PHP
Pre Hypertext Processor

Code Examples

Every code example in the presentation has a name
GitHub repo:
https://github.com/NHLStenden/Webdev-PHP
Installed in the VM
git pull to get the latest version!

Lesson 1
-
Client Server (HTTP)
-
Installation & Configuration
-
Basic Language Constructs
-
Form handling
Resources
- https://www.w3schools.com/php/
-
https://laracasts.com/skills/php (recommended video tutorial)
- PhpStorm Account (JetBrains) aanmaken:

PhpStorm Licentie
- PhpStorm Account (JetBrains) aanmaken:

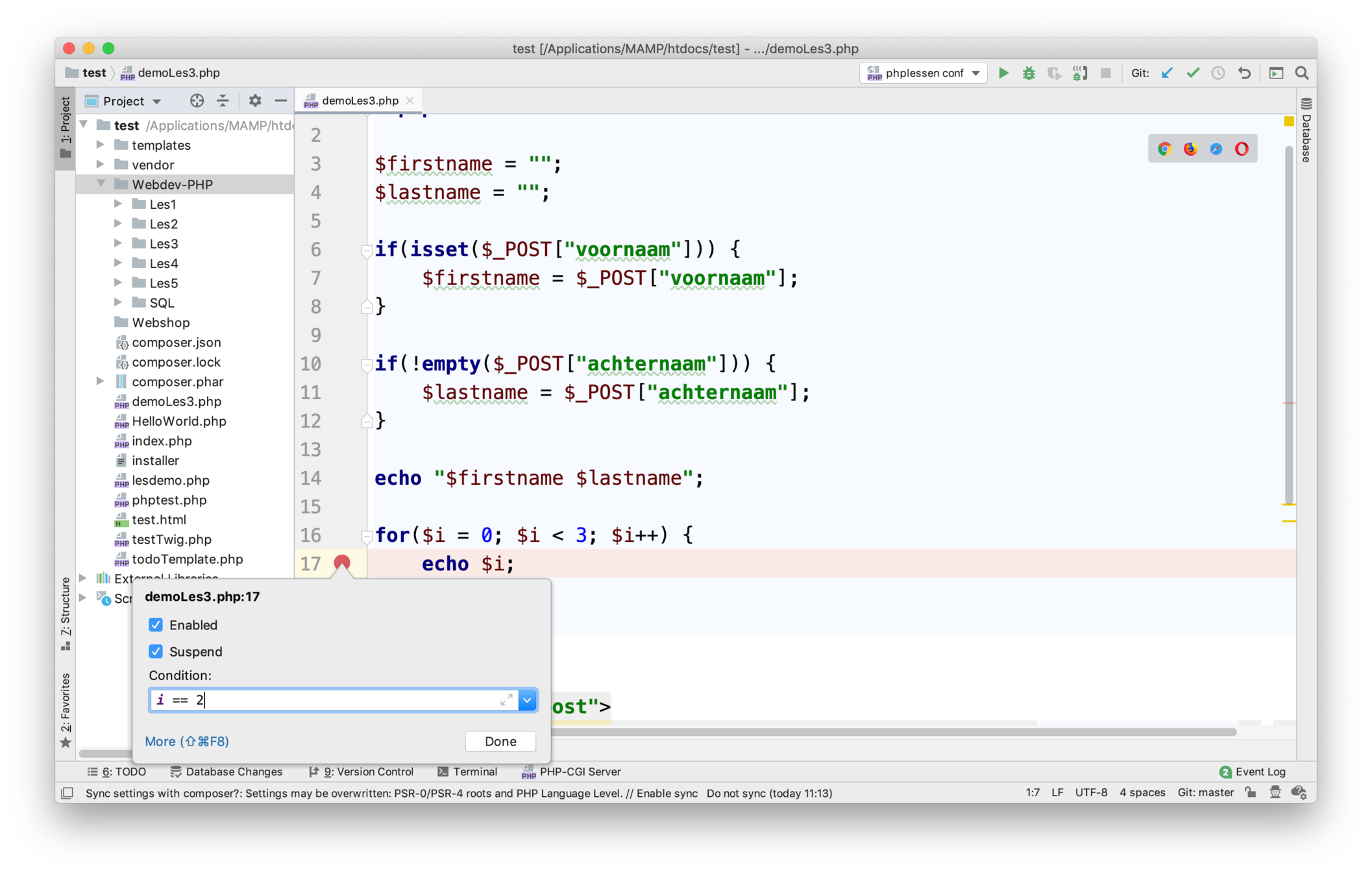
PHP - Client Server
Client = Browser
Server = Machine that server request of Clients
HTTP = HyperText Transfer Protocol

PHP - Client Server

We use: Apache
Use the VM

We use: Apache webserver + PHP + MySQL (MariaDb)
In de browser:
student.local/
docent.local/
In de directory: /home/student/websites
See Blackboard for instruction
Warning: do not start up the browser for PhpStorm!
Use the VM
Skips the next slides if you use the VM, recommended
Install Development Server

It saves your time as well as it is easy to use.XAMPP, WAMP, LAMP, MAMP are local servers that are mainly used while developing PHP websites.

Choose a Development Server Distribution, Download & Install
PHP Hello World
Place Your PHP Code in the
- locate the directory!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!-- https://www.w3schools.com/php7/ -->
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo "My first PHP script!";
?>
</body>
</html>
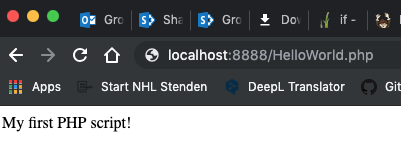
HelloWorld.php
PHP IDE
IDE == Integrated Development Environment == Text editor For programmers
PhpStorm recommended


