Python程式設計
Lesson 11: 資料夾與檔案
讀取檔案
- 認識編碼格式
- 開啟檔案: open()
- 讀取檔案內容
- 讀取整個檔案: read()
- 逐行讀取: readlines()
- 搜尋: find()
認識編碼格式

abc123
ANSI編碼
ASCII編碼
Windows 1252
中文字
萬國碼(utf-8)
(中文三碼,英文一碼)
大五碼(big5)
Windows 950
(中文兩碼,英文一碼)
使用encoding參數設定編碼
fn = 'test1.txt' # 假設檔案為UTF-8編碼
with open(fn, encoding='UTF-8') as file_Obj:
obj_list = file_Obj.readlines() # 每次讀一行
...
...
fn2 = 'test2.txt' # 假設檔案為Big5編碼
with open(fn, encoding='cp950') as file_Obj:
obj_list = file_Obj.readlines() # 每次讀一行
...
...呼叫open()函式時,指定encoding參數
讀取檔案前,要先呼叫open()開啟檔案
fname = "test.txt"
fobj = open(fname, mode="r")
print(fobj)
呼叫open()成功後,得到「檔案」物件
D:\Python
<_io.TextIOWrapper name='test.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp950'>
輸出結果
cp950是預設的編碼格式
open()開啟檔案時,必須設定讀寫模式
若不指定,則為預設模式:mode="r"
mode參數
| r | w | a | r+ | w+ | a+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 讀取 | 寫入 (覆寫) |
寫入 (附加) |
讀寫 | 讀寫+創建 (覆寫) |
讀寫+創建 (附加) |
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案, 請先新增此一檔案
file_Obj = open(fn) # 用預設mode=r開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
f1 = open('檔案1.txt', mode='a')
f2 = open('檔案2.txt', encoding='utf-8')
f3 = open('檔案3.txt', mode='r+') # 開啟檔案3, 讀寫皆可, 檔案必須存在
f4 = open('檔案4.txt', mode='a+') # 開啟檔案4, 讀寫, 檔案不存在則新建讀取檔案內容的函式之一:檔案物件.read()
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案, 請先新增此一檔案
file_Obj = open(fn) # 用預設mode=r開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
data = file_Obj.read() # 讀取檔案到變數data
file_Obj.close() # 關閉檔案物件
print(data) # 輸出變數data相當於輸出檔案檔案物件.read() 回傳檔案全部內容
讀取完畢後,呼叫「檔案物件.close()」關閉檔案
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案, 請先新增此一檔案
with open(fn) as fobj: # 預設讀取模式mode=r,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
data = fobj.read() # 讀取檔案到變數data
print(data) # 輸出變數data相當於輸出檔案with open(要開啟的檔案) as 檔案物件:
處理檔案內容的指令區塊with關鍵字搭配open(), 讓檔案讀取區塊化
使用字串處理函式rstrip(),去除檔案末端的空白行
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案, 請先新增此一檔案
with open(fn) as file_Obj: # 預設mode=r開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
data = file_Obj.read() # 讀取檔案到變數data
print(data.rstrip()) # 輸出變數data相當於輸出檔案,同時刪除末端字元
檔案有時會有多餘的空格,rstrip()可去除空格
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案, 請先新增此一檔案
with open(fn) as fobj:
num = 0 # num 記錄行號
for line in fobj: # for 迴圈, 逐行檢視檔案內容
num += 1 # 行數多1
print('第%d行: %s' % (num , line.rstrip())) # 去除空格/換行字元若要逐行讀取,可在for迴圈使用「檔案物件」
第1行: 一直以來,Google 的 Android 系統是基於 Linux 系統進行開發的。
第2行: 但是到現在,不僅僅是 Google,華為、Samsung
第3行: 等手機廠商已經將系統進行了非常大的系統底層修改,
第4行: 以適應智能手機的需求
輸出結果
類似以「檔案物件」置於for迴圈的作用
fn = 'MackayDemo.txt'
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as fobj: # 開啟檔案。編碼也可能是cp950
obj_list = fobj.readlines() # 讀取多行
for index, line in enumerate(obj_list):
