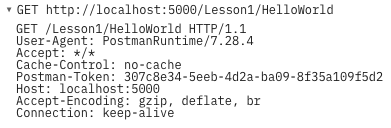
The HTTP Response
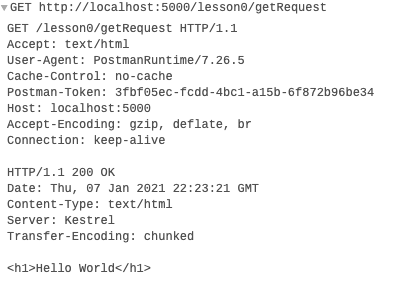
HTTP Status Code
HTTP Protocol / Version
Headers
Body (Content)
Content-Type: specifies the type of content (MIMI-type, for example: text/html, text/css)
Get Post Request Cycle
Client
Server
GET .../login
Response "Login Page"
POST .../login
Response "Login Success"
- Step 1: The GET Request
- Step 2: The POST Request
- Sometimes: redirect
GET Request in C#
Retrieve a website, with a GET Request
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
public class SynchronousSocketClient {
public static void StartClient() {
// Data buffer for incoming data.
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
// Connect to a remote device.
try {
// Establish the remote endpoint for the socket.
// This example uses port 11000 on the local computer.
IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.GetHostEntry("www.google.com");
IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0];
IPEndPoint remoteEP = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress,80);
// Create a TCP/IP socket.
Socket sender = new Socket(ipAddress.AddressFamily,
SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp );
// Connect the socket to the remote endpoint. Catch any errors.
try {
sender.Connect(remoteEP);
Console.WriteLine("Socket connected to {0}",
sender.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
string getMessage = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
//string getMessage = "GET /lesson0/getRequest HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: 127.0.0.1\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
// Encode the data string into a byte array.
byte[] msg = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(getMessage);
Console.WriteLine(getMessage);
// Send the data through the socket.
int bytesSent = sender.Send(msg);
// Receive the response from the remote device.
int bytesRec = sender.Receive(bytes);
Console.WriteLine("HTTP Response: ");
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(bytes,0,bytesRec));
// Release the socket.
sender.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
sender.Close();
} catch (ArgumentNullException ane) {
Console.WriteLine("ArgumentNullException : {0}",ane.ToString());
} catch (SocketException se) {
Console.WriteLine("SocketException : {0}",se.ToString());
} catch (Exception e) {
Console.WriteLine("Unexpected exception : {0}", e.ToString());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Console.WriteLine( e.ToString());
}
}
public static int Main(String[] args) {
StartClient();
return 0;
}
}
Use Repository from PageModel
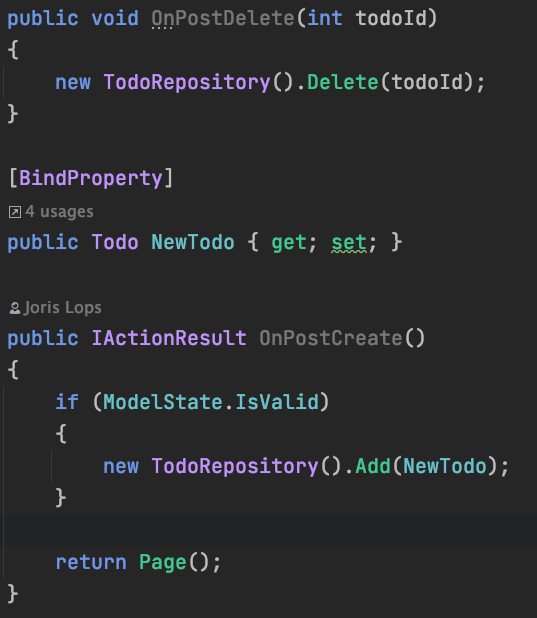
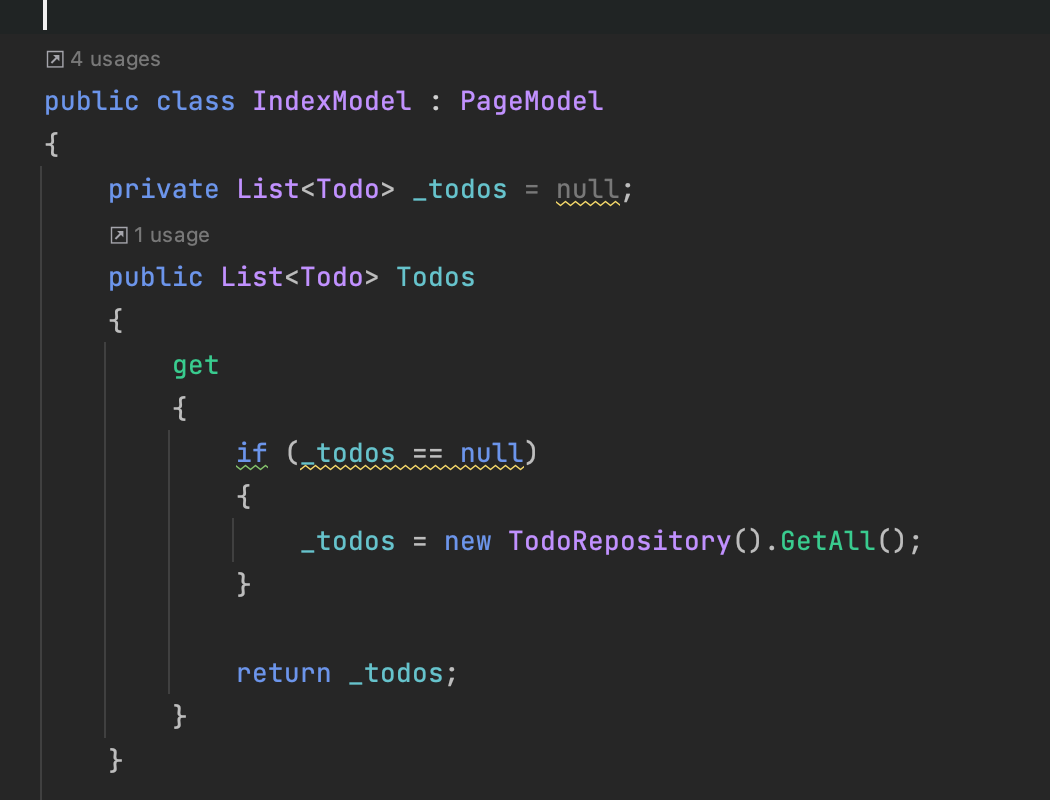
Try not to Query (READ/SELECT) in OnGet(..) or OnPost() methods!
The Server
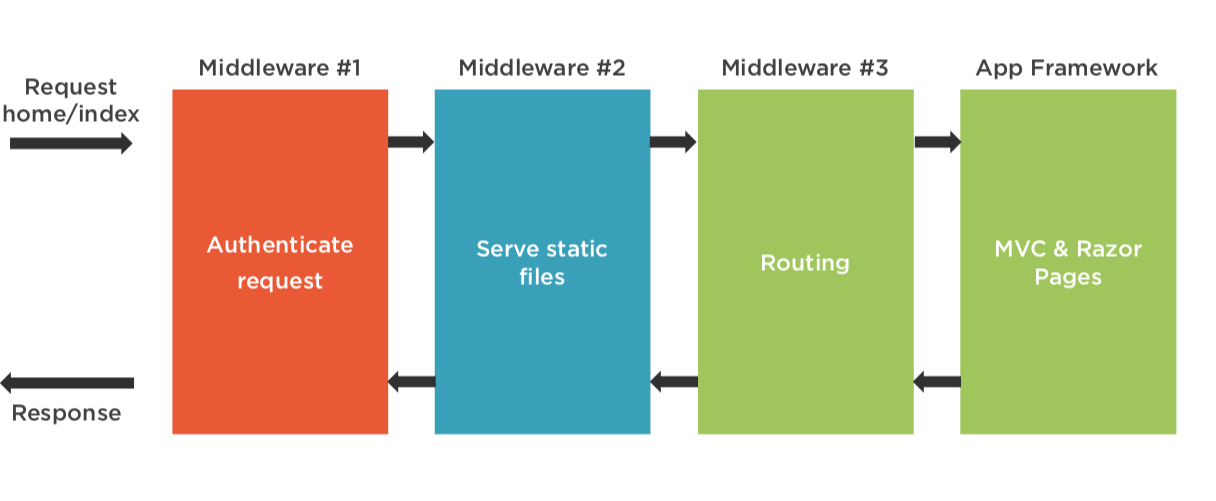
The server should process the HTTP Request and return the HTTP Response!
In ASP.NET Core the Request is processed in the Request Pipeline
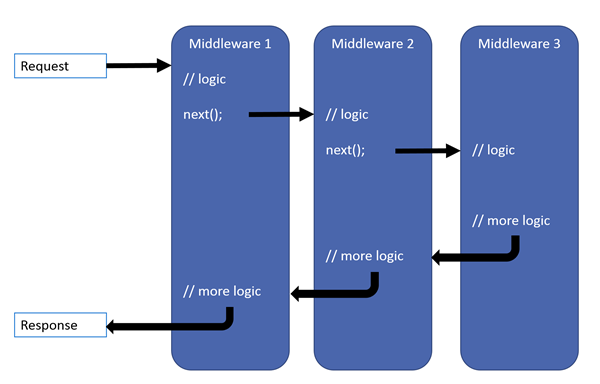
Request Pipeline - Demo
//middleware A
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
if (context.Request.Path.Value
.StartsWith("/lesson0/getRequestPipelineExample",
StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
//Write to the context.Response.Body
await context.Response.WriteAsync("<h1>Hello World</h1>");
context.Response.Headers.Add("Content-Type", "text/html");
context.Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.OK; //HttpStatusCode.OK == 200
}
else
{
await next.Invoke();
}
});
//middleware B
// app.Use(async (context, next) =>
// {
// ...
// await next.Invoke();
// });
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("<h1>Page Not Found</h1>");
});Demo - Inspect with debugger!
Lesson 1 - Razor Pages & State Mangement
-
Razor
-
Razor Pages
-
Statemangement
-
Handler Methods
-
Demo of ASP.NET Core Razor WebPages
-
Todo list
-

