ORM
with
Entity Framework
Core
ADO.NET Example
List<Customer> Customers = new List<Customer>();
string conntionStr = "Data source=localhost; initial catalog=SubwayDB; integrated security=true";
SqlConnection sqlConn = new SqlConnection(connectionStr);
string Query = "Select * from Customers where FirsName=@FN";
SqlCommand sqlComm = new SqlCommand(Query, sqlConn);
sqlComm.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text;
sqlComm.Parameters.AddWithValue("@FN", "test").DbType = System.Data.DbType.Int16;
sqlConn.Open();
SqlDataReader reader = sqlComm.ExecuteReader();
while (reader.Read())
{
Customers.Add(new Customer(){
FirstName = reader["FirstName"].ToString(),
LastName = reader["LastName"].ToString(),
Email = reader["Email"].ToString(),
});
}
reader.Close();
sqlConn.Close();
What are the problems?
Problems of prev Example
•SQL Code
•Vendor dependent
•Not compiled & Runtime errors
•SQL is a string
•Connection/resource management
•Manual conversion to object instances
•Conversion of datatypes
•SQL Types != C# Types
•Labour intensive
•Errors
•Changes in database or C# code
•Database dependent (C#)
Entity Framework (EF) Core
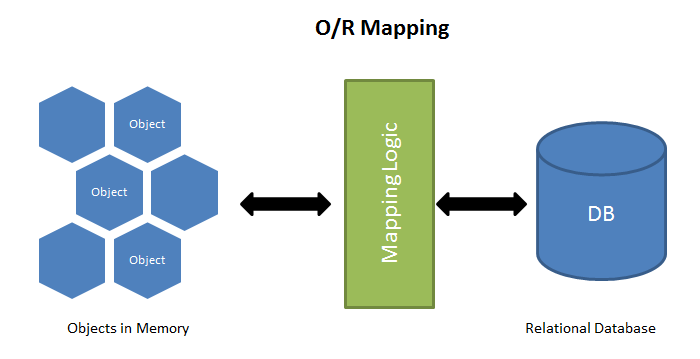
- ORM = Object Relational Mapping
- Layer between C# & Database
- Store C# Objects (instances) into a database
- Retrieve C# Objects (instances) from a database
- And much more features
- Layer between C# & Database
- Objects (class) that can be stored (and retrieved) in a database are called entities!
Entity Framework (EF) Core
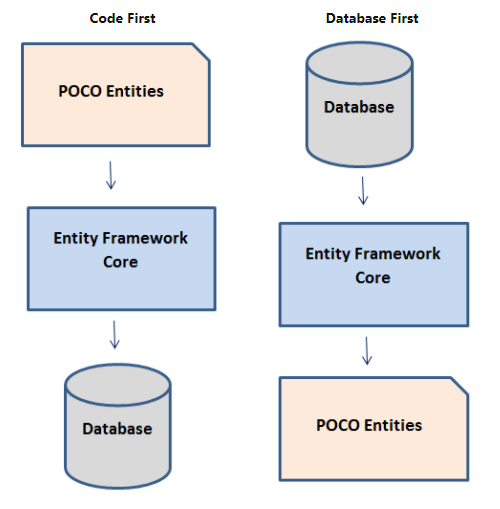
- Workflows:
- Code First
- Main focus in this
- Code First
course
- Database First
Entity Framework (EF) Core
- Build on .NET Core
- Cross Platform (Linux, Mac, Windows)
- Open Source
- Easy to use
- EF Core != Not EF6
- New implementation, not all features of EF6 :-(
- New features
- Easier to use

Week 1
- Why ORM
- EF Core = ORM framework/library
- Benefit & problems that ORM solves
- First Example with Entity Framework Core (EFCore)
- Getting started
- Required Libraries
- Model (Entities)
- DbContext
- Insert & Query
- Getting started
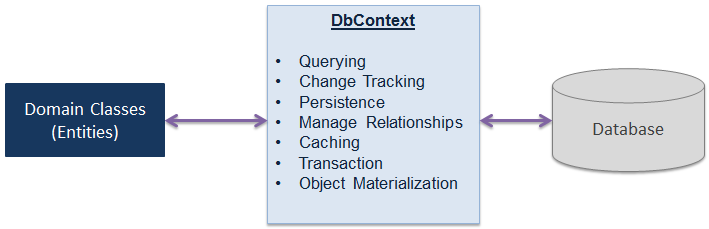
EF Architecture
- Domain classes (conceptual model / entities)
- Mapping between database structure and domain classes (DataModel)
- EF Api's to define datamodel from Domain Classes (mapping)
- Convention based
- Interaction with database
- Provider
- Queries (LINQ to entities)
- Update C# object(s) in memory
- Tracking Changes
- SaveChanges()
- Tracking Changes


EF Architecture


Mapping
- conventions
- can be changed by API
- or annotations
- can be changed by API
- Take a look at
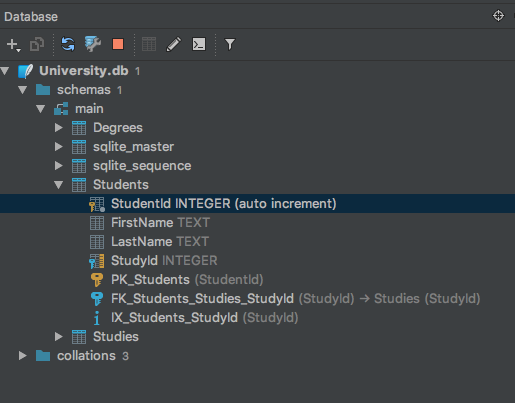
- Data Types
- Primary key
- Foreign keys
- Index
- Naming convention
- Table Name
- FK's, PK
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public Study Study { get; set; }
public List<Degree> Degrees { get; set; }
}Example - Install
- Install Entity Framework Core
- NuGet packages
