PATTERNS THAT BOOST OUR FRAMEWORKS





Why?
-
Everything is changing very fast!



2009...
-
JQuery, Tapestry, Flash, Flex, Backbone, ie...

2013...
-
AngularJS

2016...
-
Angular, Android

Today...
-
React, Stencil, Flutter, ie... :(

A solution?

A solution?
-
Following the SOLID principles :
-
Building software designs...
-
More understandable
-
Easier to maintain
-
Easier to extend
-
Contents
-
A list of commonly used patterns ;)
-
Starting by a well known structural pattern...
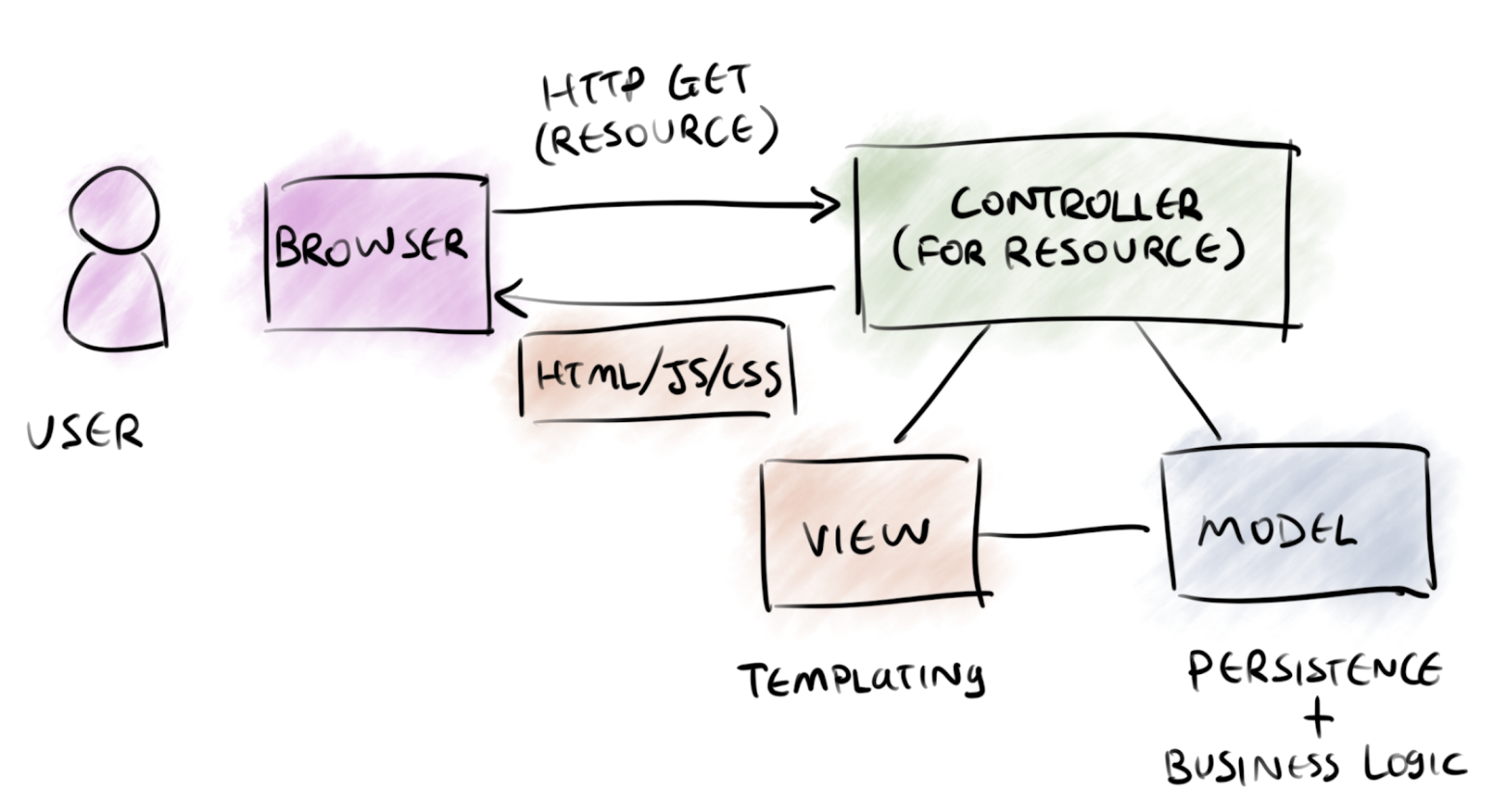
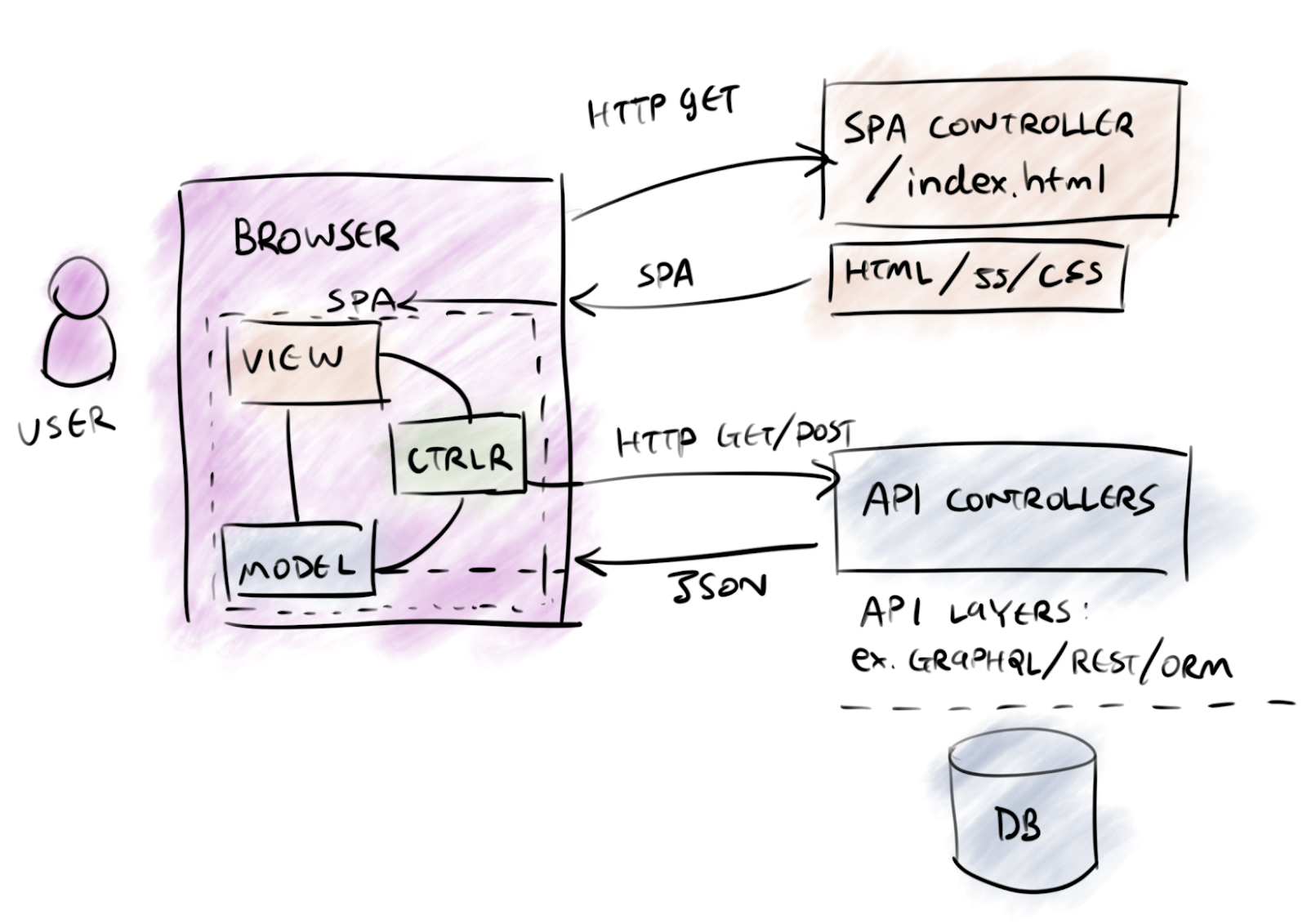
1. MVC
1. MVC
-
A long, long time ago...
