CoffeeScript & TypeScript
JavaScript
- Dynamický
- Interpretovaný (JIT)
- Slabě typovaný (typová konverze)
- C-like syntax { } ;
Jazyky kompilované do JavaScriptu
Nejznámnější jazyky:
- CoffeeScript
- Dart (Google - Flutter)
- TypeScript (Microsoft)
Snaží se vyřešit nedostatky JavaScriptu nebo ho zlepšit
CoffeeScript
- vznikl v roce 2009 (Jeremy Ashkenas)
- Kompilovaný do JavaScriptu (syntaktický cukr)
- Založený na programovacích jazycích Ruby a Python
- Neobsahuje ; a {}
- Lepší čitelnost
- Náchylné na bílé znaky
-
npm install --save-dev coffeescript

CoffeeScript - syntax
fibonacci = ->
[previous, current] = [1, 1]
loop
[previous, current] = [current, previous + current]
yield current
return
getFibonacciNumbers = (length) ->
results = [1]
for n from fibonacci()
results.push n
break if results.length is length
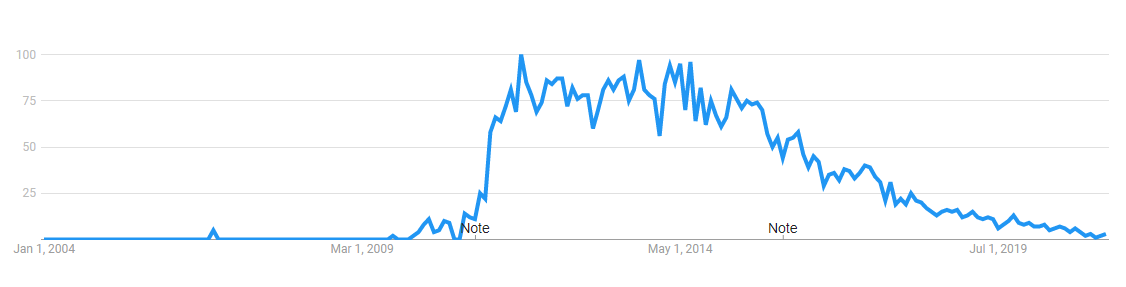
resultsCoffeeScript - Google Trends
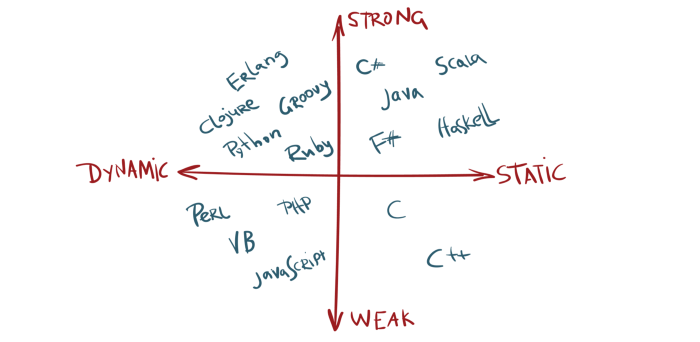
Typování v prog. jazycích
Nedostatky JavaScriptu
"b" + "a" + + "a" + "a"
// "baNaNa"
"2" + 2
// "22"
"2" + "2" - "2"
// 20
4 / []
// Infinity
{} + []
// 0
true - true
// 0
[] == ""
// trueTypeScript

- Microsoft, 2012
- Kompilovaný do JavaScriptu
- Přináší statické typy
- Je nadmnožinou JavaScriptu
- Google, Airbnb, Slack
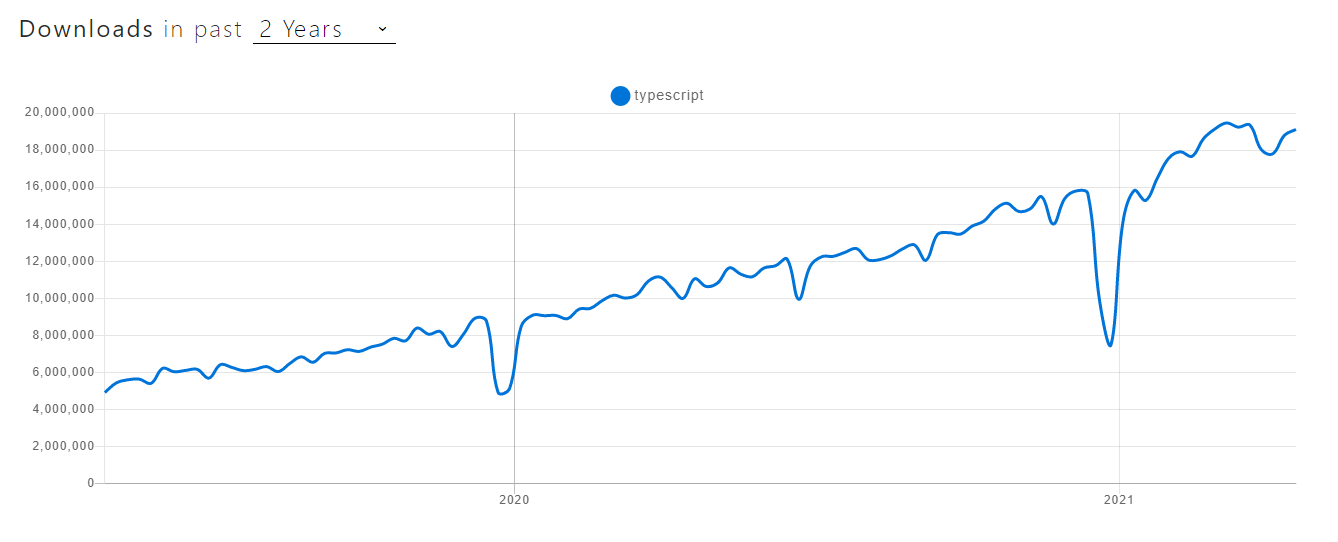
TypeScript - NPM trends
TypeScript - Výhody
- Typová bezpečnost
- Chyby při kompilaci
- Hybrid mezi dynamicky a staticky typovaným jazykem
- Nadmnožina JavaScriptu
- Autocomplete v IDE
- Konfigurovatelnost
- Implicitní typování
- Code managment
- Využití novějších verzí JavaScriptu (např. ES6)
const obj = { width: 10, height: 15 };
const area = obj.width * obj.heigth;
// Property 'heigth' does not exist on type
// '{ width: number; height: number; }'.
// Did you mean 'height'?TypeScript - Nevýhody
- Komplikovaný typový systém
- Požadovaná kompilace
- Větší objem kódu
- Setup

TypeScript - Jak začít
- Visual Studio Code
- npm -install -D typescript
- tsc --init (vytvoří tsconfig.json)
- tsc fileToCompile.ts
- npx create-react-app my-app --template typescript
tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Visit https://aka.ms/tsconfig.json to read more about this file */
/* Basic Options */
"incremental": true /* Enable incremental compilation */,
"target": "es5" /* Specify ECMAScript target version: 'ES3' (default), 'ES5', 'ES2015', 'ES2016', 'ES2017', 'ES2018', 'ES2019', 'ES2020', or 'ESNEXT'. */,
"module": "commonjs" /* Specify module code generation: 'none', 'commonjs', 'amd', 'system', 'umd', 'es2015', 'es2020', or 'ESNext'. */,
"lib": [] /* Specify library files to be included in the compilation. */,
"allowJs": true /* Allow javascript files to be compiled. */,
"checkJs": true /* Report errors in .js files. */,
"jsx": "preserve" /* Specify JSX code generation: 'preserve', 'react-native', 'react', 'react-jsx' or 'react-jsxdev'. */,