print(index+1, line.rstrip()) # 列印串列讀取檔案內容的函式之二:檔案物件.readlines()
檔案物件.readlines() 取得內容,為「串列」形式
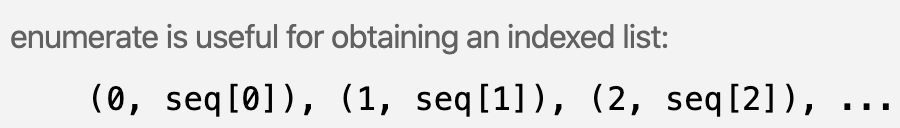
使用enumerate(),可取得串列索引值
串列可搭配enumerate() 取得索引值
檔案物件.readlines() 取得內容,為「串列」形式
for index, line in enumerate(obj_list):
print(index+1, line.rstrip()) # 列印串列列舉函式,產生0開始的編號
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案
with open(fn) as file_Obj: # 開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
obj_list = file_Obj.readlines() # 讀取全部
str_Obj = '' # 先設為空字串
for line in obj_list: # 將各行字串存入
str_Obj += line.rstrip()
print(str_Obj) # 列印檔案字串練習2.1: 將檔案各行合併為一行
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案
with open(fn) as file_Obj: # 傳回檔案物件file_Obj
data = file_Obj.read() # 讀取檔案到變數data
new_data = data.replace('滬尾', '淡水') # 新變數儲存
print(new_data.rstrip()) # 輸出檔案練習2.2: 將檔案某些字串置換
字串內容置換方式:字串物件.replace(舊字串, 新字串)
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案
with open(fn) as file_Obj: # 用預設mode=r開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
obj_list = file_Obj.readlines() # 每次讀一行
str_Obj = '' # 先設為空字串
for line in obj_list: # 將各行字串存入
str_Obj += line.rstrip()
findstr = input("請輸入欲搜尋字串 = ")
index = str_Obj.find(findstr) # 搜尋findstr字串是否存在
if index >= 0: # 搜尋檔案是否有欲尋找字串
print("搜尋 %s 字串存在 %s 檔案中" % (findstr, fn))
print("在索引 %s 位置出現" % index)
else:
print("搜尋 %s 字串不存在 %s 檔案中" % (findstr, fn))❸ 使用字串物件.find(),搜尋內容
index = 字串.find(搜尋的字串)index: 回傳字串所在的索引值 或 -1(找不到)
檔案處理功能之三: 字串物件.find()搜尋內容
fn = 'test.txt'
# 1. 開啟檔案
with open(fn, mode="r", encoding="utf-8") as fobj:
data = fobj.readlines() # 2.讀取資料
fobj.close() # 3. 關閉檔案
# 前處理: 合併字串
fstr = '' # 合併後的單一字串
for line in data:
fstr += line.strip() # 串接, 去除空白字元
while True:
mystr = input('輸入查詢字串,直接按Enter結束程式:')
if mystr.strip() == '':
break
index = fstr.find(mystr) # 搜尋
if index<0: # 找不到
print(f'搜尋{mystr} 字串不存在檔案 {fn}中')
else: # 找到
print(f'搜尋{mystr}字串出現在位置{index}的地方')
print('程式結束')
使用字串物件.find(),搜尋內容--while迴圈版
fn = 'test.txt' # 設定欲開啟的檔案
with open(fn) as file_Obj: # 開啟檔案,傳回檔案物件file_Obj
obj_list = file_Obj.readlines() # 每次讀一行
str_Obj = '' # 先設為空字串
for line in obj_list: # 將各行字串存入
str_Obj += line.rstrip()
findstr = input("請輸入欲搜尋字串 = ")
if findstr in str_Obj: # 搜尋檔案是否有欲尋找字串
print("搜尋 %s 字串存在 %s 檔案中" % (findstr, fn))
else:
print("搜尋 %s 字串不存在 %s 檔案中" % (findstr, fn))
練習:使用字串的in運算子,搜尋內容
練習3.1: 搜尋字串內容
寫入檔案
- 寫入函式: write()
將內容寫入檔案的函式之一:write()
# 寫入檔案, 編碼格式為utf-8
# 開始模式 'a+': 內容會附加在檔後;檔案若不在,則會新建
fname = 'output.txt'
text = '這是要寫入的內容'
with open(fname, 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
fobj.write(text)
fobj.close()write()只能寫入字串,無法直接寫入數值

# 開啟檔案output.txt
# 模式'r+': 可讀可寫, 檔案不存在則出現錯誤
fname = 'output.txt'
value = 101 # 某個整數
with open(fname, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
fobj.write(value)
fobj.close()...