1. MVC
1. MVC
-
Angular :
-
View
-
Controller
-
Model
-
HTML Template
-
Component
-
Service
-
React :
-
View
-
Controller
-
Model
-
View
1. MVC
<div>
<app-user-search (changed)="onCriteriaChanged($event)">
</app-user-search>
<app-users-list [users]="users$ | async"
(select)="onSelectUser($event)">
</app-users-list>
</div>
-
"View"
1. MVC
@Component({
templateUrl: './main-page.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./main-page.component.scss'],
changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush
})
export class MainPageComponent implements OnInit {
users$: Observable<User[]>;
constructor(private userService: UserService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.users$ = this.userService.fetchUsers();
}
}-
"Controller"
1. MVC
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(@Inject(USER_API_URL) private urlUsers: string,
private http: HttpClient) {}
fetchUsers(criteria: UserCriteria): Observable<User[]> {
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.urlUsers);
}
}-
"Model"
1. MVC
-
Other structuring patterns :
-
MVP (Model - View - Presenter)
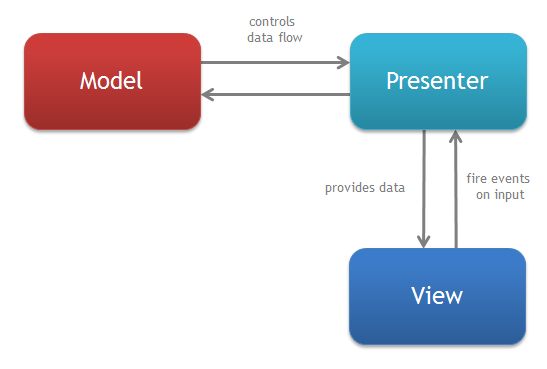
1. MVC
-
Other structuring patterns :
-
MVVM (Model - View - ViewModel)
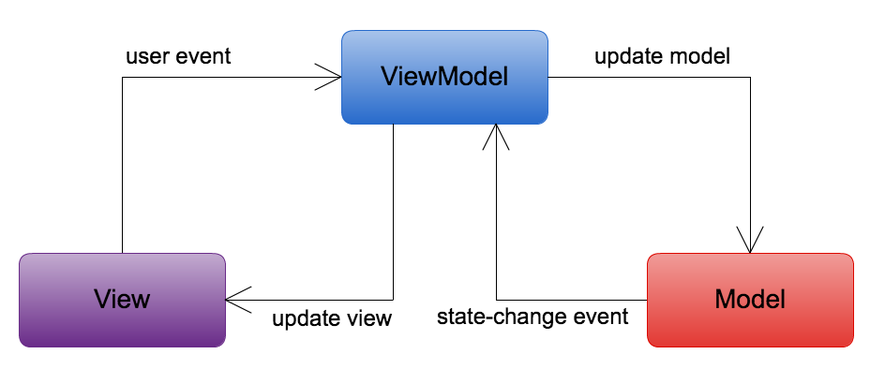
1. MVC
-
MVVM Android :
class ViewModelActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// Obtain the ViewModel component.
