Laziest maldev : when your compiler do everything
0xkylm
Whoami
Student @ 2600
VR @ FuzzingLabs
Hypervisor, compilation and maldev enthusiast
Agenda
-
Introduction
-
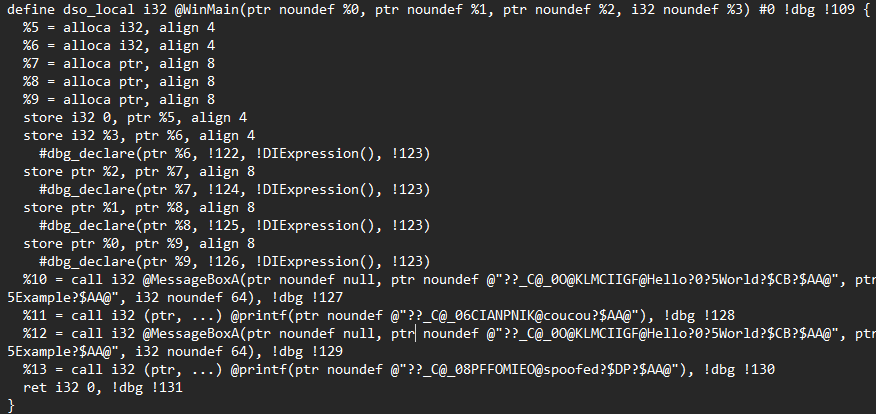
LLVM Deep Dive
-
IR level pass
-
Evasion
-
Machine level pass
Introduction
Sometimes some yara check for exact bytes or strings, if the binary change at each compile we can bypass those dumb checks
And also increases the effort required for reverse engineering
Why polymorphisme and obfuscation

Introduction
Lot's of different projects
LLVM Deep Dive
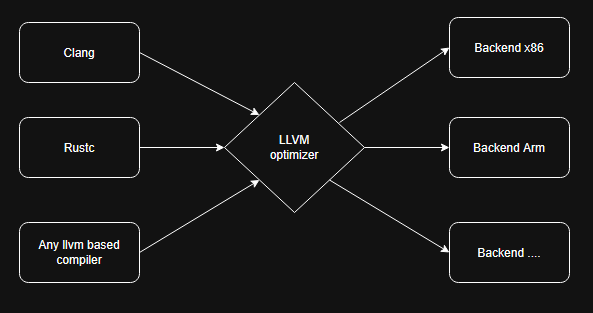
What's llvm
LLVM Deep Dive
LLVM IR
LLVM Deep Dive
How optimization works
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/618817970


LLVM Deep Dive
Simpliest pass
#include "llvm/Transforms/MyObfsPass/Obf.h"
using namespace llvm;
PreservedAnalyses ObfsPass::run(Function &F, FunctionAnalysisManager &AM) {
//print the function name
outs() << "Processing function: " << F.getName() << "\n";
if (F.getName() != "main") {
outs() << "Skipping function: " << F.getName() << "\n";
return PreservedAnalyses::all();
}
IRBuilder<> Builder(F.getContext());
bool Changed = false;
//for the current function, find parse every BasicBlocks
for (BasicBlock &BB : F) {
//For each BasicBlock, parse every instruction
for (Instruction &I : BB) {
//Get operands for all instructions
for (unsigned i = 0; i < I.getNumOperands(); i++) {
Value *Op = I.getOperand(i);
//if it's a ConstantInt we change it to 42
if (ConstantInt *CI = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(Op)) {
errs() << "Found constant: " << CI->getValue() << " in instruction: " << I << "\n";
I.setOperand(i, ConstantInt::get(CI->getType(), 42));