value = 101 # 某個整數
with open(fname, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
fobj.write(str(value))
....練習4.1: 從鍵盤輸入文字後,寫入某檔案
# 開啟檔案, 模式'a+', 編碼 utf-8
fname = 'output2.txt'
with open(fname, 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
while True:
line = input('輸入內容(直接按enter結束):')
if line == '': # 未輸入內容,直接按Enter
break # 跳出迴圈
else:
fobj.write(line) # 寫入內容
fobj.close() # 關閉檔案write()寫入內容時,不會自動換行
write()不會自動換行,需自行加上'\n'換行字元
# 開啟檔案output.txt
# 模式'a+': 附加內容於檔案後,檔案不在則會新建
fname = 'output.txt'
str1 = '附加的內容'
with open(fname, 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
for i in range(5): # 加入五行內容
fobj.write(str(i) +str1 + '\n')
fobj.close()# 開啟檔案, 模式'a+', 編碼 utf-8
fname = 'output2.txt'
with open(fname, 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as fobj:
while True:
line = input('輸入內容(直接按enter結束):')
if line == '': # 未輸入內容,直接按Enter
break # 跳出迴圈
else:
fobj.write(line + '\n') # 寫入內容
fobj.close() # 關閉檔案fn1 = 'input4.txt' # 輸入檔
fn2 = 'output5.txt' # 輸出檔
def read_file(fn, 編碼='cp950'):
'''讀取fn的檔案內容, 回傳字串串列'''
with open(fn, encoding=編碼) as fobj: # 1. 開檔
data = fobj.readlines() # 2. 讀取檔案內容
fobj.close() # 3. 關檔
return data # 回傳字串串列
def append_file(fn, data, 編碼='cp950'):
'''寫出串列資料data到fn'''
with open(fn, mode="a", encoding=編碼) as fobj:
for line in data:
fobj.write(line)
fobj.close()
# 主程式
檔案內容 = read_file(fn1, "cp950")
append_file(fn2, 檔案內容, "utf-8")讀寫範例
讀取CSV檔

文字檔案格式;csv指「逗號分格值」
可用MS Excel等試算表程式開啟
編號,船名,英文名,詞頻,起,訖,分類,航線,噸,Owner,
python提供csv模組,可用來存取csv檔
import csv
cf = open('example.csv') # 呼叫open()使用csv模組,先匯入csv
import csv匯入csv後,以open()開啟,取得csv檔案物件
import csv
with open('example.csv') as cf: # 使用with open() as
# 檔案內容存取區塊讀取內容三步驟:開啟、建立reader物件、讀取內容
使用reader物件讀取內容
fn = 'ship.csv'
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1. 開啟
data = cf.read() # 2. 讀取
print(data)import csv
fn = 'ship.csv'
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1. 開啟
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
data = list(reader) # 3. 存取內容: 此處轉換為串列
print(data)使用一般檔案讀取函式 read()
['58', '比利時號', 'SS Belgic', '2', '1881/11/8', '', 'Steamship', '舊金山-香港', '2652', 'White Star Line', '']
58,比利時號,SS Belgic,2,1881/11/8,,Steamship,舊金山-香港,2652,White Star Line,
import csv
...