"declaration": true /* Generates corresponding '.d.ts' file. */,
"declarationMap": true /* Generates a sourcemap for each corresponding '.d.ts' file. */,
"sourceMap": true /* Generates corresponding '.map' file. */,
"outFile": "./" /* Concatenate and emit output to single file. */,
"outDir": "./" /* Redirect output structure to the directory. */,
"rootDir": "./" /* Specify the root directory of input files. Use to control the output directory structure with --outDir. */,
"composite": true /* Enable project compilation */,
"tsBuildInfoFile": "./" /* Specify file to store incremental compilation information */,
"removeComments": true /* Do not emit comments to output. */,
"noEmit": true /* Do not emit outputs. */,
"importHelpers": true /* Import emit helpers from 'tslib'. */,
"downlevelIteration": true /* Provide full support for iterables in 'for-of', spread, and destructuring when targeting 'ES5' or 'ES3'. */,
"isolatedModules": true /* Transpile each file as a separate module (similar to 'ts.transpileModule'). */,
/* Strict Type-Checking Options */
"strict": true /* Enable all strict type-checking options. */,
"noImplicitAny": true /* Raise error on expressions and declarations with an implied 'any' type. */,
"strictNullChecks": true /* Enable strict null checks. */,
"strictFunctionTypes": true /* Enable strict checking of function types. */,
"strictBindCallApply": true /* Enable strict 'bind', 'call', and 'apply' methods on functions. */,
"strictPropertyInitialization": true /* Enable strict checking of property initialization in classes. */,
"noImplicitThis": true /* Raise error on 'this' expressions with an implied 'any' type. */,
"alwaysStrict": true /* Parse in strict mode and emit "use strict" for each source file. */,
/* Additional Checks */
"noUnusedLocals": true /* Report errors on unused locals. */,
"noUnusedParameters": true /* Report errors on unused parameters. */,
"noImplicitReturns": true /* Report error when not all code paths in function return a value. */,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true /* Report errors for fallthrough cases in switch statement. */,
"noUncheckedIndexedAccess": true /* Include 'undefined' in index signature results */,
"noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature": true /* Require undeclared properties from index signatures to use element accesses. */,
/* Module Resolution Options */
"moduleResolution": "node" /* Specify module resolution strategy: 'node' (Node.js) or 'classic' (TypeScript pre-1.6). */,
"baseUrl": "./" /* Base directory to resolve non-absolute module names. */,
"paths": {} /* A series of entries which re-map imports to lookup locations relative to the 'baseUrl'. */,
"rootDirs": [] /* List of root folders whose combined content represents the structure of the project at runtime. */,
"typeRoots": [] /* List of folders to include type definitions from. */,
