Full Stack Development in JavaScript

stackoverflow.com
stackoverflow.com
stackoverflow.com
stackoverflow.com
stackoverflow.com
stackoverflow.com
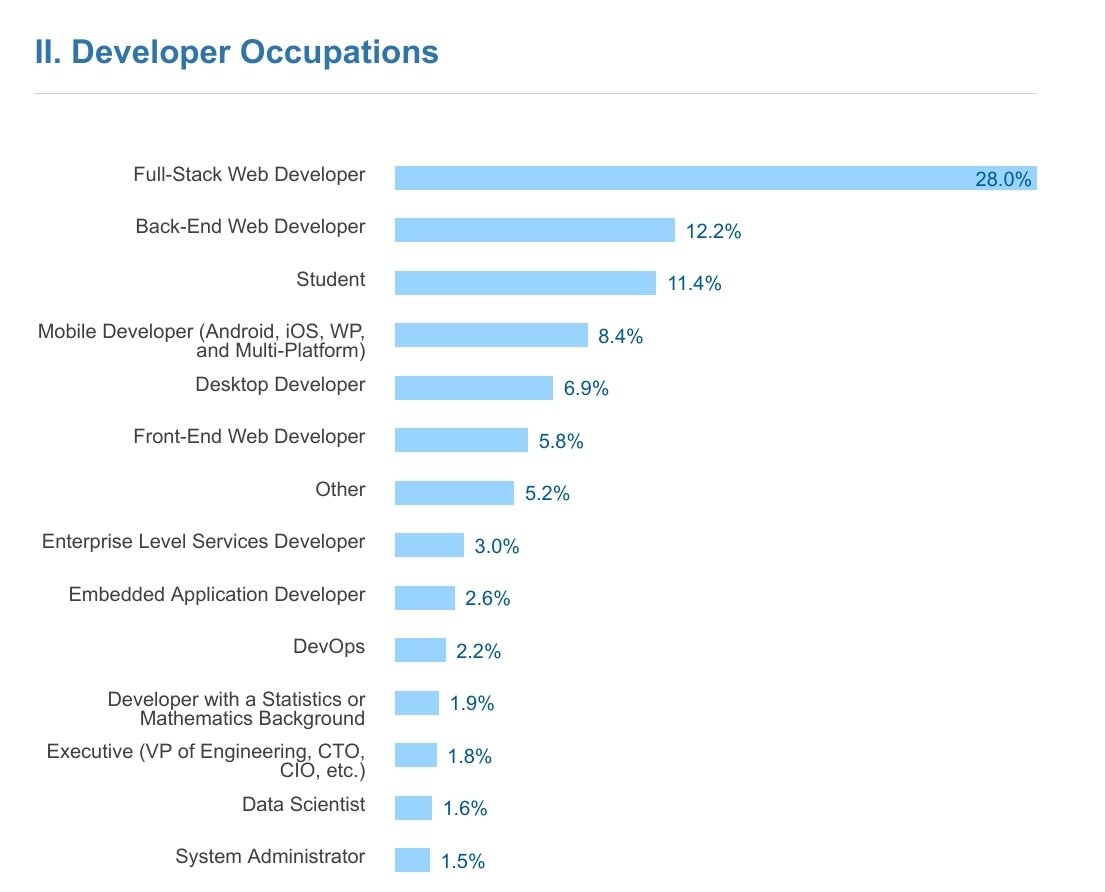
