Python
Introduction to Awesomness
from awesomness import *
Speaker
@ manoj pandey
Why Python ?
-
Fast
-
Broad
- Readability
- Easy to learn
-
Open-sourced
- Object-Oriented
-
It's dynamic
-
Python is a general purpose language
- It's cross platform
- And much more reasons
Python is fast
Python is faster than other
"scripting" languages.
Python implemented specific parts
of language in C
Python has other implementations that
provide some solutions to increase
runtime speed dramatically.
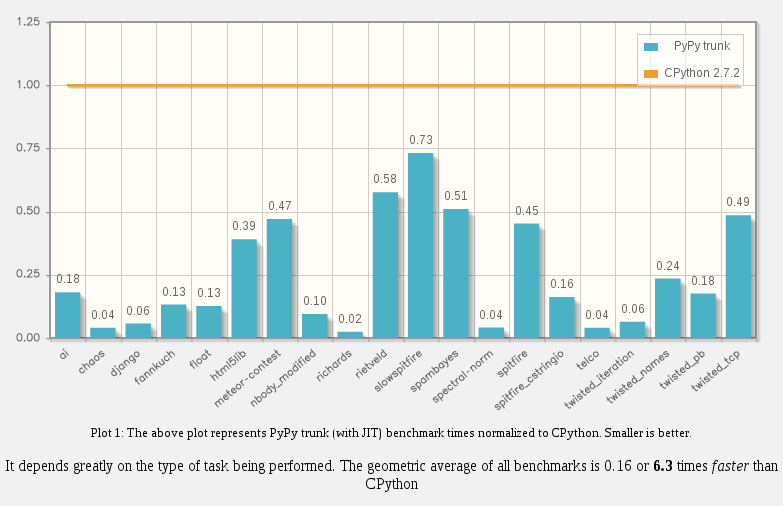
PyPy
- PyPy is an implementation of python written in python
- PyPy implemented a JIT
- It's about 5time faster that Cython ( yeah Cython )
Python is broad
Python can be used in many different
fields like:
- Web development
- System administration
- Game development
- 3D modeling
- Testing
- Analyzing big data
- . . .
Readability
Just take a look
from some_package import some_method
def say_hello (name=none):
if name is not none:
print("Hello " + name)
else:
print("Hello world")
say_hello("yottanami") It's easy to learn
- Its syntax is very simple and English like
- Python does not use wired symbols or structures
- Lots of resources out there
- Python is very popular
Free Software
Python is open source and free (libre)
It means that you can
get the source code
change it as you need
and redistribute it
People can find bugs and fix them faster
Python is dynamic
What is a dynamic language ?
new code can be executed during runtime
without limitations
What's the point ?
It means that the user does not have to go through
the compile-run-debug cycle every time he makes
a change to the code
Python is general purpose
You can use python in
- Desktop apps
- Hand held applications
- Embedded Systems
- Electronics
- Robotics
- Game development
- Manufacture
- etc
Cross Platform
This OS`s supports python:
- GNU/Linux
- BSD family
- MS Windows
- Android (It's Linux ofcourse)
- Mac
- iOS
- Solaris
- .....
Who uses python?
- NASA
- Youtube
- Dropbox
- Disqus
- Mozilla
- BitBucket
and you ?
Get Started
What do we need today ?
- Python installed
- pip, virtualenv
- An Editor or IDE
Installation
Windows
Linux/OSX
Editors & IDEs
- Sublime Text ♥
- Eclipse + pydev
- gedit
- Geany
- Wing IDE
- Visual Studio
- Emacs
- Kuso
- Atom
- Notepad++
- VIM
Hello World !
print "Hello World!" Zen of Python
import this How to use Python
- How to run python scripts
- How to use Python shell
- How python runs scripts
- How to install packages using pip
- Some useful packages
How to run a python script ?
- If target script contains hashbang section:
$ python /path/to/target_script.py $ chmod +x /path/to/target_script.py # another way $ /path/to/target_script.py - If target script does not have hashbang section:
$ python /path/to/target_script.py
Useful pakcages
- numpy
- requests
-
virtualenv
- scrapy
- beautifulsoup
- nltk
A simple trick
Learn faster by:
-
`help` function
- `dir` function
- `__dict__` method
Basics
- Variables
- General types
- Indentation & Code blocks
- Operators
- Conditions
- Loops
- Functions
- Exceptions
- Modules
- OOP
Variables
- What is a variable
- How we define a variable
- Variable scopes
Data Structures
- String
- Numbers
- Lists
- Tuples
- Dictionaries
Strings
- Strings define using single or double quote
- Strings are immutable
- characters of an string are accessible using
[] operatore
Numbers
Numbers are objects too
There are different types of numbers
Float, Integer, Long and etc
Lists
- Lists are mutable
- Think of lists as array in other langs but more flexible
- List can have elements with different types
- List elements are accessible by [] operator
Tuples
Tuples are just like lists but immutable
Dictionaries
- Dictionaries are mutable
- Dictionaries are lists with flexible indexes
- Index of dictionaries can be an object
- Dictionary values are accessible using [] operator
Indentation
- What does it means ?
- What is a code block ?
- How we defines code blocks ?
Operators
- Math operators ( +, -, *, /, **)
- Logical operators ( <, >, <>, == , <=, >=, and, or, not)
- Assignment operators (*=, +=, -=, /=)
- Binary operators (<<, >>, &, |, ^)
- Membership operators (in, not in)
Conditions & Loops
- if - if/else
- for
- while
- iterators
Functions
- What is a function
- What is a method
- How to define a function
- Function arguments
- Return values
Exceptions
- What is an exception?
- When does exceptions raises?
- How to catch exceptions
OOP
- What is OOP ?
- How does it help us?
- How can i define a class ?
- How can i define attributes ?
- How can i define methods ?
- What is inheritance ?
Where to get help ?
- Python documentation
- Search the web
- Python forums
- IRC channels
- Mailing Lists
Resources
- Learn Python the Hard Way - Zed A. Shaw
- Python For Dummies : O'reilly
- Byte of python : pdf available
- Dive into python : pdf available
Do you have any question(s) ?
Many Thanks to

@cashrulz, @thepsyguy
manoj pandey
+91-9910089606 || http://manojpandey.me
try: run_a_workshop() print("Good job guys")except PeopleDidNotLearn: print("We have to try harder")finally: print("Heeeell yeah, It's finished")
Introduction to Python
By Manoj Pandey
Introduction to Python
Basic introduction to Python programming language for newbies !
- 2,308