HTTP GET Request
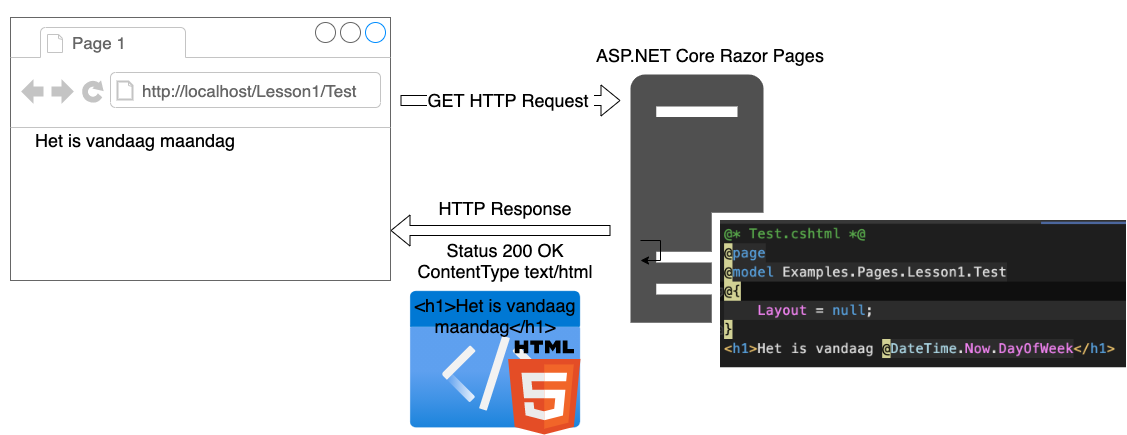
Razor Syntax
Razor is a markup syntax for embedding server-based code into webpages. The Razor syntax consists of Razor markup, C#, and HTML. Files containing Razor generally have a .cshtml file extension.
- Mix HTML & C# Code
- Razor is smart
- .cshtml files extension
- The output of a razor file is written to the HTTP Response
- A Razor file is compiled to a C# class!
Razor Syntax
Demo Time
Visual Studio:
Razor + Request
Razor Pages - Two Approaches
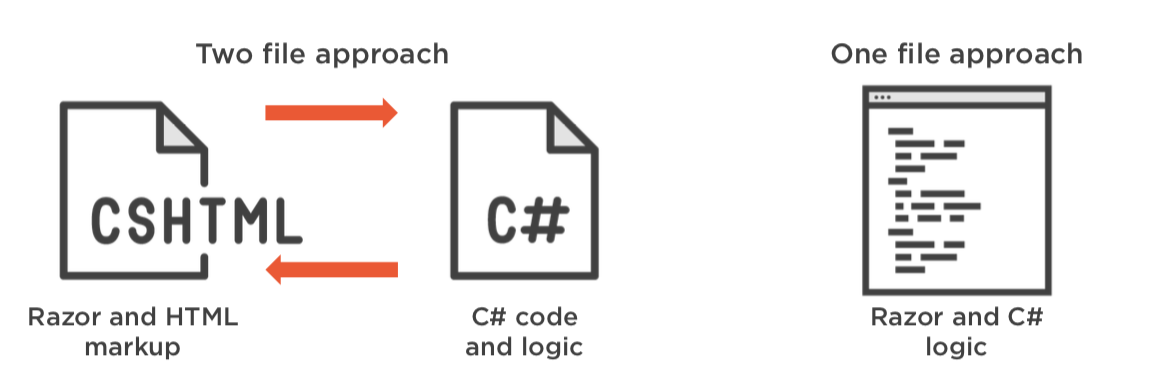

Page Centric

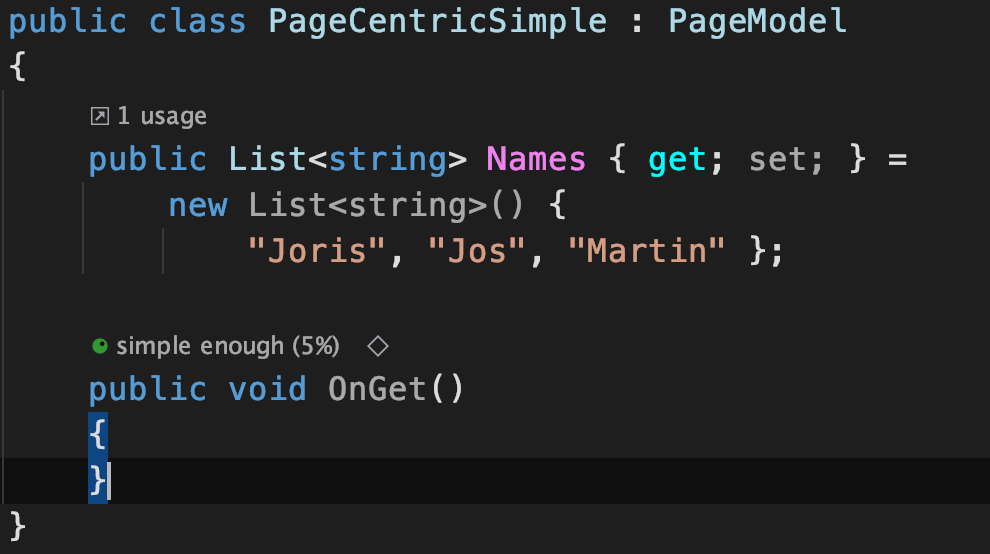
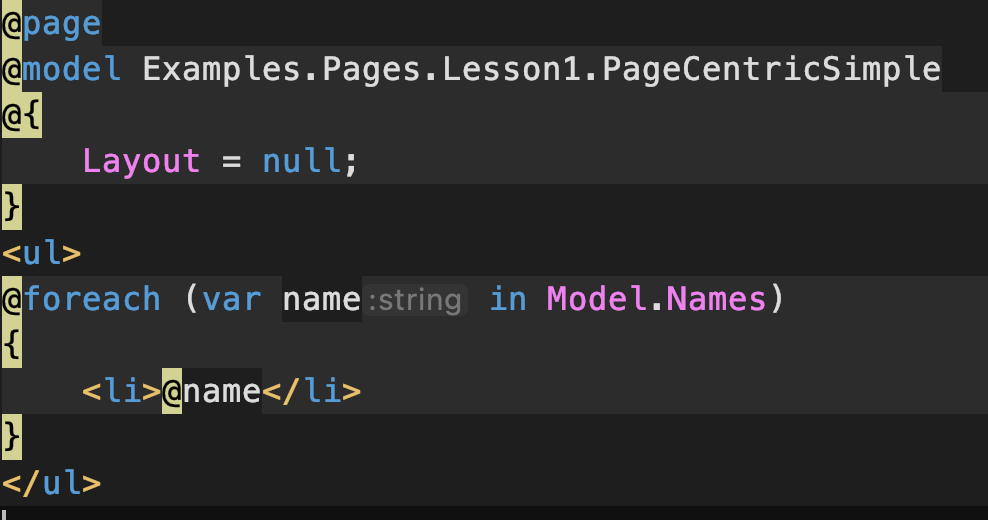
PageCentricSimple.cshtml
PageCentricSimple.cshtml.cs
Page Centric


