Introduction to Clientside frameworks
Secure Web Application Development
Joshua Mcshannon
University of Nebraska at Omaha
CYBR 8470
Today: Clientside App Frameworks
Part 1: Client-side Apps
Part 2: Case studies
- Ember.js
- React.js
Part1: Client-side Apps
Why clientside App Frameworks?
-
helps you write rich web applications that are well structured (MVC) and backend agnostic.
-
Helps you cut down the amount of boiler plate code within your application significantly
-
Easily integrates with third party JavaScript libraries and CSS libraries
-
Improves usability and app reactivity
-
Technology of tomorrow for building responsive web applications
Traditional Websites
Client-side Apps
Why clientside App Frameworks?
Traditional Websites
Client-side Apps
- HTML, CSS and JavaScript serialized on the Server-side and passed to the client
- Full-page refresh when the user clicks on links
- Heavily reliant on the traditional HTTP Request/response lifecycle
- Easy to cache the website pages on the server
-
Full JavaScript application sent on the first request
-
Subsequent requests only transmit data
-
Usually have a rich application-like user interface
-
Faster navigation and user interaction
-
Supports the rich feature set that users have come to expect from modern web based applications
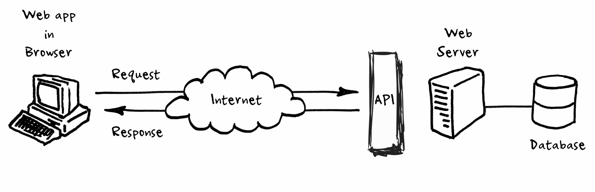
Why is client-side better?
Keeps both the application state and each user’s state on the server
If the user requests data to be updated, a complete new page is generated and transferred over the wire to the browser
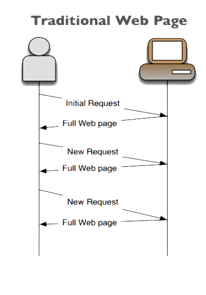
Traditional server-side app
Why is client-side better?
Still Keeps both the application state and each user’s state on the server
Still the same number of page requests and processes on the server-side, less overall data transferred results in less bandwidth consumption.

server-side app with Ajax
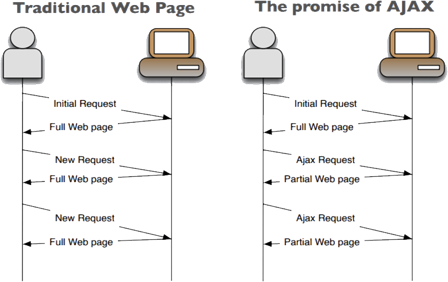
5. Partial Response
Why is client-side better?
Application and user state is maintained on the client side.
One full page request at the start of the session. Then just data requests.