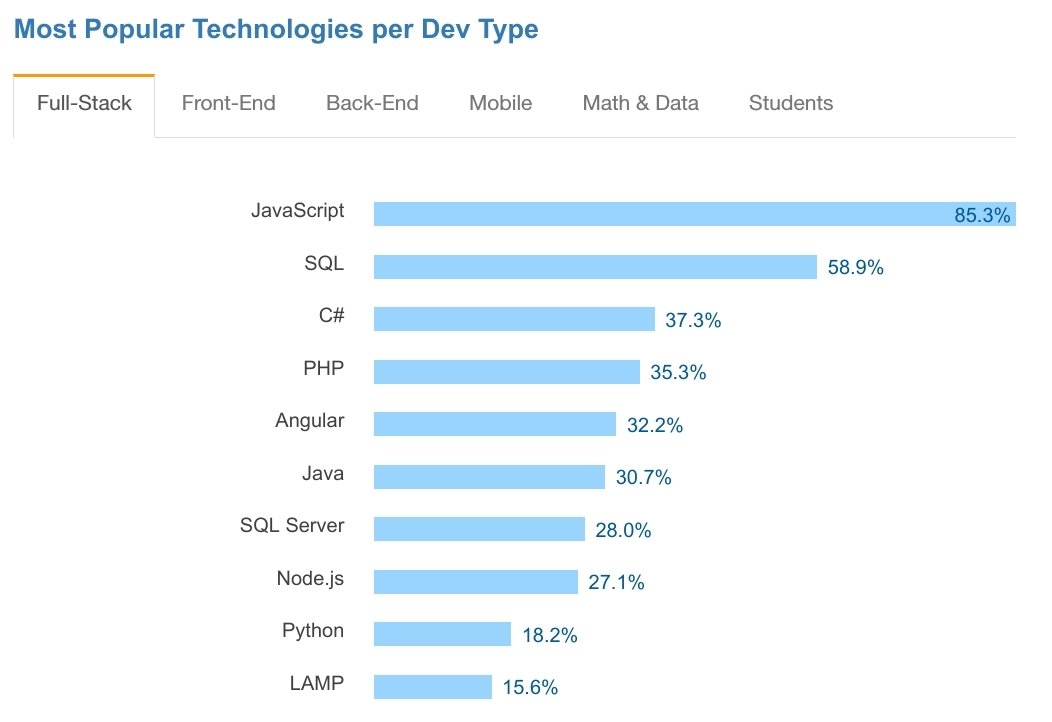
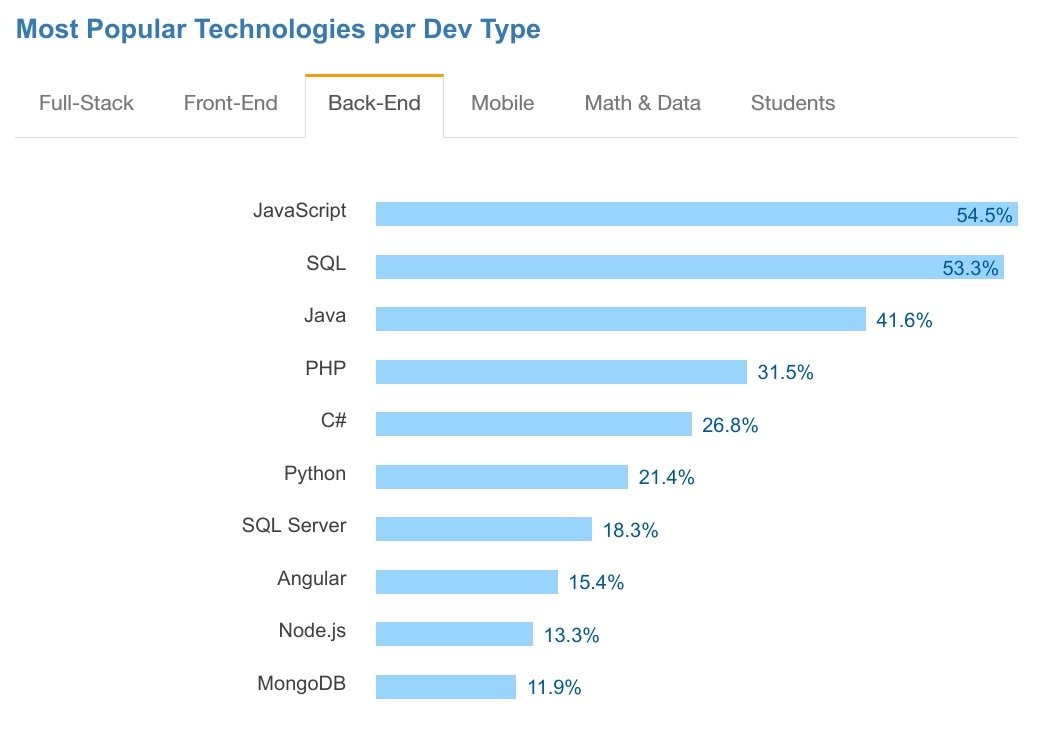
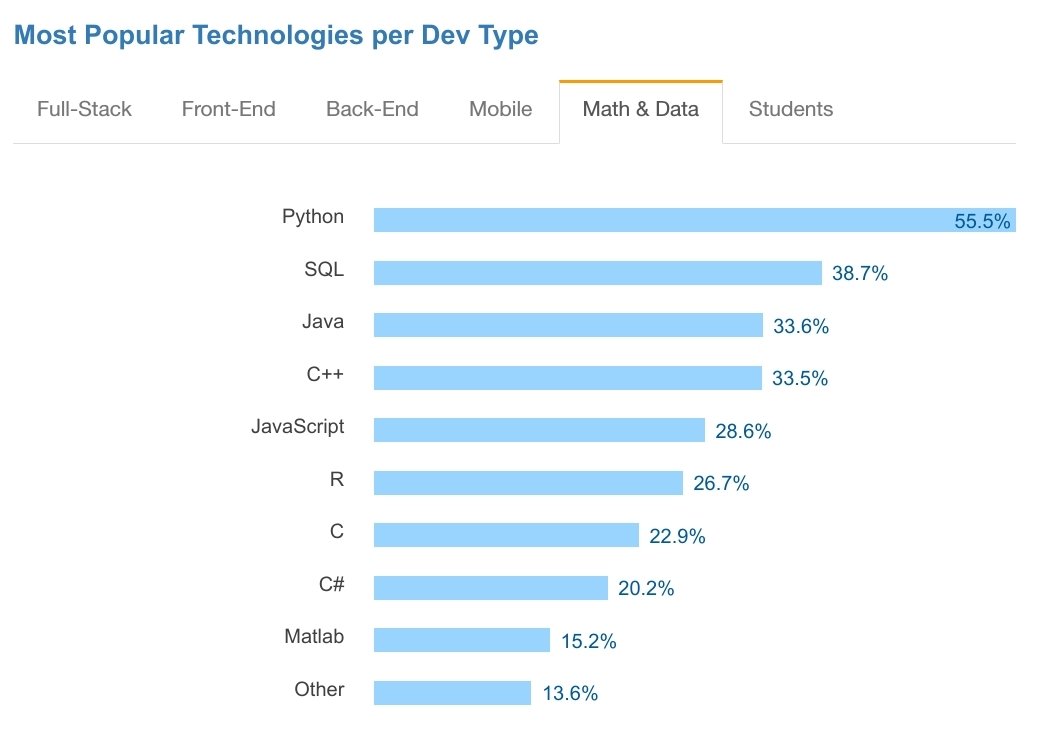
Full Stack Development