PageCentricSimple.cshtml
PageCentricSimple.cshtml.cs
Model gives access to Page Model public properties & methods & variables
Content Page must have @model directive to couple Page Model
Page Centric - HTTP
- return Page();
- fills the ContentType, StatusCode, etc
- Use IActionResult
- Let's try something else:
- return BadRequest();
- return Redirect("www.google.com")
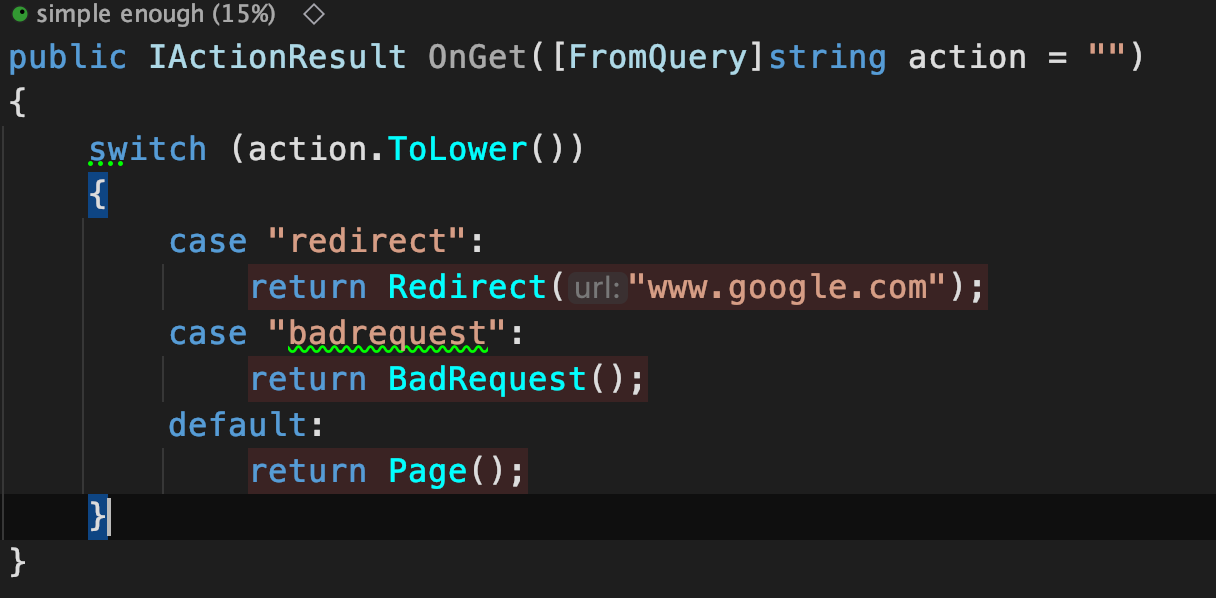
/Lesson1/PageCentricSimple
- Redirect
- Error
- Het is vandaag maandag
Show in Chrome & Debugger & IDE
Razor Pages
- ASP.NET Core Razor Pages = page-centric frameworks
-
Razor Pages is built on top of ASP.NET Core MVC
- Core MVC != Razor Pages
- MVC is technically coupled to Razor Pages, a different programming model!
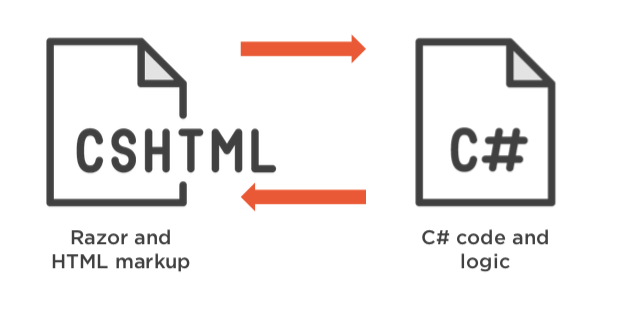
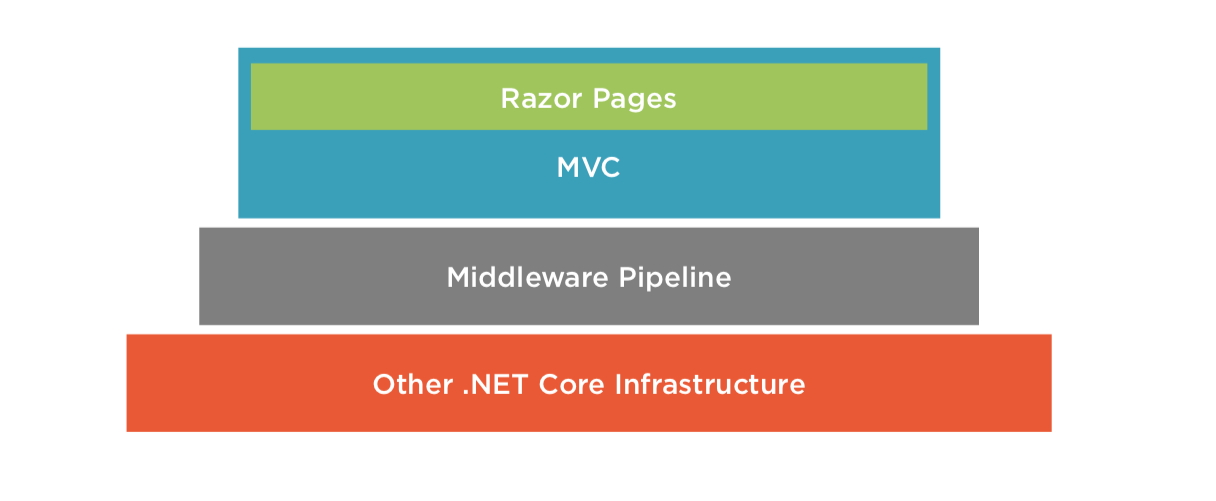
Anatomy of Razor Page
- Content Page (.cshtml)
- @page directive
- @model directive
- Model.PropertyName
- Model Page (.cshtml.cs)
- OnGet(...) Method
- OnPost(...) Method
- public properties/methods/variables can be accessed by Content Page @Model
Anatomy of Razor Page
How a Request is
processed
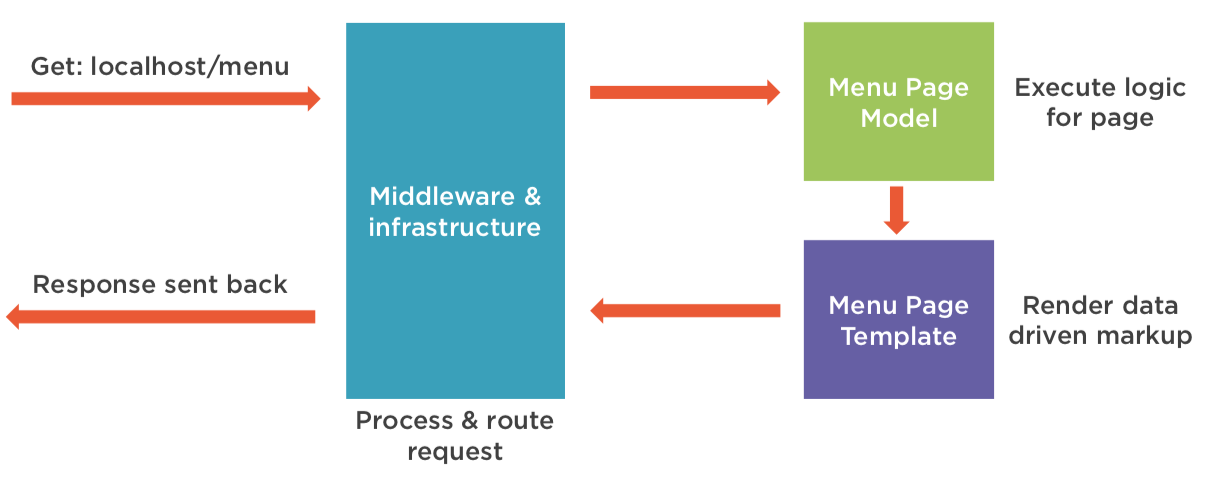
Razor Page Example
State Management
- HTTP is stateless protocol - it has no memory of prior connections and cannot distinguish one request from another
- Demonstrate stateless, next example
- Solution: state management
No state (stateless)
State Management
- Client-Side
- Query Strings
- Route Data
- Form
- Hidden Form Fields
- Server Side
- Cookies
- TempData
- (Server Side) Sessions
- Cookies
Query String
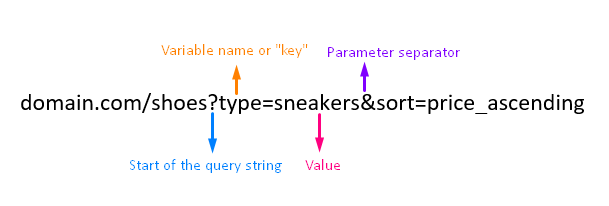
Three ways to get the Query String value(s):
-
Model binding
-
Request.Query Object-
Request.Query["key"]
-
-
Parameters in the OnGet([FromQuery]string key)
- The preferred method
-
[BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)]
- Can be problematic, in a GET request!
- read-only in GET in combination with Validation!
- Can be problematic, in a GET request!
-
GET Request
GET Request
Parameters in the OnGet
BindProperty
Request.Query
Route Data / Parameters
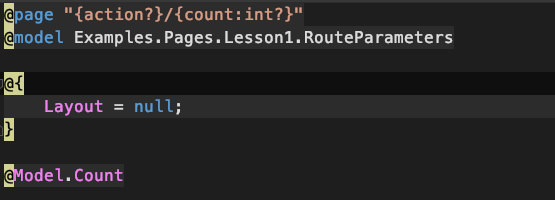
<a href="/Lesson1/RouteParameters/decrement/0">decrement</a>
String after @page is called the Route Template
- ? = optional
- int = constraint (there are more, take a look at the docs)
Examples:
- @page "{category}/{subcategory?}"
- @page "{category}/{productid:int}
- https://www.coolblue.nl/televisies/oled/2020
- @page "{category}/{subcategory?}/{type?}/{year:int?}
- Why Route Templates/ Route Data?: SEO & findability
Three ways to get the Route Data values:
-
Request.RouteValues Object-
Request.RouteValues["key"]
-
-
Parameters in the OnGet([FromRoute]string key)
- The preferred method
-
BindProperty-
Can be problematic, in a GET request!Method binding, read-only in GET!
-

<a href="/Lesson1/RouteParameters/decrement/0">decrement</a>
String after @page is called the Route Template
Route Data / Parameters
Route Data / Parameters
Get Post Request Cycle
Client
Server
GET .../login
Response "Login Page"
POST .../login
Response "Login Success"
- Step 1: The GET Request
- Step 2: The POST Request
- Sometimes: redirect

Posts
- Send data to the Server with a form
- Three possibilities:
- [BindProperty] string Username { get; set;}
- Parameters
- OnPost([FromForm] string username)
Request.Form["username"]
<form method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<button type="submit">Verzenden</button>
</form>method="post"
Get - Post Request Cycle
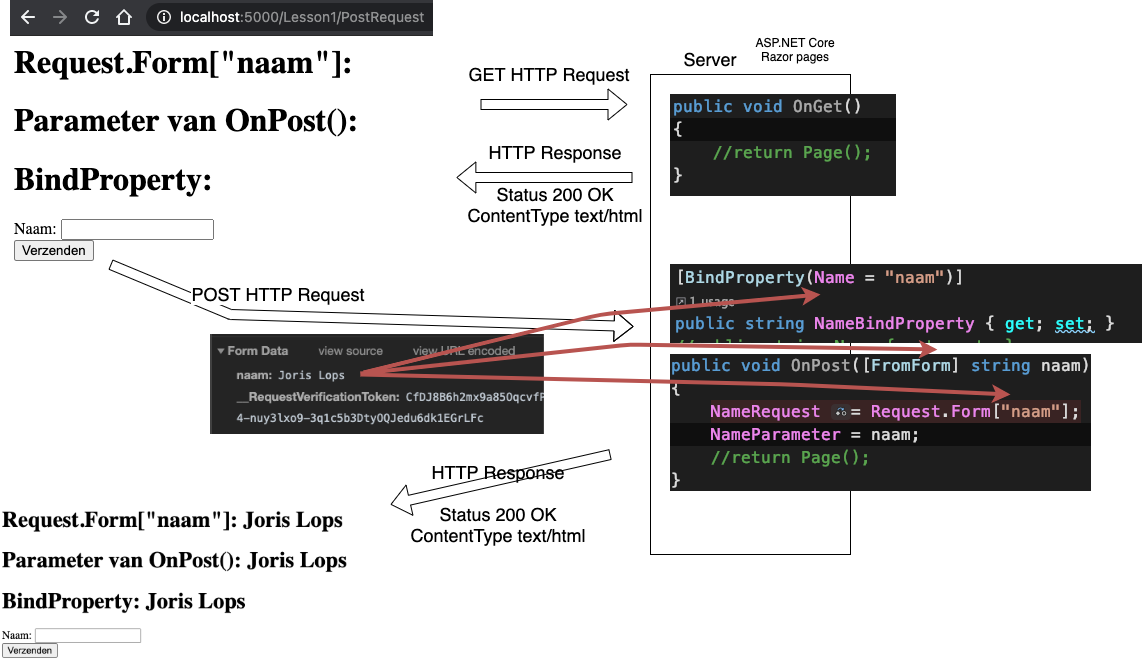
Post Request
Hidden Form Fields
- They are hidden, that's scary!
- They only work in POST request
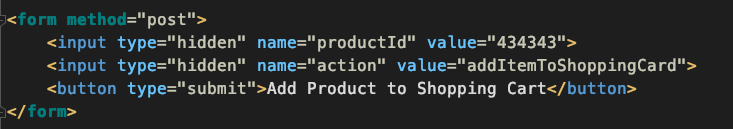
Three ways to get the form data:
Request.Form- as parameters: OnPost([FromForm] int productId, ...)
-
BindProperty (works great for posts!)
- In combination with Model Validation
Hidden Form Fields
State Management
- Client-Side
- Query Strings
- Route Data
- Hidden Form Fields
- Let's do a demo
- Todo list, we can apply all the client-side state management techniques!
Handler Methods
- Naming convention (On + HTTP-Verb)
OnGetHandlerName- OnPostHandlerName
- Call from html with a tag-helper
- asp-page-handler="HandlerName"
- form or button or link
- pass "parameters" to handler
- asp-route-parametername
- asp-page-handler="HandlerName"
- When OnPost(...) is called, it's always called from a form with method=POST!
Handler Methods
State Management
- Server Side
- Cookies
- TempData
- Sessions
- Cookies
Cookies
- Cookies are created by the server
- Stored in the client
- Send with each request
- Used for: user-ids, session-id, preference (language, etc), etc