PHP Change Some Settings
Change the following in the php.ini file:
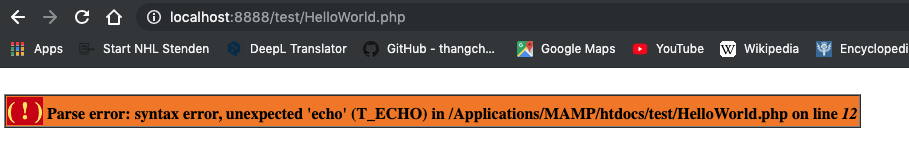
<?php
$text = ""
echo $text;
?>
<?
$text = "";
echo $text;
?>Use <? instead of <?php
short_open_tag = On
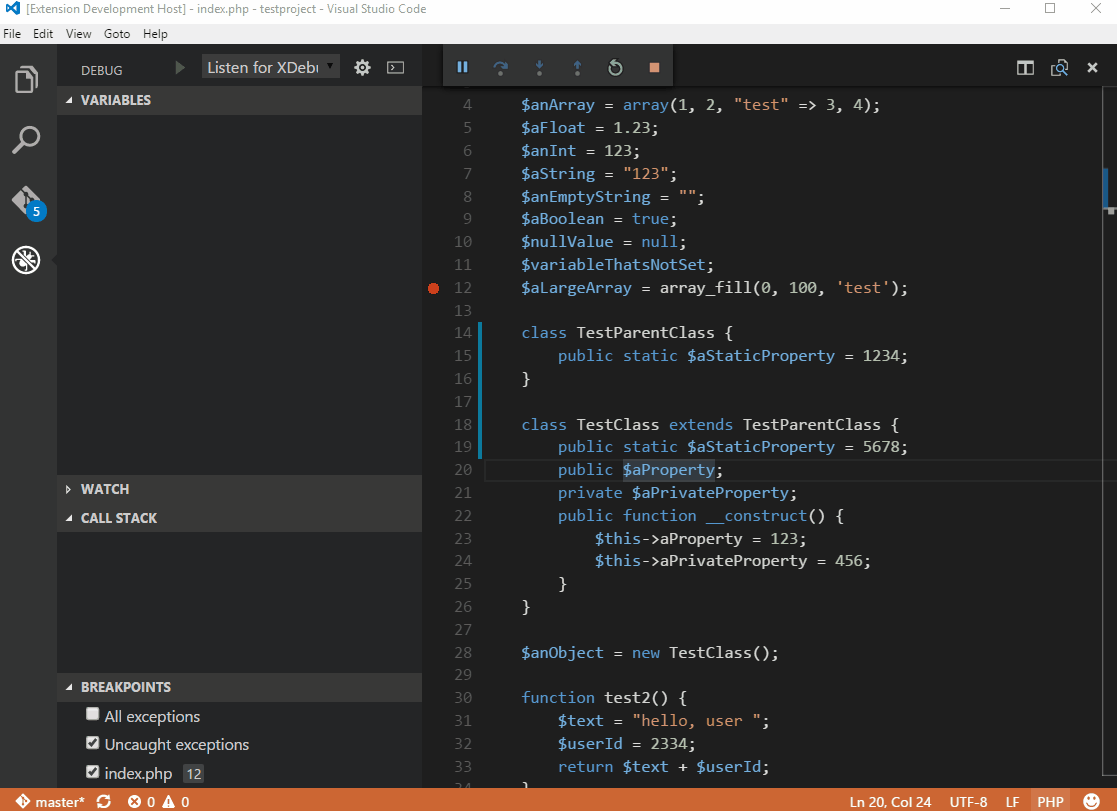
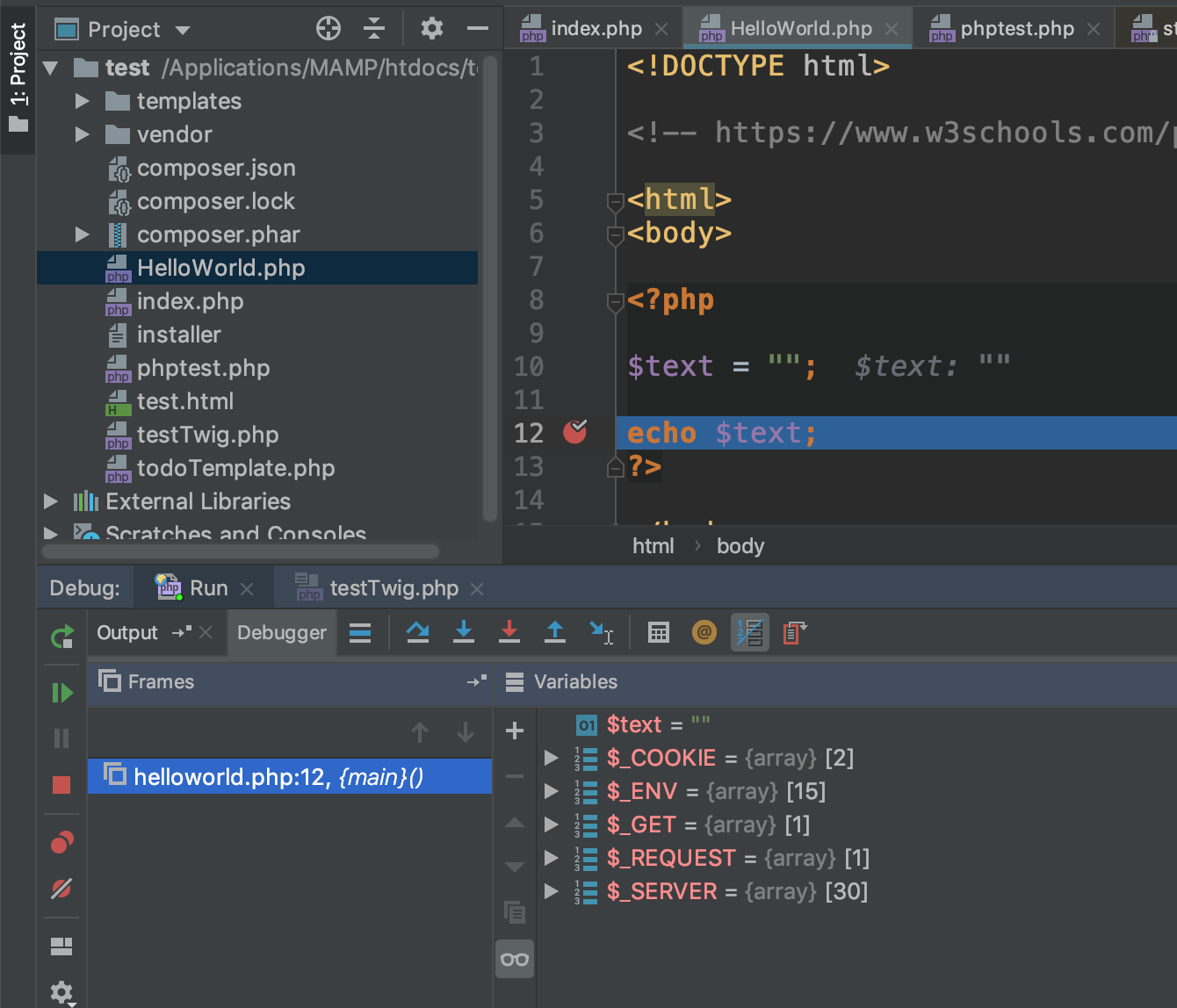
display_errors = OnPHP Debugger
- works inside VM
- xDebug
Follow youtube videos to help you!
search terms: xampp xdebug phpstorm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VL60RCKv7lQ&t=9s
For Mac OSX I had only success with:
PHP Language Constructs
- W3Schools
- https://www.w3schools.com/php/
-
https://www.w3schools.com/php7/
- fewer articles
<?php
$txt = "Hello world!";
$x = 5;
$y = 10.5;
echo "x: $x";
print("y: $y");
print("HW: " .$txt);
?>Types? Determined by assignment.
i.e. dynamic typing
Tip: decide which type a variable has, don't change it!
PHP Language Constructs
- W3Schools
- https://www.w3schools.com/php/
-
https://www.w3schools.com/php7/
- fewer articles
<?php
$txt = "Hello world!";
$x = 5;
$y = 10.5;
echo "x: $x";
print("y: $y");
print("HW: " .$txt)
?>Types? Determined by assignment.
i.e. dynamic typing
Tip: decide which type a variable has, don't change it! I'm guilty in some examples (form validation).
PHP Data Types
<?php
//string
$x = "Hello world!";
$y = 'Hello world!';
echo $x;
echo "<br>";
echo $y;
//integer
$x = 5985;
var_dump($x);
//float
$x = 10.365;
var_dump($x);
//boolean
$x = true;
$y = false;
//array
$cars = array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota");
var_dump($cars);
?><?php
//object
class Car {
function Car() {
$this->model = "VW";
}
}
// create an object
$herbie = new Car();
// show object properties
echo $herbie->model;
//null
$x = null;
var_dump($x);
?>Strings
<pre>
<?php
$hw = "Hello World";
$h = "Hello";
$s = " ";
$w = "World";
$hw2 = $h . $s . $w; //concat
$hw3 = "Hello $w"; //string interpolation
echo $hw2 ."\n";
print($hw3 ."\n");
//string functions
echo strlen("Hello World!\n");
echo str_word_count("Hello world!\n");
echo strrev("Hello world!") ."\n";
//https://www.w3schools.com/php7/php7_ref_string.asp
echo "test $h \n";
//echo "test $(1+2)"; not possible
?>
</pre>
Conditional Statements
<?php
$t = date("H");
if ($t < "10") {
echo "Have a good morning!";
} elseif ($t < "20") {
echo "Have a good day!";
} else {
echo "Have a good night!";
}
?>If-statement
<?php
$favcolor = "red";
switch ($favcolor) {
case "red":
echo "Your favorite color is red!";
break;
case "blue":
echo "Your favorite color is blue!";
break;
default:
echo "Your favorite color is neither red, blue, nor green!";
}
?>Switch-statement
Operators
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 10;
echo $x == $y; //true
$x = 10.0;
echo $x == $y; //true
echo $x === $y; //false
$w = null;
$x = $w ?? 'leeg'; //$x == 'leeg'
$y = "t";
$y = 10;
$x = $y == 10 ? "tien" : "geen tien"; //$x == "tien"
$y = 8;
$x = $y == 10 ? "tien" : "geen tien"; //$X == "geen tien"
$x = 10 == 10 && 11 == 11;
$x = 10 == 9 || 11 == 11;
$x = $x or false and 'test' == 'Test' xor 3;
?>Loops
<?php
$x = 1;
while($x <= 5) {
echo "The number is: $x <br>";
$x++;
}
//https://www.w3schools.com/php7/php7_loop_while.asp
?><?php
for ($x = 0; $x <= 10; $x++) {
echo "The number is: $x <br>";
}
//https://www.w3schools.com/php7/php7_loop_for.asp
?><?php
$colors = array("red", "green", "blue", "yellow");
foreach ($colors as $value) {
echo "$value <br>";
}
//https://www.w3schools.com/php7/php7_loop_for.asp
?>Loops - Foreach
<?php
$colors = array("red", "green", "blue", "yellow");
foreach ($colors as $value) {
echo "$value <br>";
}
//https://www.w3schools.com/php7/php7_loop_for.asp
?>To modify values in the
<?
$arr = array(1, 2, 3, 4);
foreach ($arr as &$value) {
$value = $value * 2;
}
print_r($arr);
//https://www.php.net/manual/en/control-structures.foreach.php
?><?
foreach (array("red", "green", "blue", "yellow") as $key => $value) {
// $arr[3] will be updated with each value from $arr...
echo "{$key} => {$value} ";
}
print_r($arr); //prints array of object, very useful
?>Array
<?php
$cars = array("Volvo", "BMW", "Toyota");
print_r($cars);
?>Array initialization/creation:
<?php
$cars[0] = "Volvo";
$cars[1] = "BMW";
$cars[2] = "Toyota";
print_r($cars);
?><?php
$cars[] = "Volvo";
$cars[] = "BMW";
$cars[] = "Toyota";
print_r($cars);
?>Array - Loop
<?php
$cars = array("Volvo", "BMW", "Toyota");
$arrlength = count($cars);
for($x = 0; $x < $arrlength; $x++) {
echo $cars[$x];
echo "<br>";
}
?>Array - Associative Array
<?
$age = array("Peter"=>"35", "Ben"=>"37", "Joe"=>"43");
print_r($age);
echo "Peter is " . $age["Peter"] . " years old.";
foreach($age as $x => $x_value) {
echo "Key=" . $x . ", Value=" . $x_value;
echo "<br>";
}
?>- Key => Value
- Key is the index in the associative array
- Value is the value of an element in the associative array
Array
-
Array is also an associative array a stack and a list
-
Arrays can be used as a stack
-
array_pop(), array_push()
-
- Arrays can grow dynamic (think of it like a List as in C#)
- Arrays (associative arrays) are the same as dictionary in C#
Useful array methods:
https://www.php.net/manual/en/ref.array.php
Functions
<!-- functions.php -->
<?php
function add($x, $y, $z = 0) {
return $x + $y + $z;
}
print add(3, 2);
print "<br/>";
print add(5, 4, 2);
?>- Be careful name must be unique, i.e. no overloading!
- PHP is a scripting language!
- Solution: use default parameters!
Functions in PHP (documentation):
https://www.php.net/manual/en/funcref.php
There is a lot of functionality available!
Forms - POST/GET & ACTION
<!-- form_post -->
<form action="process_post_form.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form><!-- process_post_form.php -->
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?><br>
Your email address is: <?php echo $_POST["email"]; ?>
<!-- form_post.php -->
<form action="process_post_form.php" method="get">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form><!-- process_form_get.php -->
Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?><br>
Your email address is: <?php echo $_GET["email"]; ?>POST
GET
Forms - POST VS GET
- GET sent variables in URL-variables
- Visible to everyone, sending no sensitive data
- Limited to 2000 characters
- Can be bookmarked
- Not a good choice for actions with side effects!
- for example, delete/update/insert a record from a database
-
POST sends variables to the server in the HTTP Request Body