Why JavaScript?
- native scripting language in the browser
- first class server support (Node.js)
- same language for backend and frontend
- JSON as native data structure
- asynchronous IO and network operations
- best practices learned from Java are applicable
- dynamic language
- multi-paradigm language
- procedural programming
- object-oriented programming
- functional programming
- reactive programming (with RxJS)
Why NOT JavaScript?
- single-threaded in the browser
- use webworkers for background work
- implementation differencies in browsers
- use shims, frameworks, compile to ES5
- single-threaded on server
- IO and network operations are non-blocking
- run process per core
- front end code is visible to everyone
- use uglify
- too dynamic language
- here comes TypeScript
We can live with it

JavaScript vs ECMAScript
ECMAScript versions
- ES3 - old browsers
- ES5 - current browsers
-
ES6 (ES2015) - major release
- classes, modules, generators, promises, import/export
- compiling to ES5 by Babel
- ES7 (ES2016) - Array includes, exponential operator **
- ES8 (ES2017) - async/await
- ES.Next - dynamic name for next proposals

JavaScript implementations
| Implementation | Applications | ECMAScript edition |
|---|---|---|
| SpiderMonkey | Firefox, Gecko layout engine, Adobe Acrobat | 2017 |
| V8 | Google Chrome, Node.js, Opera | 2016, features from 2017 |
| JavaScriptCore | WebKit, Safari, Qt 5 | 2017 |
| Chakra | Microsoft Edge | 5.1, features from 2015, 2016 and 2017 |
| JScript 9.0 | Internet Explorer, Trident layout engine | 5.1 |
| Nashorn | Java | 5.1 |
Functional JavaScript
First-class functions
-
Pass functions as parameters into other functions
-
Assign function as a value to a variable
- Return a function from other function
function runFunction(fn, data) {
return fn(data);
}var myFunc = function() {
// do something
}
const myArrowFunc = param => param * param;function sumFn() {
return function(a, b) { return a + b };
}First-class functions
Callbacks and non-blocking IO
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('./myFile.txt', 'utf-8', function(err, data) {
// this is a callback, it gets executed
// once the file has been read
});First-class functions
Simple dependency injection
// fetch.js
import axios from 'axios';
export function fetchSomething(fetch = axios) {
return fetch('/get/some/resource');
}// someModule.js
import { fetchSomething } from './fetch';
fetchSomething()
.then(/* do something */)
.catch(/* handle error */);// someOtherModule.js
import axios from 'axios';
import { fetchSomething } from './fetch';
const fetcherWithHeaders = axios({
// pass some custom config
timeout: 1000
});
fetchSomething(fetcherWithHeaders)
.then(/* do something */)
.catch(/* handle error */);Functional JavaScript
Higher-order functions
- takes one or more functions as arguments
- returns a function as its result
Functional JavaScript
Higher-order functions
-
Python example
- JavaScript example
>>> def add3(x):
... return x + 3
>>> def twice(f):
... return lambda x: f(f(x))
>>> g = twice(add3)
>>> g(7)
13function add3(v) {
return v + 3;
}
function twice(f) {
return function (v) {
return f(f(v));
}
}
var g = twice(add3);
console.log(g(7)); // 13Functional JavaScript
Higher-order functions
-
Python example
- ES6 example
>>> def add3(x):
... return x + 3
>>> def twice(f):
... return lambda x: f(f(x))
>>> g = twice(add3)
>>> g(7)
13let add3 = v => v + 3;
let twice = f => v => f(f(v));
let g = twice(add3);
console.log(g(7)); // 13Higher-order functions
Array#map