Let's take a look at Coolblue in the Chrome Development Tools
Cookies
Temp Data
- Usage: message, to a different page
- Can be used once (one Response)
- Cookie-based (show in Chrome Devtools)
- Use only when to redirect and the message should not appear in the address-bar
//To write
TempData["Lievelingsgetal"] = lievelingsgetal.ToString();
//Redirect
return RedirectToPage("ShowTempData");//To read
@TempData["Lievelingsgetal"]TempData - Cookies
Sessions
Sessions
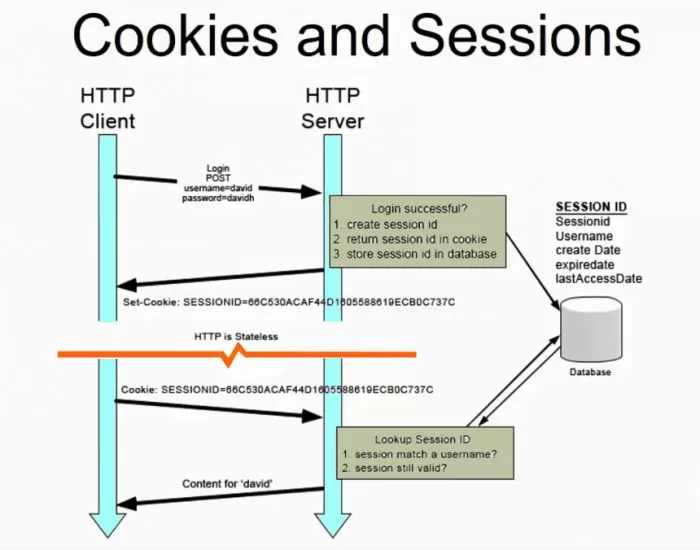
Session
- SessionId is stored (set-cookie) by the client
- SessionId is stored in the webserver memory
- The SessionId is used to get access to stored data on the server
- Data can be null or empty
- Convert to correct type
string strCount = HttpContext.Session.GetString("count");
if (strCount != null)
{
Count = Convert.ToInt32(strCount);HttpContext.Session.SetString("count", Count.ToString());Usage: store temporary data (20 minutes by default)
Sessions
Doesn't work in live preview!
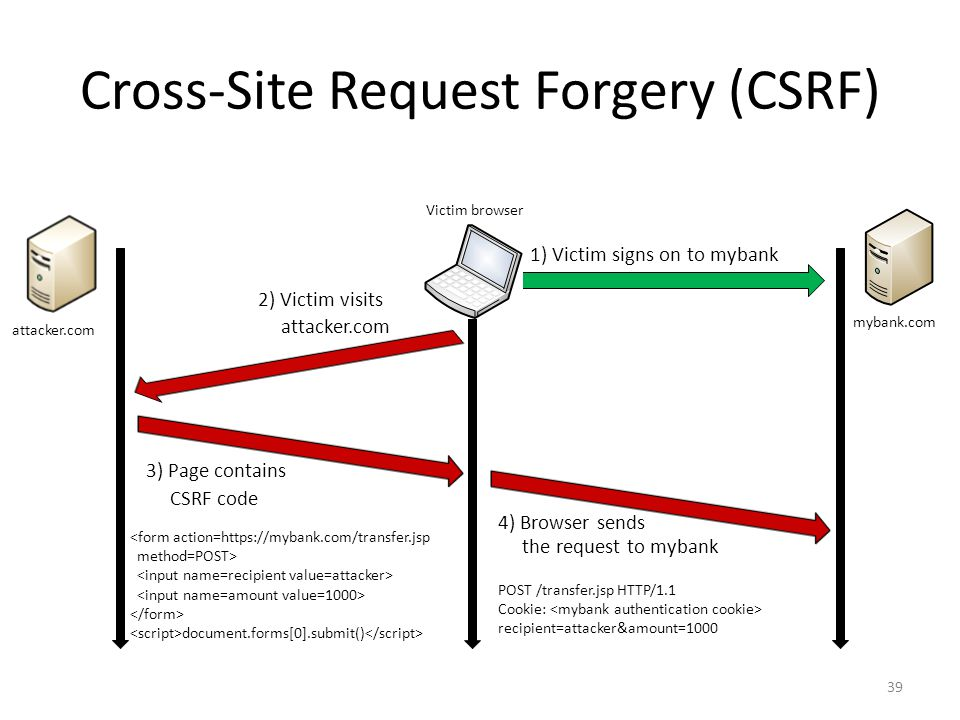
XSRF/CSRF attacks
- Only works with HTTP Post requests
- ASP.NET get you covered
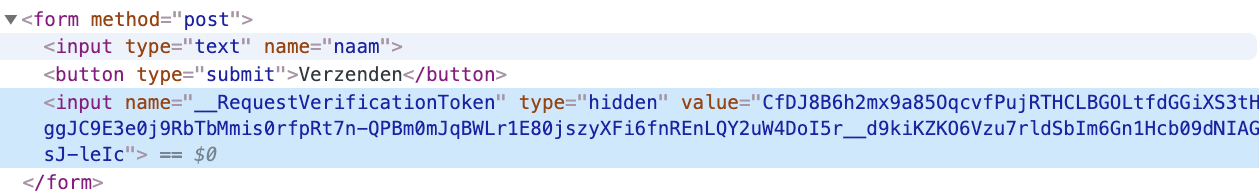
- _RequestVerificationToken
- Let's take a look at Chrome Development Tools (Pages/Lesson1/PostRequest)
- _RequestVerificationToken
Lesson 2 Page Structure & Validation
- TagHelpers
- BindProperty
- Validation
- Return Values
- Layout Pages
- _Partial Pages
- ViewComponents

Tag Helpers
- Tag helpers are reusable components for automating the generation of HTML in Razor Pages. Tag helpers target specific HTML tags.
- Let's see the result (rendered html)
- Let's take a look at some important once:


Tag Helpers
- Generate HTML and will help us!
- Previously @HTML methods, don't use them anymore!
- It's possible to create your own
- Can be difficult
Validation
- Validation == check if input is correct
- To inform the user when input is incorrect
- To prevent invalid input to enter the system
- Database
- Assumptions in code (like type, range, etc..)
- if assumptions incorrect
- bugs
- runtime errors / exception
- if assumptions incorrect
- Always check input @
- Client-side
- Server-side
ModelBinding
Three techniques:
-
Direct- Request.Query, Request.Form, Request.RouteValues, etc.
- As Parameter (input only)
- public void OnGet([FromRoute] string categoryName) { ... }
- Input & validation, no output (we have to copy)
-
BindProperty
- Input & Output (can be used in razor)
- Complex object binding
-
Input from forms
- to add or edit object
- Request, Routes, etc
- Let's explore in more depth
- Enables validation
Validation - Step 1
- Enhance model with DataAnnotation Attributes
Validation - Step 2
- Handle Error Message in razor page
- asp-validation-for
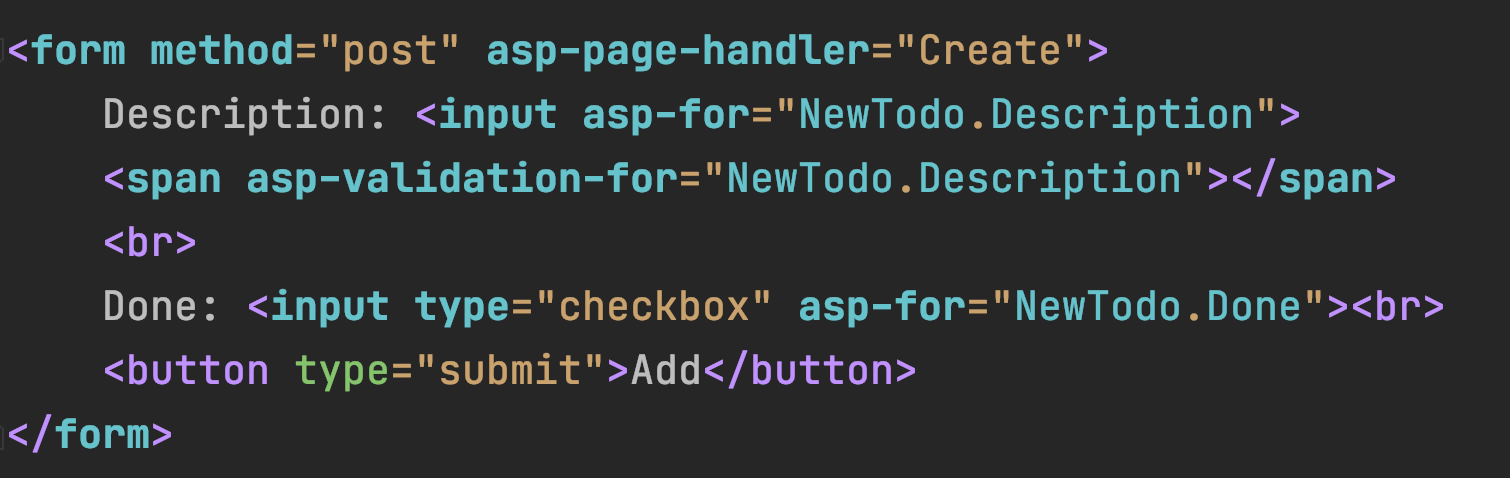
Validation - Step 3
- Check if Model is valid (ModelState.IsValid)
- Invalid --> return Page()
- Displays error message automatically
- Invalid --> return Page()
- Model that is Validated is NewTodo

Validators

Attributes are applied to properties on the inbound model - typically a PageModel or ViewModel
Validators
Attributes are applied to properties on the inbound model - typically a PageModel or ViewModel
public class Product
{
public int ProductId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Naam mag niet leeg zijn"), MinLength(2), MaxLength(12),
Display(Name = "Naam", Prompt = "Geef een geldige product naam op")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[MaxLength(128)]
[DefaultValue("Geen beschrijving aanwezig")]
public string Description { get; set; }
[Required, Range(0, 10000)]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public decimal? SalePrice { get; set; }
//[DefaultValue(typeof(DateTime), DateTime.Now)]
//https://www.learnrazorpages.com/razor-pages/forms/dates-and-times#:~:text=The%20default%20value%20for%20a,00%3A00%20in%20the%20control.
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime InShopDate { get; set; } = DateTime.Today;
[Required]
public int CategoryId { get; set; }
public Category Category { get; set; }
}Validators - Client Side
Take a look with chrome dev tools how they are rendered
@section Scripts
{
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
<script>
var settings = {
validClass: "is-valid",
errorClass: "is-invalid"
};
$.validator.setDefaults(settings);
$.validator.unobtrusive.options = settings;
</script>
}Validation
Page Structure
- Don't Repeat Yourself
- Razor Pages:
-
Layout Pages
- Section
- Nested (Layout in Layouts)
- Partial Pages Content Page (view/cshtml)
- ViewComponent: Content Page + Page Model (logic)
- ViewStart
- ViewImport
-
Layout Pages
- Razor Pages:
Layout Page
-
_Layout.cshtml (convention: in the Shared folder)
- RenderBody()