- Can send sensitive information (password), invisible to others
- Upload files (for example images)
- The prefered way to handle forms
- For action with side effects
Forms - EMPTY
<!-- empty_action.php -->
<?php
if(isset($_POST["name"])) {
var_dump($_POST["name"]);
}
if(!empty($_POST["email"])) {
var_dump(isset($_POST["email"]));
}
?>
<form method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
- Use isset() if variable is not null!
- $_POST["key"] can be null --> Error
- empty() can be used to check if the variable is set and has value
If the action attribute in a form is empty (not specified) than the input can be processed on the same page!
Forms - Check for method
<!-- check_method.php -->
<?php
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'POST') {
if(isset($_POST["name"])) {
var_dump($_POST["name"]);
}
if(isset($_POST["email"])) {
var_dump(isset($_POST["email"]));
}
} else { // else if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET')
?>
<form method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
<?php
}
?>- When a page is requested for the first time it's always a GET request
- $_SETVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] returns the request method (POST or GET)
Forms - Hackers
<!-- hacked.php -->
<?php
if(isset($_GET['name'])) {
echo $_GET['name'];
}
?>
<form method="get">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>- Always filter/sanatize input: correct type & cleanup input
- Older browsers allow script input!!!
- Command Line Tools (curl)
Example:
!!!Use filter_var()!!!!
Forms - Validate input
- Check if input is empty (required)
-
if (available FILTER_VALIDATE_[TYPE])
- VALIDATE input - checks for correct format
- else Sanatize input (cleanup)
- Display errors
<!-- form_validation.php -->
<?php
$nameErr = $ageErr = "";
$name = $age = "";
$error = true;
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST") {
$error = false;
if(empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameErr = "name is required";
$error = true;
} else {
$name = filter_var($_POST["name"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
}
if(empty($_POST["age"])) {
$ageErr = "age is required";
$error = true;
} else {
$age = filter_var($_POST["age"], FILTER_VALIDATE_INT);
if($age === false) {
$ageErr = "age is incorrect";
$age = "";
$error = true;
} else {
if($age < 18) {
$ageErr = "to young";
$error = true;
}
}
}
}
?>
<form method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name">* <?php echo $nameErr ?>
Age: <input name="age">* <?= $ageErr ?>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<?php
if(!$error) {
echo "Name: $name <br/> Age: $age ";
}
?>Forms - Filter input validation
- filter_var(), filter_input()
- FILTER_VALIDATE_[TYPE] (recommended!)
- FILTER_SANITIZE_[TYPE]
<!-- form_validation2.php -->
<?php
$name = $price = $description = $email = "";
$errorPrice = $errorDescription = $errorEmail = $errorName = "";
$minPrice = 1.0; $maxPrice = 100.0;
$error = false;
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST")
{
//SANITIZE
if(empty($_POST['name'])) {
$errorName = "Name Required";
$error = true;
} else {
$name = filter_var($_POST['name'], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
if($name === false) {
$errorName = "Error in name";
$error = true;
$name = "";
}
}
//SANITIZE
if(empty($_POST['description'])) {
$errorDescription = "Description is empty";
$error = true;
} else {
$description = filter_var($_POST['description'], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
if($description === false) {
$errorDescription = "Error in Description";
$error = true;
}
}
//VALIDATE FLOAT!
if(!empty($_POST['price'])) {
$price = filter_var($_POST['price'], FILTER_VALIDATE_FLOAT);
if($price === false) {
$errorPrice = "No valid Price between $minPrice and $maxPrice";
$error = true;
}
}
//VALIDATE EMAIL!
if(!empty($_POST['email'])) {
$email = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'email', FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL);
if($email === false) {
$errorEmail = "Invalid Email";
$error = true;
}
}
}
?>
<? if($error) {
print "<b>Invalid input</b>";
}
?>
<form method="post">
<label>Name*</label> <input type="text" name="name" value="<?= $name ?>">
<span class="error"><?= $errorName ?></span>
<br/>
<label>Description*</label> <input type="text" name="description" value="<?= $description ?>">
<? if(!empty($errorDescription)) { ?>
<span class="error"><?= $errorDescription ?></span>
<? } ?>
<br/>
<label>Price</label> <input type="text" name="price" value="<? echo $price ?>">
<span class="error"><?= $errorPrice ?></span>
<br/>
<label>Email</label> <input type="text" name="email" value="<?= $email ?>">
<?= isset($errorEmail) ? "<span class='error'>$errorEmail</span>" : '' ?>
<br/>
<button type="submit">Add Product</button>
</form>
<style>
.error {
background-color: red;
}
</style>Forms -- Multiple
- Multiple Forms
- One form with hidden inputs
<?php
if(isset($_POST["add"])) {
echo "Add";
}
if(isset($_POST["delete"])) {
echo "Delete";
}
if(isset($_POST["operation"])) {
$operation = $_POST["operation"];
switch ($operation) {
case "add": echo "Add"; break;
case "delete": echo "Delete"; break;
}
}
?>
<form method="post">
<button name="add">Add</button>
<button name="delete">Delete</button>
</form>
<form method="post">
<input type="submit" name="add" value="Add">
<input type="submit" name="delete" value="Delete">
</form>
<!-- multiple forms -->
<form method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="operation" value="add">
<button type="submit">Add</button>
</form>
<form method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="operation" value="delete">
<button type="submit">Delete</button>
</form>
Homework & Questions
- See Blackboard
- Questions
Lesson 2
- State Management
State Management
- We need state
- state is information (data) that we need over multiple request
- user preferences, userid, session-id, etc
- state is information (data) that we need over multiple request
- A HTTP request will not know what was done in the previous requests (stateless)
- Solution: use state management techniques
- Tricks to maintain state over multiple request
State Management
-
State Management Categories
-
Client Side
-
Query Parameters (GET)
-
Query String
-
-
Hidden form fields (POST)
-
-
Server Side
-
Cookies
-
Sessions (uses cookies)
-
-
-
Limited to strings only (except Session)
-
casting to right datatype
-
-
Categories are a little bit artificial