Huge reduction in server-side resources, since application only invokes API methods when data is needed, not necessarily whenever a new page is viewed.

Why is client-side better?
Comparison: Click on 10 static pages (100KB/ea) and perform 5 dynamic actions on data (10KB) in each page (with 10,000 daily users).
Per Day
server-side
10∗10,000 = 100,000 page loads
10 ∗ 5 ∗ 10,000 = 500,000 loads with data
100,000 ∗100KB + 500,000 ∗110KB
= 65 GB bandwidth consumed
server-side w/ajax
10∗10,000= 100,000 page loads
10∗5∗10000=500,000 partial page loads
100,000 ∗100KB + 500,000∗10KB
= 15 GB bandwidth consumed
Faster page transitions
client-side
1 ∗ 10,000 page loads
10 ∗ 5 ∗ 10000=500,000 data api calls
10,000 ∗ 100KB + 500,000∗10KB =
6 GB bandwidth consumed
Instant page transitions
Why is client-side better?
Comparison: Click on 10 static pages (100KB/ea) and perform 5 dynamic actions on data (10KB) in each page (with 10,000 daily users).
The savings adds up
59 GB / Day
413 GB / Week
21535 GB / Year (21.5TB)
Amazon WS Charges about 8¢ per GB
So… over the year that’s about $1722 in savings from pure server-side to client-side app. If you scale up to 100k daily users its $17,220, 1M daily users $172,200…etc