Changed = true;
}
}
}
}
return Changed ? PreservedAnalyses::none() : PreservedAnalyses::all();
}
[PassPluginLibraryInfo.... ]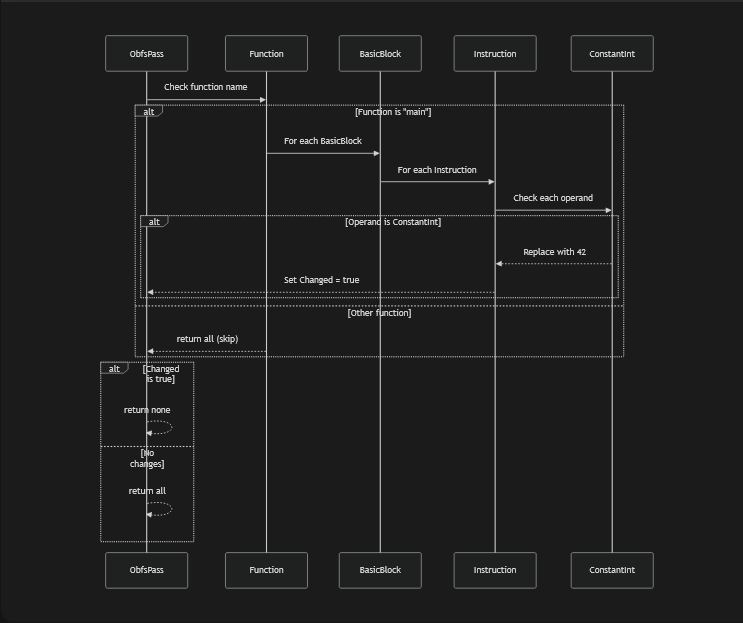
LLVM Deep Dive
Simpliest pass
#add.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a = 10;
int b = 12;
printf("a + b = %d",a+b);
return 1;
}
----------------------
Processing function: main
Found constant: 1 in instruction: %1 = alloca i32, align 4
Found constant: 1 in instruction: %2 = alloca i32, align 4
Found constant: 1 in instruction: %3 = alloca i32, align 4
Found constant: 0 in instruction: store i32 0, ptr %1, align 4
Found constant: 10 in instruction: store i32 10, ptr %2, align 4, !dbg !33
Found constant: 12 in instruction: store i32 12, ptr %3, align 4, !dbg !35
Found constant: 1 in instruction: ret i32 1, !dbg !37
Processing function: _vsprintf_l
IR lvl pass
Back2Hack : Encrypt Strings
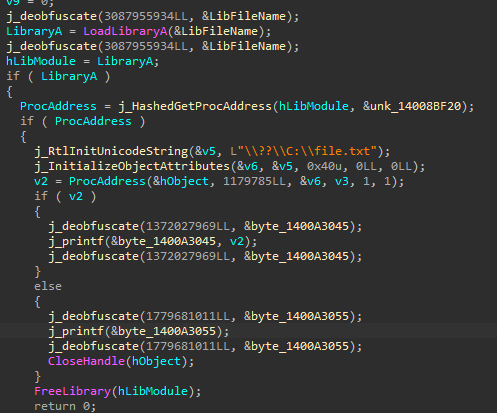
IR lvl pass
Back2Hack : Encrypt Strings
Objectives :
- What a string?
- Find them
- Xor them compile time
- Add stub to decrypt / encrypt again
- enjoy
IR lvl pass
Back2Hack : Encrypt Strings
Well cheat a little bit
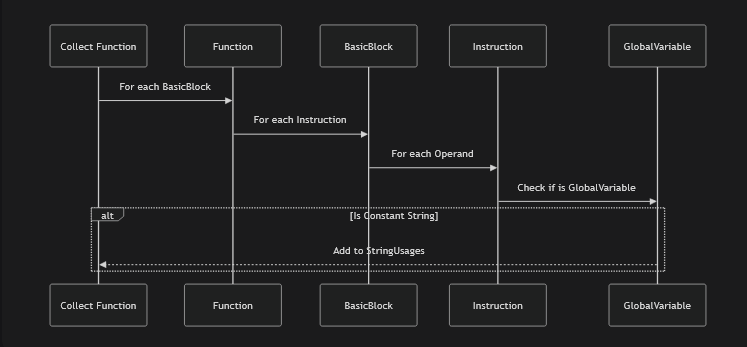
std::vector<StringUsage> collectStringUsages(Function &F) {
std::vector<StringUsage> Usages;
for (BasicBlock &BB : F) {
for (Instruction &I : BB) {
for (unsigned i = 0; i < I.getNumOperands(); ++i) {
Value *Op = I.getOperand(i);
auto *GV = dyn_cast<GlobalVariable>(Op);
if (!GV)
continue;
if (!GV->isConstant() || !GV->hasInitializer())
continue;
auto *CA = dyn_cast<ConstantDataArray>(GV->getInitializer());
if (!CA)
continue;
if (!CA->isString())
continue;
Usages.push_back({&I, GV, i});
[...]