"types": [] /* Type declaration files to be included in compilation. */,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true /* Allow default imports from modules with no default export. This does not affect code emit, just typechecking. */,
"esModuleInterop": true /* Enables emit interoperability between CommonJS and ES Modules via creation of namespace objects for all imports. Implies 'allowSyntheticDefaultImports'. */,
"preserveSymlinks": true /* Do not resolve the real path of symlinks. */,
"allowUmdGlobalAccess": true /* Allow accessing UMD globals from modules. */,
/* Source Map Options */
"sourceRoot": "" /* Specify the location where debugger should locate TypeScript files instead of source locations. */,
"mapRoot": "" /* Specify the location where debugger should locate map files instead of generated locations. */,
"inlineSourceMap": true /* Emit a single file with source maps instead of having a separate file. */,
"inlineSources": true /* Emit the source alongside the sourcemaps within a single file; requires '--inlineSourceMap' or '--sourceMap' to be set. */,
/* Experimental Options */
"experimentalDecorators": true /* Enables experimental support for ES7 decorators. */,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true /* Enables experimental support for emitting type metadata for decorators. */,
/* Advanced Options */
"skipLibCheck": true /* Skip type checking of declaration files. */,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true /* Disallow inconsistently-cased references to the same file. */
}
}
Základní typy
- undefined
- null
- boolean
- number
- string
- object
const a: undefined = undefined;
const b: null = null;
const c: boolean = true;
const d: number = 5;
const e: string = "hey!";
const f: object = {};any vede ke ztrátě výhod TypeScriptu
const anything: any = {};
console.log(anything.prop);Pole
const numberArray1: number[] = [1, 2, 3];
const numberArray2: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3];- Genericlý typ
- typ zapisujeme do špičatých závorek
Funkce
const add = (a: number, b: number): number => a + b;- Typy vstupu
- Typ výstupu (TypeScript umí automaticky odvozovat)
- Možnost definice typu celé funkce
type Add = (a: number, b: number) => number;
const add: Add = (a, b) => a + b;Optional Properties
const addNumbers = (a: number, b?: number) => {
b = b || 0; // b je typu number | undefined
return a + b; // b je typu number
};
const obj: { name: string; age?: number } = { name: "John" };- Typ je potencionálně undefined
- Musíme kontrolovat před použitím
Union Types
let unionType: number | boolean;
unionType = 5;
unionType = true;
// unionType = "Hello world" by vedlo k chybě- Vymezení několika různých typů
- Využití dynamičnosti
Typový alias
type CarBrand = "ferrari" | "audi" | "porsche" | "bmw";
interface Car {
brand: CarBrand;
speed: number;