Hidden Form Fields
-
Client Side
-
Hidden form fields (POST)
-
Examples:
-
Id's, Action
-
-
<!-- hiddenFormField.php -->
<?php
$count = (int)($_POST["count"] ?? 0);
$count++;
?>
<?= $count ?>
<hr/>
<form method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="count" value="<?= $count ?>"/>
<button>Inc</button>
</form>
Hidden Form Fields
-
Action Example
<!-- multipleButtons.php -->
<?php
$operation = $_POST['operation'] ?? "";
if($operation === "add") {
echo "Add Button Clicked";
} else if ($operation === "sub") {
echo "Sub Button Clicked";
}
?>
<form method="post">
<button name="operation" value="add" type="submit">+</button>
<button name="operation" value="sub" type="submit">-</button>
</form>Hidden Form Fields
-
ID + Action in Buttons
<!-- part of the code of the todo example -->
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST") {
if (isset($_POST["ACTION"])) {
$action = $_POST["ACTION"];
if ($action === "DeleteTodo") {
//delete todo item
} else if ($action === "EditTodo") {
//edit todo item
}
}
}
//code to load todo items in $rows
?>
<ul>
<? foreach ($rows as $row) { ?>
<li>
<?= $row["Description"] ?>
<form method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="todoId" value="<?= $row["TodoId"] ?>">
<button type="submit" name="ACTION" value="DeleteTodo">Delete</button>
<button type="submit" name="ACTION" value="EditTodo">Edit</button>
</form>
</li>
<? } ?>
</ul>Query Parameters
-
GET Request
-
Can be bookmarked
-
test.php?key1=value1&key2=value2
-
limited compared to forms
-
size, no uploads, everything is visable
-
<!-- queryparameter.php -->
<?php
$count = (int)($_GET["count"] ?? 0);
$count++;
?>
<?= $count ?>
<hr>
<form method="get">
<input type="hidden" name="count" value="<?= $count ?>"/>
<button type="submit">Inc</button>
</form>
</hr>
<a href="queryparameter.php?count=<?= $count ?>">Inc</a>Query Parameters
Example with action and Id
<?php
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "GET") {
if (isset($_GET["todoId"]) && !filter_input(INPUT_GET, "TodoId",
FILTER_VALIDATE_INT)) {
$todoId = (int)$_GET["todoId"];
//rest of code
}
}
?>
<ul>
<? foreach ($rows as $row) { ?>
<li>
<?= $row["Description"] ?>
<a href="todoExample.php?action=EditTodo&todoId=<?= $row['TodoId'] ?>">
Edit
</a>
</li>
<? } ?>
</ul>URL Path Segments
Example:
https://www.coolblue.nl/mobiele-telefoons/merk:apple
Not possible with PHP without a framework!
Server Side
- Cookies
- Store preference, user-tracking (id's)
-
Sessions
-
Links session-id (cookie) to private memory on server
-
- It's actually a combination between client side & server side, but is called a server side techniques.
Take a look at Example
- Example visit Coolblue, inspect the network traffic
Cookies
- Server request the client to store a cookie (name + value)
- On every subsequent request all cookies are send
- Use-Cases: User identification, Tracking / Analytics, Session Management
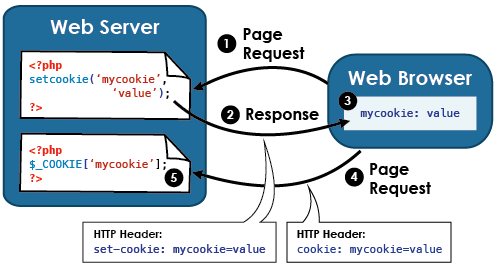
Cookies
<?php
$expires_time = 5; //5 seconds
$count = 0;
if(!isset($_COOKIE["count"])) {
$_COOKIE["count"] = 0;
} else {
$count = (int)$_COOKIE["count"];
}
$count++;
if($count % 5 == 0) {
setcookie("count", $count, time() - $expires_time);
} else {
setcookie("count", $count, time() + $expires_time);
}
?>
<?= $count ?>
<hr>
<a href="cookies.php">Inc</a>
Sessions
- Associate a piece of server memory to requests from a particular client
- Sessions are closed when the browser is closed
- Sessions are stored on server
- Safer than Cookies, user can't change values
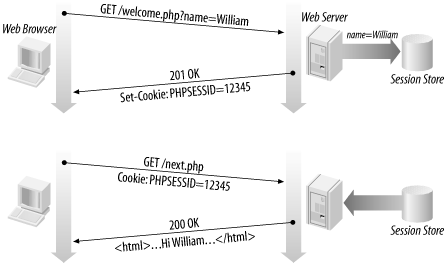
Sessions
<?php
//https://www.tutorialspoint.com/php/php_sessions.htm
session_start();
//read-session var count or initialize to 0
$count = (int)($_SESSION['count'] ?? 0);
$count++;
//write-session var count
$_SESSION['count'] = $count;
if($count % 5 == 0) {
unset($_SESSION['count']);
//to destroy all session vars use:
//session_destroy();
}
?>
<? echo $count ?>
<hr/>
<form action="session.php">
<button type="submit">Request page again</button>
</form>Session - Objects
<?php
class MyUser
{
public $name;
public $password;
}
session_start();
if(!isset($_SESSION['user'])) {
$user = new MyUser();
$user->name = "Joris";
$user->password = "Geheim";
$_SESSION["user"] = $user;
echo "Session Created, refresh/reload page!";
} else {
$user = (MyUser)$_SESSION["user"];
echo "Username: " .$user->name;
echo "Password: " .$user->password;
}
?>- Sessions can be used with Objects!
- It's a lot easier to have one "session object" than a lot of session-variables
Login Examples
<?php
$username = $_POST["username"] ?? "";
$password = $_POST["password"] ?? "";
if($username === "user" && $password === "session") {
session_start();
$_SESSION["user_id"] = uniqid();
header('Location: logout.php');
}
?>
<form method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="password" name="password">
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form>
Login Examples
<?php
session_start();
$logged_in = false;
if(isset($_POST["logout"])) {
if(isset($_SESSION["user_id"])) {
unset($_SESSION["user_id"]);
echo "logged out with session";
}
} else {
$user_id = $_SESSION["user_id"] ?? "";
if(!empty($user_id)) {
echo "Logged in Session with user_id: $user_id";
$logged_in = true;
}
if(!$logged_in) {
echo "Not logged in";
}
}
?>
<? if($logged_in) { ?>
<form method="post">
<button name="logout" type="submit">Logout</button>
</form>
<? } else { ?>
<form action="login.php">
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form>
<? } ?>Tracking Cookies
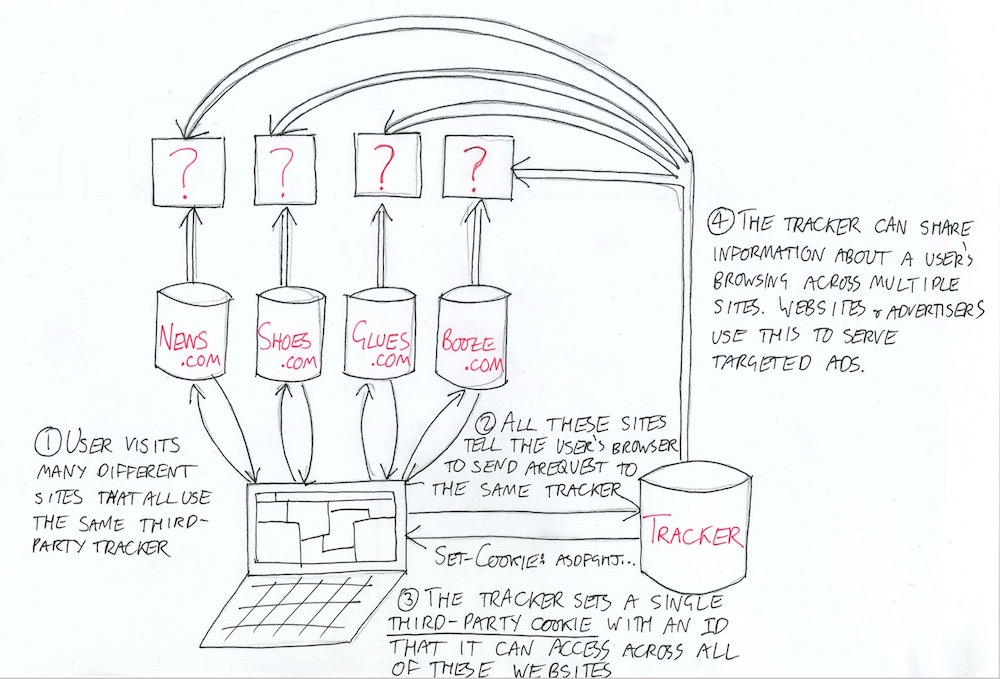
Other need to knows
<?php
//redirect
$url = "/test.php?a=b";
header("Location: " .$url);
die();
?><?php
//checkSamePage.php
function currentUrl( $trim_query_string = false ) {
$pageURL = (isset( $_SERVER['HTTPS'] ) && $_SERVER['HTTPS'] == 'on') ? "https://" : "http://";
$pageURL .= $_SERVER["SERVER_NAME"] .':' .$_SERVER["SERVER_PORT"] . $_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"];
if( ! $trim_query_string ) {
return $pageURL;
} else {
$url = explode( '?', $pageURL );
return $url[0];
}
}
function requestIsFromSamePage()
{
$current_url = currentUrl(true);
$request_page = explode('?',$_SERVER['HTTP_REFERER'] ?? "")[0];
return $current_url === $request_page;
}
if(requestIsFromSamePage()) {
echo "Same page";
} else {
echo "Different page";
}
?>
<form>
<button type="submit"></button>
</form>
Conclusion
Use a combination of techniques
Gut feeling

