OSLC-KM
A Knowledge Management specification for OSLC-based resources
Jose María Alvarez-Rodríguez, Juan Llorens, Manuela Alejandres and Jose Fuentes
INCOSE IS 2016
Context
-
Multiple domains
- Different types of artifacts
- Need of intra-operability
- Intra-domain
- Need of interoperability
- Inter-domain
Intra-operability
Open Services for Life-cycle Collaboration

OSLC
Interoperability

Purposed solution by existing OSLC specs.
Source: http://open-services.net/
OSLC resource to
OSLC resource
individual problem solving
Real Situation
Point to point connections-> Combinatorial explosion

A barrier for the full application of the OSLC view

...so What to do?

?
OSLC
Preliminary Evaluation
- Great effort on interoperability
- Community (industry) effort
- Different types of artifacts (resource shapes)
- OASIS standards (Core, Change Management, etc.)
- ...
Challenges (among others)
- Increase of interoperability complexity when new domains are defined
- Provision of services to all the resource shapes
which leads to the need of a
more universal approach
KCSE
Knowledge-centric Systems Engineering
KCSE: notion of an OSLC bus

Representation
Services
COMMON
How many different types of artifacts are generated during the development life-cycle?
tools, formats, protocols, query languages, etc.
Representation
Needs and Challenges
- A common representation model
- Interoperability
- ...
Services
- Language Uniformity
- Quality checking
- Visualization
- Traceability
- Human machine interface
- ...

Needs and Challenges
- A common representation model
- Interoperability
- Knowledge Management processes
- Natural language to express queries
- ...
OSLC-KM
New domain
New resource shape
RDF
Resource Description Framework
- Common & shared Data model
-
Triples
- (subject, object, predicate)
- Binary relationships
- Underlying Directed Graph
- W3C Recommendation (2004)
- Query languages
RDFS
RDF Schema
- Data modeling for RDF data
- Classes
- Properties (domain & ranges)
- RDF serialization
- W3C Recommendation (2004)
OWL
Ontology Web Language
- Vocabulary for defining formal ontologies
- Logic-oriented
- RDF serialization
- Flavours (2.0): EL, QL, RL
- W3C Recommendation (2012, v2.0)
RIF
Rule Interchange Format
- Exchange of business rules
- Rule-oriented
- Flavours: Core, PRD, BLD, etc.
- XML serialization
- W3C Recommendation (2013, v2.0)
RSHP
Relationship "arship"
- Property Graph
- Any kind of relationship
- Arity and Cardinality
- Industry-oriented
- Native tool support
- Queries based on natural language
- First publication 2004
Others
- SBVR
- Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Rules
- ODM
- Ontology Definition Metamodel
- RAS
- Reusable Asset Specification
Preliminary Evaluation


-
RDF good option for exchange data on the web
- Restrictions: arity and cardinality of relationships, lack of native tools, logics, etc.
-
RDFS and OWL
- Oriented to define formal ontologies
-
RSHP
- High level of Expressivity
- Native tool support
- ...
Our approach
OSLC
(Data Exchange)
RSHP*
(Internal representation: metadata+contents
and services)
The Specification
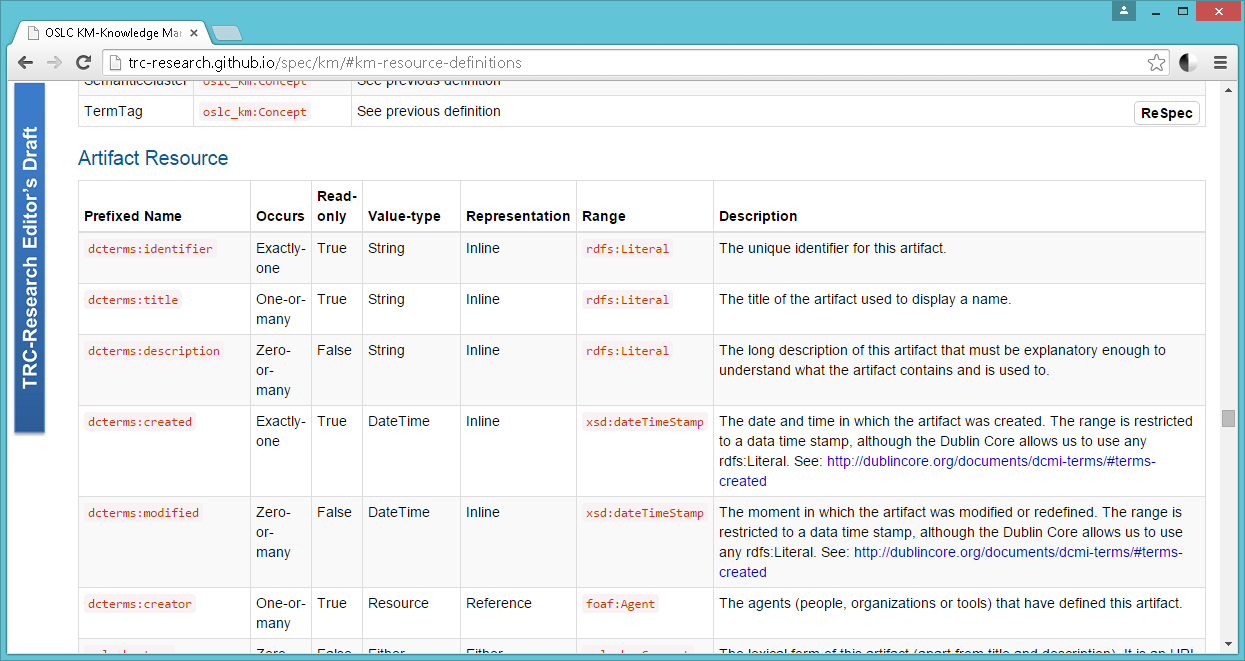
Shape for KM resources
Metadata+Contents
Resource Shape