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
- Choose a Provider
- MySql.EntityFrameworkCore
- Npgsql.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL
- or
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- etc
- NuGet packages
SQL Lite has some drawbacks, it's better to choose a real relational database!
Example - Domain Model
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public Study Study { get; set; }
public List<Degree> Degrees { get; set; }
}
public class Study
{
public int StudyId { get; set; }
public string UniversityName { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime Completion { get; set; }
}
public class Degree
{
public int DegreeId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime Received { get; set; }
}Example - DbContext
public class UniversityDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Study> Studies { get; set; }
public DbSet<Degree> Degrees { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder);
optionsBuilder.UseSqlite("Data Source=University.db");
}
}using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
db.Database.EnsureDeleted();
db.Database.EnsureCreated();
} - Create the database in code or use Migrations
Model = Domain Model (entities) + DabaseContext
Example - Add Data
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
db.ConfigureLogging(s => Console.WriteLine(s), LoggingCategories.SQL);
var cs = new Study() {
Name = "Computer Science"
};
db.Students.Add(new Student() {
FirstName = "Jan",
LastName = "Hendriks",
Study = cs,
Degrees = new List<Degree>() {
new Degree() {
Name = "bachelor computer science",
Received = new DateTime(2011, 6, 1)
}
//... add more data
}
});
//add more data
db.SaveChanges();
}- Enable Logging, let's take a look at the documentation
Week 2
-
Constraints
- Required, Length,
Email
- Required, Length,
- Modelling different type of relations
- one-to-one (reference)
- one-to-many (collections)
- many-to-many (collection on both ends)
- Query's
- Changing Data
Basic Mapping
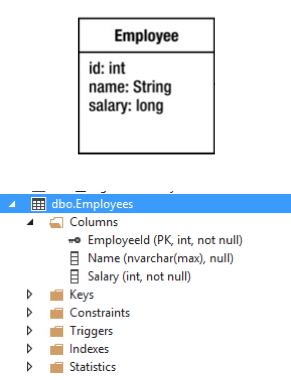
- Pay attention
- Naming conventions
- Basic Type mapping
- Primary Key
- Null, Not Null
-
Nullable reference types —
string?, Person? -
Nullable value types —
int?,bool?,DateTime?
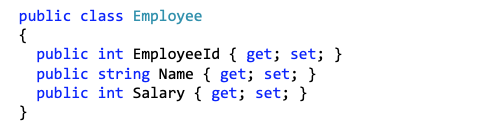
Change Basic Mapping
- Model Attributes
public class Employee
{
public int EmployeeId { get; set; }
[Required, MinLength(3), MaxLength(50)]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required, MinLength(3), MaxLength(50)]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[NotMapped]
public string FullName {
get { return $"{FirstName} {LastName}"; }
}
[Required, EmailAddress]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Phone]
public int Phone { get; set; }
[Range(1, 5)]
public int WorkdayCountInWeek { get; set; }
[Required, Range(0, 5000)]
public int Salary { get; set; }
[Url]
public string IntranetPage { get; set; }
}
Problem is:
- Email, Phone, URL, Range? Not used by database!