IR lvl pass
Back2Hack : Encrypt Strings
Creating stub
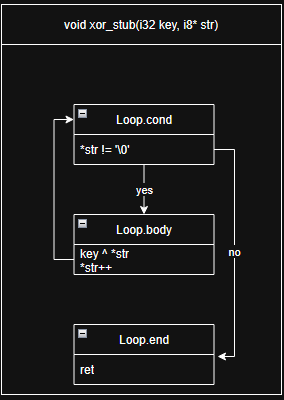
BasicBlock *LoopCond = BasicBlock::Create(Ctx, "loop.cond", DeobfFunc);
BasicBlock *LoopBody = BasicBlock::Create(Ctx, "loop.body", DeobfFunc);
BasicBlock *LoopEnd = BasicBlock::Create(Ctx, "loop.end", DeobfFunc);
B.CreateBr(LoopCond);
// cond
B.SetInsertPoint(LoopCond);
PHINode *PtrPhi = B.CreatePHI(Type::getInt8Ty(
Ctx)->getPointerTo(), 2, "ptr");
PtrPhi->addIncoming(StrPtrArg, EntryBB);
Value *Cur = B.CreateLoad(Type::getInt8Ty(Ctx), PtrPhi, "cur");
Value *IsNotNull = B.CreateICmpNE(Cur, B.getInt8(0));
B.CreateCondBr(IsNotNull, LoopBody, LoopEnd);IR lvl pass
Back2Hack : Encrypt Strings
Enjoy
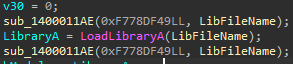
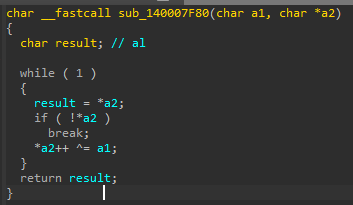
Decipher string, use it and cipher again
Evasion
Modularity is the key
LLVM uses LLVM IR modules, each compilation unit creates an IR module. Based on this, we can link a module even if it's not part of the project, allowing us to add bytecode via LLVM passes
We got all the symbols no strip yet, and already play with ir instruction creation with the strings encryption