Layout Pages
//Lesson2/Products/Index.cshtml
@page
@model Examples.Pages.Lesson2.Products.Index
@{
Layout = "Products/_ProductsLayout";
}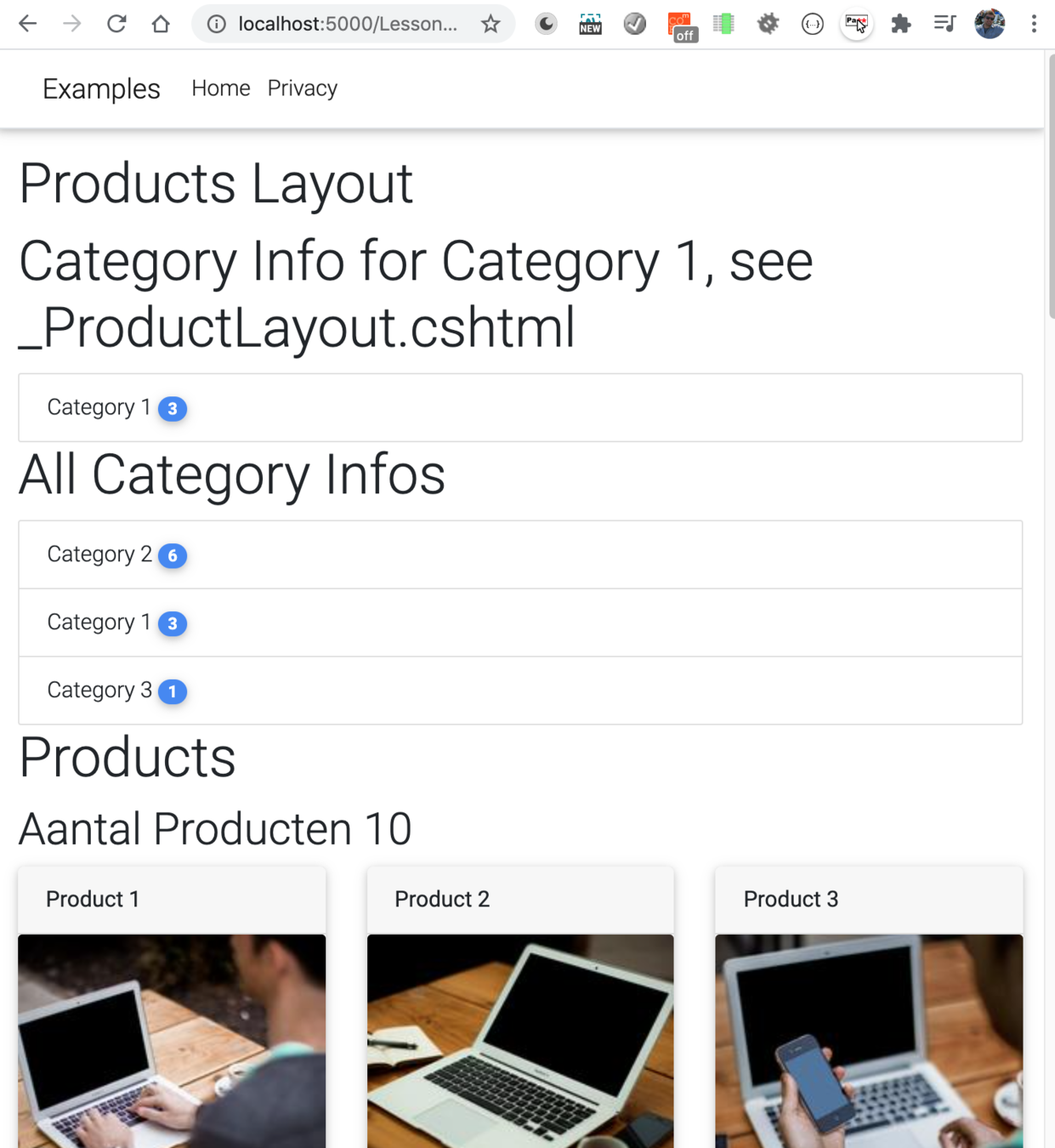
//Lesson2/Products/_ProductsLayout.cshtml
@{
Layout = "Shared/_Layout";
}
<h1>Products Layout</h1>
<h1>Category Info for Category 1, see _ProductLayout.cshtml</h1>
@await Component.InvokeAsync("CategoryInfoComponent", "Category 1")
@RenderBody()//Shared/_Layout.cshtml
//check in Code EditorLayout Page
Section
- Sections (optional parts for content pages, which are "placed" in the Layout Page)
@* In the _Layout page *@
if(IsSectionDefined("Scripts")) {
RenderSection("Scripts");
}
@* In a Content Page */
@section Scripts {
<script src="popupWidget.js"></script>
}
---------------------------------------
if(IsSectionDefined("Footer")) {
RenderSection("Footer");
} else {
@* Default Footer *@
}
@* In a Content Page */
@section Footer {
@* optional footer *@
}Partials
-
Reusable piece of cshtml (view)
- can have a model
- no page model (
@Page)
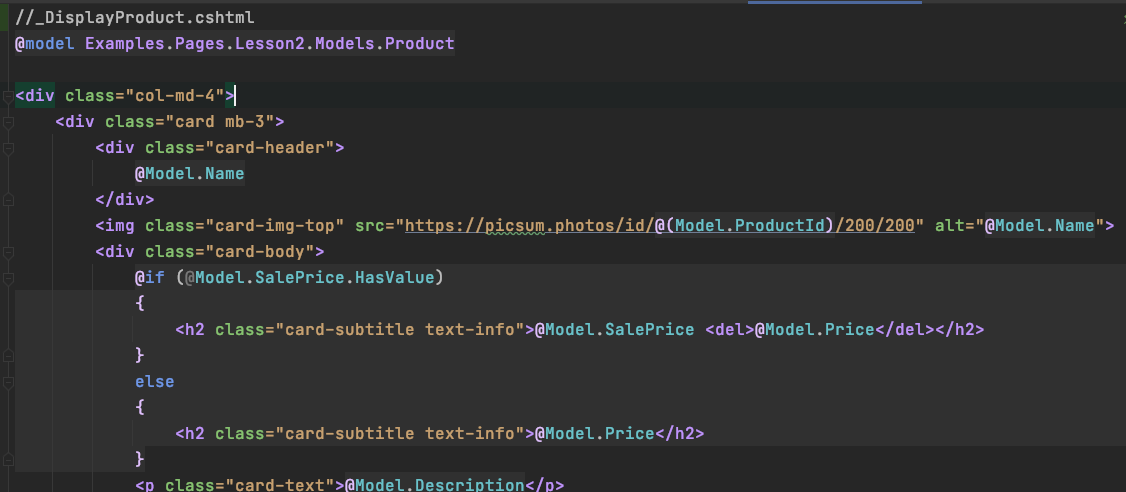
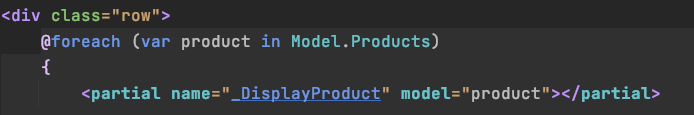
View Components
-
View Component =
- Reusable piece of cshtml (view) +
- Page Model (ViewComponent Class)
-
Directories names are important
- /Pages/Components/<component name>/Default.cshtml
- /Views/Shared/Components/<component name>/Default.cshtmlClass)
View Component View
- Is Strongly typed
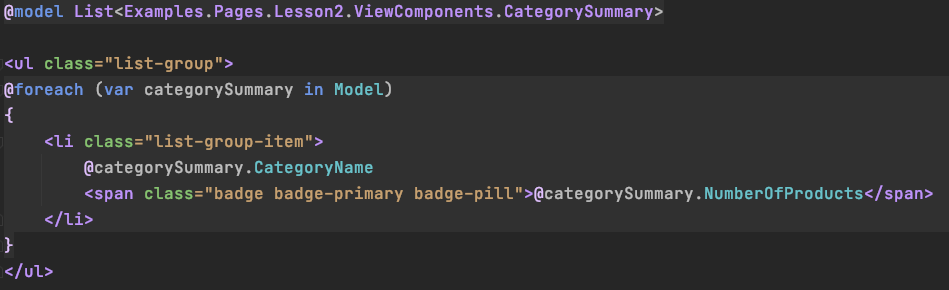
View Component Page Model
- Inherits ViewComponent
- Implements the Invoke(....) method
- Name ends with ViewComponent
public class CategoryInfoComponent : ViewComponent
{
private ProductsRepository _productsRepository;
public CategoryInfoComponent()
{
_productsRepository = new ProductsRepository();
}
public IViewComponentResult Invoke(string categoryName = null)
{
var products = _productsRepository.GetProductsInShop()
.OrderBy(x => x.Name)
.ToList();
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(categoryName))
{
products = products.Where(x => x.Category.Name == categoryName).ToList();
}
List<CategorySummary> categorySummaries = new List<CategorySummary>();
foreach (var productByGroup in products
.GroupBy(x => x.Category))
{
categorySummaries.Add(new CategorySummary()
{
CategoryName = productByGroup.Key.Name,
NumberOfProducts = productByGroup.Count()
});
}
// ReSharper disable once Mvc.ViewComponentViewNotResolved
return View(categorySummaries);
}
}View Component Usage
- Two methods:
1. InvokeAsync("viewComponentname", <Param1>, <Param2>,...)
2. web components (kebab case naming), not working for me

Parameters

View Start & View Imports
- View start & view import get executed before the actual page is executed
- _ViewImports.cshtml: include all using directives
- saves a lot of usings
- tag handlers are registered here
- _ViewStart.cshtml
- A good place to put in code that must be executed before
- Login check
- A good place to put in code that must be executed before
- _ViewImports.cshtml: include all using directives
Action Results
- IActionResult is the base return type
- When type is void, then Page() is returned automatically (by Razor Pages)
Validation With URL's
@page "{filterCategory?}"//startup.cs --> public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services
.AddMvc()
.AddRazorPagesOptions(options =>
{
options.Conventions.AddPageRoute("/Archive/Post", "Post/{year}/{month}/{day}/{title}");
});@page "{year:int}/{month:int}/{day:int?}"
@model TodoExample.Pages.Todo.TestUrls
<h1>Test</h1>
@Request.RouteValues["year"]
<br>
@Request.RouteValues["month"]
<br>
@Request.RouteValues["day"]
<br>public void OnGet(int year, int month, int? day)
{
}Custom Validator
public class ProductIdExistsConstraint : IRouteConstraint
{
public bool Match(HttpContext? httpContext, IRouter? route, string routeKey, RouteValueDictionary values,
RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
var value = values["productid"];
if (value == null)
return false;
int productId;
if (int.TryParse(value.ToString(), out productId))
{
var productsRepository = new ProductsRepository();
var product = productsRepository.GetProductById(productId);
return product != null;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}//Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.Configure<RouteOptions>(options =>
{
options.ConstraintMap.Add("productIdExists", typeof(ProductIdExistsConstraint));
});
...
}@page "{productid:productIdExists}"
@model Examples.Pages.Lesson2.Products.Details
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
<div class="row">Register:
Use:
Just Practice
Get some feeling when to use which technique to reduce code duplication and improve code reuse.
Dry (Don't Repeat Yourself):
If you do a lot of times the same task (code) think about the techniques of this lesson and OOP in general to avoid this!
Lesson 3 Database - Dapper
- How to connect to a database
- Dapper
- Query
- SELECT
- Execute Commands
- INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE
- Query
- SQL Injection (how to prevent)