Change Basic Mapping
public class EmployeeContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>()
.ToTable("Emp");
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>()
.Property(x => x.FirstName)
.IsRequired().HasMaxLength(50);
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>()
.Property(x => x.Phone)
.HasColumnName("Phone Number");
}
}- Fluent API (method chaining)
- Overlap with Annotations
One to One Relation
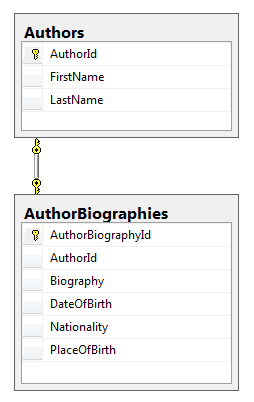

- Optional Relation, use AuthorId?
One to One Relations
- Requires FK (StudentId) on Child (Dependent)
- Navigation Property on (Principle) not required on (Dependent)
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
....
public ContactInfo ContactInfo { get; set; }
public int StudyId { get; set; }
public Study Study { get; set; }
...
}
public class ContactInfo
{
public int ContactInfoId { get; set; }
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public Student Student { get; set; }
...
}Principle
Dependent
One to Many Relation
-
ICollection<T>, let's take a look at the documentation
- List if ordering is important
- FK is in book (AuthorID)
- AuthorId is not required (EF will then generate it in the database) --> It's a good idea to include the FK's. Later on some libraries (mappers) depend on them!!!
public class Author
{
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; } = new();
}
public class Book
{
public int BookId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public Author Author { get; set; }
}Many to Many Relations
- Specify the Primary Key
- use HasKey method
public class CourseStudent
{
public int CourseId { get; set; }
public Course Course { get; set; }
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public Student Student { get; set; }
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<CourseStudent>()
.HasKey(x => new {x.CourseId, x.StudentId});
}Example - Delete a student
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
Student student = db.Students.Find(1);
db.Students.Remove(student);
db.SaveChanges();
}- SQLite Error 19: 'FOREIGN KEY constraint failed'. Solution:
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
Student student = db.Students
.Include(x => x.Degrees)
.Single(x => x.StudentId == 1);
foreach (var degree in student.Degrees)
{
db.Degrees.Remove(degree);
}
db.Students.Remove(student);
db.SaveChanges();
}- There are other methods to delete related entities, cascade delete
Delete Entities
- Load entity (tracked by context)
- Delete
- If related entities must be deleted, do it manually or use cascade!
Query: load Entities with Projection
- Select(x=> new ...)
var studentDegrees = db.Students.Where(x => x.StudentId == 1)
.Select(x => new
{
x.LastName, x.FirstName,
x.Degrees,
DegreeBefore2014 = x.Degrees.Where(d => d.Received < new DateTime(2014, 1, 1))
})
.ToList();in EFC 6+
Eager Loading: load related entities, multiple levels
- Include(x=> ....).ThenInclude(x => ...)
var students = db.Students.Where(x => x.StudentId == 1)
.Include(x => x.CourseStudents)
.ThenInclude(x => x.Course)
.ToList();
foreach (var student in students)
{
Console.WriteLine(new string('-', 20));
Console.WriteLine($"{student.LastName}, {student.FirstName.First()} ");
foreach (var cs in student.CourseStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine(cs.Course.Name);
}
Console.WriteLine(new string('-', 20));
}- The SQL has multiple Queries, it is more efficient than one big query --> EF Core constructs relationships
The prefered way to work (my opinion)!!!!
Explicit loading: load related entities, after the query
- Reference(), Collection(), Load()
var students = db.Students;
foreach (Student student in students)
{
if (student.LastName == "Hendriks")
{
db.Entry(student).Reference<Study>(x => x.Study).Load();
if (student.Study.Name == "Computer Science")
{
Console.WriteLine($"{student.LastName}");
db.Entry(student).Collection(x => x.Degrees)
.Query()
.Where(x => x.Received < new DateTime(2014, 1, 1))
.Load();
foreach (var degree in student.Degrees)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{degree.Name}");
}
}
}
}!!!!Be careful, can be expensive!!!! N+1 Query Problem!