const myArr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ];
const mappedArr = myArr.map(num => num * num);
console.log(mappedArr);
// [ 1, 4, 9, 16 ]const myArr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ];
const mappedArr = myArr.map(function(num) {
return num * num;
});
console.log(mappedArr);
// [ 1, 4, 9, 16 ]ES6
const myArr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ];
const mappedArr = myArr.map(num => num * num)
.map(num => num - 1);
console.log(mappedArr);
// [ 0, 3, 8, 15 ]Higher-order functions
Array#filter
const myArr = [ 5, 10, 4, 50, 3 ];
const multiplesOfFive = myArr.filter(num => num % 5 === 0);
console.log(multiplesOfFive);
// [ 5, 10, 50 ]const myArr = [ 5, 10, 4, 50, 3 ];
const multiplesOfFive = myArr.filter(function(num) {
return num % 5 === 0;
});
console.log(multiplesOfFive);
// [ 5, 10, 50 ]ES6
Higher-order functions
Array#reduce
const myNumbers = [ 1, 2, 5 ];
const sum = myNumbers.reduce((sum, num) => sum + num, 0);
console.log(sum); // 8const myWords = [ 'These', 'all', 'form', 'a', 'sentence' ];
const sentence = myWords.reduce((res, word) => {
return res + ' ' + word
});
console.log(sentence);
// 'These all form a sentence'Higher-order functions
- No loops
- Side-effect free
- Declarative Code Optimisations
- Effective Functional JavaScript
var newArr = [];
var myArr = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
for(var i = 0; i < myArr.length; i++) {
newArr.push(myArr[i] * 2);
}
console.log(newArr); // [ 2, 4, 6 ]const double = x => x * 2;
const doubled = myArr.map(double);
console.log(doubled); // [ 2, 4, 6 ]More about Functional programming
JavaScript modules
- unit of independent, reusable code
- exports a value
- object literal
- function
- constructor
- string (HTML, CSS, ...)
- modules are singletons
- if module is imported multiple times, only single instance exists
- necessary for building non-trivial JavaScript application
JavaScript modules
-
relative paths
('../model/user') -
absolute paths
('/lib/js/helpers') -
module names
('lodash')
JavaScript modules
- CommonJS
- AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
- UMD (Universal Module Definition)
- ES6
JavaScript modules
var customerStore = require('store/customer');
var when = require('when');
module.exports = function (id) {
return when(id).then(customerStore.load);
};- CommonJS
- AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
- UMD (Universal Module Definition)
- ES6
JavaScript modules
define(['store/customer', 'when'], function (customerStore, when) {
return function (id) {
return when(id).then(customerStore.load);
};
});- CommonJS
- AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
- UMD (Universal Module Definition)
- ES6
JavaScript modules
- CommonJS
- AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
- UMD (Universal Module Definition)
- ES6
(function (root, factory) {
// AMD
if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
define(['jquery', 'lodash'], factory);
// CommonJS
} else if (typeof exports === 'object') {
module.exports = factory(require('jquery'), require('lodash'));
// Window global
} else root.share = factory(root.jquery, root.lodash);
}(this, function ($, _) {
// Return public API
return {};
}));
JavaScript modules
import { load } from 'store/customer';
import when from 'when';
export default = function (id) {
return when(id).then(load);
};- CommonJS
- AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
- UMD (Universal Module Definition)
- ES6
JavaScript tools
- package manager
- IDE
- compiler
- task runner
- module bundler
- test tools