UserModel userModel = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity())
.get(UserModel.class)
// Inflate view and obtain an instance of the binding class.
val binding: UserBinding =
DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.user)
// Assign the component to a property in the binding class.
binding.viewmodel = userModel
}
}1. MVC
-
MVVM Android :
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/rememberMeCheckBox"
android:checked="@{viewmodel.rememberMe}"
android:onCheckedChanged="@{() -> viewmodel.rememberMeChanged()}" />2. REACTIVE PrograMMING
2. Reactive Programming
-
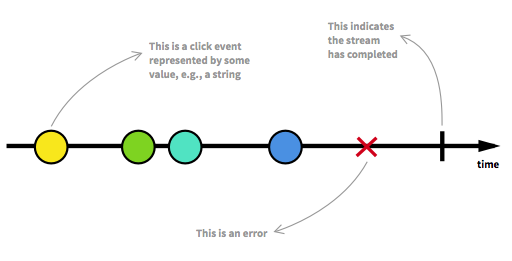
Asynchronous data streams
2. Reactive Programming
-
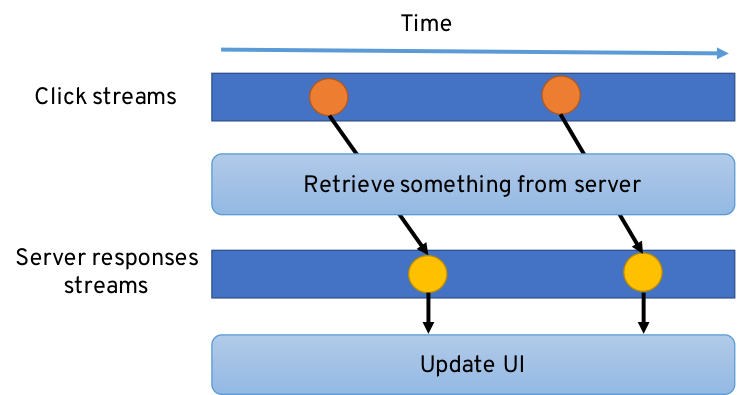
Everything is a stream :
2. Reactive Programming
-
Declarative approach using :
-
Pure functions
-
Iterator pattern
-
const products$: Observable<Product[]> =
fromEvent(this.input.nativeElement, 'keyup')
.pipe(
map(event => event.target.value),
filter((search: String) => search.length > 2),
debounceTime(250),
distinctUntilChanged(),
switchMap(search => this.fetchProducts(search))
);
2. Reactive Programming
-
ReactiveX implementations :
-
RxJS
-
RxJava
-
RxKotlin
-
RxDart
-
RxPython
-
...
-

2. Reactive Programming
-
Common uses :
-
Angular HttpClient, ReactiveForms...
-
Android LiveData
-
Flutter FutureBuilder/StreamBuilder
- ...
-
2. Reactive Programming
-
Heavily depends on...
Observer pattern
3. OBSERVER
3. Observer
-
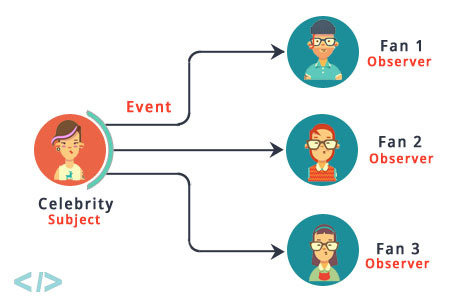
Event handling :
-
Observers
-
Subjects
3. Observer
-
Event handling :
3. Observer
-
Subject :
-
Observer :
-
registerObserver(observer)
-
unregisterObserver(observer)
-
notifyObservers()
-
notify()
3. Observer
-
Main goal :
Separation of concerns
4. SINGLETON
4. Singletons
-
Single instance
-
Coordinate actions across the system
-
Perfect to store data
-
Lazy construction
4. Singletons
-
Angular Services
-
Business specific
-
Transverse
-
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(@Inject(USER_API_URL) private urlUsers: string,
private http: HttpClient) {}
fetchUsers(): Observable<User[]> {
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.urlUsers);
}
}4. Singletons
-
Angular Services
-
Easy to use...