Lazy loading
- Is supported in EF Core 2.1+
- I'm not a fan of lazy loading
- n+1 problem
- I'm not a fan of lazy loading
- Lazy loading: data is retrieved from database when needed, automatically.
- Pro:
- easy to program for connected context
- Cons:
- potential performance problem
- can't be used in disconnected scenario (webapi)
- Pro:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/querying/related-data
Query: load related entities
- Projection (not recommended, n+1 problem?)
-
Eager Loading Include()
- ThenInclude() multi-level relationship
- Lazy loading (not recommended, n+1 problem is lurking)
- Explain n+1 problem.
SELECT * FROM Students /* return n records */
SELECT * FROM Degrees WHERE StudentId = 1
SELECT * FROM Degrees WHERE StudentId = 2
...
SELECT * FROM Degrees WHERE StudentId = nQueries - Deferred Execution
- Deferred execution
- Query is executed when iterated over query or when an LINQ method is called that forces it to load results into memory, such as ToList()
- load data in memory: ToList(), Find(), First(), FirstOrDefault(), Single(), SingleOrDefault(), Count(), Min(), Max(), etc.
var csStudents = db.Students.Where(x => x.Study.Name == "Computer Science");
foreach (var csStudent in csStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {csStudent.LastName}, {csStudent.FirstName.First()}");
}var csStudents2 = db.Students.Where(x => x.Study.Name == "Computer Science").ToList();Solution to open connection!
- During deferred execution, connection is open all the time, this can be expensive
- Solution:
var csStudents = db.Students.Where(x => x.Study.Name == "Computer Science")
foreach (var csStudent in csStudents)
{
//Do lots of work
}var csStudents = db.Students.Where(x => x.Study.Name == "Computer Science").ToList();
foreach (var csStudent in csStudents)
{
//Do lots of work
}Queries: Single() or SingleOrDefault()
- Defaults: return null if the result is empty
- No default: throw an exception if the result is empty
Student s1 = db.Students.Single(x => x.LastName == "Lops");
//exception if no student exists with Lastname equals "Lops"
Student s2 = db.Students.SingleOrDefault(x => x.LastName == "Lops");
if (s2 == null)
{
//do something
}- First() or FirstDefault()
- Single() or SingleDefault()
- Last() or LastDefault()
ChangeTracker
- Entities are tracked by default (by the ChangeTracker)
- Property level (for updates)
- SaveChanges() --> Updates/Inserts
- ChangeTracker is expensive: add .AsNoTracking() to queries when you only display the data!
- Please watch the video below:
Some mistake:
Week 3
- Queries
- Extension methods, lambda
- Fake/Dummy Data
- Migrations
- Homework
Queries
- Extension Methods
- LINQ --> Extension Methods
- Anonymous Type
- new { StudentName = s.StudentName, .... }
- Can only be used inside the "function"
var studentNames = studentList.Where(s => s.Age > 18)
.Select(s => s)
.Where(st => st.StandardID > 0)
.Select(s => s.StudentName);var teenStudentsName = from s in studentList
where s.age > 12 && s.age < 20
select new { StudentName = s.StudentName };Extension Methods
- Extension Method 101
- add new functionality (extension methods)
- static class, static method
- this-keyword in the parameter list
public static class ExtensionMethodsExamples
{
public static string UppercaseFirstLetter(this string value)
{
if (value?.Length > 0)
{
return char.ToUpper(value[0]) + value.Substring(1);
}
return value;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("aap noot mies".UppercaseFirstLetter());Lambda
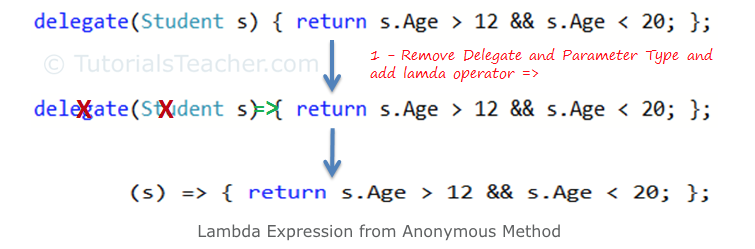
Take a look at all the different syntaxis!