Evasion
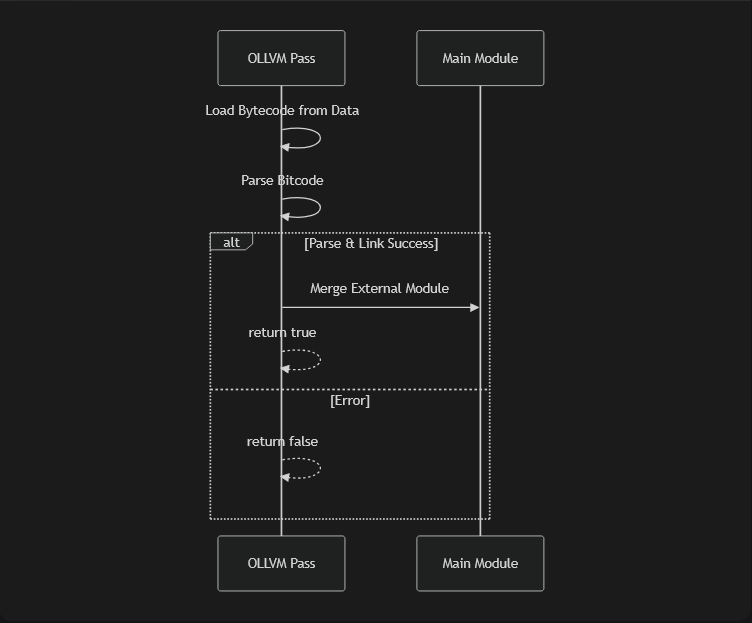
Loading bitcode
bool ObfsPass::loadByteCode(llvm::Module &M, const unsigned char Bc[], unsigned int BcLen) {
llvm::LLVMContext &Context = M.getContext();
auto MemBuffer = llvm::MemoryBuffer::getMemBuffer(
llvm::StringRef(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(Bc), BcLen),
"embedded_bitcode",
false
);
auto Module = llvm::parseBitcodeFile(MemBuffer->getMemBufferRef(), Context);
if (!Module) {
llvm::errs() << "Error parsing embedded bitcode :( \n";
return false;
}
std::unique_ptr<llvm::Module> ExternalMod = std::move(*Module);
ExternalMod->setModuleIdentifier("embedded_module");
llvm::Linker L(M);
if (L.linkInModule(std::move(ExternalMod))) {
llvm::errs() << "[-] Failed to link :(\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
Evasion
Replace funcs
if (!loadByteCode(M, sub_bc, sub_bc_len)) {
return Changed ? PreservedAnalyses::none() : PreservedAnalyses::all();
}
// Now let's find it (because we linked it into current module)
Function *SubFunction = M.getFunction("sub");
Function *AddFunction = M.getFunction("add");