Lesson 3
-
Connect to a database
-
MySQL
-
Admin Tool
-
-
PDO
-
-
Prevent SQL Injection
-
Prevent XSS (Cross Side Scripting)
MySQL - Admin Tool
-
MySQL (MariaDB) is a Relational Database Management System (RDMS)
-
Admin Tools for Database
-
Use WebStorm or other IDE (plugin)
-
phpMyAdmin
-
-
Demo:
- create table
-
insert data
-
select data
Database Design
-
Every table needs a primary key
-
AUTO_INCREMENT
-
Name of table + ID (for example TodoId)
-
-
NOT NULL columns are preferred
-
Choose correct datatypes for columns
-
important
-
PDO Resources
Connect to Database
-
Go to the terminal
-
start --> system tools --> LXTerminal
-
-
Type het volgende commando (install PDO):
-
sudo apt install php7.3-mysql
-
enter
-
voer het password in (student)
-
enter
-
sudo service apache2 restart
-
enter
-
Demo Video on Blackboard
For Flex students
Create a database steps
See video on previous page how to do this!
- Create a schema (database)
- TodoDb
- Create a table
- Execute create table (CreateTable.sql)
- INSERT Records into the Todos Table
- Commit INSERTS
- Check if records are inserted!
PHP Database overview
-
Steps:
-
Connect to a database
-
Prepare a statement (prepared statement)
-
Statement = Query
-
-
Execute the statement
-
Send the Query to the database
-
-
Process the result
-
Close connection!
-
Connect to database
-
connection string
-
creating object (new PDO(...), connection)
-
handeling errors, with exception (try, catch)
-
close connection ($conn = null)
<?php
//connectToDatabaseAndClose.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
//enables exception mode, exception is throw when an error occurs
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
echo "Connected successful";
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if($conn != null) {
//$conn->close();
$conn = null;
}
}
?>Query Database
-
Prepare Statement
-
PDO::FETCH_ASSOC
-
foreach ($stmt->fetchAll() as $row)
$row["columnName"]
<?php
//queryData.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "SELECT TodoId, Description, Done FROM Todos";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
foreach ($stmt->fetchAll() as $row) {
echo $row["Description"]
." "
.($row["Done"] ? "completed" : "") ."<br/>";
}
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "Connection failed: $ex";
} finally {
$conn = null;
}
?>Insert Data
-
!!!!Dangerous example (line 17)!!!!
-
Show the problem!
<?php
//insertData.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$description = $_POST["description"] ?? false;
if($description !== false) {
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
//don't do this!!! SQL INJECTION!!!!!!!!!
$sql = "INSERT INTO Todos (Description) VALUES ('$description')";
//don't do this!!! SQL INJECTION!!!!!!!!!
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "Inserted Record";
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if(isset($conn)) {
$conn = null;
}
}
}
?>
<form method="post">
<input name="description" type="text">
<button name="AddTodo" type="submit">Add Todo</button>
</form>
SQL Injection
Simple explanation:
Longer explanation:
SQL Injection
- Don't make your own SQL strings
- Don't use $conn->query(...)
- Add "' OR 1 = 1; --" on the querystring
<?php
//sqlInjectionExample.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
if(isset($_GET["searchDescription"]) && $_GET["searchDescription"])
{
$searchDescription = $_GET["searchDescription"];
//default username, password for wamp is root, empty/blank
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
//Add the following string to the querystring searchDescription: "' OR 1 = 1; --"
//Or something like this: "'; DROP TABLE Todos; --"
$sql = "SELECT TodoId, Description, Done FROM Todos WHERE Description = '$searchDescription'";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
foreach ($stmt->fetchAll() as $row) {
echo $row["Description"]
." "
.($row["Done"] ? "completed" : "")
."<br/>";
}
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
}
} else {
echo "invalid input!";
}
?>
<form method="get">
<input name="searchDescription" type="text">
<button type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
Line 21
SQL Injection
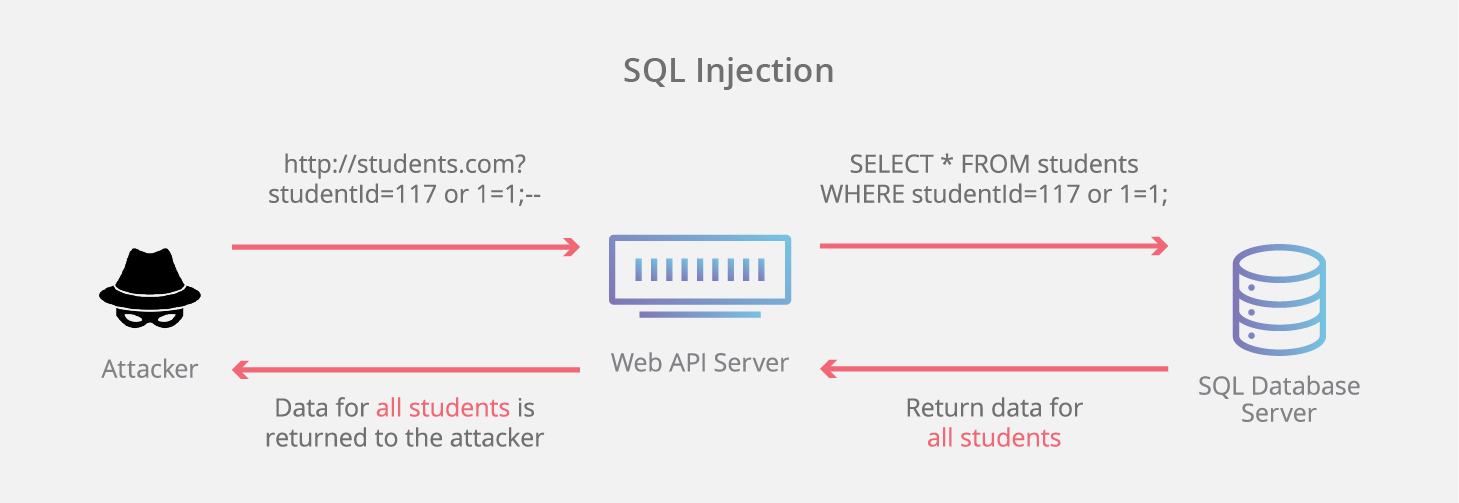