Node.js
-
JavaScript cross-platform runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine
- executing JavaScript server-side
-
uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient
-
Node.js' package ecosystem, npm, is the largest ecosystem of open source libraries in the world
- open-source

Install Node.js
- install via download page
https://nodejs.org/en/download/
- Ubuntu: install default version
- Ubuntu: install using PPA (recommended)

sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nodejs
sudo apt-get install npmcurl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_7.x -o nodesource_setup.sh
sudo bash nodesource_setup.sh
sudo apt-get install nodejs
sudo apt-get install build-essentialNode.js versions
- install n tool (may need sudo)
- install latest node.js version
- Install specific version
- Select from available versions (use arrows and enter)

sudo npm install -g nsudo n latestsudo n 7.10.0sudo n
node/6.9.1
ο node/7.10.0
node/0.12.7Node package manager
Already installed with node.js
Install package globally
npm install -g typescriptInitialize new package
- wizard for package name, version, license, etc.
- creates package.json
npm init
Install package locally
-
installs package into local
node_modulesdirectory -
save package to
"dependencies"intopackage.json -
use
--save-devto save into"devDependencies"
npm install --save lodashInstall all packages in
package.json
npm installNode package manager
Typical
package.json will look similar
{
"name": "typescript-starter",
"version": "1.6.0",
"license": "MIT",
"main": "build/index.js",
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc -p tsconfig.json",
"docs:html": "typedoc src/index.ts --mode file --out build/docs",
"version": "npm run build && npm publish --access restricted",
"postversion": "git push --follow-tags"
},
"dependencies": {
"tslib": "^1.6.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^8.0.4",
"typedoc": "^0.7.1",
"typescript": "^2.4.1"
}
}

Run script from package.json:
-
all installed packages in
node_modulesare available for script
npm run buildNode package manager

Remove package locally
-
remove package from local
node_modulesdirectory -
remove package from
"dependencies"in thepackage.json -
use
--save-devfor"devDependencies"
npm uninstall --save lodashLink local package as global dependency (may need sudo)
- e.g. inside ncbin-reader directory
npm linkUse linked package in other package
-
useful for local testing of packages
without publishing a package
npm install --save ncbin-reader
npm link ncbin-readerNode package manager

Release new version
- before releasing make sure all changes are committed into git
-
increase the
patchpart of versionmajor.minor.patch,
e.g.1.6.1 -> 1.6.2 -
Use one of following identifiers:
major | minor | patch | premajor | preminor | prepatch | prerelease | from-git | <specific-version>
npm version patch -m "message"Running npm version will do following tasks:
-
run
preversionscript -
bump version in
package.json -
run
versionscript - commit changes to Git
- create a git tag for newly created version
-
run
postversionscript
Node package manager

Push new version tag to Git
git push --follow-tagsPublish new version to npm
npm publishThese tasks can be automatized in postversion script in
package.json
{
...
"scripts": {
...
"postversion": "git push --follow-tags && npm publish"
}
}JavaScript frameworks


















CSS frameworks
- CSS engine
- Design & Layout









Full Stack JavaScript
By Michal Moravcik
Full Stack JavaScript
- 170