if(!SubFunction && AddFunction ){
return Changed ? PreservedAnalyses::none() : PreservedAnalyses::all();
}
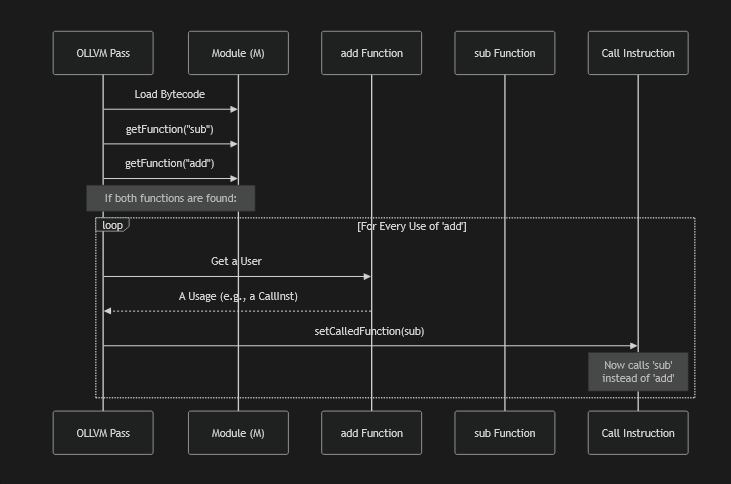
//replace all calls to "sub" with a call to "add"
//get all call of AddFunction, and for each one change to SubFunction
for (auto &U : AddFunction->uses()) {
if (CallInst *CI = dyn_cast<CallInst>(U.getUser())) {
CI->setCalledFunction(SubFunction);
}
}
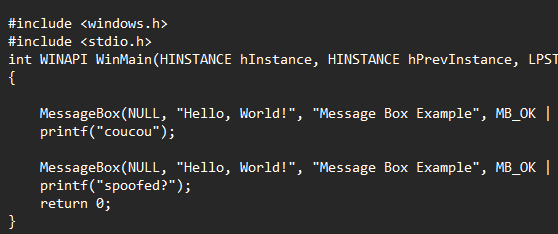
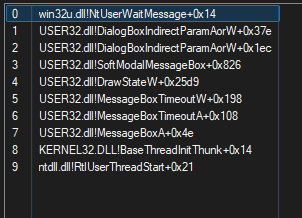
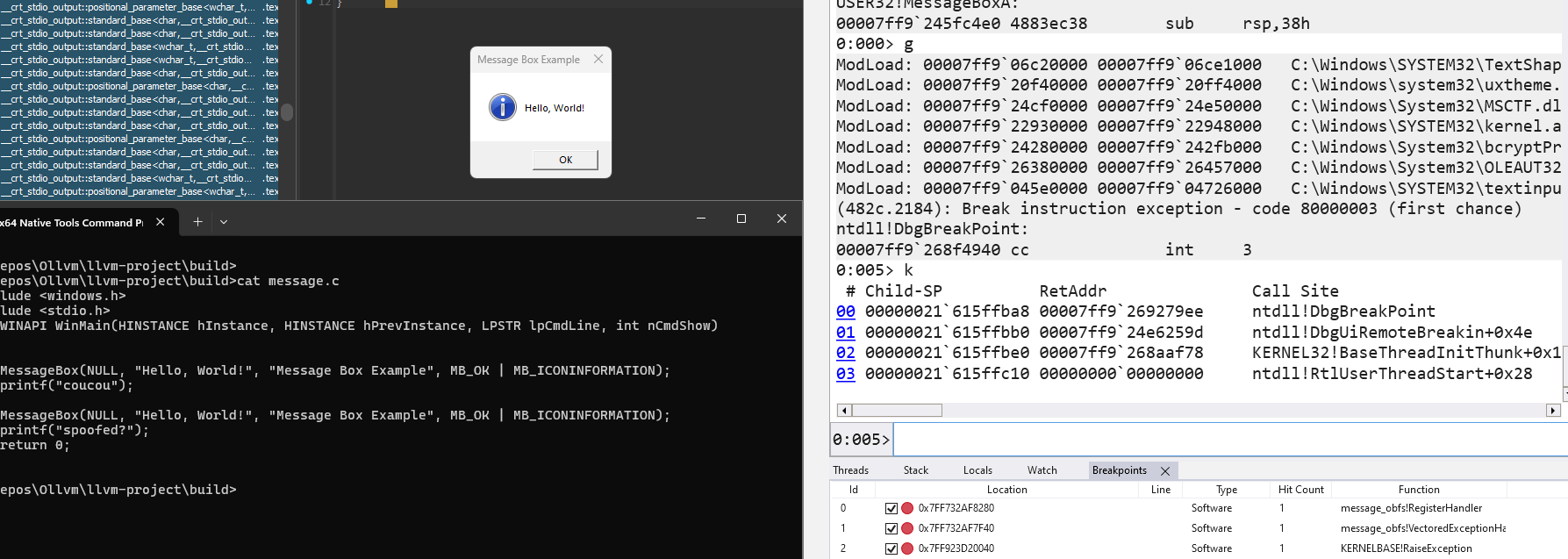
Evasion
CallstackSpoof
Machine level pass
Optimizing machine code
During the compilation process, while code generation there are also some optimizations, those optimizations are machine-level passes. Let's play with them
Machine level pass
Breaking Ghidra
Rex, are prefix use in x86 to tell the cpu the next opcode is a x64, but what if we use 2,3 or 10 Rex ?
Not all instructions require a REX prefix. The prefix is necessary only if an instruction references one of the extended registers or uses a 64-bit operand. If a REX prefix is used when it has no meaning, it is
ignored.