-
Thanks to Dependency Injection
-
@Component({
templateUrl: './detail-page.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./detail-page.component.scss'],
changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush
})
export class DetailPageComponent implements OnInit {
users$: Observable<User[]>;
constructor(private userService: UserService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.users$ = this.userService.fetchUsers();
}
4. Singletons
-
Angular Services
-
Best place to store business data
-
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
private _users$: Observable<User[]>;
get users$(): Observable<User[]> {
return this._users$;
}
constructor(@Inject(USER_API_URL) private urlUsers: string,
private http: HttpClient) {
this._users$ = this.http.get<User[]>(this.urlUsers).pipe(
shareReplay()
);
}
}4. Singletons
-
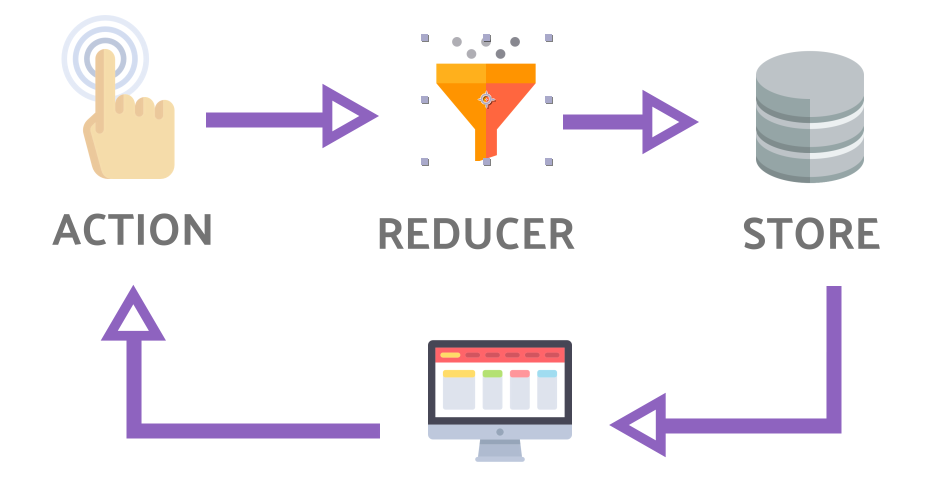
Redux Store
4. Singletons
⚠️ Warning ⚠️
-
Testability -
Dependency hiding
-
Concurrency
5. FACTORY
5. FACTORY
-
Creational pattern
-
One interface and several implementations
-
Using the Right implementation for a given case
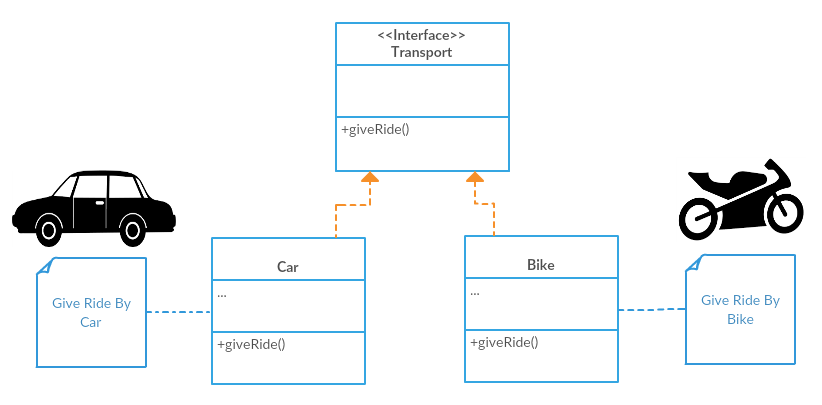
5. FACTORY
-
Generally used with a DI mechanism :
-
Angular services
-
Android libraries (Dagger 2, Koin)
-
Flutter libraries (Inject)
-
5. FACTORY
-
Angular Injection Tokens :
// user.service.ts
export const USER_SERVICE =
new InjectionToken<UserService>('USER_SERVICE');
export interface UserService {
fectchAll(): Observable<User[]>;
fectchOne(): Observable<User>;
}5. FACTORY
-
Angular module :
// app.module.ts
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
imports: [
...