To Prevent SQL Injection

Always, Use Prepared Statements in combination with Parameter Placeholders!


Query Parameter Placeholders
-
Use Query Parameter Placeholders
-
for example: :description, :done
-
-
Use a prepare statements
-
Creates a sql statement that can be executed on the server
-
-
Use bindValue(...)
-
Fills in the value in the SQL
-
<?php
//query with named placeholders
$sql = "INSERT INTO Todos (Description, Done) VALUES (:description, :done)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindValue("description", $description, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindValue("done", $done, PDO::PARAM_BOOL);
$stmt->execute();
?>SQL Injection Solved
<?php
//insertDataWithNamedPlaceholders.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
if(!empty($_POST["description"]))
{
$description = filter_var($_POST["description"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
if($description === false) {
echo "Error in description";
die();
}
$done = isset($_POST["done"]) ? true : false;
//default username, password for wamp is root, empty/blank
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO Todos (Description, Done) VALUES (:description, :done)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindValue("description", $description, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindValue("done", $done, PDO::PARAM_BOOL);
if($stmt->execute()) {
echo "Inserted Record";
} //else is in the Exception (an error occurred)!
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if($conn != null) {
$conn = null;
}
}
} else {
echo "invalid input!";
}
?>
<form method="post">
<input name="description" type="text">
<input name="done" type="checkbox">
<button name="AddTodo" type="submit">Add Todo</button>
</form>
- Query Parameter Placeholders (line 25)
- :description, :done
- Filled with value (line 28, 29)
Insert
<?php
//insertIdAndResult.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
if(!empty($_POST["description"]))
{
$description = filter_var($_POST["description"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
$done = isset($_POST["done"]) ? true : false; //this is a trick (only possible with checkbox)
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO Todos (Description, Done) VALUES (:description, :done)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindParam("description", $description, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam("done", $done, PDO::PARAM_BOOL);
if($stmt->execute()) {
$todoId = $conn->lastInsertId();
echo "Inserted record with TodoId: $todoId";
} else {
//never executed, exception is thrown
echo "Inserted failed";
}
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if(isset($conn)) {
$conn = null;
}
}
} else {
echo "invalid input!";
}
?>
<form method="post">
<input name="description" type="text">
<input name="done" type="checkbox">
<button name="AddTodo" type="submit">Add Todo</button>
</form>
- To get the Primary Key (PK) value of insert.
- $conn->lastInsertId();
Line 27
Insert
<?php
//insertCrossSideScriptingAttack.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
if(!empty($_POST["description"]))
{
$description = $_POST["description"];
$done = isset($_POST["done"]) ? true : false; //this is a trick (only possible with checkbox)
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO Todos (Description, Done) VALUES (:description, :done)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindParam("description", $description, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam("done", $done, PDO::PARAM_BOOL);
if($stmt->execute()) {
$todoId = $conn->lastInsertId();
echo "Inserted record with TodoId: $todoId";
} else {
//never executed, exception is thrown
echo "Inserted failed";
}
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if(isset($conn)) {
$conn = null;
}
}
} else {
echo "invalid input!";
}
?>
<form method="post">
<input name="description" type="text">
<input name="done" type="checkbox">
<button name="AddTodo" type="submit">Add Todo</button>
</form>
- Without filter_var
Cross Site Scripting (XSS)