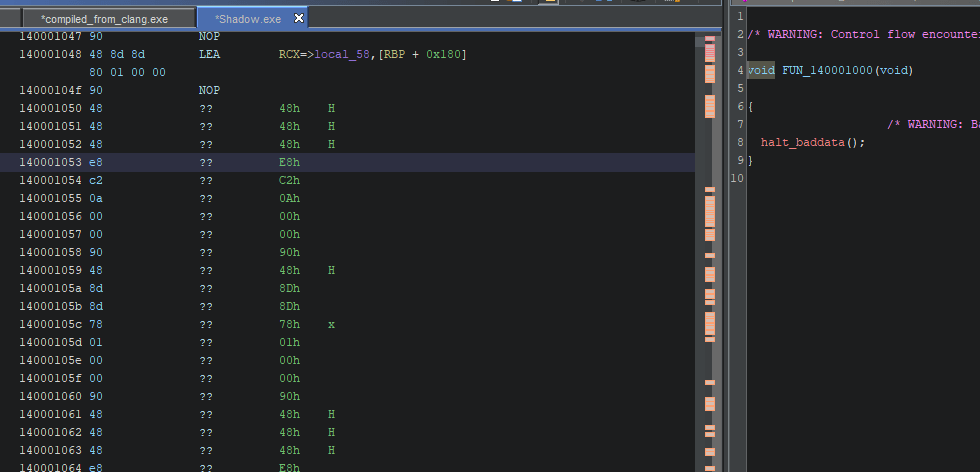
Machine level pass
Breaking Ghidra
Buuuuuuut Ghidra and other compiler don't work like a cpu and sometimes bugs can occured
Machine level pass
Breaking classical code path
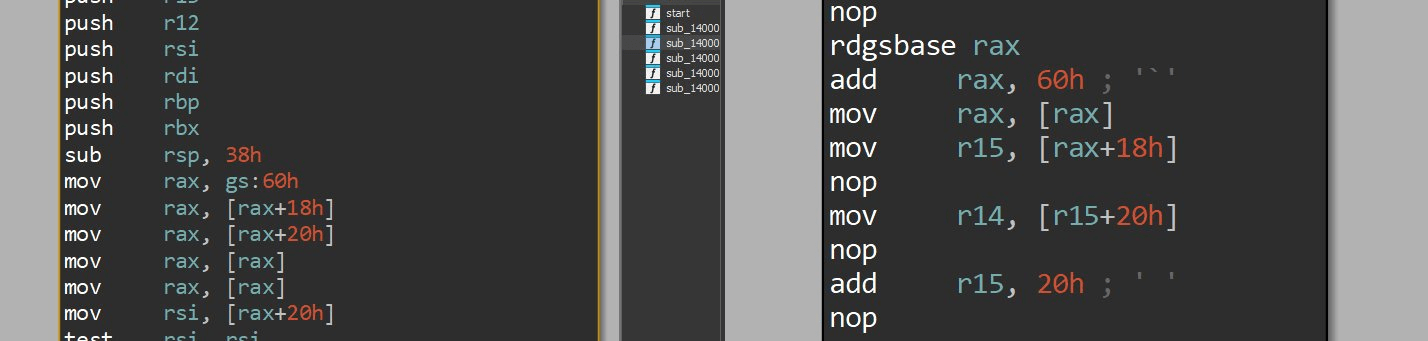
Machine level pass
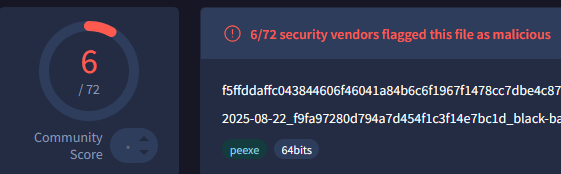
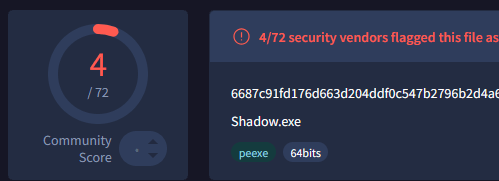
VT test
Okay this is not insane cuz it's not a very famous sample but
(only machine lvl pass)
Questions ?
Laziest maldev : when your compiler do everything
By 0xkylm
Laziest maldev : when your compiler do everything
- 54



