UX Research
- UX research
- Why, when
- Methods (qualitative/ quantitative)
- Interviews, Questionairs, others
- Cognitive bias
- Data analysis
- AI
Agenda

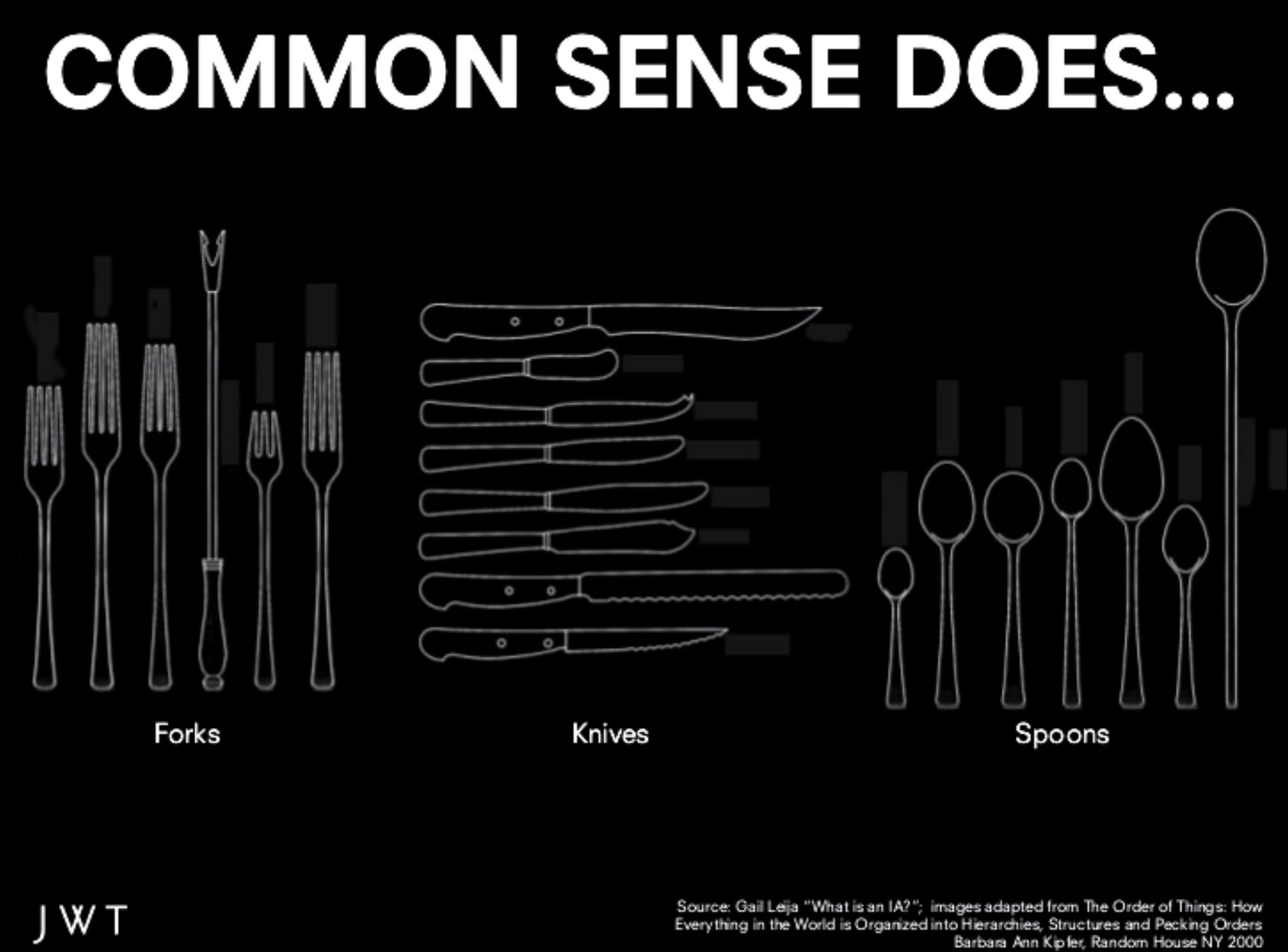



User Research
Process of understanding the needs, behaviors, and attitudes of users to inform the design and development of products or services. It involves collecting and analyzing data about users through various methods such as surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
Why do we need research?