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1. 開啟
cf_reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
...呼叫csv.reader()時,以檔案物件為參數
reader物件須轉換為list等資料結構,才能讀取內容
import csv
fn = 'ship.csv'
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1. 開啟
cf_reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
data = list(cf_reader) # 3. 存取內容: 此處轉換為串列
print(data)['58', '比利時號', 'SS Belgic', '2', '1881/11/8', '', 'Steamship', '舊金山-香港', '2652', 'White Star Line', '']
經過reader的處理,逗號已被刪除,且建立起各個欄位
import csv
with open('ship.csv', encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1.開啟檔案
cf_reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
# 3. for迴圈直接以reader物件為處理對象
for line in cf_reader:
print(line)以for迴圈直接處理csv reader物件
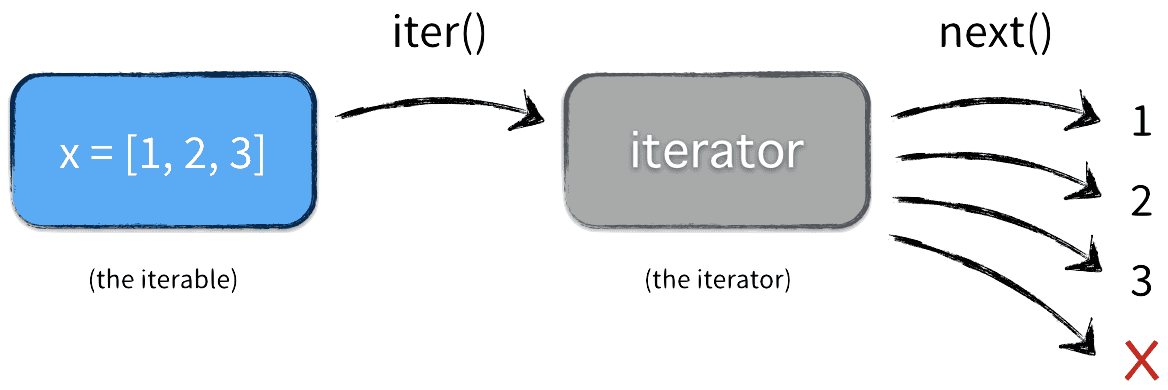
reader物件本身便是iterable物件,可用於for迴圈
如果「某物件」有實作__iter__()方法,該方法會產生迭代器(iterator, 可逐一檢視內容的物件),則「某物件」便是iterable物件
import csv
with open('ship.csv', encoding='utf-8') as cf: # 1.開啟檔案
cf_reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
data = list(cf_reader) # 3.1 轉換為串列
# 3.2 for迴圈處理串列
for line in data:
print(line)以for迴圈處理轉為串列的csv reader物件
串列也是iterable物件,可用於for迴圈
csv reader物件記錄行號的「指標屬性」: line_num
import csv
.....
cf_reader = csv.reader(cf) # 2. 建立reader物件
# 3. for迴圈直接以reader物件為處理對象
for line in cf_reader:
print('第%d行: %s' % (cf_reader.line_num, line))for迴圈逐一檢視cf_reader內容時,line_num值由1開始逐一遞增

for迴圈逐一檢視
line_num=1
line_num=8
-
從馬偕日記中,找出「海龍號」出現的次數與日期
-
找出任意關鍵字出現的次數
任務
import csv
fn = 'MackayDemo-cp950.csv' # 日記檔, cp950編碼
with open(fn) as cf: # 開啟,預設模式'r', 預設編碼cp950
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 建立 reader
for line in reader: # 逐行讀取,
print(line) # 印出每一行,串列:[日期,日記內文]import csv
fn = 'MackayDemo-cp950.csv' # 日記檔, cp950編碼
with open(fn) as cf: # 開啟,預設模式'r', 預設編碼cp950
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 建立 reader
for line in reader: # 逐行讀取,
print(line[1]) # 只印出日記內文開啟csv,印出內容,需注意編碼
範例: 開啟檔案,印出所有內容
範例: 使用「串列索引值」印出部份內容
import csv
fn = 'MackayFull-cp950.csv' # 日記檔, utf-8編碼
word = '海龍號'
total = 0
with open(fn) as cf: # 開啟,預設模式'r', cp950編碼
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 建立 reader
for line in reader: # 逐行讀取,