Lambda: short way to represent an anonymous method
Extension Methods
- IEnumerable
- base for most collections in .NET
- predicate is a condition
public static IEnumerable<string> UppercaseFirstLetter(this IEnumerable<string> values)
{
foreach (var value in values) {
yield return value.UppercaseFirstLetter();
}
}
"aap noot mies".Split(" ").UppercaseFirstLetter()
.ToList().ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine(x));
public static IEnumerable<TSource>
Where<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> values, Predicate<TSource> predicate)
{
foreach (var value in values) {
if (predicate(value)) {
yield return value;
}
}
}
"Aap noot Mies".Split(" ")
.Where(x => x.Length > 0 && char.IsUpper(x[0]))
.ToList()
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine(x));Extension Methods
- Calling Extension Methods
- Take a look at some overloads
- Where
- Func<string, bool>
- Notation Func<T1, T2, TResult>
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>
(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,int,bool> predicate);
int[] numbers = { 0, 30, 20, 15, 90, 85, 40, 75 };
IEnumerable<int> query =
numbers.Where((number, index) => number <= index * 10);
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>
(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,bool> predicate);
List<string> fruits =
new List<string> { "apple", "passionfruit", "banana", "mango",
"orange", "blueberry", "grape", "strawberry" };
IEnumerable<string> query = fruits.Where(fruit => fruit.Length < 6);Linq Extension Methods
Example - Query data with LINQ
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
var csStudents = db.Students.Where(x => x.Study.Name == "Computer Science");
foreach (var csStudent in csStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {csStudent.LastName}, {csStudent.FirstName.First()}");
}
}- LINQ Extension methods (my preference)
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
var csStudents = from s in db.Students
where s.Study.Name == "Computer Science"
select s;
foreach (var csStudent in csStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {csStudent.LastName}, {csStudent.FirstName.First()}");
}
}- LINQ (Language Integrated Query)
Example - Migrations
- Modified DbContext or Data Model
- Depends on NuGet Package/Tool:
-
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
-
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef
-
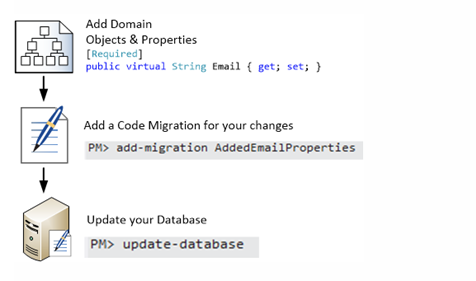
- Demonstration add Email
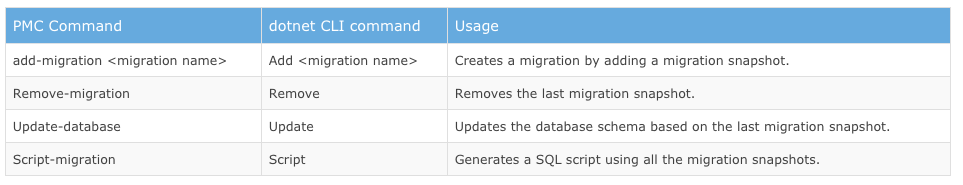
- Commands
- ef migration
-
dotnet ef migrations add init
-
dotnet ef migrations add emailToStudent
-
dotnet ef database update
-
- add-migration (PowerShell, NuGet console)
- ef migration
Example - Migrations
Add Email
Required!
