Sports Nutrition
By Mital Patel (1506758)
What are Nutrients
There are two main catergories for the nutrients and how they are divided:
Macronutrients which are the Carbohydrates, Fats and Protein.
Micronutrients which are the Vitamins and Minerals.
What are Macronutrients
•Macro Nutrients are substances that are used for the energy, growth and functions by the organisms. Depending on the nutrients there are small or large amounts which are needed and the macronutrients are the ones which are usually the larger quantity.
•The three different types of macronutrients which are required for a human are carbohydrates, Protein and Fats:
•Carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are the ones which mainly consists of sugars and starch, which is used as a energy system to the human body
•Protein – Proteins are a substance which is found in a wide range of food such as meats, eggs, fish, which will allow the body to grow and become stronger.
•Fats – Another name for fats is lipids and they are a substance which is found in both solids and liquids, it contains Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen which allows the body to use the energy

What are Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are the ones which mainly consists of sugars and starch, which is used as a energy system to the human body. Carbohydrates can be healthy and unhealthy. Some of the food which is known to be high in Carbohydrates is bread, beans, rice, potatoes, pasta, milk, and many other foods. Any of the food which is high in carbohydrates is very important in a healthy diet. The food which is high in carbohydrates is good for the body because it is giving the body a source of glucose and then the body converts the glucose into energy for the body to use.
In the healthier side of the carbohydrates includes the food such as whole grain foods, vegetables, fruits and beans, this is because they are good at delivering vitamins, minerals and fibres and that they are good for your body; but on the hand the unhealthier side of carbohydrates is eating the foods which are not as great for you which are, white bread, pastries, fizzy drinks and refined food, such as refined sugars.
The daily amount of carbohydrates for all humans to intake is:
•Males – 300g of carbohydrates a day
•Females – 230g of carbohydrates a day
•Children (5-10 years old) – 220g of carbohydrates a day

What are Proteins?
Proteins - are found all around the body, places such as your muscles, bones, skin, hair and near enough every part of the body or the tissue on the body. You need proteins to maintain a healthy diet as it will help repair the cells and replace the ones that have been damage; proteins are also very important for the growth of children, teens and woman.
The main type of acid which is needed by the body is amino acids which are found mainly in animal sources such as meat, eggs, milk and fish, but an alternative for those who are vegetarian and they do not eat meat or chicken, they can eat things such as soy, beans, grains and many other things as well.
•Essential Amino Acids are acids which cannot be made by the body but they have to be made by the food that you eat. The Nonessential Amino acids are the acids which are made by the body and has a normal break down of the proteins. The Conditional Amino acids is the acids which are used to treat an illness and any types of stress.
The daily amount of proteins for a human is:
•Males – 55g of protein a day
•Females – 45g of protein a day
•Children (5-10 years old) – 24g of protein a day

What are Fats?
Fats- another name for fats is lipids and they are hydrocarbons which are making the structure and the functions of the living cells and there are three types of fats and they are unsaturated fats, saturated fats and trans fat. Unsaturated Fats – There are two types of unsaturated fats and they are Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated. The monounsaturated fats are fats that are high in concentration. The food which is categorised as avocado, olives, nuts such as almonds and also seeds such as pumpkin seeds; on the other hand the second type is polyunsaturated and this is when they are high in concentration and some of the food that can be categorised in this is sunflower seeds, walnuts and flax seeds. Saturated fats – Most meals such as chicken has a small amount of saturated fat, but it has not got as much compared to foods such as beef and cheese. Saturated fats are mainly in meat items such as beef, meat, chicken, but it is also found in some plant foods such as coconuts, coconut oils. Refined carbohydrates which is foods which is good for you as it reduces LDL cholesterol, but it is has a worse effect rather than the saturated fats having a bad impact on the heart. Trans Fats – would usually occurs when heating up vegetable oil, but they do smell like something has gone off, it turns the oils into to solids which can then be used for things such as margarine; even when hydrogenated oils is mainly used for cooking such as in restaurants and fast foods restaurants because the oils do not break down when they are being reheated constantly, therefore near enough all restaurants and fast food places use these types of oils as they do a lot of cooking and frying and do not want the oils to break down. The daily amounts of fats for a human is: Males – 95g of fats per day ; Females – 70g of fats per day; children (5-10 years old) – 70g of fats per day.
What are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients only have a small part to the body and the micronutrients are helping the humans develop and also be well. This is including the metabolism, heartbeat and the bone density. If there is a lack of the micronutrients lead to the growth not being the best and also it can lead to many diseases which are caused, the diseases which are caused are lack of vitamin D, lack of vitamin C and lack of Calcium.
There are two types of micronutrients and they are vitamins and minerals.
Vitamins:- vitamins are a group of compounds which are needed for the growth and the nutrition of a diet because they cannot be produced by the body.
Minerals:- minerals are substances which are needed in order to maintain a good health.
What are Vitamins?
Vitamins are vital for the human body and it is needed in small quantities. They are there to stop any diseases which are happening. Many of the vitamins that are in the body are not produced by the body they are coming from what you are eat and the food that you are taking in. Vitamin D is produced by the sunlight coming onto the skin but then there is Vitamin K which is produced by the bacteria in the intestines. The vitamins are needed to maintain the metabolic rate of body and when they are releasing energy. They also support the body in growth, the functions of the nervous system and the production of hormones. A large number of Fat soluble vitamins should not be taken in because it can cause harm to the body and the health.
There are two types of vitamins and they are Fat-soluble vitamins and Water-soluble vitamins:
Fat-soluble Vitamins are vitamins that are found in fatty or oily parts of the food, when they are digested they are then able to get straight to the blood and they don't come out in the urine instead they would be in the liver for example Vitamins A,D,E and K are all categorised in the Fat soluble category.
Water-soluble Vitamins are vitamins which are with your body when it is using the energy, any extra water soluble vitamins are then come out by the urine because there is only limited space in the body. There is many times where the water soluble vitamins are destroying the food being processed and the preparation of the food in the stomach for example Vitamin B and C.
What are Minerals?
Minerals are also known as the non-caloric nutrients which are needed in life and there is a small quantity which is required. All the minerals which are taken into the body are needed in the body because it supports the bones, the connective tissue, enzymes and the hormones. Some of the minerals also help in the function of the nervous system and also do help in the muscle contractions. There are some minerals which are adjusting to the fluid balance in the body. There are two types of minerals and they are Macro minerals and Trace Elements:
The Macrominerals is where there is large amounts of a mineral which is needed. Such as milk which contains Calcium there would be hundreds of milligrams which are needed per day to keep the levels of calcium higher up.
The Trace elements are also known as micro mineral which is when there is a small amount of copper or another element which is needed in the body in order for it to survive.