Facebook has 936M daily users
Hence this kind of change is about 159 million dollars in savings yearly for them.
Reference Architecture
REST API
Endpoint
Endpoint
Endpoint
Endpoint
Client-side app
Part 2: Case STudy - Ember.js
What is ember
-
Browser-based MVC framework
-
Eliminates spaghetti code
-
Provides a standard (good) architecture for building apps
-
Makes hard things (variable bindings) easy to do
-
Uses Virtual DOM Diffing for efficient rendering
-
Very Opinionated framework

Who uses ember?


Ember (High level) Architecture
REST API
Endpoint
Endpoint
Endpoint
Endpoint
Model
Model
Model
Model
Data Store
Router
Components
Components
Components
Components
Components
Templates
Components
Components
Routes
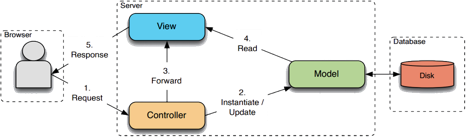
Workflow
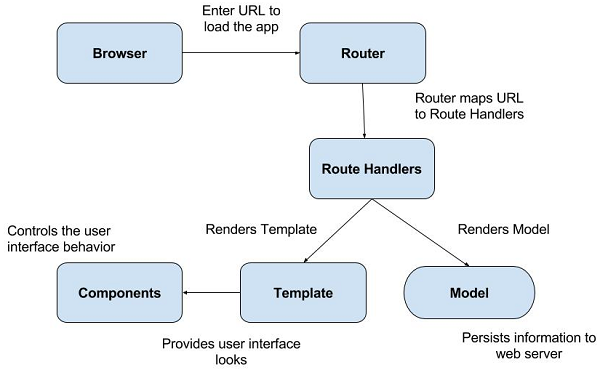
Credit: https://images.app.goo.gl/doSiuXjjm2523Yxx9
Client and Server workflow
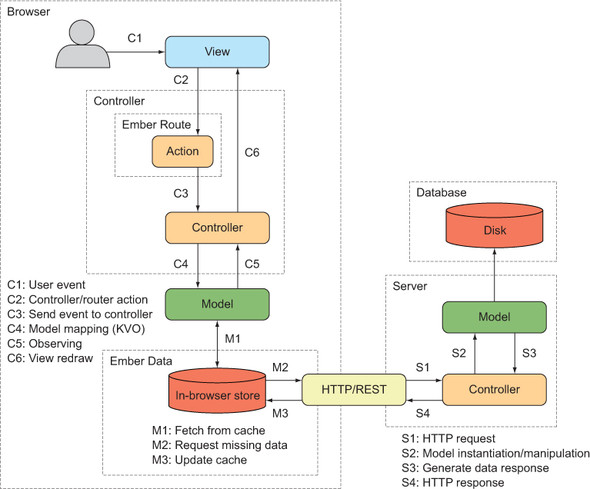
Credit: https://images.app.goo.gl/doSiuXjjm2523Yxx9
Ember Detailed
Architecture