txt = line[1]
num = txt.count(word)
if num != 0: # 有出現
total += num # 次數累加
print(num,' ',line[0]) # 印出次數與日期
print('%s 總共出現 %d次' % (word,total)) # 印出總出現次數字串物件.count() 可統計出現次數
範例: 特定關鍵字,用字串物件.count(關鍵字)統計出現次數
import csv
fn = 'MackayFull-cp950.csv' # 日記檔, utf-8編碼
with open(fn, encoding='cp950') as cf: # utf-8編碼
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 建立 reader
while True:
word = input('輸入要尋找的關鍵字:')
if word.strip() == '':
break
else:
cf.seek(0)
total = 0
for line in reader: # 逐行讀取,
txt = line[1]
num = txt.count(word)
if num != 0: # 有出現
total += num # 次數累加
print(num,' ',line[0], line[1]) # 次數 日期 內容
print('%s 總共出現 %d次' % (word,total)) # 印出總出現次數
print('輸入空白字元,程式結束')檔案物件.seek(0): 跳回檔案最開頭處
範例: 輸入關鍵字,用字串物件.count(關鍵字)統計出現次數
import csv
fn = 'out_file.csv'
data = [] # 檔案內容儲存
with open(fn, encoding='utf-8') as cf:
reader =csv.reader(cf)
for row in reader:
data.append(str(row[5]).strip()) # 只存第6欄位
cf.close()
find_str = '洋基'
for line in data:
pos = str(line).find(find_str) # 搜尋字串
if pos>=0:
substr = line[pos:pos+len(find_str)] # 切下find_str
residual = line[pos+len(find_str):] # 剩下的文字
print(f'{find_str}出現的位置{pos}, 切出來的子字串:{substr}')
print(f'剩下的字串:{residual}')字串物件.find(): 尋找第一次出現的位置
範例: 指定關鍵字,字串物件.find(關鍵字) 找出第一次出現的位置
洋基
substr
residual
丟掉
寫入CSV檔
寫入csv三步驟:開啟檔案、寫入內容、關閉檔案
import csv
cf = open('example.csv', 'w') # 1. 開啟
... # 2. 寫入內容
cf.close() # 3. 關閉以open(檔名,'w')開啟,最後要呼叫close()關閉檔案
import csv
with open('example.csv') as cf: # 1. 開啟檔案
# 2. 區塊指令:寫入內容
# 3. 區塊結束,檔案關閉以with open(檔名, 'w') as開啟,最後會自動關閉檔案
檔案若未關閉,可能被鎖定,造成下次檔案無法開啟
csv寫入檔案的「開啟模式」與「換行字元」
下列開啟模式皆可寫入檔案
with open('f1.cvs', 'w') as cf: # 1. 開啟檔案with open('f2.cvs', 'w+') as cf: # 1. 開啟檔案with open('f3.cvs', 'r+') as cf: # 1. 開啟檔案with open('f4.cvs', 'a+') as cf: # 1. 開啟檔案避免寫入時多空一行,設定newline=' '
with open('f3.cvs', 'r+', newline='') as cf: 寫入內容: 建立writer物件, 呼叫writerow()
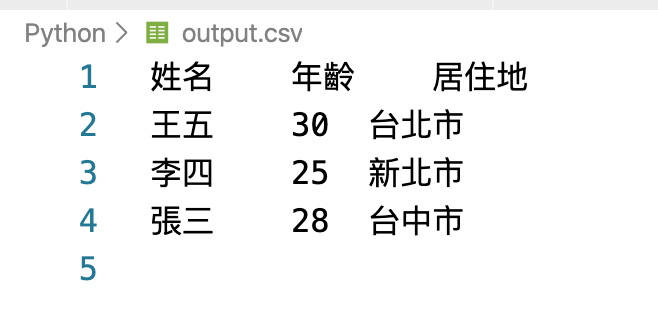
import csv
fn = 'output.csv'
with open(fn, 'a+', newline='') as cf: # 'a+'為附加模式
cf_writer = csv.writer(cf)
cf_writer.writerow(['姓名','年齡','居住地']) # 標題列
cf_writer.writerow(['王五',30,'台北市']) # 第一筆
cf_writer.writerow(['李四',25,'新北市']) # 第二筆
