Open Lab
notebooks
and
workflow systems
26 September 2014
PLOS
Workflow systems
- The provenance of the research
- how did the conclusions come about?
- what iterations did the data go through?
- System (local or cloud) to keep track of experiments
- including protocols, documentation, analysis
- Both high-level and code-based systems
- Very popular in some fields, non-existent in others
Types
High-Level
- most popular
- express computations in higher-level components
- each component performs a small, well-defined task
- code is underlying, but written by someone else
- researcher connects pre-existing components
Command-Line
If there is no pre-existing componentor tool, the researcher can build his/ her own,
which requires writing the code to create it. Often used in tandem with other programs that offer a GUI.
Outcome of use
- specific fields of study
- used across many fields & published
- text, raw data, code, workflow system
Fields
-
Most documented in computer and information sciences
- In specific fields, researchers can use already established workflows
- Bioinformatics is popular
- Energy Biosciences Institute (EBI)
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
- provide resources in REST or WDSL formats
- can easily be incorporated into workflow systems
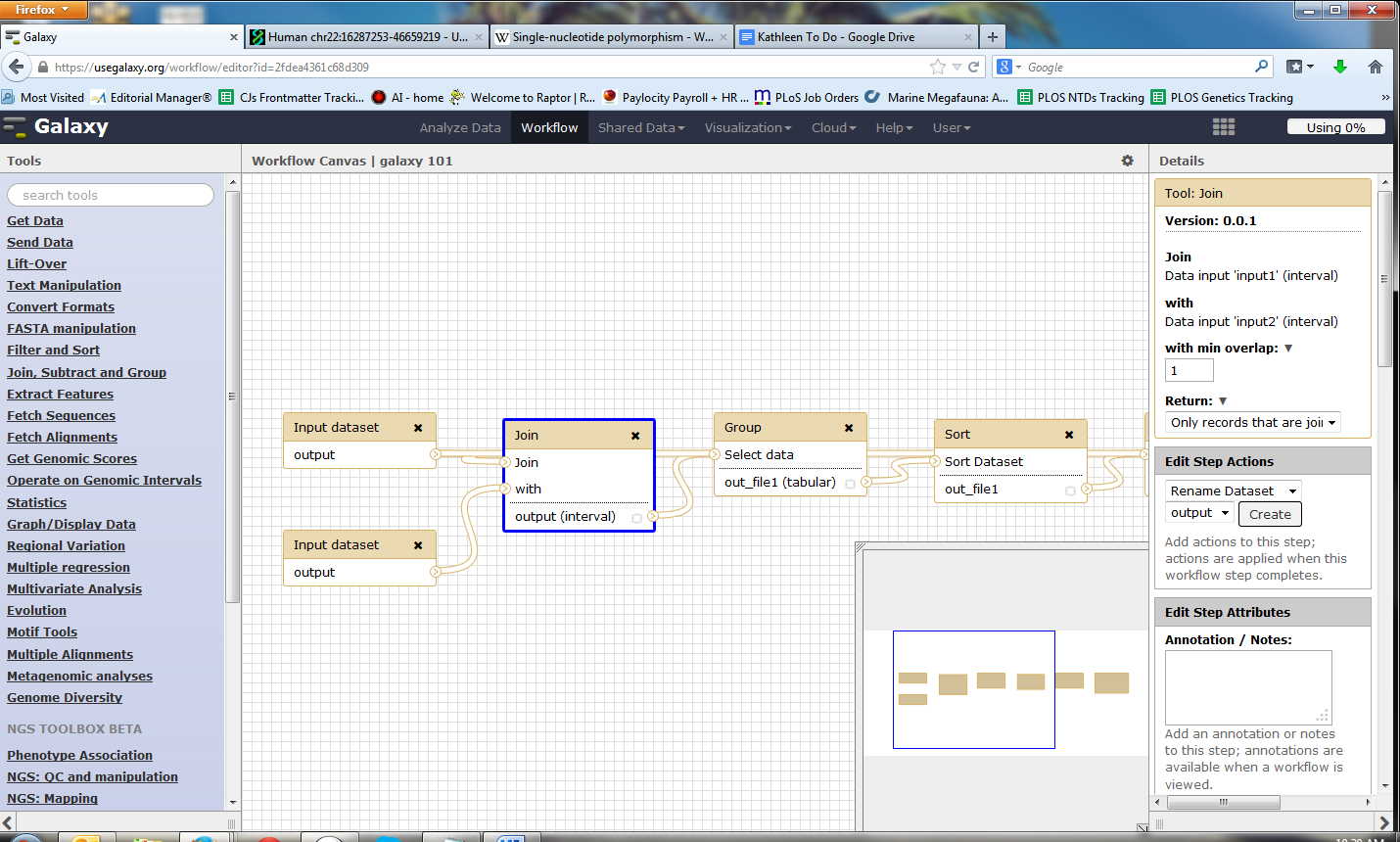
Galaxy
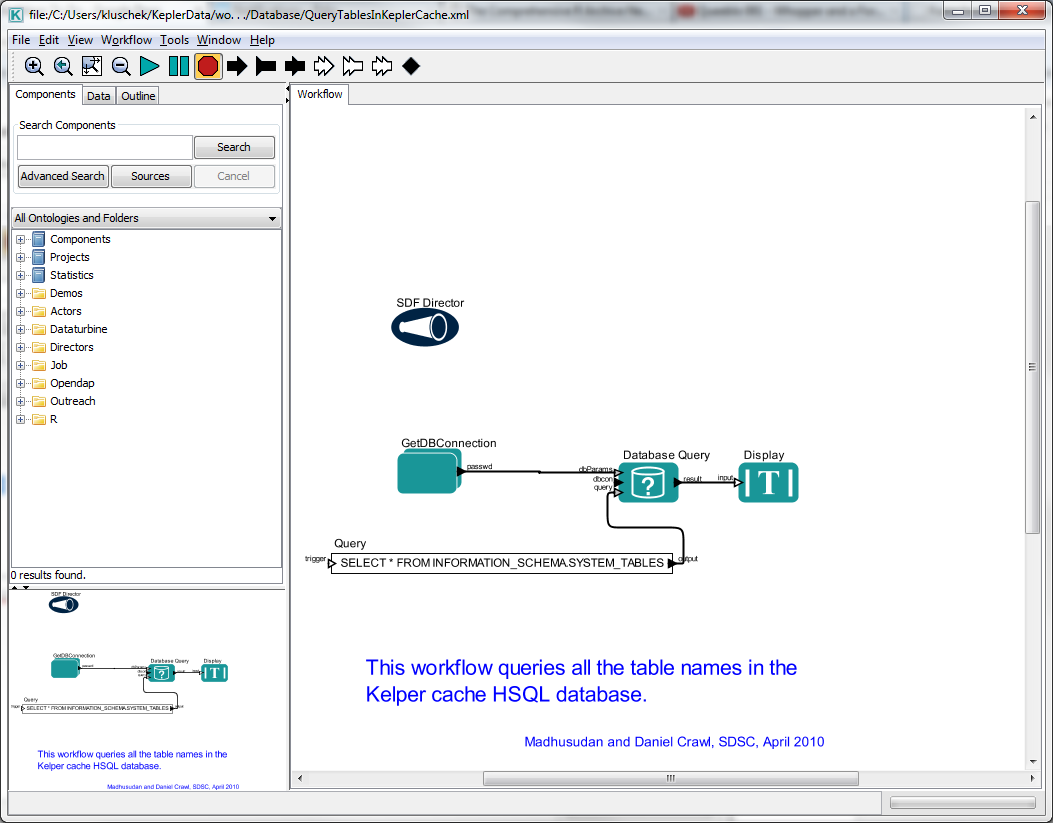
Kepler Project
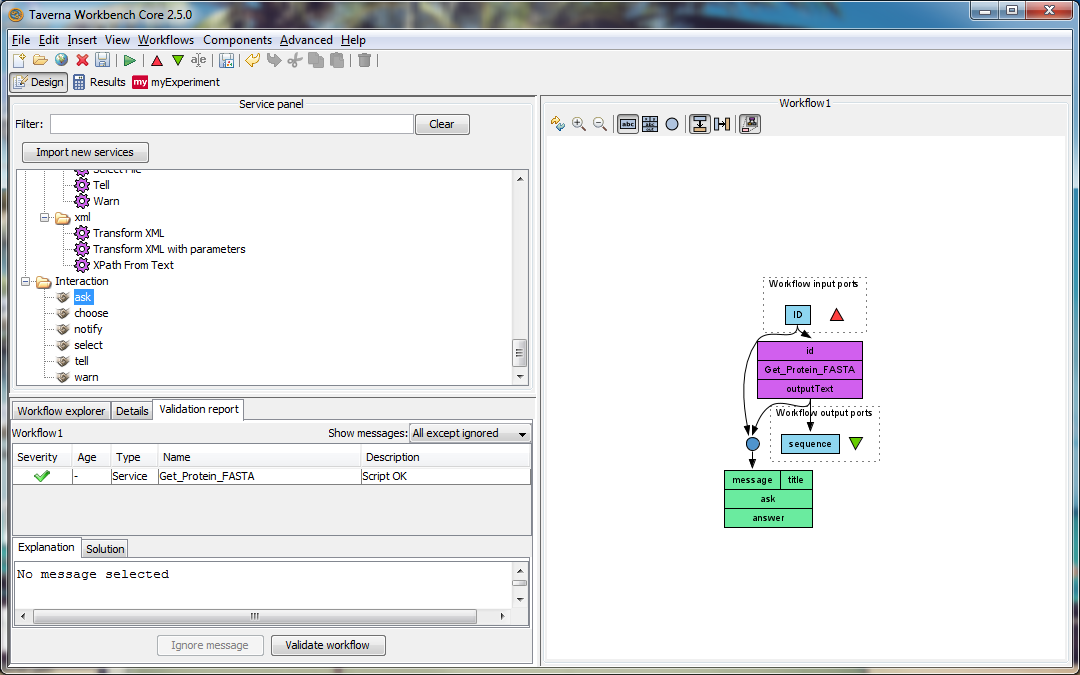
taverna
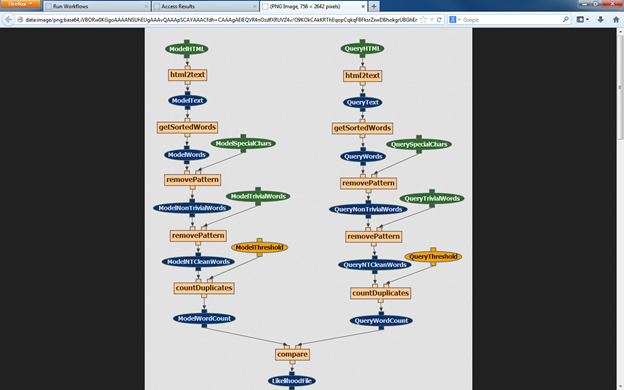
wings
Lab Notebooks/Workflows
By Kathleen Luschek
Lab Notebooks/Workflows
PLOS 2014
- 468