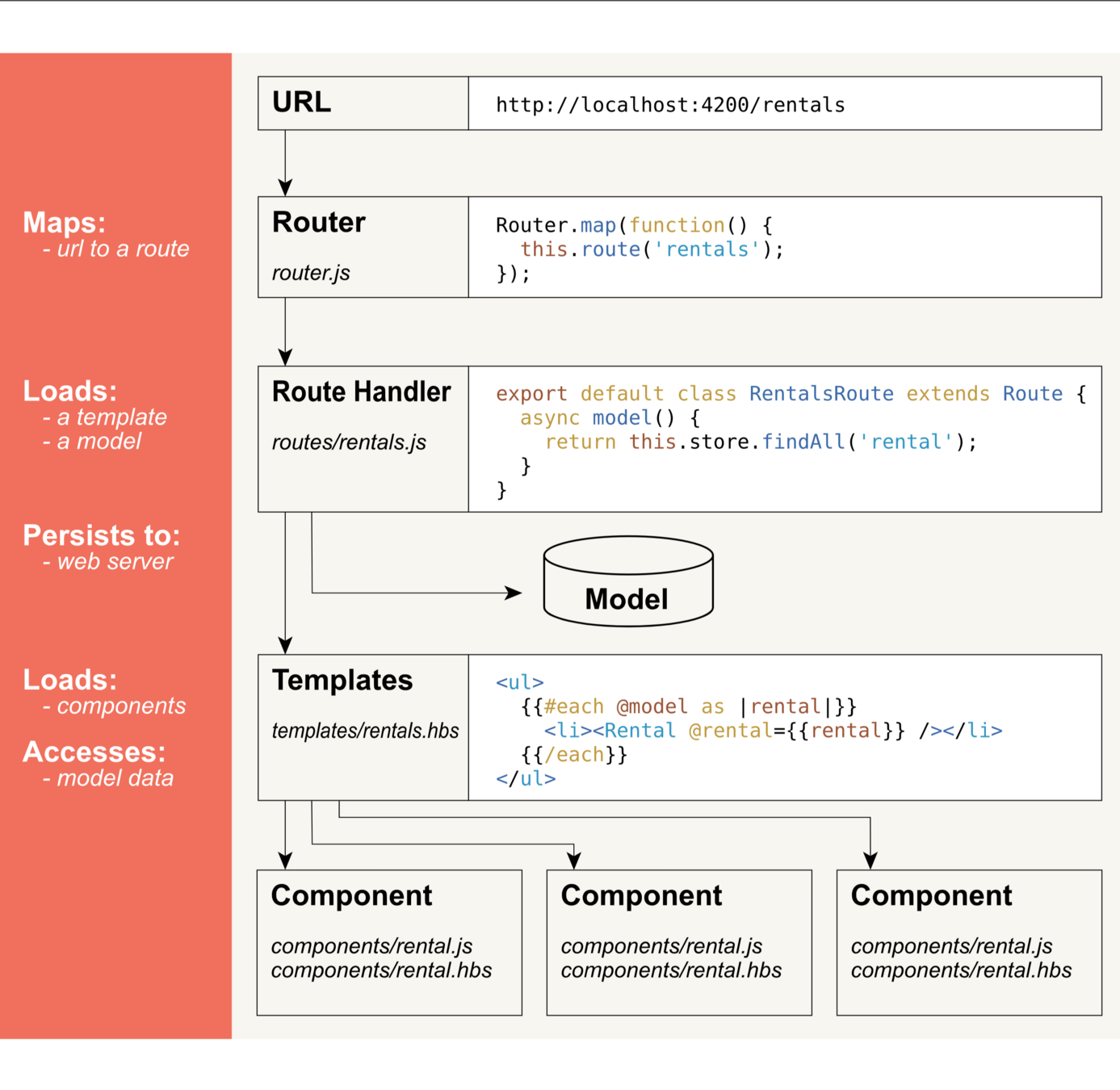
Key Concepts - Router & Routes
- Router is a switchboard that maps urls to routes and manages state
- Routes fetch data and setup a model for template, can be nested
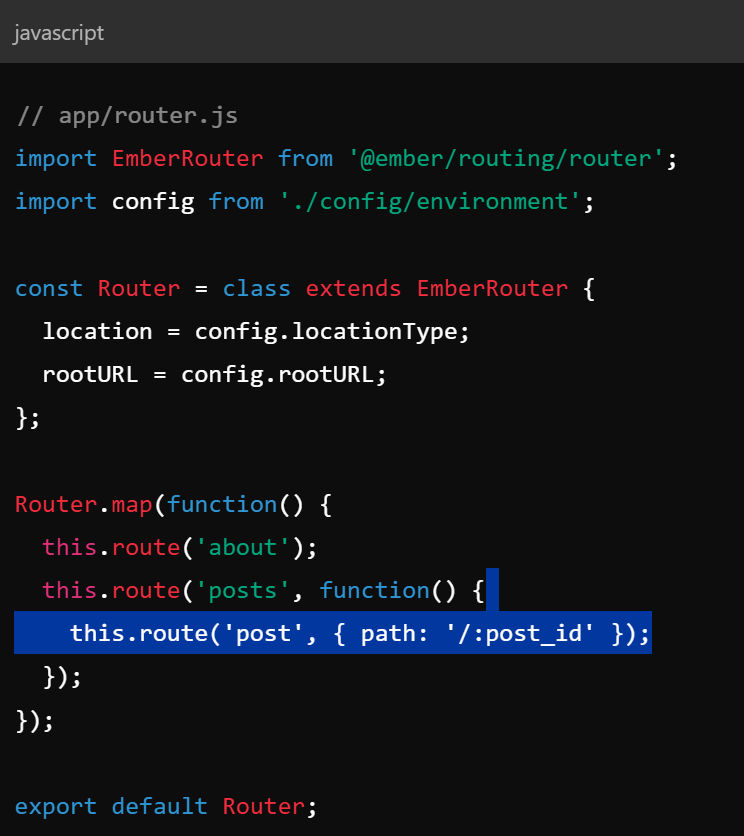
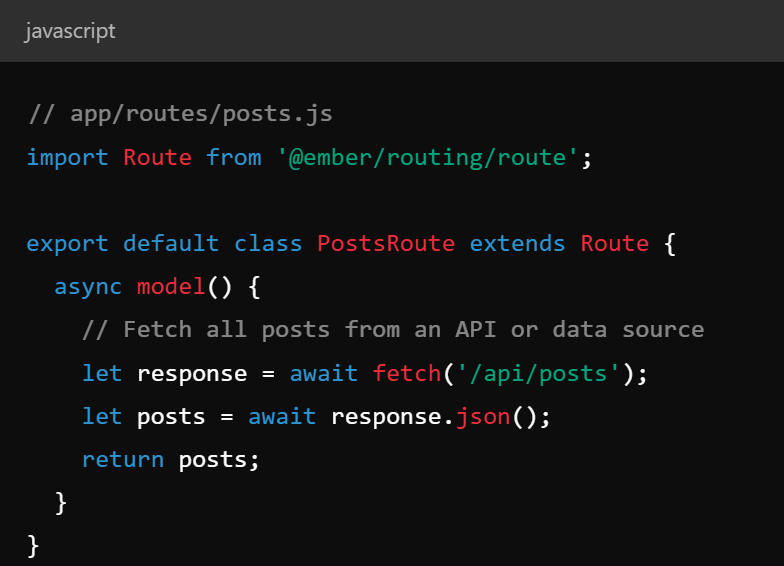
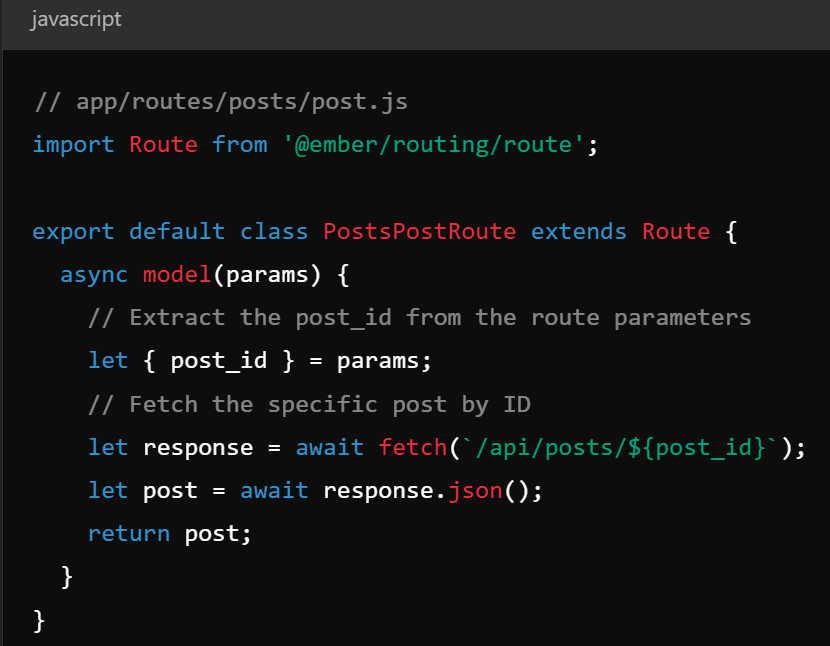
Key Concepts - Models & Ember Data
- Models - represent data objects, similar to django models
- Ember data - provides a consistent way to manage data, handles CRUD with REST or graphQL
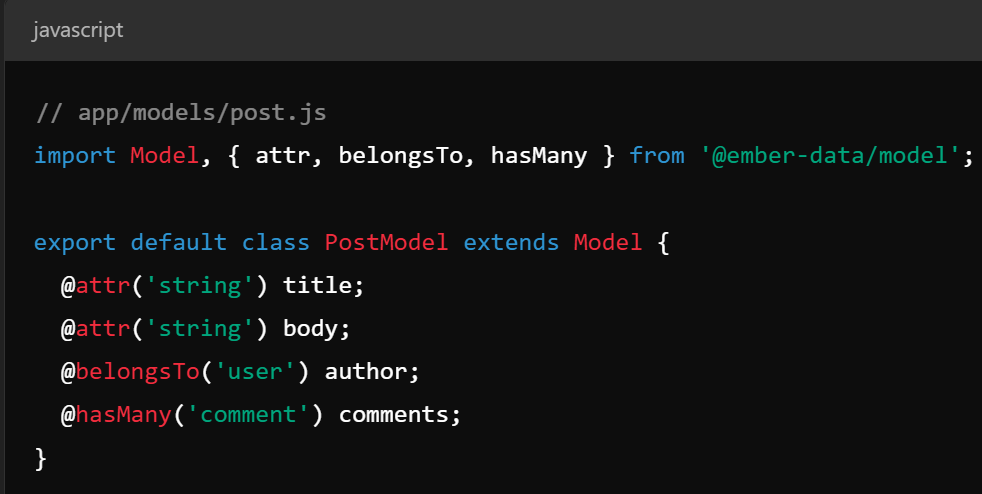
Key Concepts - Templates
- Templates - the UI portion of a route or component, written in handlebars
- Templates render as HTML and are automagically updated when state changes using bindings
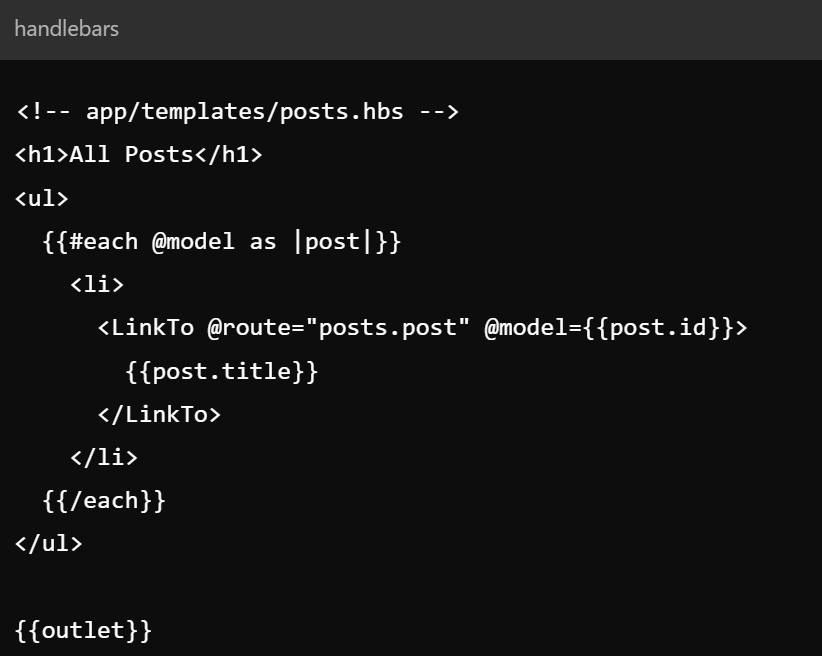
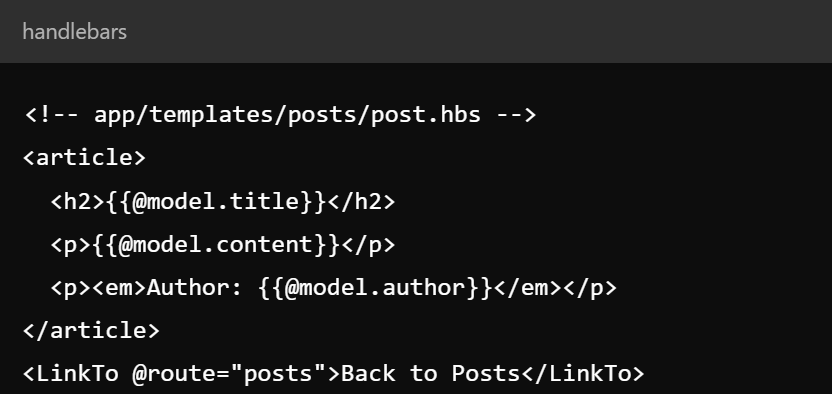
Key Concepts - Components
- Reusable UI elements encapsulating markup and logic
- Used for creating interactive parts of the UI
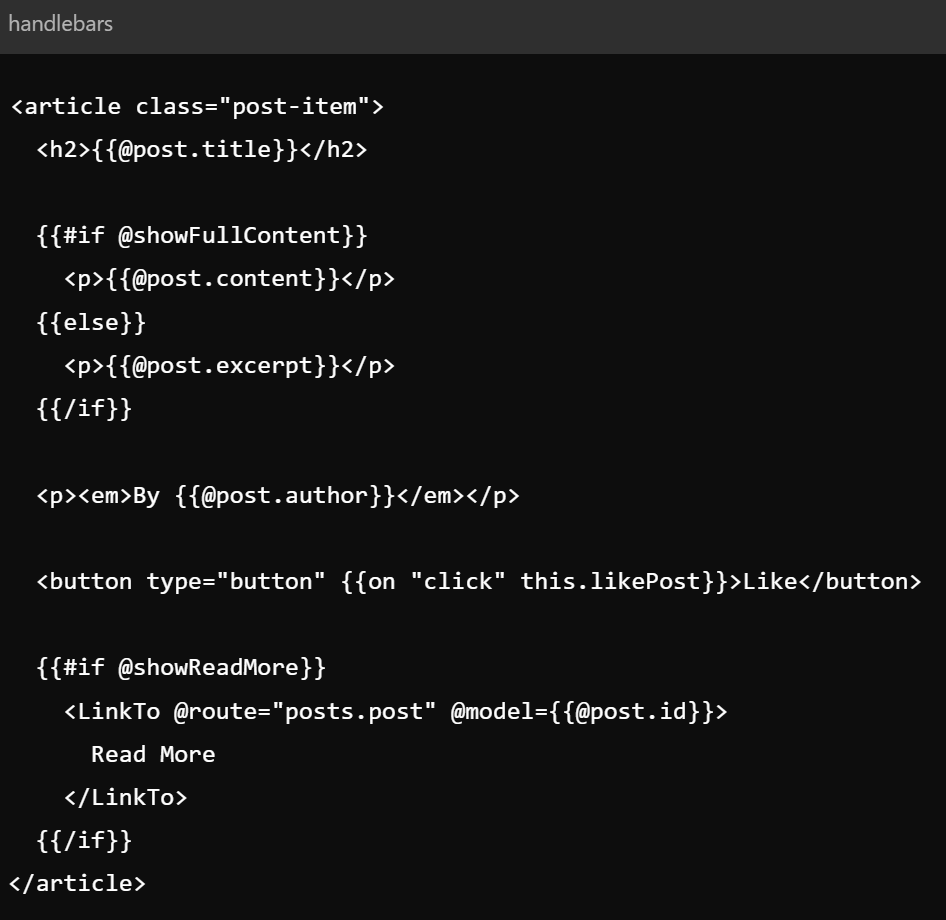
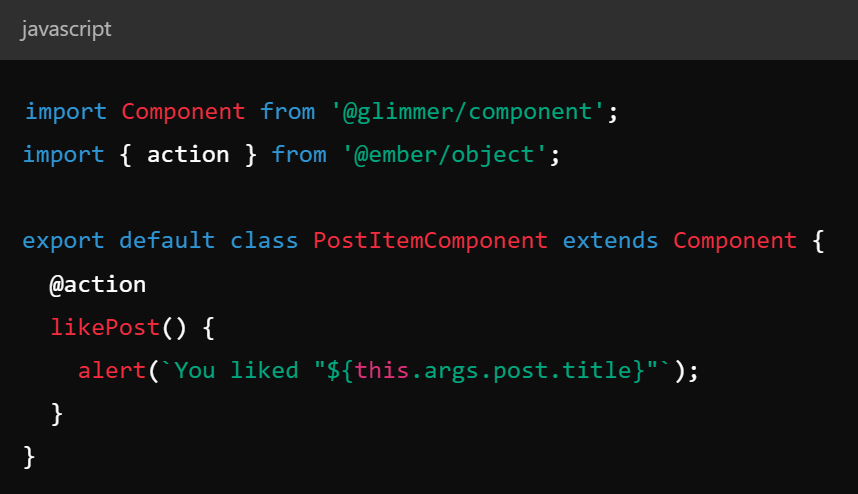

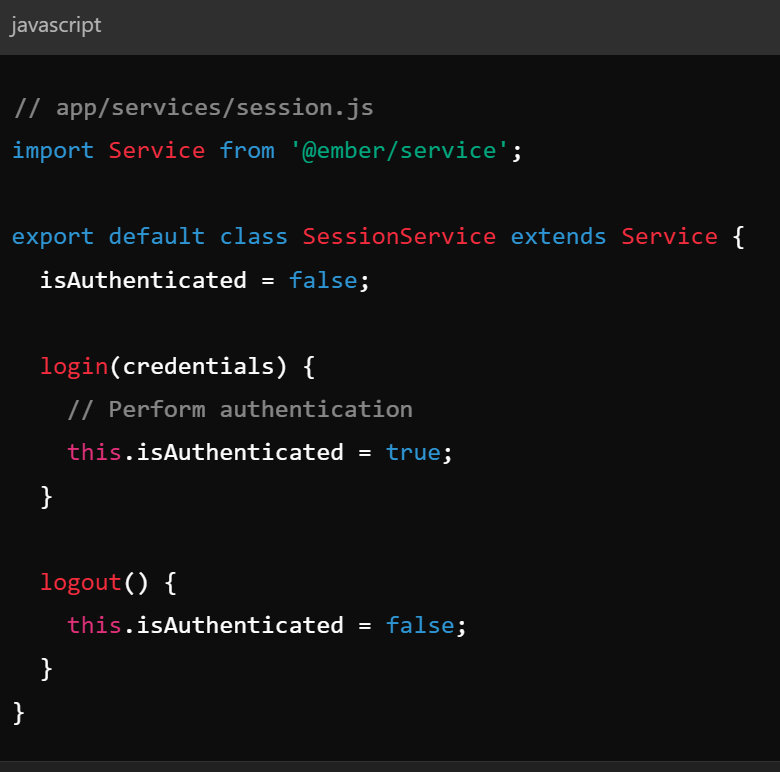
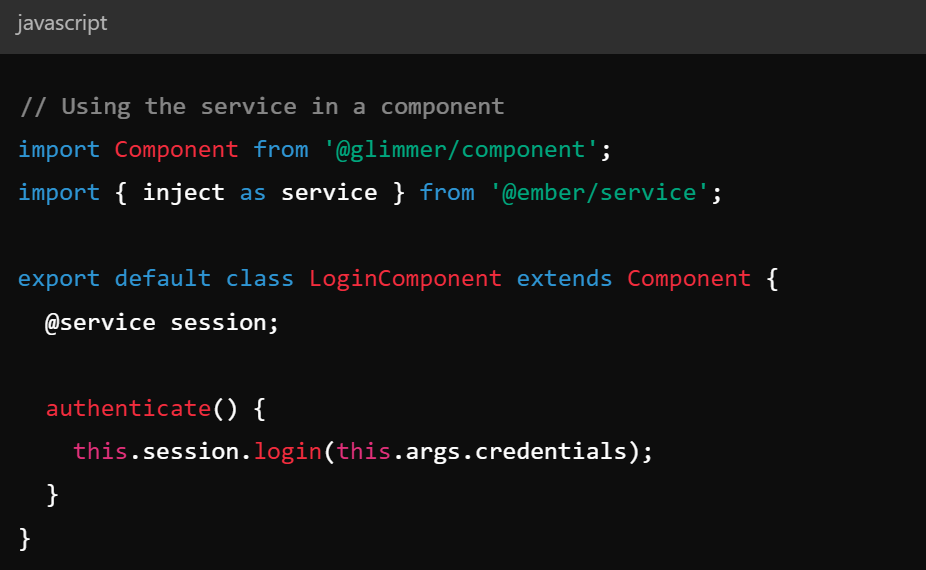