cf_writer.writerow(['張三',28,'台中市']) # 第三筆設定delimiter可改變分隔符號(預設為逗號)
import csv
fn = 'output.csv'
with open(fn, 'w+', newline='') as cf:
cf_writer = csv.writer(cf, delimiter='\t') # 設定分隔符號為Tab
cf_writer.writerow(['姓名','年齡','居住地'])
cf_writer.writerow(['王五',30,'台北市'])
cf_writer.writerow(['李四',25,'新北市'])
cf_writer.writerow(['張三',28,'台中市'])delimiter設定於呼叫csv.writer()時
輸出結果
資料夾與檔案路徑
資料夾與檔案路徑
絕對路徑:d:\python\期中考\exam1.py
相對路徑:部份路徑,"期中考\exam1.py", "exam1.py"
❶ os模組:與檔案路徑有關的模組
import os
print(os.getcwd()) # 列出目前工作目錄工作目錄:讀寫檔案的預設資料夾
with open('test.txt') as fobj:
data = fobj.read()
fobj.close()
print(data)
C:/Python
test.txt


reader.py
同一個資料夾

C:/Python
test.txt


reader.py

第十二章
工作目錄
工作目錄
資料夾與檔案路徑
❷ 檢查檔案的路徑: os.path
import os
print("檔案或資料夾存在 = ", os.path.exists('ch14'))
print("檔案或資料夾存在 = ", os.path.exists('D:\\Python\\ch14'))
print("檔案或資料夾存在 = ", os.path.exists('ch14_4.py'))
print(" --- ")
print("是絕對路徑 = ", os.path.isabs('ch14_4.py'))
print("是絕對路徑 = ", os.path.isabs('D:\\Python\\ch14\\ch14_4.py'))
print(" --- ")
print("是資料夾 = ", os.path.isdir('D:\\Python\\ch14\\ch14_4.py'))
print("是資料夾 = ", os.path.isdir('D:\\Python\\ch14'))
print(" --- ")
print("是檔案 = ", os.path.isfile('D:\\Python\\ch14\\ch14_4.py'))
print("是檔案 = ", os.path.isfile('D:\\Python\\ch14'))
資料夾與檔案路徑
❸ 檢查與目錄的操作: os.mkdir(), os.rmdir()
# 建立資料夾 os.mkdir()
import os
mydir = 'testch14'
# 如果mydir不存在就建立此資料夾
if os.path.exists(mydir):
print("已經存在 %s " % mydir)
else:
os.mkdir(mydir)
print("建立 %s 資料夾成功" % mydir)# 刪除資料夾os.rmdir()
import os
mydir = 'testch14'
# 如果mydir存在就刪除此資料夾
if os.path.exists(mydir):
os.rmdir(mydir)
print("刪除 %s 資料夾成功" % mydir)
else:
print("%s 資料夾不存在" % mydir)資料夾與檔案路徑
❸ 檢查與目錄的操作(續)
# 刪除檔案 os.remove()
import os
myfile = 'test.py'
# 如果myfile存在就刪除此檔案
if os.path.exists(myfile):
os.remove(myfile)
print("刪除 %s 檔案成功" % myfile)
else:
print("%s 檔案不存在" % myfile)資料夾與檔案路徑
❸ 檢查與目錄的操作(續)
# mkdir(), chdir(), getcwd()的綜合運用
import os
newdir = 'D:\\Python'
currentdir = os.getcwd()
print("列出目前工作資料夾 ", currentdir)
# 如果newdir不存在就建立此資料夾
if os.path.exists(newdir):
print("已經存在 %s " % newdir)
else:
os.mkdir(newdir)
print("建立 %s 資料夾成功" % newdir)
# 將目前工作資料夾改至newdir
os.chdir(newdir)
print("列出最新工作資料夾 ", os.getcwd())