Dapper Architecture
- Dapper
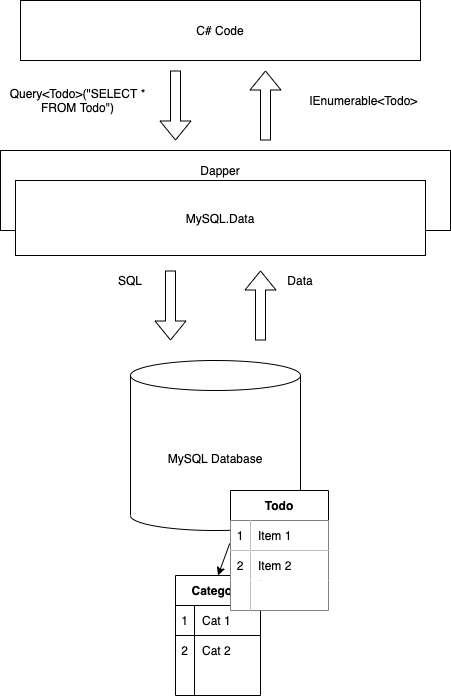
Installation
- Install a database
- Other Tools:
- Dapper - a simple library to interact with a database
- How to install
-
dotnet add package Dapper
-
- Install a driver (MySql.Data)
-
dotnet add package MySql.Data
-
- Go, start programming
DB Tools 101
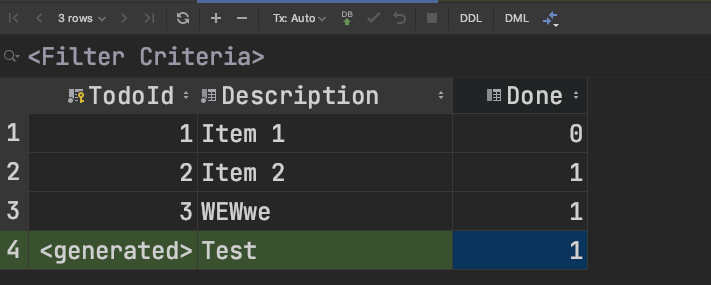
- Demo
- Commit after edit/update/delete!

Dapper
- Go, start programming
- 1 Make connection
- Connection String
- https://www.connectionstrings.com/
- Docs from vendor
- Connection String
- 2 Execute some SQL
- Query or Command
- 3 Do something useful with the result
- 1 Make connection
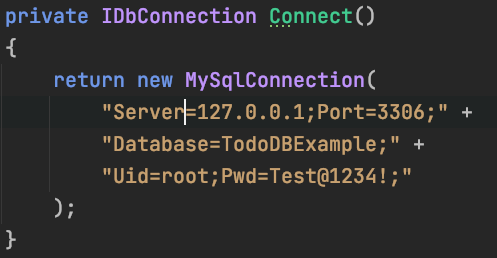
var connectionString = "Server=127.0.0.1;Port=3306;Database=Examples;Uid=root;Pwd=Test@1234!;"
using var db = new MySqlConnection(connectionString);
var todos =
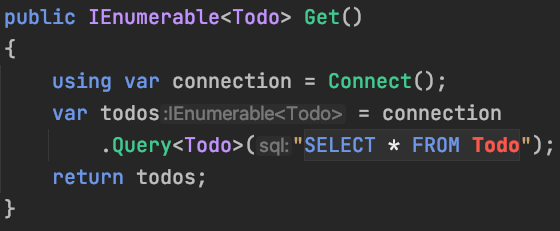
db.Query<Todo>("SELECT * FROM Todo")
.ToList();Repository
- Repsitory: a central location in which data is stored and managed.
- To interact with a Database use a Repository class
- In the PageModel methods use this class
- It's a good idea to separate "database code (Dapper)" from other code
- In the PageModel methods use this class
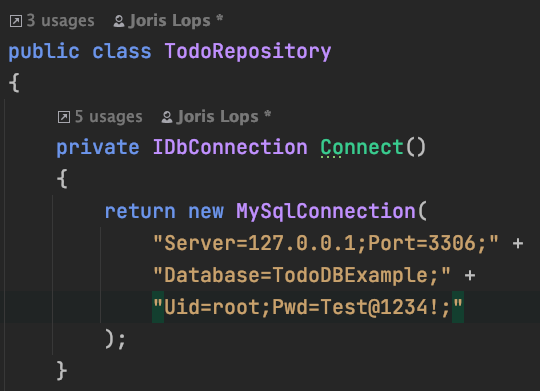
Class <----> Table
Column names and Properties must match!

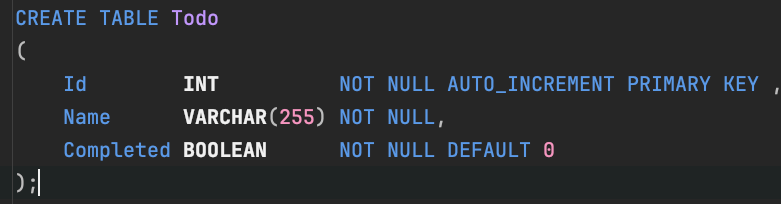
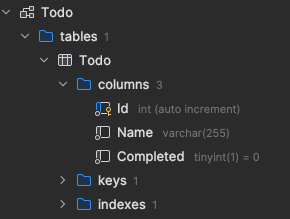
SELECT ... FROM Todo
-
using var
- when the method Get() is finished, the connection is disposed
- disposable pattern == resource (connection) management
- List<T> is an IEnumerable<T>,
- use ToList() to convert to a List<T>
- Query<T> converts the result of the query to IEnumerable<T>, where T is a class
public static List<Todo> Get()
{
using var connection = new MySqlConnection(GetConnectionString());
return connection.Query<Todo>("SELECT Id, Name, Completed FROM Todo")
.ToList();
}QuerySingleOrDefault() + Parameter
- QuerySingleOrDefault<Todo>(sql, param)
- returns one Todo or null (nullable is ?)
-
SQL Parameter placeholder (@Id)
- start with @
- Filled by: new {Id = id}
- anonymous object
public static Todo? Get(int id)
{
string sql = "SELECT Id, Name, Completed FROM Todo WHERE Id = @Id";
using var connection = new MySqlConnection(GetConnectionString());
return connection.QuerySingleOrDefault<Todo>(sql, new { Id = id });
}Delete
- Execute(sql, param) return numRowsEffected
- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE (without selecting the changed row)
- Most of the time: delete records with the Primary Key (Id)
public static void Delete(int id)
{
using var connection = new MySqlConnection(GetConnectionString());
var sql = "DELETE FROM Todo WHERE Id = @Id";
connection.Execute(sql, new { Id = id });
}Insert
- INSERT
- ExecuteScalar<int>(sql, param) --> numRowEffected
- Parameters are mapped automatically
public static Todo Create(Todo todo)
{
using var connection = new MySqlConnection(GetConnectionString());
var sql = "INSERT INTO Todo (Name, Completed) VALUES (@Name, @Completed); " +
"SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();";
var id = connection.ExecuteScalar<int>(sql, todo);
todo.Id = id;
return todo;
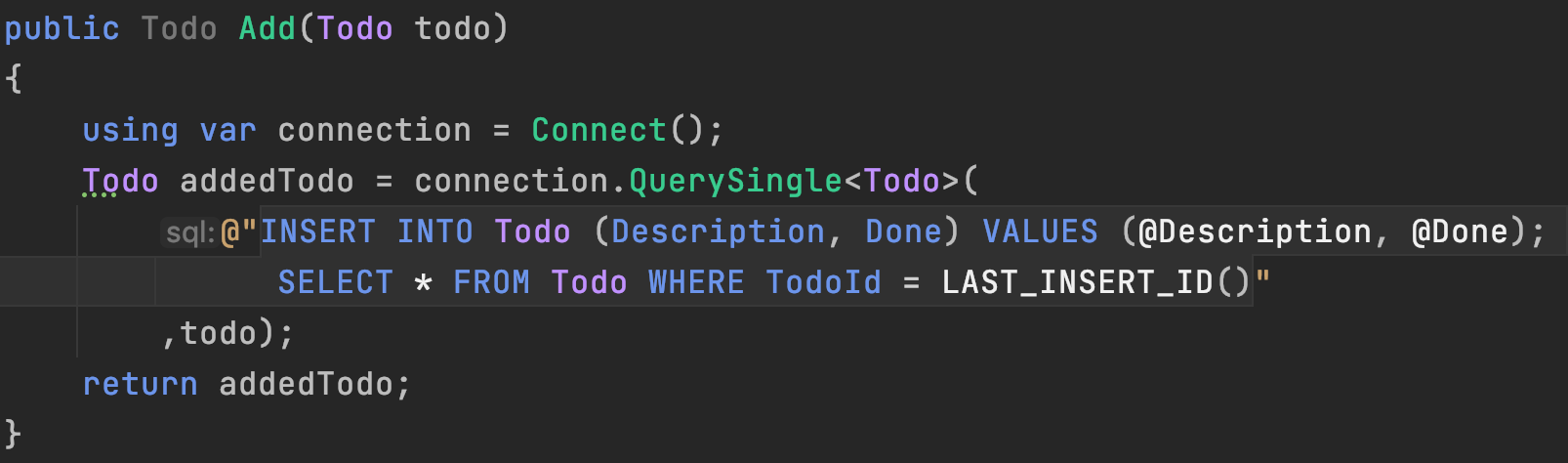
}Insert + Select
- INSERT --> SELECT the inserted row
- LAST_INSERT_ID();
- Parameters are mapped automatically
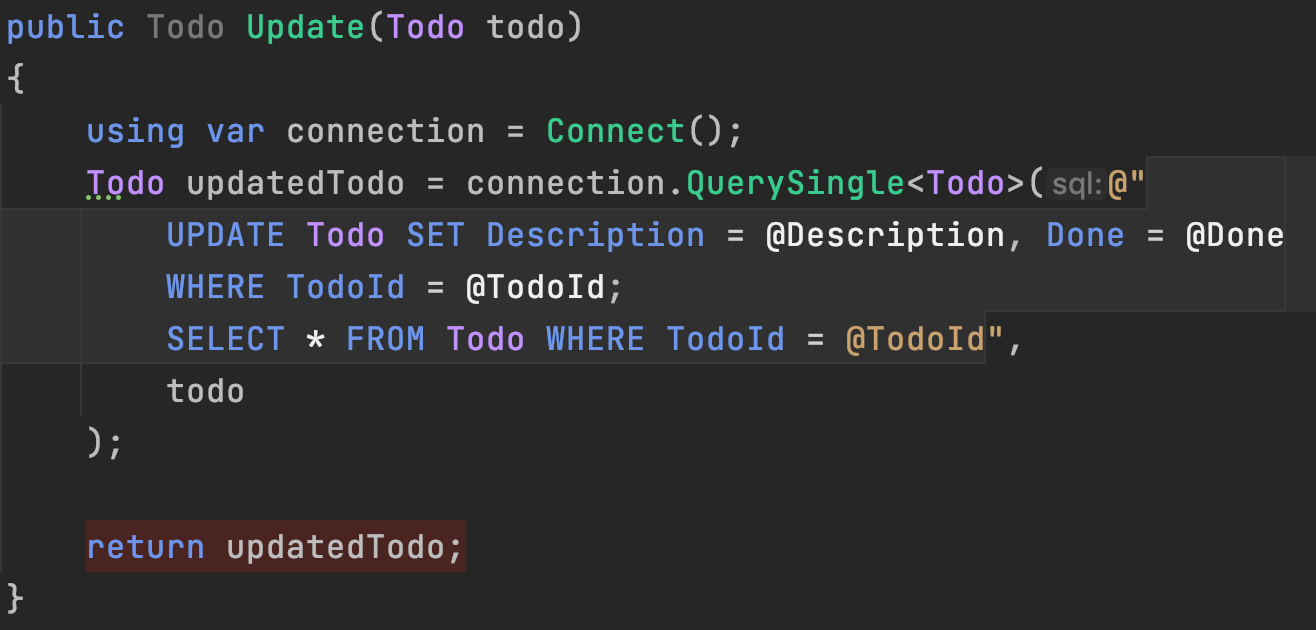
Update + Select
- Same idea as with the insert
- LAST_INSERT_ID() can't be used (insert only)
CRUD