Risk reduction
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
YOU ARE NOT YOUR USER
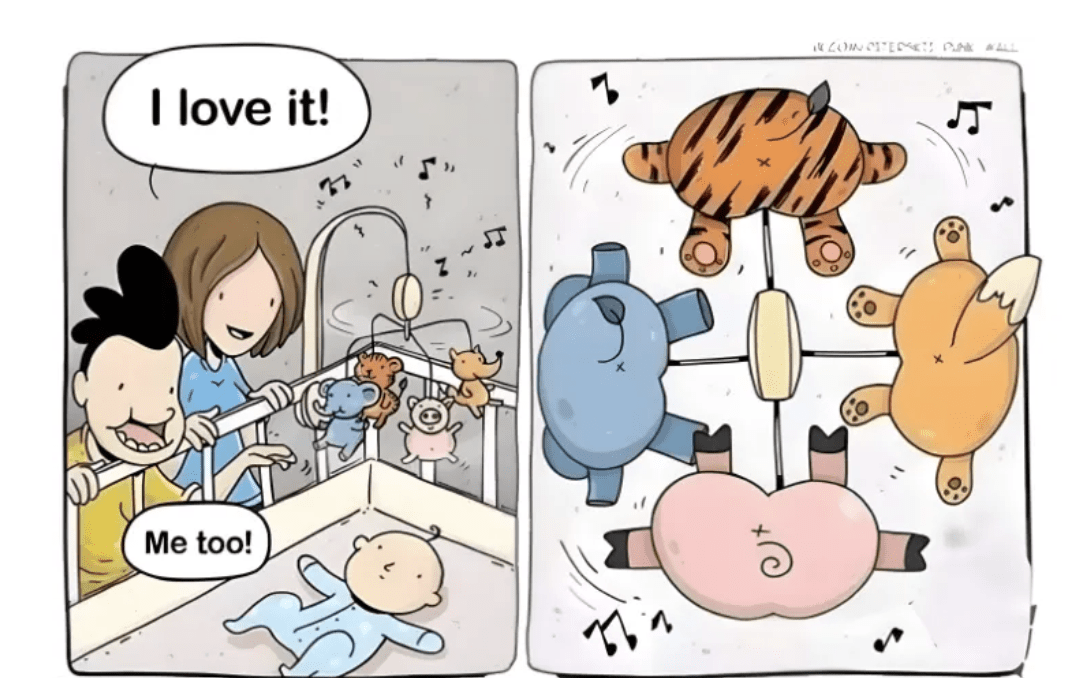


Drill
story
Do you really
need a drill...?
People don't buy products, they hire them to do the job.

Methods
Methods
| Country | Methods | Questions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | interviews, usability testing, etnographic studies, card sorting | Why? How? | Time-consuming, expensive, deep dive, 7 people |
| Quantitative | surveys, benchmarking, A/B test, | How many? How often? | quicker, superficial, data from analytics |
+ Desk research
Methods
What they say
What they do
Quantitative
Qualitative
Tree testing
Observation
Love letter
Card sorting
Questionnaire
Focus group
Moderated usability testing
SUS usability testing
Interview
Unmoderated usability testing
Page analytics
A/B testing
Ethnographic/field studies
Eye tracking
If I had asked people what they wanted, they would have said faster horse
-Henry Ford
who never said that
Interviews
What can we learn?
- A deeper understanding of the customer
-
Who are they? Goals and needs
-
Personas, segments
-
Mental models
-
How do they think about this? What do they expect?
-
Customer journey
-
What are their processes?
-
How do they use it?
Opportunities
-
What are they missing?
-
What makes them angry?
-
What is important to them?
What we cannot
-
Future behaviour (I would pay...)
-
Quantification
Interviews
- Structured - rigid, script, easy to compare data (basically a moderated survey)
- Unstructured - free-flowing
- Semi structured - script but ability to deep dive into topics
Types of questions:
-
Sequence: "Tell me about your day."
-
Specific example: "Tell me about the last time you bought shoes."
-
Detailed list: "Tell me all the apps you use."
-
Also ask about feelings: "How did that make you feel?" or "What feelings came up for you?"
Active listening techniques
Active listening techniques
Techniques
- Paraphrasing: Restating what the other person has said in your own words to show you've understood.
- Mirroring: Repeating the last few words or key phrase the person said to encourage them to elaborate.
- Silence: Pausing to give the other person time to think and speak.
- Unfinished questions: Starting a sentence and leaving it open-ended to prompt the other person to complete the thought (e.g., "You mentioned the meeting was...").
- Boomerang: Turning a question back to the person who asked it (e.g., "How is this supposed to work?" becomes "What do you think?").
- 5 whys vs. no whys
Tips and tricks
-
Establish a relationship of trust and respect
-
Use open-ended questions
-
Nodding and affirming
-
Active listening
-
Inquiring and probing
-
"Why" (but use a different word)
-
Always return to the topic
-
Replace "typically" with "the last time you"
- Don't judge or comment
-
Don't explain
-
Don't lead (no leading questions)
-
Don't interrupt
-
Don't use closed-ended questions
-
Don't use double-barreled questions
-
Don't use hypothetical questions
What kind of features would be valuable in this type of app?
-
Speculative
-
Features are solutions to user needs.
-
Stop thinking in features, start thinking in needs
-
Too vague
-
Valuable for whom and to do what
Would you be willing to pay for a premium of the app with additional features?
If so, which features?
- Future behaviour
- Money is always problematic
- Two questions
- Features are solutions to user needs.
Cognitive biases
The tendency to interpret new evidence as confirmation of one's existing beliefs or theories.
Confirmation bias
Positive first impression in one area leads to a positive overall judgment, influencing perceptions of other unrelated qualities.
"This brand can't do anything bad..."
Halo effect
Using immediate/first examples that come to a person's mind when evaluating a specific topic, concept, method, or decision.
(brands)
Availability bias
Order of questions can change people's answers.
Order bias
Questioned framed in a leading positive/negative way influencing the answer.
Framing effect