Fake Data

Week 4
- Queries
- Homework
- Migration
- Disconnected vs connected
Migrations

Reverse Engineerng
From database to domain classes (Entities)
Connected
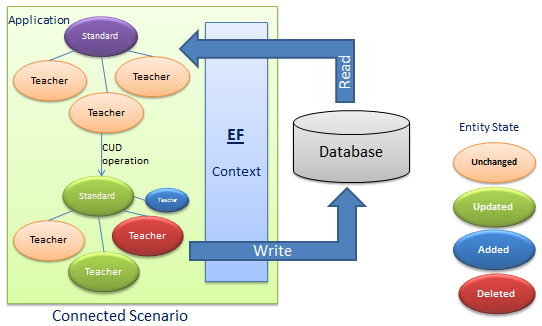
Connected vs Disconnected
- Disconnected Scenario
- web application
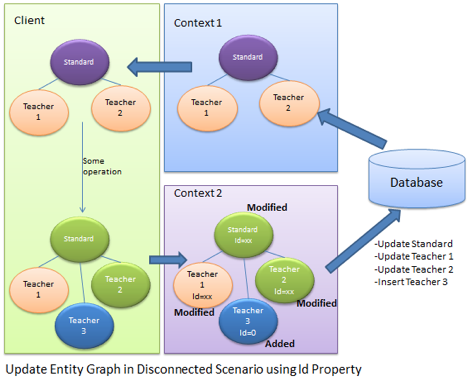
Connected vs Disconnected
- Disconnected Scenario, all fields (properties) are updated in SQL Query
- Connected Scenario, only changed fields are updated by SQL Query
public static void ConnectedObjectUpdate()
{
Student studentToUpdate = null;
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
studentToUpdate = db.Find<Student>(1);
studentToUpdate.FirstName += studentToUpdate.FirstName.First();
db.SaveChanges();
}
}
public static void DisconnectObjectUpdate()
{
Student studentToUpdate = null;
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
studentToUpdate = db.Find<Student>(1);
}
studentToUpdate.FirstName += studentToUpdate.FirstName.First();
using (var db = new UniversityDbContext())
{
db.Students.Update(studentToUpdate);
db.SaveChanges();
}
}Entity States
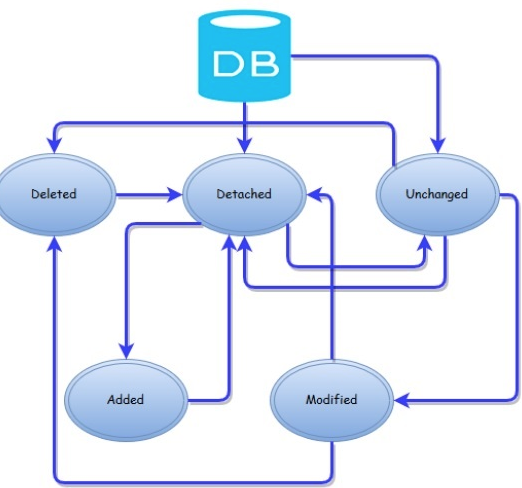
EntityState: Unchanged, Added, Modified, Delete, Detached
private static void DisplayStates(IEnumerable<EntityEntry> entries)
{
foreach (var entry in entries)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Entity: {entry.Entity.GetType().Name},
State: {entry.State.ToString()} ");
}
}- Attach() to "connect object" to context

Entity State
- Attach() to "connect object" to context
Deletes / Updates Disconnected
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27176014/how-to-add-update-child-entities-when-updating-a-parent-entity-in-ef
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17723626/entity-framework-remove-vs-deleteobject
- Trackable Entities or Breeze
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/saving/disconnected-entities
- IPropertyChangeNotification?
Raw SQL
- https://www.learnentityframeworkcore.com/raw-sql
Shadow Properties
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().Property<DateTime>("LastModified");
foreach (var entityType in modelBuilder.Model.GetEntityTypes())
{
modelBuilder.Entity(entityType.Name).Property<DateTime>("LastModified");
}
}Query of shadow properties
public override int SaveChanges()
{
foreach (var entry in ChangeTracker.Entries()
.Where(x => x.State == EntityState.Added || x.State == EntityState.Modified))
{
entry.Property("LastModified").CurrentValue = DateTime.Now;
}
return base.SaveChanges();
}No Tracking
- Can be used in disconnected scenario
- Web Api
//disable tracking for all operations on context
db.ChangeTracker.QueryTrackingBehavior = QueryTrackingBehavior.NoTracking;
//no tracking for one query
db.Students.AsNoTracking();Testing with EF
[Fact]
public void TestSQLiteOk()
{
//SETUP
//Here create the options using SQLite CreateOptions
var options = SqliteInMemory
.CreateOptions<MyContext>();
//I create an instance of my DbContext
using (var context = new MyContext(options))
{
//You have to create the database
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
context.SeedDatabaseFourBooks();
//ATTEMPT
context.Books.First().Title = "New Title";
context.SaveChanges();
//VERIFY
context.Books.First().Title.ShouldEqual("New Title");
}
}Entity Framework
By Joris Lops
Entity Framework
- 537


