
-Beginners
Install git:
-
Linux(Debian)
- sudo apt-get install git
-
Linux(Fedora)
- sudo yum install git
-
Mac
- http://git-scm.com/download/mac
-
Windows
- http://git-scm.com/download/win
What is verison control system?
- A system that keeps record of your changes
- Allows for collaborative development
- Allows you to know who made what changes and when
- Allows you to revert any changes and go back to a previous state
What is verison control system?
- Distributed version control
- User keeps entire code and history on their location machines
- Users can make any changes without Internet access
- (Except pushing and pulling from a remote server)
What is git?
- Git isn't the only version control system

How does git work?
- Lets look at some important git terminology
Key concept: Snapshot
- The way git keeps track of your code history
- Essentially records what all your files look like at a given point in time
- You decide when to take a snapshot, and of what files
- Have the ability to go back to visit any snapshot
Key concept: Commit
- The act of creating a snapshot
- Can be a noun or verb:
- "I commited code"
- "I just made a new commit"
- Essentially, a project is made up of a bunch of commits
Key concept: Commit
- A commit contains three pieces of information:
- Information about how the files changed from previously
- Called the "diff"
- A reference to the commit that came before it
- Called the "parent commit"
- A hash code name
- will look something like this:
- a007db19dc4d0034r12b55bb00a
- Information about how the files changed from previously
Key concept: Repository
- Often shortened to "repo"
- A collection of all the files and the history of those files
- Consists of all your commits
- Place where all your hard work is stored
Key concept: Repository
- Can live on a local machine or on a remote server (Github!)
- The act of copying a repository from a remote server is called cloning
- Cloning from a remote server allows team to work together
Key concept: Repository
- The process of downloading commits that don't exist on your machine from a remote repository is called pulling changes
- The process of adding your local changes to the remote repository is called pushing changes
Key concept: Branches
- All commits in git live on some branch
- But there can be many, many branches
- The main branch in a project is called the master branch

Key concept: Merging
- Once you are done with your feature, you merge it back into master
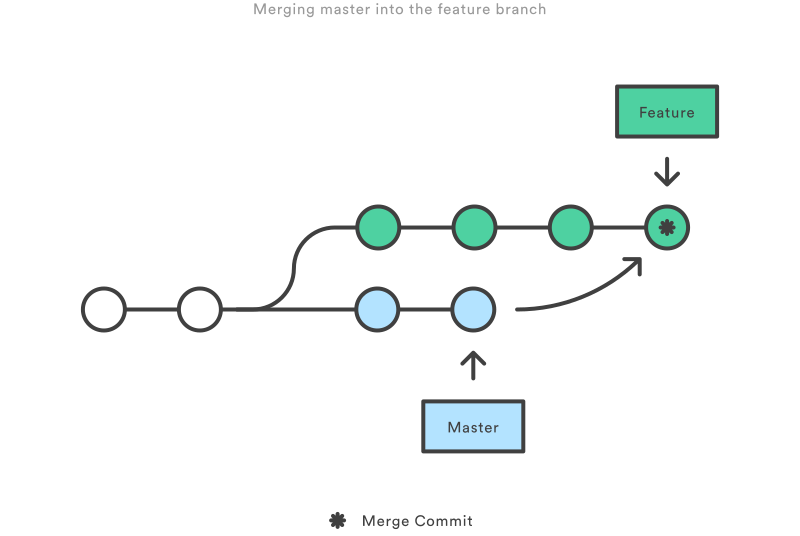
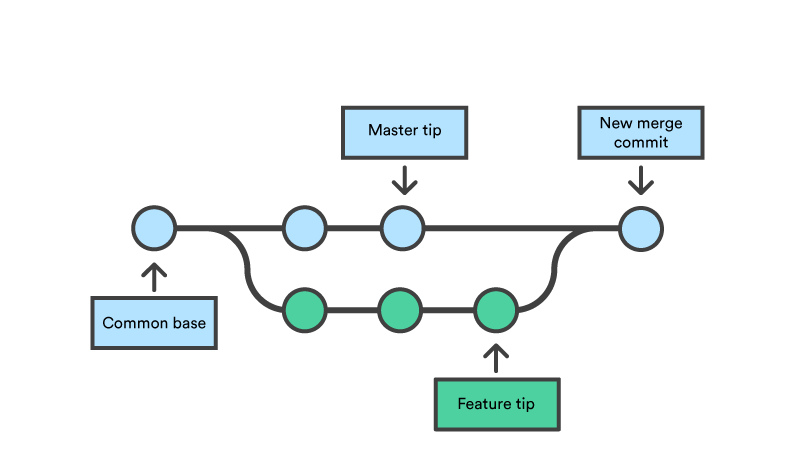
How do you make a commit anyway?
- When a file is ready to be put in a commit, you add it onto the "staging" or "index"
- $ git add file.txt
- Commit the changes added into "staging" area
- $ git commit
Basic commands:
- $ git init
- initialize a repository
- $ git status
- get status of your repository
- $ git add
- Add files into the staging area for git
- $ git commit
- Commit the files you have changed/removed/added
- $ git branch
- To checkout what is your current branch in local repo
Basic commands:
- $ git branch feature1
- create a new branch named feature1
- $ git checkout feature1
- switch to the branch named feature1
- $ git merge
- merge the changes into current branch from feature1
- $ git clone <remote_url>
- Clone repository from a remote server
- $ git pull
- pull the changes from remote repository
- $ git push
- push the changes into remote repository
Hurray!
I know how git works :)
Git for Beginners
By Sushil Khanchi
Git for Beginners
Introduction to git (version control system)
- 853