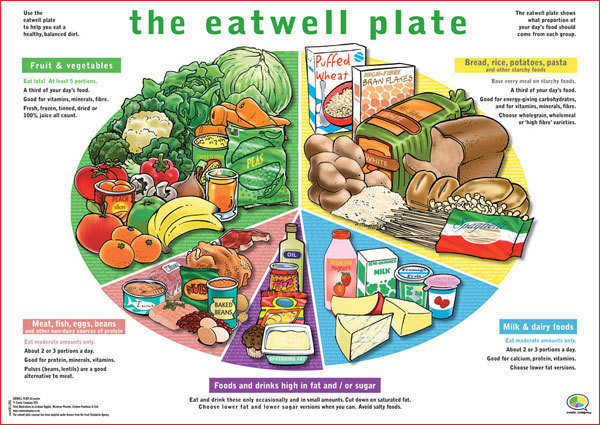
What are the National Nutritional Requirement
.The Government would recommend that all the individuals should consume a diet that contains some of the following:
-
Plenty of starchy foods such as rice, bread, pasta and potatoes
-
Plenty of fruit and vegetables; at least 5 portions of a variety of fruit and vegetables a day
-
Some protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs, beans and non dairy sources of protein, such as nuts and pulses
-
Some milk and dairy, choosing reduced fat versions or eating smaller amounts of full fat versions or eating them less often
-
Just a little saturated fat, salt and sugar
It is seen to be that when recommending the fat, carbohydrates and the fibre the people should have no more than 11% of saturated fatty acids, 6.5% of polyunsaturated fatty acids, 13% monosaturated fatty acids, not more than 2% of the trans fatty acid and not more than 35% of fat. They should have 50% of carbohydrates.
Reference
http://www.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/multimedia/pdfs/nutrientinstitution.pdf; http://www.foodlabel.org.uk/label/gda_values.aspx
http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-macronutrients-definition-functions-examples.html; http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/; http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/protein/; http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/; https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002467.htm; http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/nutrition/fat/overview.html; http://cholesterol.about.com/od/cholesterolnutrition101/f/monovspolyfats.htm; http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/types-of-fat/; http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-micronutrients-definition-types-foods-importance.html; http://www.comiccompany.co.uk/?category=2&collection=134; http://fitnut.in/blog/index.php/the-basics-of-macronutrients/; http://www.34-menopause-symptoms.com/fatigue/articles/vitamins-and-minerals-to-stop-menopausal-fatigue.htm; http://www.beleura.com.au/2015/09/07/the-carbohydrate-phenomenon/; http://www.kshealthyhomes.org/lead_poisoning_prevention.htm; http://www.functionalfitmag.com/blog/2012/07/30/protein-foods-protein-powder-2/; http://www.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/multimedia/pdfs/nutrientinstitution.pdf
sports nutrition
By Mital Patel
sports nutrition
- 852



