MVC
Introduction
- Stands for Model View Controller
- Architectural pattern to organise your code
- Core of every framework is a concept of pattern
- Front-end & Back-end can work together without interfering either party
Model
- Also called "data layer"
- Contains business logic for the application
- Interface between an application and data
- It processes data
- Can have a relationship with a database
View
- Also called "presentation layer"
- Depends on the model to render data
- Contains no business logic
- Typically HTML, could be used for e.g. XML feeds
Controller
- Also called "organization layer"
- Coordinates the Model and View
- Mediates UI interactions and updates to the model
The flow
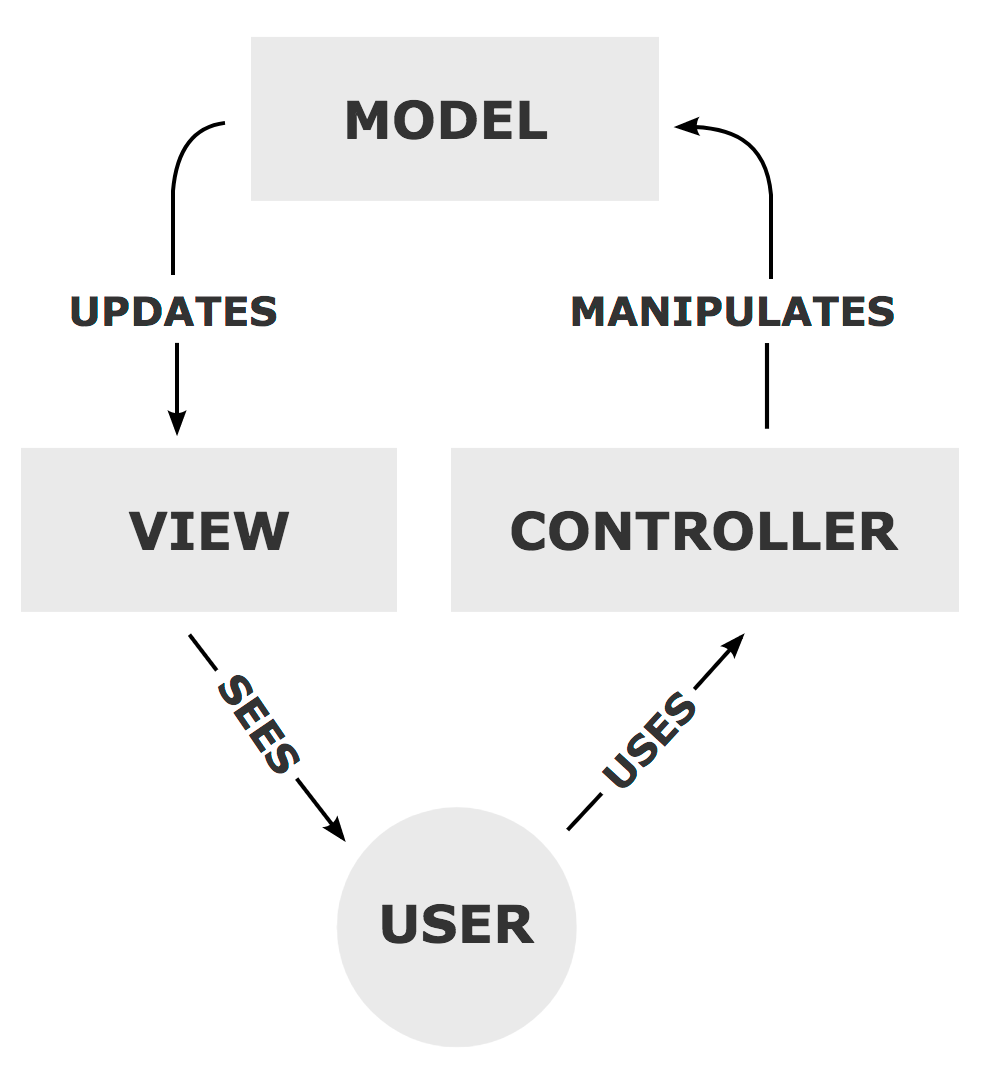
-
Data comes from the database to the Model
-
Then from the Model to the Controller
-
The Controller coordinates the Model van View. It handles user requests by implementing rules/logic.
-
The Controller communicates with the Model to process data retrieval in storage which then provides the data back to the Controller.
-
The Controller then sends the collected Model data to the View to render this
Example
- A user clicks on a button or adds an item to the cart in the View
- The input gets handled by the Controller
- The Controller handles the logic, e.g. a callback and notifies the Model for changes/updates
- The Model updates where necessary and sends back the data
- The Controller sends this to the View for rendering
- The user sees the item added to the cart
MVC
By Kim Massaro
MVC
Model View Controller
- 690