Key Concepts - Services
- Services - objects that persist across the application and allow for state sharing
- Often used for authentication, logging, etc
- Can be accessed across routes / components
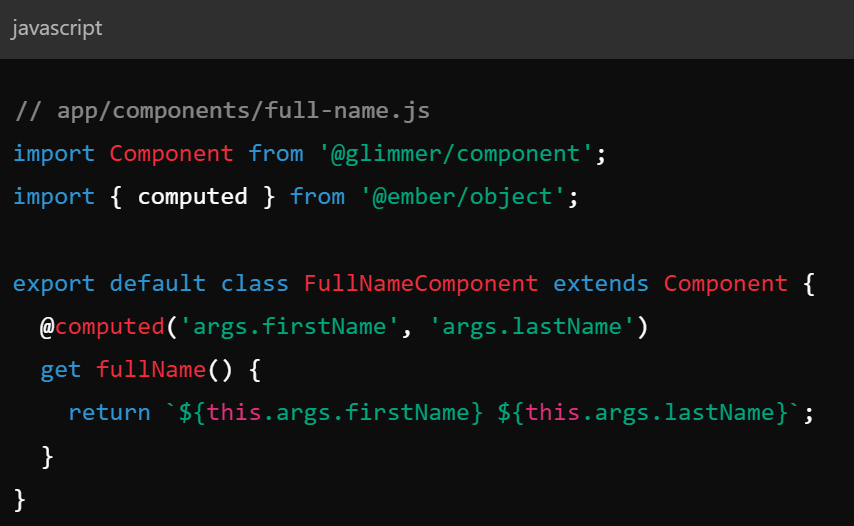
Key Concepts - Computed Properties / Observers
- Computed Properties - dynamically updated values computed from other properties
- Observers - watch or changes on properties and execute code
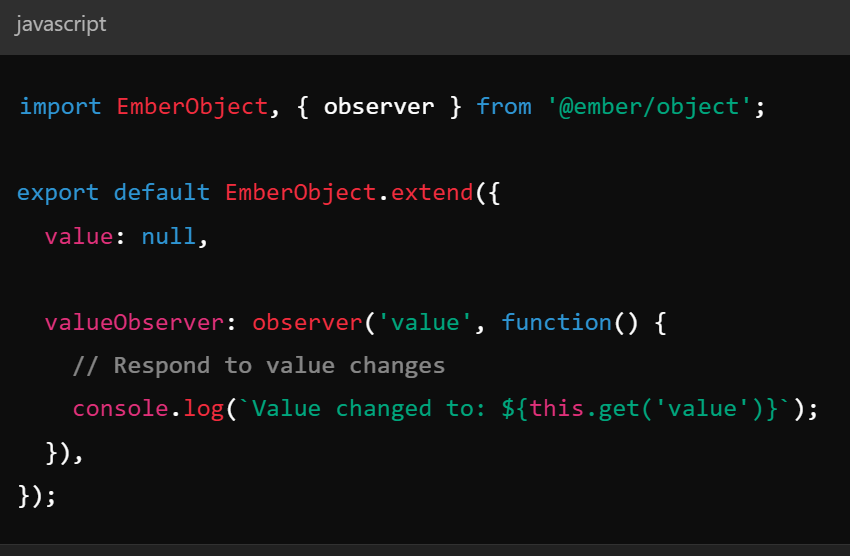
Key Concepts - Actions and hooks
- Actions - used to handle user interactions
- Hooks - Execute code based on state
(of a router or component)
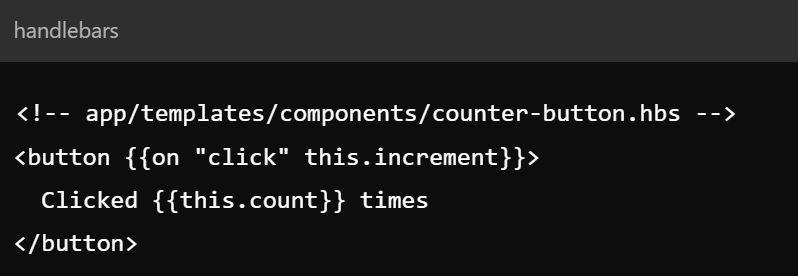
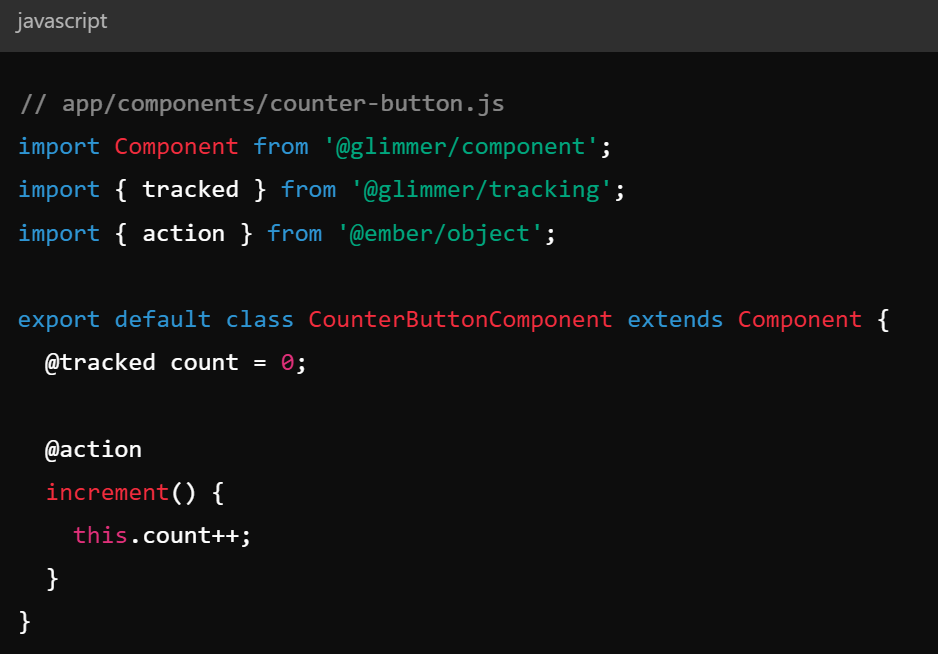
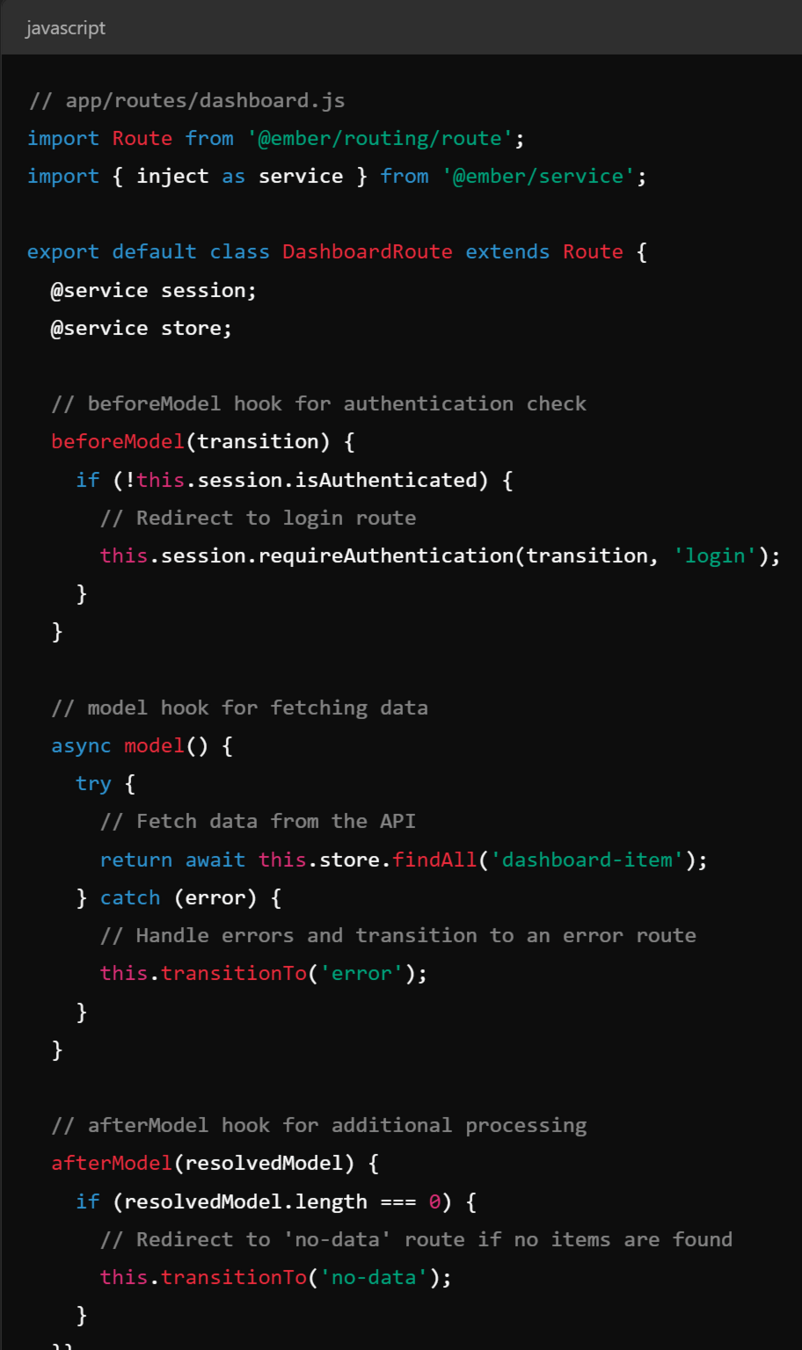
Part 2: Case STudy - REACT.js
What is REact.js?
- Javascript library primarily focused on user interfaces
- Built/maintained by Facebook (Meta)
- Component-based architecture
- Uses Virtual DOM diffing for efficient rendering
- Has a server-side/mobile version (React Native)
- Much less unopinionated than Ember









Who uses REACT?