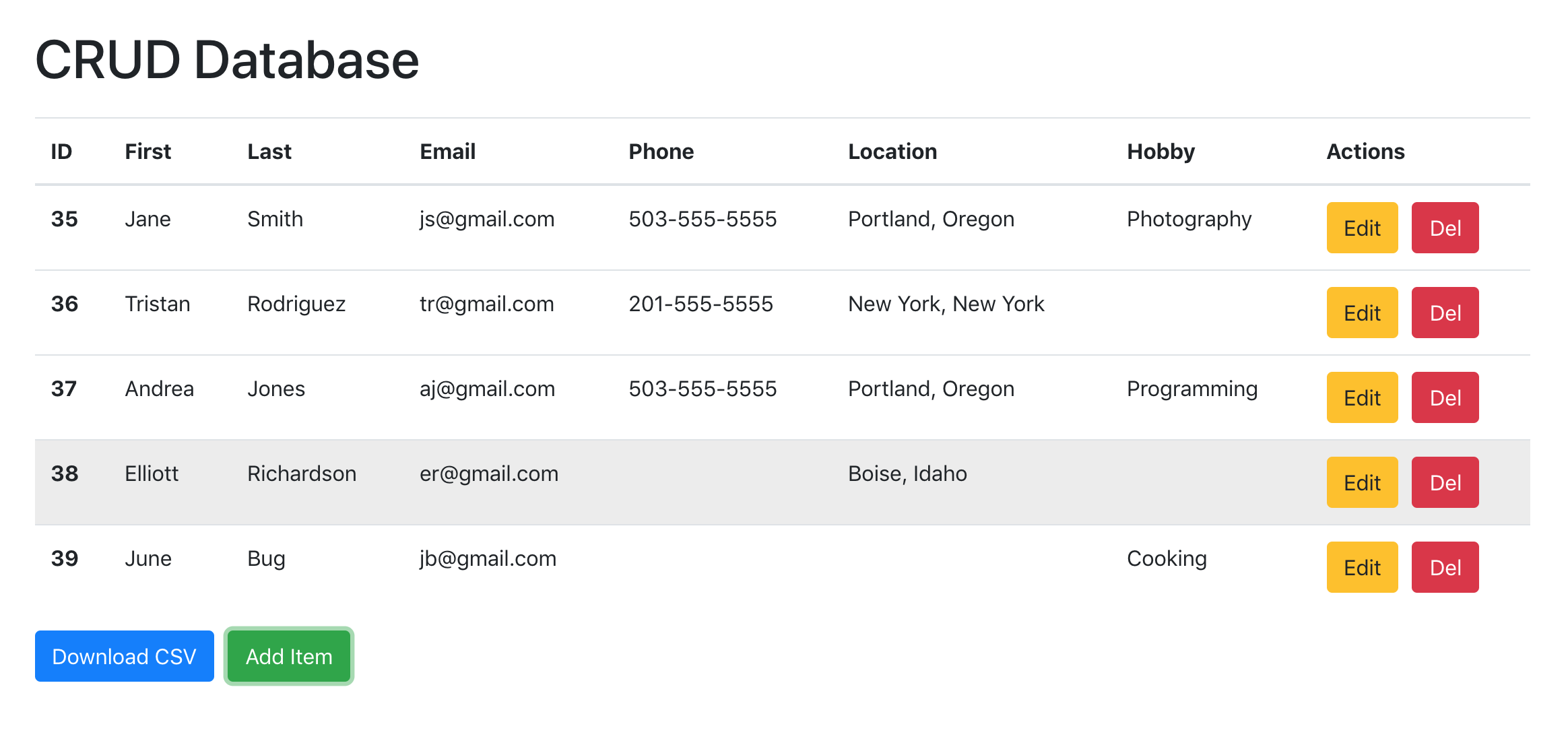
| CRUD | Repository | SQL |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Add(...) | INSERT |
| Read | GetById(id), GetAll(), Get(), etc | SELECT |
| Update | Update(...) | UPDATE |
| Delete | Delete/Remove | DELETE |
Demo / Example
- Examples/Lesson3/LesDemo
- Examples/Lesson3/

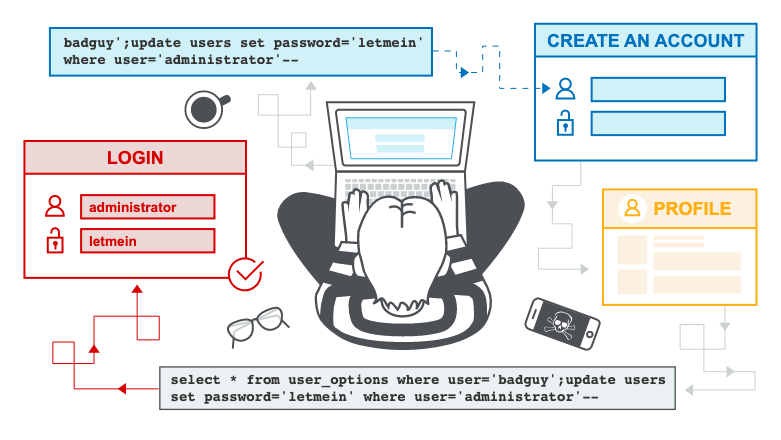
SQL Injection
Simple explanation:
Longer explanation:
SQL Injection
- Don't make your own SQL strings
- Add "Desc 1' OR 1 = 1; #" on the querystring (filter)

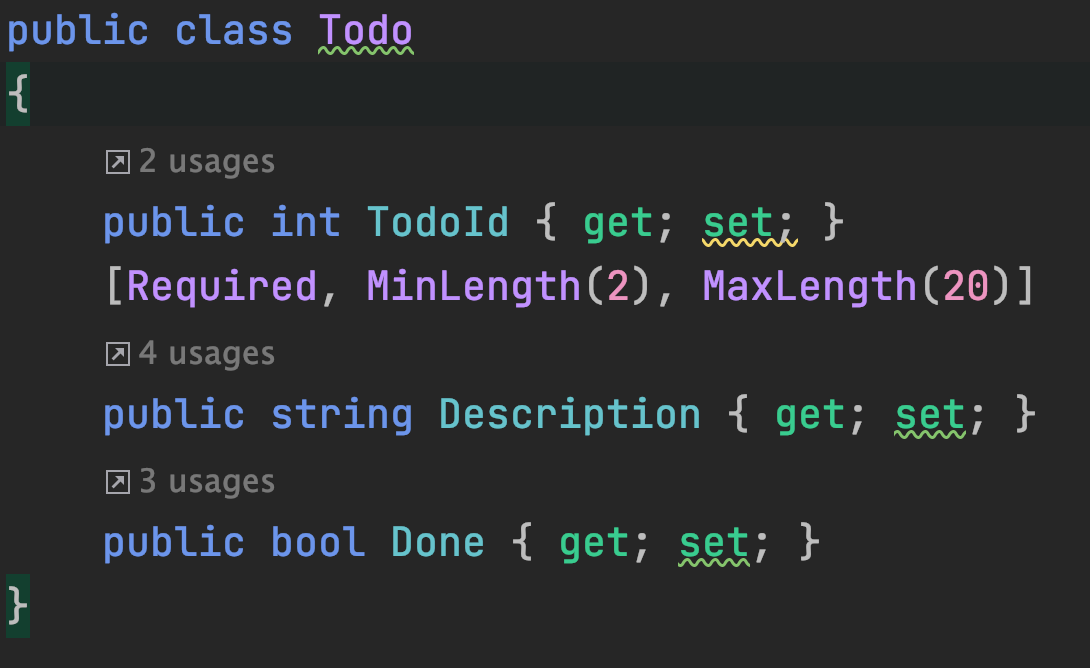
public List<Todo> GetWithSQLInjection(string filter)
{
var todos = new List<Todo>();
try
{
//De code is anders, omdat SQL injectie anders alsnog wordt tegengehouden
using (var connection = Connect())
{
//Doe dit nooit zelf een querystring in elkaar zetten!
//!!!SQL INJECTIE!!! Alle gegevens kunnen gestolen worden, etc :-(
var sql = @"SELECT TodoId, Description, Done
FROM Todo WHERE Description LIKE '%" + filter + "%'";
//todos = connection.Query<Todo>(sql).ToList();
var reader = connection.ExecuteReader(sql);
while (reader.Read())
{
todos.Add(new Todo()
{
TodoId = reader.GetInt32(0),
Description = reader.GetString(1),
Done = reader.GetBoolean(2)
});
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
return todos;
}SQL Injection
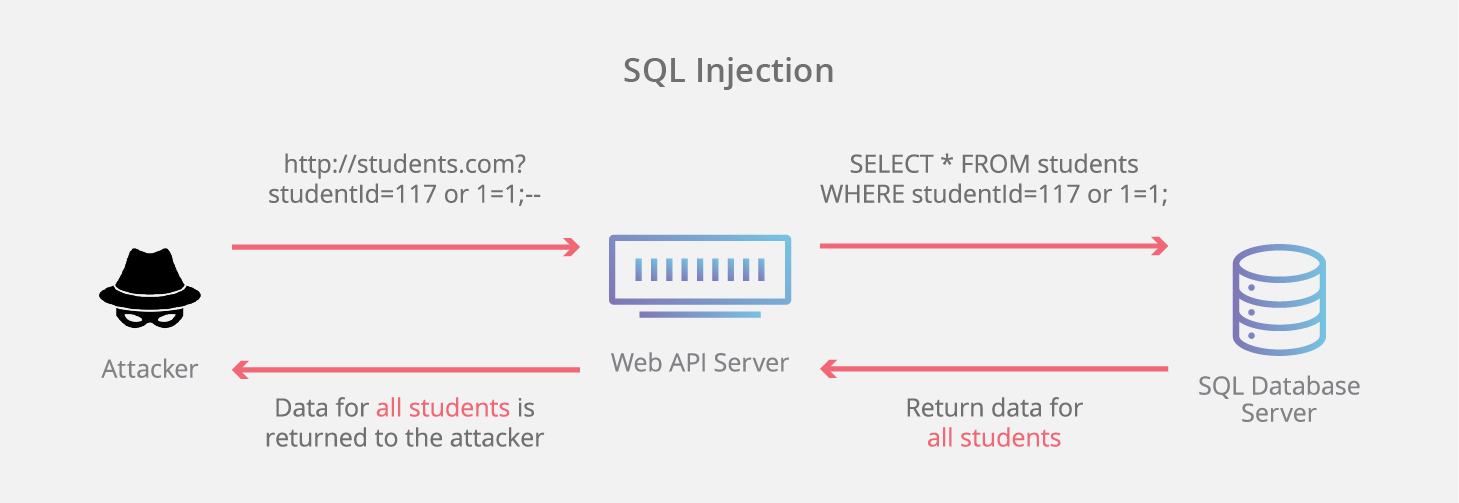