Based on the W3C SKOS Recommendation
Simple Knowledge Organization System
OSLC Core
Provenance*
Access (W3C HTTP Access)
Metadata (Dublin Core, traces, etc.)
Contents (resource shape)
Visualization (SVG)
Summary of Properties
Properties
All in one...
One implementation

...on top of...
Knowledge Manager by
The REUSE Company

Vocabulary
& Conceptual Model
- Normalization
- Standardization
- Suggestions
- X Breakdown Structures
- ...
Patterns
- Restrictions
- Examples
- Suggestions
On-going work...

Process any kind of OSLC Resource or RDF data...
E.g. Modelica
Summary
- Use of the W3C Recommendations
- Concepts and relationships are the entities to be exchanged
- Services for: search, trace, naming, visualize, etc.

Metadata+Contents
Artifact
OSLC KM
Knowledge Centric Systems Engineering to govern the development lifecyle

SRL
Inputs
Outputs
...
Common services
Representation
OSLC KM
Not a dream!

SRL
Inputs
Outputs
...
Common services
Representation
Advantages
- Standard exchange of data: OSLC
- Enhance expressiveness (RSHP)
- Reuse of existing standards and vocabularies
- Native Tool support (Knowledge Manager)
- Cross-cutting services (semantic-based)
- Elastic approach
- ...
Drawbacks
- Scope of knowledge management (needs)
- Potential overlapping with other tools and specs
- Need of spread the approach
Conclusions
-
Knowledge Management: a key process
-
REUSE!
-
- Need of:
- Reuse of standards and service-oriented functionalities (OSLC)
- Take the most for data exchange (OSLC) and representation (RSHP)
- Bring technology to a human-oriented environment (NLP)
- Technical issues
- Completeness of the specification?
- Implementation
Future work
-
Merge and extend the spec with other knowledge standards
-
E.g. STEP, Industrial Internet activities
-
-
Refine of the resource shape
-
Full implementation and support to all services
-
Integration patterns governed by knowledge
-
...
Industrial Linked Data
OSLC applications
- Semantic Impact Analysis
- Risk Analysis
- Continuous Engineering
- ...

Speakers


-
Dr. Jose María Alvarez-Rodríguez
- Carlos III University of Madrid, Spain
- Member of INCOSE and the OSLC RM working group
- E-mail: josemaria.alvarez@uc3m.es
- WWW:
-
Prof. Dr. Juan Llorens
- Carlos III University of Madrid, Spain
- Member of INCOSE
- CTO of The Reuse Company Inc.
- E-mail: llorens@kr.inf.uc3m.es
- WWW:


OSLC-KM INCOSE 2015-v2
By Jose María Alvarez
OSLC-KM INCOSE 2015-v2
Presentation of the paper OSLC KM in INCOSE SI 2015.
- 1,782