# 將目前工作資料夾返回
os.chdir(currentdir)
print("列出返回工作資料夾 ", currentdir)資料夾與檔案路徑
❹ 路徑組合:os.path.join()
# os.path.join()
import os
print(os.path.join('D:\\', 'Python', 'ch14', 'ch14_9.py')) # 4個參數
print(os.path.join('D:\\Python', 'ch14', 'ch14_9.py')) # 3個參數
print(os.path.join('D:\\Python\\ch14', 'ch14_9.py')) # 2個參數
# 使用串列,結合路徑與檔案名稱
import os
files = ['ch14_1.py', 'ch14_2.py', 'ch14_3.py']
for file in files:
print(os.path.join('D:\\Python\\ch14', file)) 資料夾與檔案路徑
❹' 路徑組合 搭配 絕對路徑 os.path.abspath()
import csv
import os
# 取得目前資料夾之絕對路徑
__location__ = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
fn = 'MackayFull-cp950.csv' # 日記檔, utf-8編碼
word = '灰窯仔' # 灰窯
total = 0
with open(os.path.join(__location__, fn)) as cf:
reader = csv.reader(cf) # 建立 reader
for line in reader: # 逐行讀取,
txt = line[1]
num = txt.count(word)
if num != 0: # 有出現
total += num # 次數累加
print(num,' ',line[0], line[1]) # 印出次數與日期

dirname(檔名):檔案所在的絕對路徑
__file__:內建變數, 目前執行的檔案名稱

C:/Python
test.txt


reader.py
同一個資料夾
資料夾與檔案路徑
❺ 獲得檔案大小
# os.path.getsize()
import os
# 如果檔案在目前工作目錄下可以省略路徑
print(os.path.getsize("ch14_1.py"))
print(os.path.getsize("D:\\Python\\ch14\\ch14_1.py"))
# os.listdir()
import os
print(os.listdir("D:\\Python\\ch14"))
print(os.listdir(".")) # 這代表目前工作目錄
❻ 獲得工作目錄的內容
資料夾與檔案路徑
import os
totalsizes = 0
print("列出D:\\Python\\ch14工作目錄的所有檔案")
for file in os.listdir('D:\\Python\\ch14'):
print(file)
totalsizes += os.path.getsize(os.path.join('D:\\Python\\ch14', file))
print("全部檔案大小是 = ", totalsizes)練習:列出特定目錄所有檔案的大小
資料夾與檔案路徑
import glob
print("方法1:列出\\Python\\ch14工作目錄的所有檔案")
for file in glob.glob('D:\\Python\\ch14\*.*'):
print(file)
print("方法2:列出目前工作目錄的特定檔案")
for file in glob.glob('ch14_1*.py'):
print(file)
print("方法3:列出目前工作目錄的特定檔案")
for file in glob.glob('ch14_2*.*'):
print(file)❼ 獲得特定工作目錄內容:glob模組
可以使用「萬用字元」:*
資料夾與檔案路徑
import os
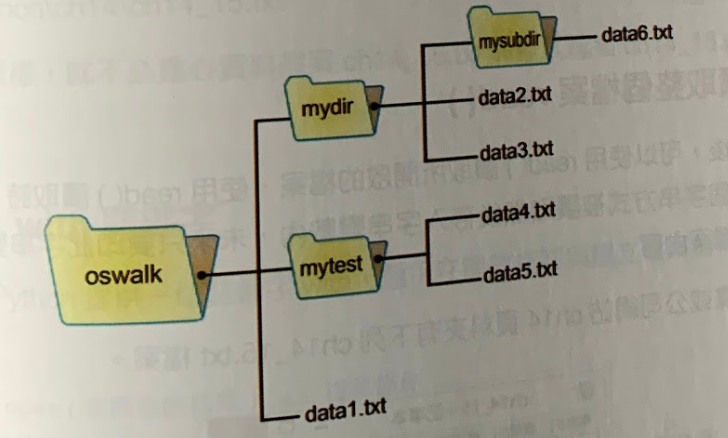
for dirName, sub_dirN, fileNames in os.walk('oswalk'):
print("目前工作目錄名稱: ", dirName)
print("目前子目錄名稱串列: ", sub_dirN)
print("目前檔案名稱串列: ", fileNames, "\n")❽ 走訪所有目錄樹節點:os.walk()
回傳3個值: 工作目錄名稱, 子目錄串列, 檔案串列
Python程式設計-檔案與資料夾
By Leuo-Hong Wang
Python程式設計-檔案與資料夾
Lesson 11: 檔案與資料夾
- 1,556