To Prevent SQL Injection

Always, Use Prepared Statement (Dapper will do this for us!) in combination with Parameter Placeholders!


Parameter Placeholders
-
Use (Query) Parameter Placeholders
-
for example: @Description, @Done
-
-
Use a prepare statements
-
Creates an SQL statement that can be executed on the server (Dapper will do this for us)
-
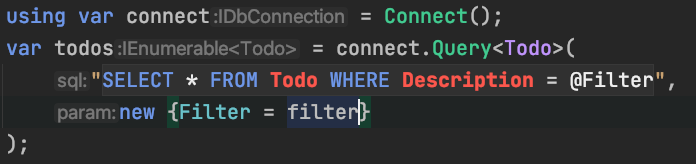
!!SQL Injection Prevented!!
ExecuteScalar<T>(...)
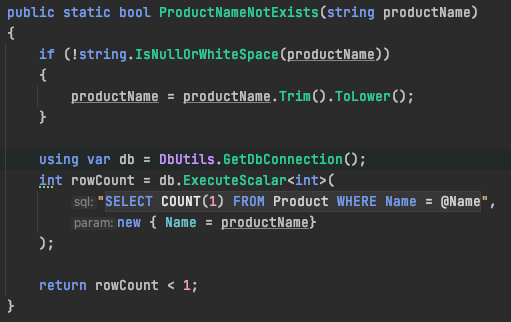
- selecting scalar (simple single value)
Query --> Class
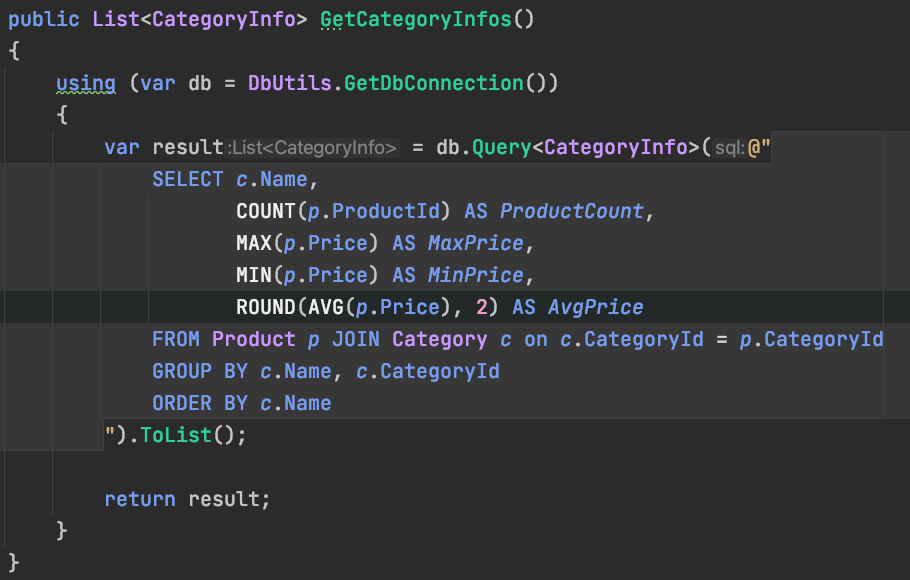
- Map to class
- Property in class should match column name (AS keyword)
When to use which method
- Take a look at the dapper documentation
- Tip:
Relationship (Joins)
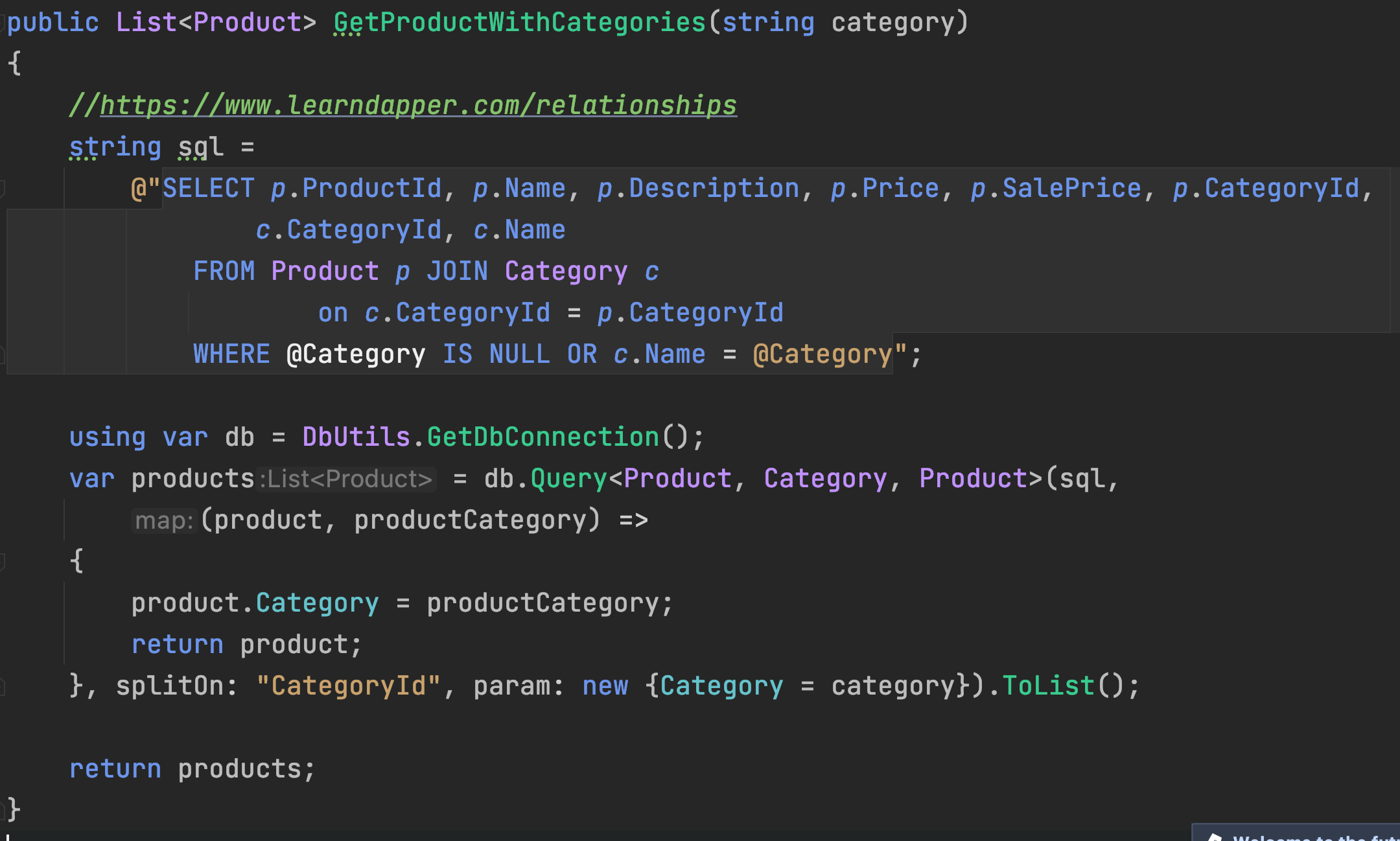
Tip & Resources
- Try the query
- Some IDE's (Rider) have code completion & warn for SQL Errors
- Examples
- Documentation of Dapper
- https://www.learndapper.com/
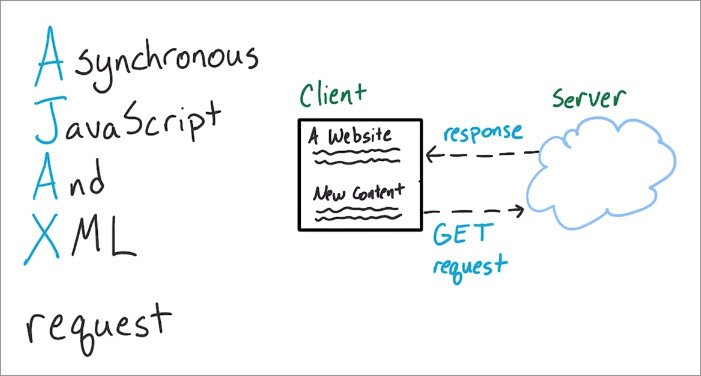
Lesson 4
- AJAX
- Partial Page Updates
- Request/Post to Server
- JavaScript (jQuery)
- Partial Page Updates
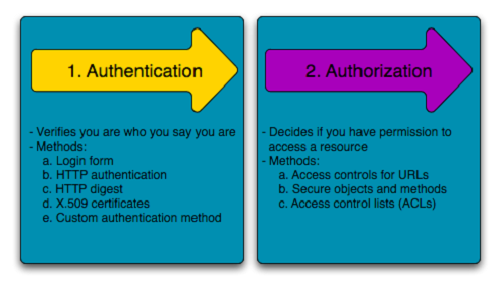
- Authentication & Authorization
- Login & Roles
ASP.NET Core Razor Pages
By Joris Lops
ASP.NET Core Razor Pages
- 1,389