Insert
- Without filter_var
Cross Site Scripting (XSS)



<script>alert("test");</script>- Load the queryData.php
- What happens?
alert("test"); is not dangerous, but other scripts are really dangerous!
Rember
Always:
- use filter_var(...)
- AND
-
use prepare statements with
- query parameter placeholder
Otherwise:

Probably some script that searches the internet for hackable sites




Delete
<?php
//deleteDoneTodos.php
$host = "localhost";
$databaseName = "TodoDb";
$connectionString = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$databaseName";
$username = "student"; //root is default in most cases
$password = "student"; //root is default in most cases
//pay attention, isset($_POST["DeleteTodos"]) instead of !empty($_POST["DeleteTodos"])
//because the button has no value
if(isset($_POST["DeleteTodos"]))
{
$conn = null;
try {
$conn = new PDO($connectionString, $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "DELETE FROM Todos WHERE Done = true";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
if($stmt->execute()) {
$deleteCount = $stmt->rowCount();
echo "Deleted $deleteCount todo records";
} else {
//never executed, exception is thrown
echo "No todos delete";
}
} catch (PDOException $ex) {
echo "PDOException: $ex";
} finally {
if(isset($conn)) {
$conn = null;
}
}
}
?>
<form method="post">
<button name="DeleteTodos" type="submit">Delete Done Todos</button>
</form>
- Get the number of affected rows
- $stmt->rowCount(); //line 26
Line 26
Todo Example
Two examples:
- Multipage (easy)
- Singlepage (harder)
The techniques combined from the first three lessons
Conclusion
- To prevent SQL injection use a prepared statement with query parameter placeholders!
- Validate all input when you do an insert/update/delete
- filter_var(....)
- prevents Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks
- filter_var(....)
- Don't forget to close the connection!
- if not needed anymore
Lesson 4
-
Structuring and reuse of code in web application
-
includes / requires
-
functions
-
classes
-
-
Separation of Concerns
-
Code & UI --> Template Library (Twig)
-
- Todo Example from previous lesson is terrible!
- Code redundancy
- UI & Code combined
Include / Require
-
include(), include_once() emit warning (file not found)
-
require(), require_once() emit fatal error (file not found)
<?php
//method1/page1.php
$_title = "Page 1";
//include "_header.php"
require "_header.php";
?>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-4">
<h3>Page 1 Column 1</h3>
</div>
</div>
<?php
require "_footer.php";
?>Sharing Variables
- Assumptions are wrong to make
- Tip: use functions instead
<!-- $_title is defined on other page -->
//part of _header.php
<div class="jumbotron text-center">
<h1>Company Logo & Text</h1>
<p><?= $_title ?></p>
</div>
<?php
//method1/page1.php
$_title = "Page 1";
//include "_header.php"
require "_header.php";
?>Use Functions
-
Use functions instead, can be placed in separate file and included
-
HTML Helpers, simple function that generate html!
-
Very useful
-
return type can be seen as html code!
-
<?php
//method1/htmlHelpers.html
function displayHeader($title)
{
?>
<html>
<head>
<title><?= $title ?></title>
</head>
<body>
<?
}
function displayFooter($title) {
?>
<h1><?= $title ?></h1>
</body>
</html>
<?
}
?>
<?php
displayHeader("My Title");
displayFooter("End of Page")
?>
Template Library
-
Separates code (Logic) form User Interface
-
Separation of Concerns (SOC)
-
Increases maintainability, readability
-
Php has many template libraries:
-
We use Twig as an example
-
native support in PhpStorm (and other IDE's)
-
-
- To install Twig use Composer
- Composer = Dependency Manager for PHP
- Package Manager: install/update/remove libraries and maintains dependencies
- Composer = Dependency Manager for PHP
Twig installation
In the terminal, execute the following commands:
- sudo apt install composer
- in the project-directory
- composer require twig/twig
For Windows Users:
https://getcomposer.org/doc/00-intro.md#installation-windows
Twig Example
<?php
<!-- https://twig.symfony.com/doc/2.x/api.html -->
require_once '/path/to/vendor/autoload.php';
$loader = new \Twig\Loader\ArrayLoader([
'index.html' => 'Hello {{ name }}!',
]);
$twig = new \Twig\Environment($loader);
echo $twig->render('index.html', ['name' => 'Fabien']);
?>- Template (line 5)
- special syntax
- To render a template (line 6)
- fill template variables
- Use FileLoader instead of ArrayLoader
Twig Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Webpage</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="navigation">
{% for item in navigation %}
<li><a href="{{ item.href }}">{{ item.caption }}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<h1>My Webpage</h1>
{{ a_variable }}
<h2>Not set variable: {{ empty_var }}</h2>
</body>
</html>- {% %} to execute statements (for-loop, if, etc)
- {{ }} outputs variable or expression
- {# comments #}
- Don't use HTML comments <!-- --> results in error
Twig Example
<?php
require_once ($_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'] .'/vendor/autoload.php');
$loader = new \Twig\Loader\FilesystemLoader('Templates');
$twig = new \Twig\Environment($loader);
$template = $twig->load("example.twig");
//echo $template->render(['todos'=> $todos, 'rowToEdit' => $rowToEdit]);
echo $template->render([
'navigation' => [
['href'=>"index.html", "caption"=>"home"],
['href'=>"contact.html", "caption"=>"contact"]
],
"a_variable" => "<script>alert('test');</script>"
]);
- Using a template
- Array syntax
- auto escape of dangerous input
- if variable is empty, no problem
Template Syntax
- important things:
- iterative-statements, conditional-statements
- reuse
- template inheritance
- template include
- macro's
- functions that return html
- can be used if some functionalitity is needed many times
- functions that return html
Todo Example
- Classes
- for database interaction
- for entities (object that we store in database), in this example Todo
- templates for layout (Twig)
- see todo.php in example code
Lesson 5 - AJAX


Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
AJAX
- A = Asynchronous
- No refresh or redirect
- J = JavaScript
- A = And
- XML = eXtensible Markup Language
- XML nowadays replaced by JSON
Tip: use jQuery for Ajax!
Normal HTTP Request
The complete page is updated!
Idea: Only update what's changed!