REact.js ARCHITECTURE
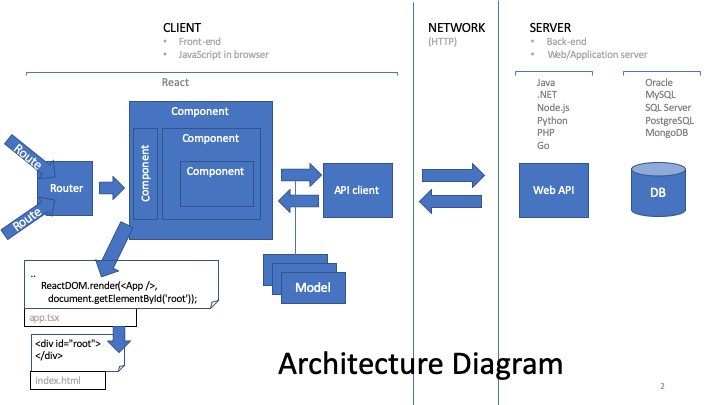
img credit: https://handsonreact.com/docs/architecture
Key Concepts - Components / JSX
- Components - reusable, independent pieces of UI
- JSX - A syntax extension that allows mixing HTML with JavaScript
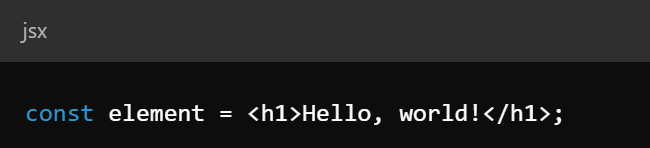
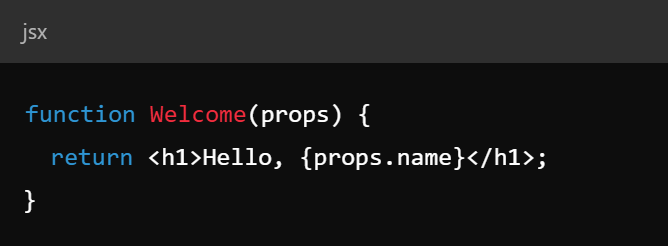
Key Concepts - State and Props
- State - mutable data managed within components
- Props - read-only data passed to components
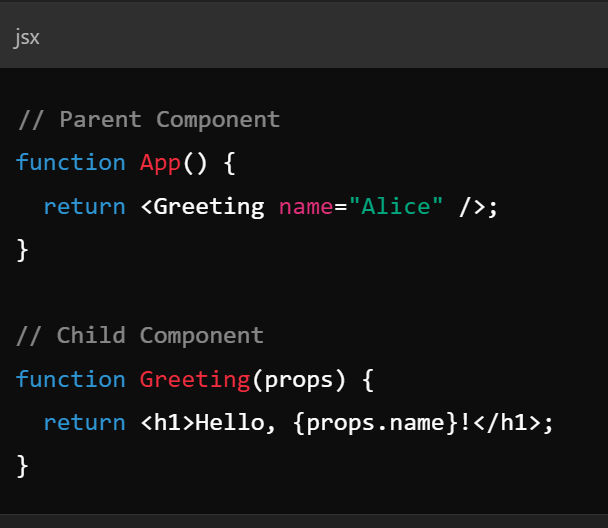
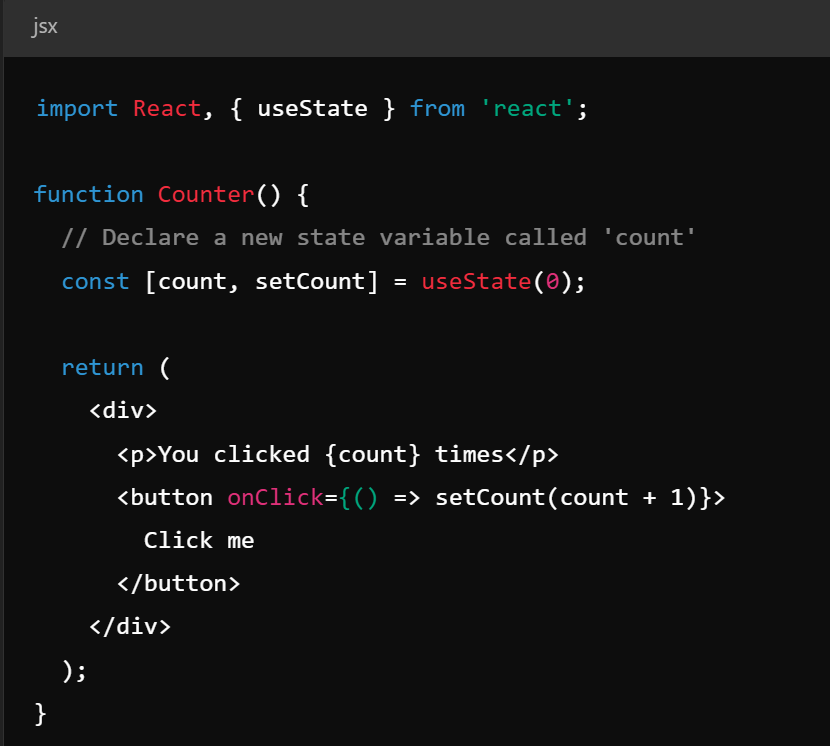
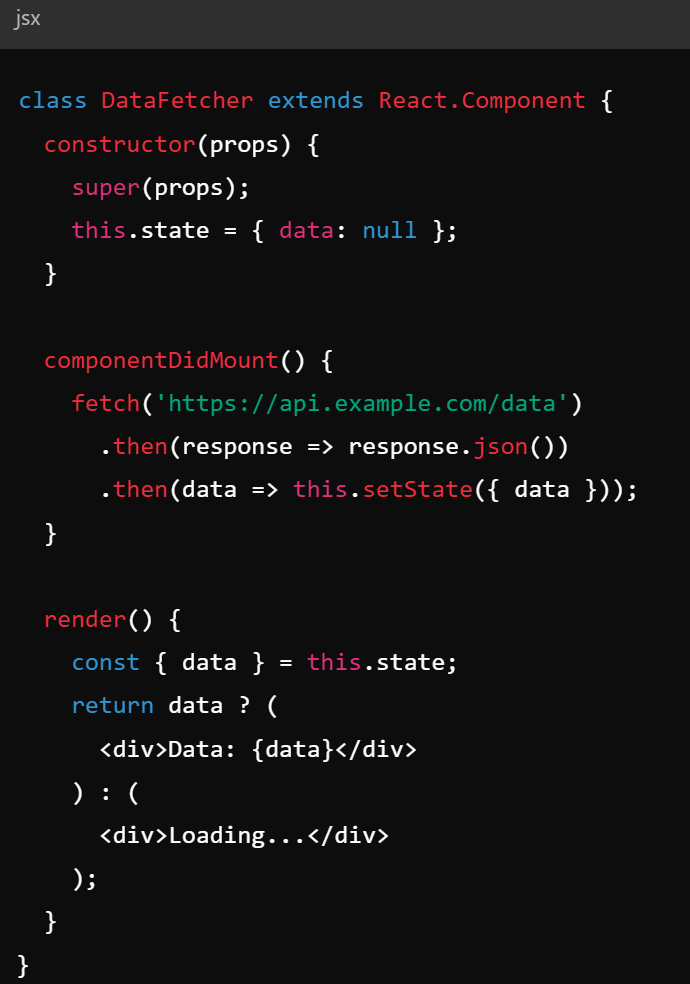
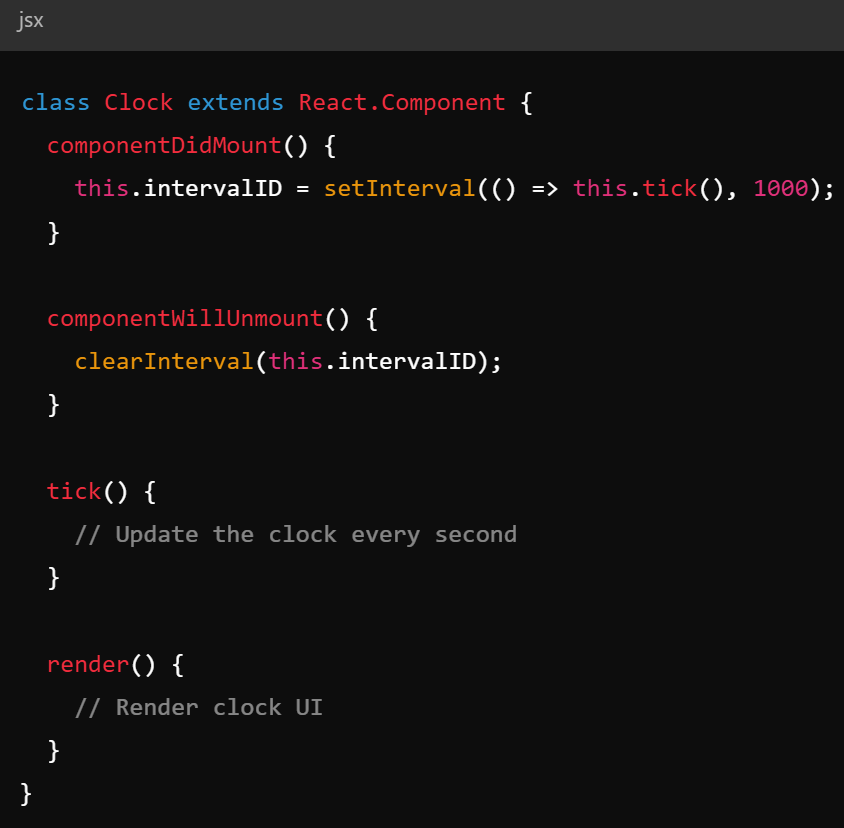
Key Concepts - Lifecycle Methods
- Lifecycle methods - invoked at different stages of a components life
- React components go through at least 3 phases
- Mounting (componentDidMount())
- Updating (componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState))