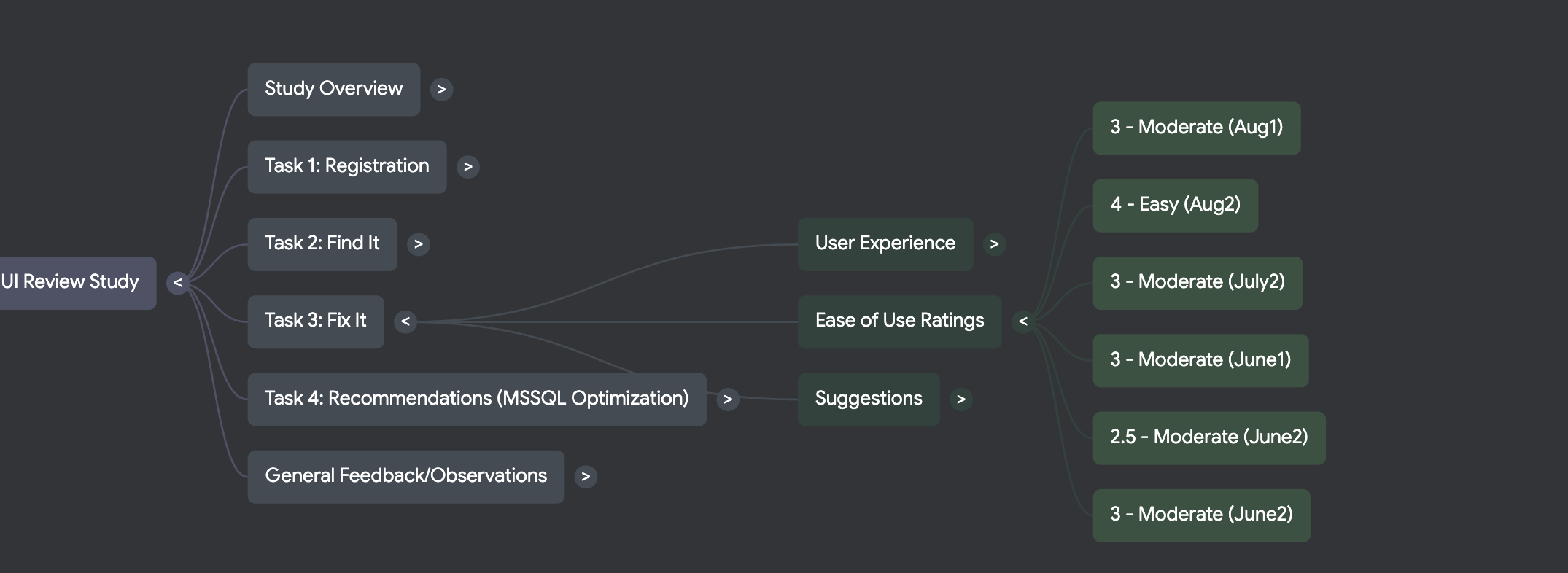

Data analysis
Fictive typical representative of the user segment
Goal is to build an empathy and focus
Personas
Personas should not be about demographics. They should be about the problems and challenges people face