AJAX Request - Idea
- Event Occurs --> JavaScript --> Ajax Request
- The server returns only data
- nowadays it's JSON instead of XML
- Update the DOM with the data returned
- HTML Model of webpage in memory of webbrowser
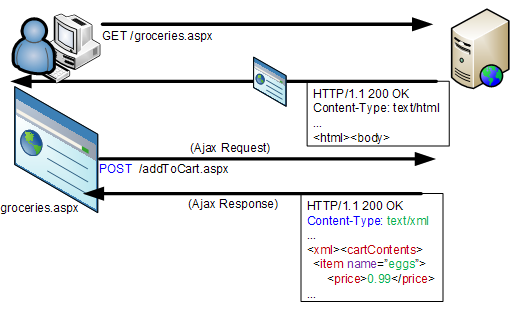
AJAX Request - Idea
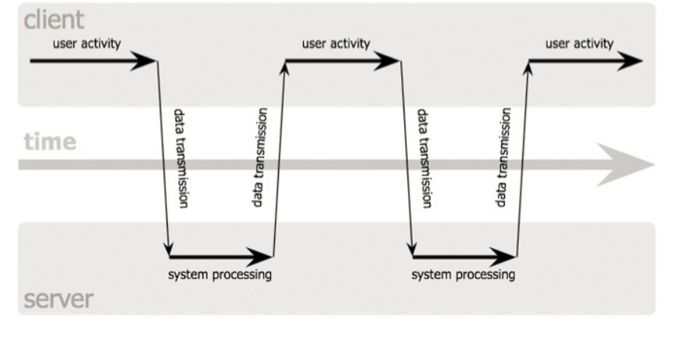
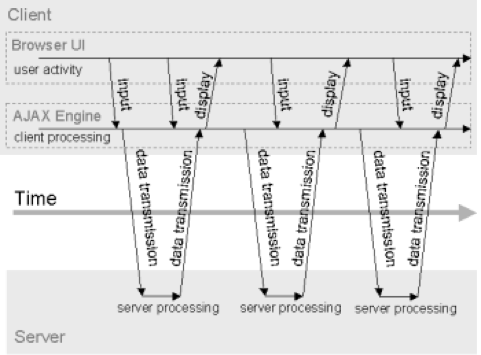
Text
- Normal (above)
- Asynchronous (right)
- AJAX Model
AJAX Request - Idea
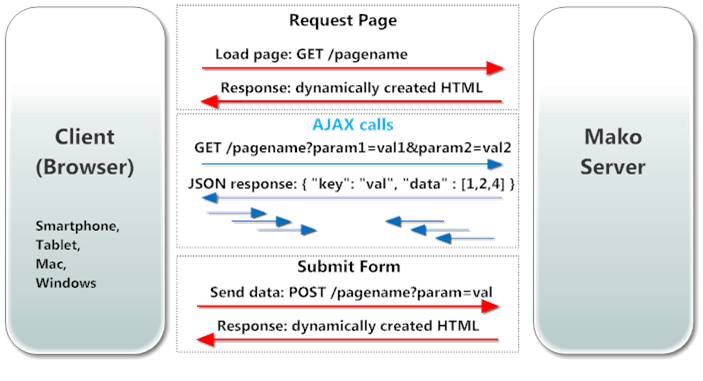
XMLHttpRequest - JS Object for AJAX
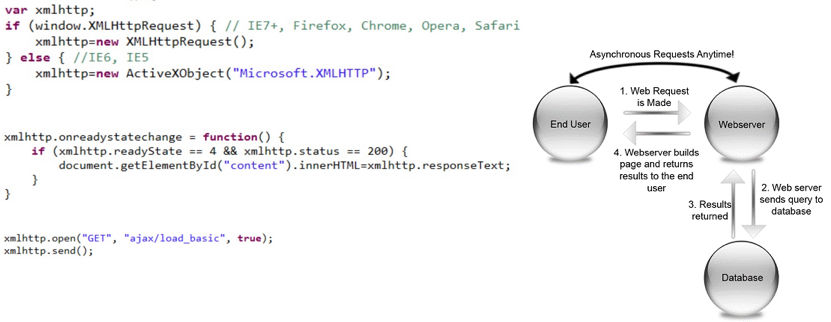
Returned data

More examples:
JSON
- JSON: JavaScript Object Notation
- Lightweight data-interchange format
- Easy to use and read
- Subset of JavaScript
- Only data
- More efficient than XML
jQuery

- jQuery makes it possible to easily
- respond to an event
- send AJAX request
- manipulate the DOM
- etc
jQuery
- Tip: take a jQuery tutorial/course
- Tip: w3schools.com
- jQuery is worth the investment
- still today
Disable Cache!
Simple Ajax Example - Client
<!-- /Les5/SimpleExamples/nocommentversion.php -->
<!-- Import JQUERY -->
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.4.1.min.js" integrity="sha256-CSXorXvZcTkaix6Yvo6HppcZGetbYMGWSFlBw8HfCJo=" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<p id="text-load"></p>
<p id="text-post"></p>
<p id="text-json"></p>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#text-load").load("textGenerator.php", {
action: "load",
food: "pizza"
});
$.post("textGenerator.php", {
action: "calculateSum",
number1: 5,
number2: 6
}, function(data) {
$("#text-post").text("Sum: " + data);
});
$.post("textGenerator.php", {
action: "sendPersonInfo"
}, function(data, status) {
if (status != "success") {
// You can output an error message here if something went wrong with the request
}
else {
$("#text-json").text("Name: " + data.name + ", Age: " + data.age + ", Country: " + data.country);
}
}, "json")
});
</script>
Simple Ajax Example - Server
<?php
if (isset($_POST["action"])) {
$action = $_POST["action"];
// You don't "need" to use a switch statement and separate functions
// This is just one way, but it makes your code look extremely clean and readable:
switch ($action) {
case "load": sendFood();
break;
case "calculateSum": calculateSum();
break;
case "sendPersonInfo": sendPersonInfo();
break;
}
}
function sendFood() {
$food = $_POST["food"];
// You need to echo what gets returned. For example: echo $food;
// Or you can escape php in order to echo HTML,
// and inside the HTML you can even include PHP variables again (useful if you echo a big block of HTML):
?>
<b><i>My favorite food is <?= $food ?></i></b>
<?php
}
function calculateSum() {
$number1 = $_POST["number1"];
$number2 = $_POST["number2"];
$sum = $number1 + $number2;
echo $sum;
}
function sendPersonInfo() {
$jsonData["name"] = "Bob";
$jsonData["age"] = "30";
$jsonData["country"] = "Netherlands";
// This converts your array into json format which can be sent and read
echo json_encode($jsonData);
}Example 2 - Client
<!-- Les5/ajax.html -->
<form class="js-ajax-php-json" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8">
<input type="text" name="favorite_beverage" value="" placeholder="Favorite restaurant" />
<input type="text" name="favorite_restaurant" value="" placeholder="Favorite beverage" />
<select name="gender">
<option value="male">Male</option>
<option value="female">Female</option>
</select>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit form" />
</form>
<ul class="the-return">
[HTML is replaced when successful.]
</ul>
<script
src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.4.1.js"
integrity="sha256-WpOohJOqMqqyKL9FccASB9O0KwACQJpFTUBLTYOVvVU="
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$("document").ready(function(){
$(".js-ajax-php-json").submit(function(){
var data = {
"action": "test"
};
data = $(this).serialize() + "&" + $.param(data);
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
dataType: "json",
url: "ajax.php",
data: data,
success: function(data) {
console.log(data);
$(".the-return").empty();
$ul = $(".the-return").append("<ul></ul>");
for (var key in data) {
if (data.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
$ul.append(`<li>Key: ${key} -- Value: ${data[key]} </li>`)
}
}
$(".the-return").append($ul);
}
});
return false;
});
});
</script>Example 2 - Server
<?php
//Les4/ajax.php
function is_ajax() {
return isset($_SERVER['HTTP_X_REQUESTED_WITH']) && strtolower($_SERVER['HTTP_X_REQUESTED_WITH']) == 'xmlhttprequest';
}
if(is_ajax()) {
if (isset($_POST["action"]) && !empty($_POST["action"])) { //Checks if action value exists
$action = $_POST["action"];
switch($action) { //Switch case for value of action
case "test": test_function(); break;
}
}
}
function test_function(){
$return = $_POST;
//Do what you need to do with the info. The following are some examples.
//if ($return["favorite_beverage"] == ""){
// $return["favorite_beverage"] = "Coke";
//}
//$return["favorite_restaurant"] = "McDonald's";
//$return["json"] = json_encode($return);
header('Content-type: application/json');
echo json_encode($return);
}
?>Discussion of previous example
- UI Update logic & interaction is programmed in JS Code (jQuery)
- The server checks input and returns data (JSON)
- Template library in JavaScript
- https://www.jsviews.com/#jsrender
- makes UI programming easier
Php
By Joris Lops
Php
- 1,480


