arXiv:1302.5843v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech]
Ising formulations of many NP problems

arXiv:1302.5843v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech]
Ising formulations of many NP problems
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
Ising model?
Quantum Version?
How is related to TSP?
the ising model
Ludmila Augusta Soares Botelho
History time: around 100 years ago
Is there is a very simple model to describe ferromagnetism?
Is there a phase transition in the magnetism of a linear sequence of little magnetic moments where only neighbors are energetically coupled?
(Ferro)magnetism


Wilhelm Lenz
{
{
{
$$z$$
History time: around 100 years ago
(Ferro)magnetism

Wilhelm Lenz

Ernst Ising
?
!

Wilhelm Lenz

Ernst Ising
?
Model

It does not have phase transition!
... what about some quantum mechanics?
... more dimensions?
History time: around 100 years ago

( the best time)
Why do we care about Statistical Mechanics?
Physics time

( the best time)
Physics time
Why do we care about Statistical Mechanics?
It relates the
microscopic
with the
MACROSCOPIC

How is that possible?
$$(x,y,z)$$
$$m$$
$$m$$
$$\vec{p}$$
$$(x,y,z, p_x,p_y,p_z)$$
$$(x,y,z)$$
$$\vec{v}$$
Statistical mechanics
$$m$$
$$(x,y,z, p_x,p_y,p_z)$$
- Microstate
Statistical mechanics
m
j=(x,y,z,px,py,pz)
- Microstate
j=(x1,...,x3np1,...,p3N)
- For N particles:
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
Statistical mechanics
m
- Microstate
j=(x1,...,x3np1,...,p3N)
- For N particles:
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
Statistical mechanics
m
- Microstate
j=(x1,...,x3np1,...,p3N)
- For N particles:
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
m

Statistical mechanics
- Microstate
j=(x1,...,x3np1,...,p3N)
- For N particles:

thermodynamic Quantities
- Macrostate



- Equilibrium observable state

microstate
thermodynamic Quantities
- Macrostate
Condensed matter physics
The bridge
$$\Omega(E) =\text{Number of Microstates} $$
$$S = -k_b\sum_i p_i \ln p_i$$
- Entropy
$$S = k_b\ln W$$
$$W = \frac{N!}{\prod_i N_i }$$
$$S = k_b\ln \Omega$$
- Gibbs Entropy
- Postulate: All microstates are equally probable

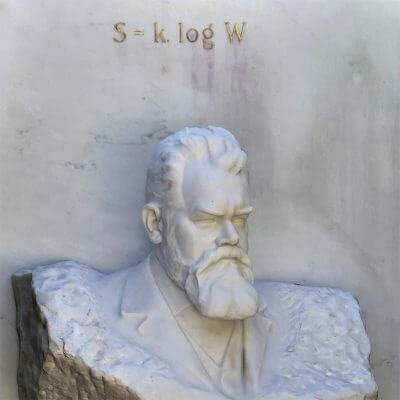
The bridge
- Entropy
$$S = k_b\ln \Omega$$
- State Function/Fundamental Equation
$$S = S(U,V,N)$$
$$ \frac{1}{T}= \frac{\partial S}{\partial U}$$
$$ \frac{p}{T}= \frac{\partial S}{\partial V}$$
$$ \frac{-\mu}{T}= \frac{\partial S}{\partial N}$$
temperature
pressure
chemical potential
The bridge
- Helmholtz Free Energy
$$F= U - TS$$
$$U =-\vec{\mu} \vec{H}$$
$$m =-\left. \left( \frac{\partial F}{\partial H} \right)\right |_{T,N}$$
$$z$$
$$\vec{H}$$
- Legendre Transformation for internal energy \(U = Q +W \)
$$\chi (T,H) =-\left. \left( \frac{\partial F}{\partial H} \right)\right |_{T,N}$$
$$U =-\mu_0 {H}$$
$$ \rightarrow \frac{CH}{T}$$
$$M =N\langle{m} \rangle$$
$$\mathrm{d}F= M\mathrm{d}H - S\mathrm{d}T$$
Statistical Mechanics
Why do we care about Statistical Mechanics?
It relates the
microscope
with the
MACROSCOPE
- Few assumptions
Canonical Ensemble
S
R
~
~
~
- Probability of particular microscopic state
$$P_j = \frac{e^{-\beta E_j}}{Z} $$
$$Z = \sum_{\sigma}e^{-\beta E_\sigma}$$
ustandssumme
- Partition function
(T, V, N)
- Few assumptions
Canonical Ensemble
S
- Probability of particular microscopic state
$$P_j = \frac{e^{-\beta E_j}}{Z} $$
$$Z = \sum_{\sigma}e^{-\beta E_\sigma}$$
ustandssumme
- Partition function
(T, V, N)
- Free Energy
- Systems Total Energy
- Heat Capacity
Connection with Thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Magnetic Susceptibility
- Magnetization
R
Statistical Mechanics
quiz: why the "-" signal?
Systems energy
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} s_i s_{i+1} - h\sum_i^N s_i$$
- Hamiltonian
{
interaction
{
external field
$$Z=?$$
$$z$$
$$h$$
$$\cdots$$
$$\cdots$$
{
Free Energy
Magnetization
Partition Function
1D

quantum mechanics
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} s_i s_{i+1} - h\sum_i^N s_i$$
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z $$
Pauli Matrices
Reduces to classical version
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z - h\sum_i^N \sigma_i^z$$
$$E = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i \sigma_{i+1} $$
transverse field
energy levels \( \sigma_i =\pm 1 \)
diagonal!
- It has phase transition!
-Ferromagnetic vs Paramagnet
$$ \sigma_i^\alpha = I^{\otimes i-1} \otimes \sigma^\alpha I^{\otimes N-i} $$
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z - h\sum_i^N \sigma_i^x$$
quantum mechanics
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z - h\sum_i^N \sigma_i^x$$
$$\mathcal{H} = - \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i}^N \left[ J_x \sigma_i^x \sigma_{i+1}^x +J_y \sigma_{i}^y \sigma_{i+1}^y+ J_z \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z - h\sigma_i^z\right]$$
$$\mathcal{H} = - \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i}^N \left[ J_x \sigma_i^x \sigma_{i+1}^x +J_y \sigma_{i}^y \sigma_{i+1}^y+ - h\sigma_i^z\right]$$
$$J_x = \left( \frac{1+ \gamma}{2} \right)$$
$$J_y = \left( \frac{1- \gamma}{2} \right)$$
- Tensor Networks
- Quantum Many-Body Problems
- Heisenberg Model
- XY Model
- 1D Quantum Ising Model
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z - h\sum_i^N \sigma_i^x$$
$$J > 0$$
$$J < 0$$
$$J = ?$$
$$\mathcal{H} = -J \sum_{i} \sigma_i^z \sigma_{i+1}^z$$
Ground state
Spin Glass Model
$$\mathcal{H} = - \sum_{i,j} J_{i,j}\sigma_i^z \sigma_{j}^z$$

\(\leq\)
}
$$min$$
?

magnet
Thank you!
Dziękuję Ci!
Obrigada!
धन्यवाद!
Teşekkür ederim!
Ising Model
By ludmilaasb
Ising Model
- 333