https://www.mockplus.com/blog/post/user-persona-template
- Born 1948, grew up in England
- Likes dogs
- Male
- Married twice
- 2 kids
- Wealthy and famous
- Lives in a castle
Persona 1
Persona 2
- Born 1948, grew up in England
- Likes dogs
- Male
- Married twice
- 2 kids
- Wealthy and famous
- Lives in a castle

King Charles
Ozzy Osbourne



Milkshake
story
Once upon a time in McDonald...
(jtbd)
When (situation), a user needs to..., so they can...
Persona: Mark, 24, a university student, stays up late at night, likes latenight coffee.
Story: When studying late at night, Mark wants to stay focus and productive longer, so he can finish his paper.
User story
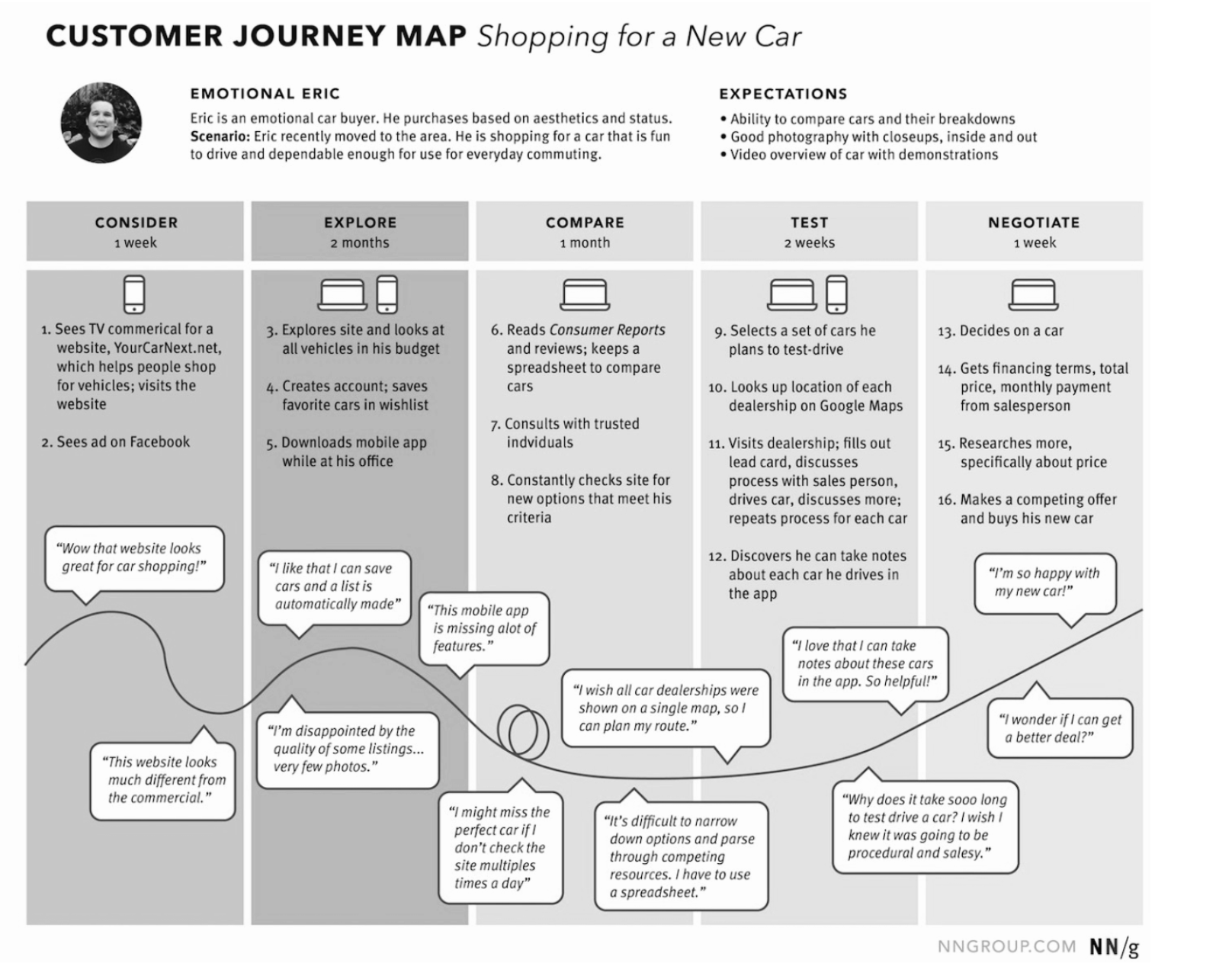
Visual representation of the entire process a customer goes to when interacting with company, product service.
Customer journey maps
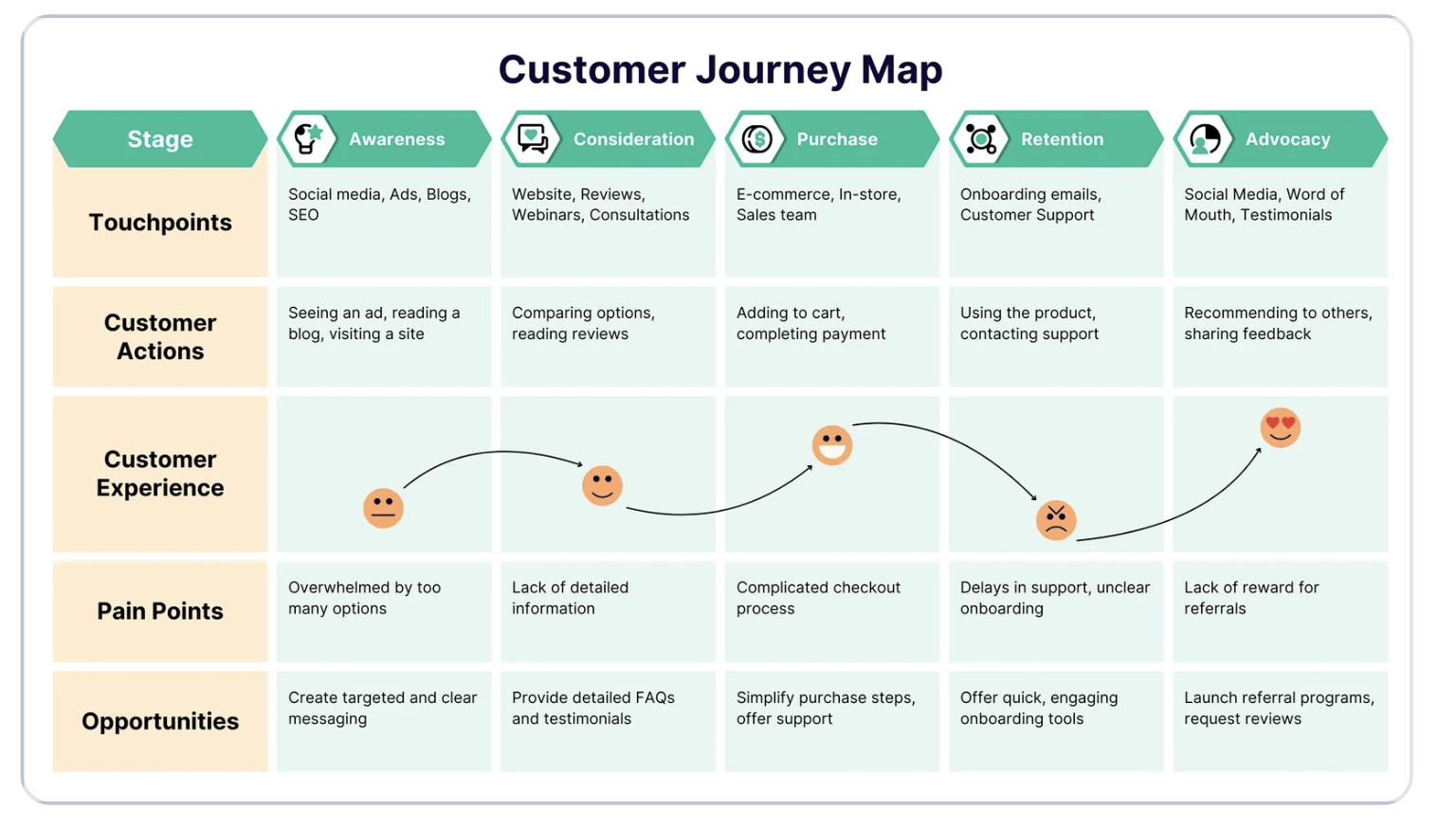
- Identify insights, topics
- Define problems (with context)
- Prioritisation (e.g. MoSCoW)
And now what?