],
providers: [
{ provide: USER_SERVICE, useClass: UserServiceHttpImpl },
...
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}5. FACTORY
-
Angular Environments
// app.module.ts
@NgModule({
...
providers: [
{ provide: USER_SERVICE, useClass: environment.userServiceImpl },
...
]
})
export class AppModule {}// environment.ts
{
userServiceImpl: UserServiceHttpImpl
}6. STRATEGY
6. STRATEGY
-
Encapsulates a family of algorithms
-
Makes them interchangeable.
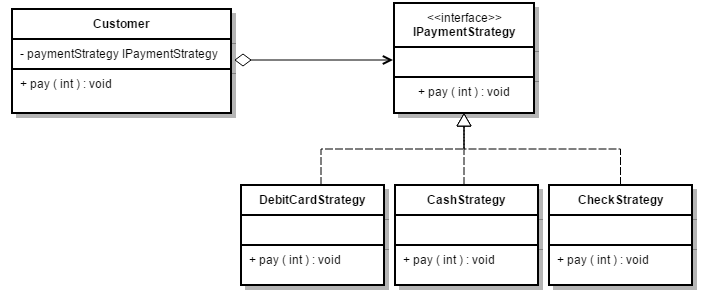
6. STRATEGY
-
In a component architecture :
-
Dumb - Smart components
- Presentational - Container components
-
// detail-page.component.ts
<div class="user-detail-content" *ngIf="user$ | async as user">
<h1>{{ user.firstName }}</h1>
<app-user-form [user]="user" (validate)="onValidate($event)">
</app-user-form>
</div>
7. DECLARATIVE UI
7. Declarative UI
-
The new standard in front development?
-
Declarative API to define UI components
export default class App extends Component {
...
render() {
return (
<div>
<Header />
<List items={this.state.items} />
<Footer />
</div>
);
}
}7. Declarative UI
-
More than just "UI" components :
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) => FutureBuilder<Restaurant>(
future: restaurantService
.fetchRestaurantDetail(context: context, restaurant: restaurant)
.then((restaurant) => restaurantService.fetchRestaurantRatings(
restaurant: restaurant,
limit: 4
)),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasError) print(snapshot.error);
return snapshot.hasData
? RestaurantWidget(restaurant: snapshot.data)
: AppProgressIndicator();
});7. Declarative UI
-
At last on Android :
-
Android Jetpack Compose
-
class ComposeActivity : Activity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent { CraneWrapper { MyApp() } }
}
@Composable
fun MyApp() {
MaterialTheme {
Text(
text = "Hello world!",
style = +themeTextStyle { h3 }
)
}
}
}Question :
I have developed a components library and want to implement a "disabled" and "tabIndex" state on all of them... ?
8. MIXIN
8. MIXIN
-
Solves a common Class limitation :
-
Single Super Class
-
Share a common behavior between different classes
-
8. MIXIN
-
Mixins can be done in Typescript
-
But it can be a bit tricky
-
Used in some component libraries (Angular Material) to define common behavior such as "color", "disabled"...
8. MIXIN
-
Well implemented in Dart 2.X :
mixin Coder {
void code() {
print("Trying to use design patterns...");
}
}
class Laurent extends Person with Coder {}
void main() {
const laurent = Laurent();
laurent.code();
}8. MIXIN
-
With interface default implementations in Kotlin :
interface Developer {
fun code() {
...
}
}
class UserCodeEnSeine : User, Developper {
...
}8. MIXIN
-
React hooks are Mixins done right :
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>Vous avez cliqué {count} fois</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Cliquez ici
</button>
</div>
);
}conclusion
To conclude...
-
Patterns are the first thing to learn.
-
Frameworks use them to solve common software development problems.
-
Their implementation differs, but the logic remains the same.
THANKS! 🙏
web-patterns
By Laurent WROBLEWSKI
web-patterns
- 398