}
// (car: Car) => CarBrand
const getCarBrand = (car: Car) => {
return car.brand;
};
const getCarSpeed = (car: Car) => {
return car.speed;
};- Znovupoužitelné typy
- Type alias: Jméno pro typ / Pojmenování typu
Interface
interface Car {
brand: CarBrand;
speed: number;
}
interface Car {
price: number;
}
const car: Car = {
brand: "audi",
speed: 200,
price: 1000000,
};- Na rozdíl od typového aliasu je možné ho rozšiřovat
- Popis rozhraní pro komunikaci uvnitř aplikace i mimo ni
Type assertions
const myCanvas = document.getElementById("main_canvas") as HTMLCanvasElement;
// nelze: const x = "hello" as number;- Pomocí slovíčka as
- Pouze na více nebo méně specifický typ
- Nelze kompletně změnit typ
- Využití pro popsání typu o kterém TypeScript nemůže vědět
Literal types
type CarBrand = "ferrari" | "audi" | "porsche" | "bmw";
const brand: CarBrand = "audi";- Přímo určené specifické hodnoty, kterých může proměnná nabývat
- Možné použít pro řetězce a čísla
Literal types - as const
const myObj = { method: "POST" } as const;
const foo = (a: "GET" | "POST") => {
console.log(a);
};
foo(myObj.method);- nelze přiřadit typ string do typu konkrétního řetězce (literal type)
- můžeme použít as const pro konverzi celého objektu na type literal
Kontrola pomocí typeof
function printId(id: number | string) {
if (typeof id === "string") {
// In this branch, id is of type 'string'
console.log(id.toUpperCase());
} else {
// Here, id is of type 'number'
console.log(id);
}
}- typeof vrací název typu jako řetězec
- "string", "boolean", "number" ...
- Vhodné pro vyloučení určitých typů proměnné
Rozšiřování typů
interface BasicAddress {
name?: string;
street: string;
city: string;
country: string;
postalCode: string;
}
interface AddressWithUnit extends BasicAddress {
unit: string;
}- klíčové slovo extends
- možné rozšířit více typů oddělených čárkou
Intersection
interface Base {
print: (value: number) => number;
}
type Intersected = Base & {
print: (value: string) => string;
};
// -- error --
// interface Extended extends Base {
// print: (value: string) => string;
// }- Pomocí &
- Podobné rozšiřovaní pomocí extends
Generické typy
interface Box<T> {
content: T;
}
const booleanBox: Box<boolean> = {
content: true,
};
const stringBox: Box<string> = {
content: "lorem ipsum",
};- Příklad: Array<T>
- Pro type alias i interface
Typy pro knihovny
- Pro většinu knihoven jsou typy již definované
- Repozitář DefinitelyTyped
- Poskytuje typy pro existující JavaScript
- npm install --save-dev @types/node
Kdy použít TypeScript
- Větší aplikace
- Týmové projekty
Kdy TypeScript nemusí být výhodou
- Malé aplikace
- Sólo projekty
Nicméně je těžké argumentovat pro jeho nepoužití, jelikož se jedná o nadmnožinu JavaScriptu a můžeme si vybrat, kdy chceme typové kontroly využít
To je vše
zdroje:
CoffeeScript & TypeScript
By Michal Čížek
CoffeeScript & TypeScript
- 56