AI in discovery research
- Research preparation
- Data gathering (transcripts, synthetic research)
- Analysis and summary
- Visualisation (Persona creation, mind maps)
Activities
- Claude, CHatGPT
- Gemini gems
- Dovetail, Notebooklm,
- EnjoyHQ, Quadrilics
Tools
Notebooklm - interface
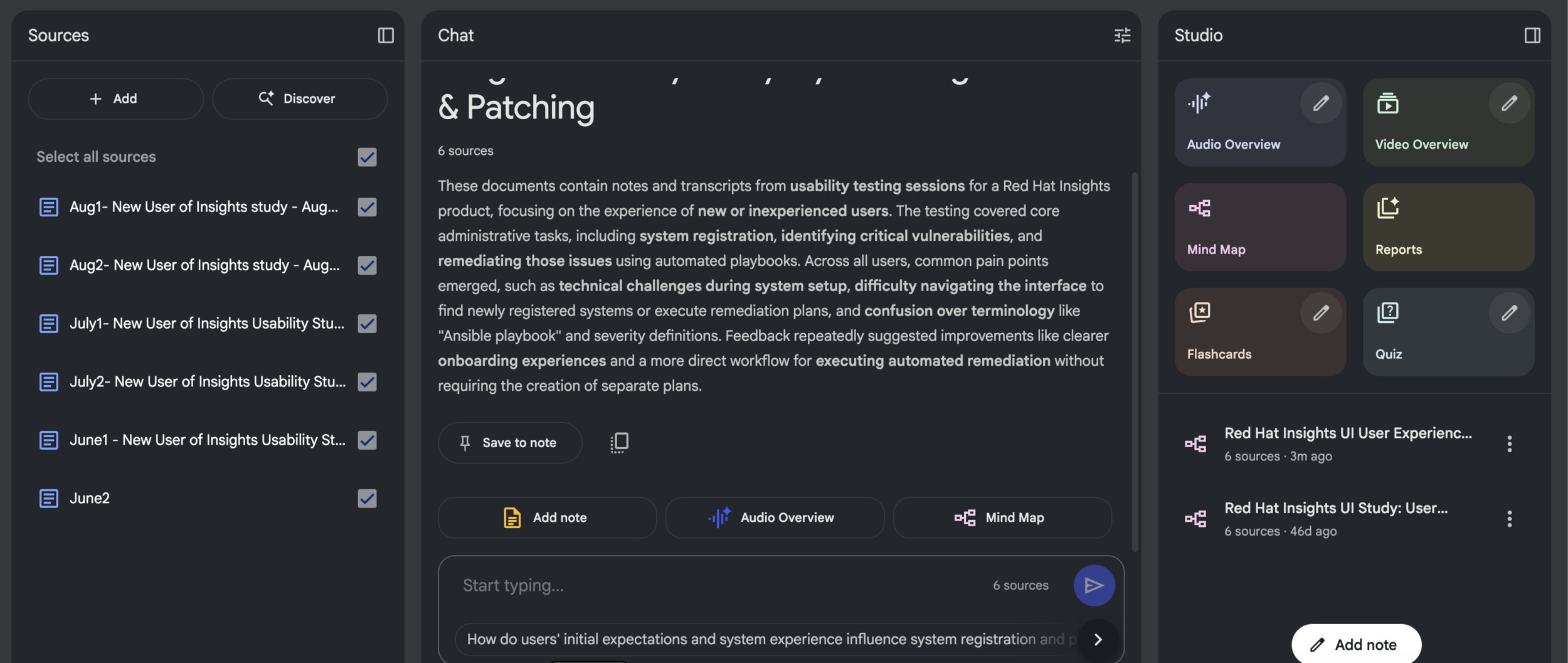

Notebooklm
- mind map
Palette
By Mari Švi
Palette
- 66