- Unmounting (componentWillUnmount())
- Functions allow operations on these states

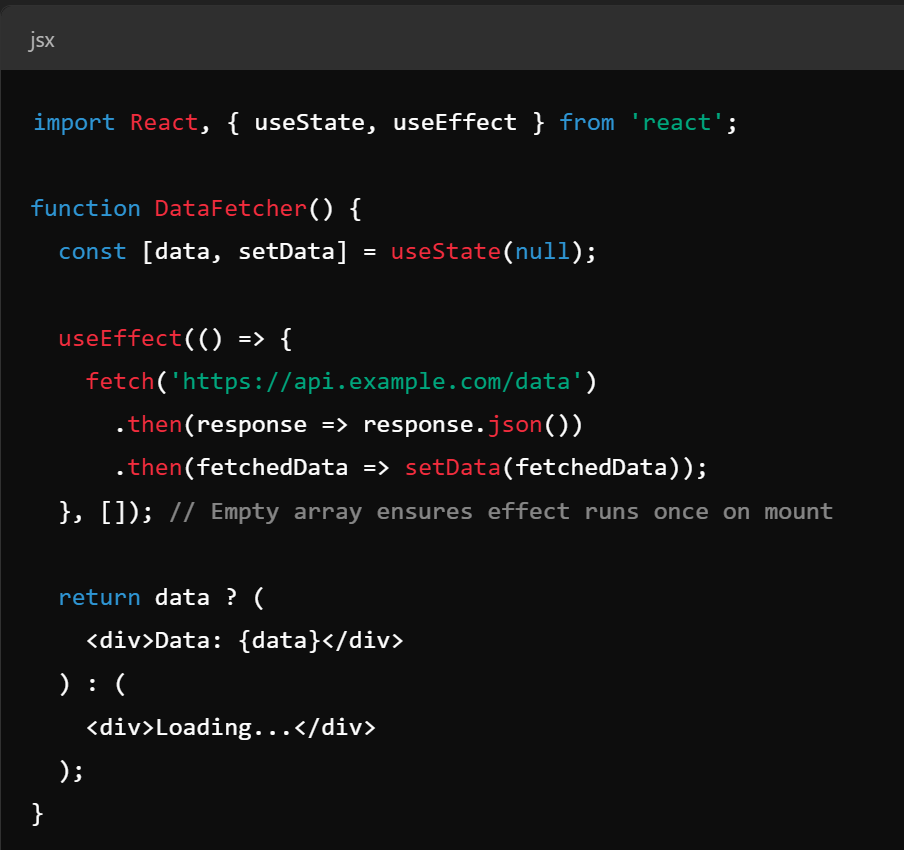
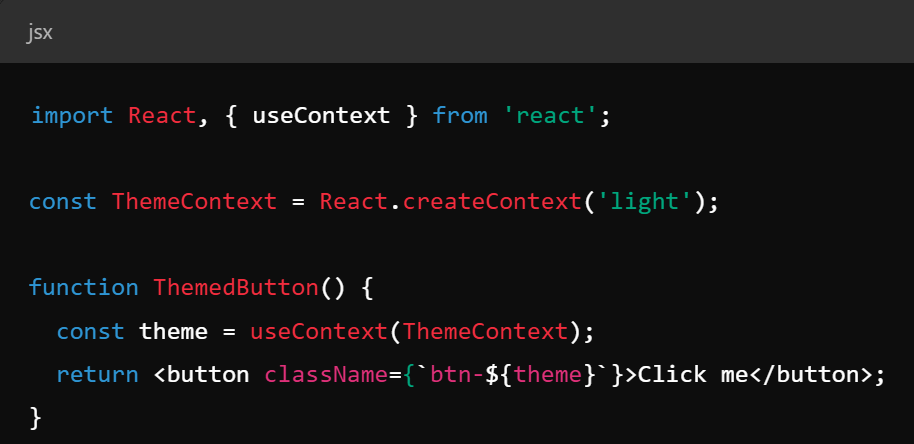
Key Concepts - Hooks
- In newer react (16.8+, current version is 18 at time of writing), the concept of "hooks" has been introduced to allow state management without a class
- eliminates the need for class components
- reuses stateful logic between components
- useEffect, useContext, useState most common
Questions?
©2024 Matthew L. Hale


Matt Hale, PHD
University of Nebraska at Omaha
Associate Professor, Cybersecurity
Director, School of Interdisciplinary Informatics
Director, NebraskaCYBER
mlhale@unomaha.edu
twitter: X: @mlhale
slides.com/matthale/8470-clientside-frameworks
8470-clientside-frameworks-josh
By Matt Hale
8470-clientside-frameworks-josh
- 57



