Manuel Pichardo Marcano (Fisk/Vanderbilt)
Karan Jani (Vanderbilt)
Detection of the most massive white dwarf mergers with LILA


Double WD Binaries

Caltech/NASA
- Gravitational Wave Sources
- WDs with masses 1.3 to 1.4 M⊙
- Detached
- Circular Orbit
- Porb
- 15 seconds to merge
- fgrav = 2 x forb
Type Ia Supernova
- Type Ia
- Chandrasekhar Mass (Mch = 1.4M⊙)
- Cosmological standard candles
- Hubble Tension
- Heavy-element factories

Accretion-induced Collapse
- Formation of Neutron Stars (e.g. Nomoto et al. 1979)
- Important in GCs (Grindlay et al. 1988)
- Predicted EM:
- Gamma Rays (e.g. Dar et al. 1992)
- Radio (e.g. Piro et al. 2013)
- Optical (Sousa et al. 2023)

NASA, ESA, and J. Anderson (STScI)
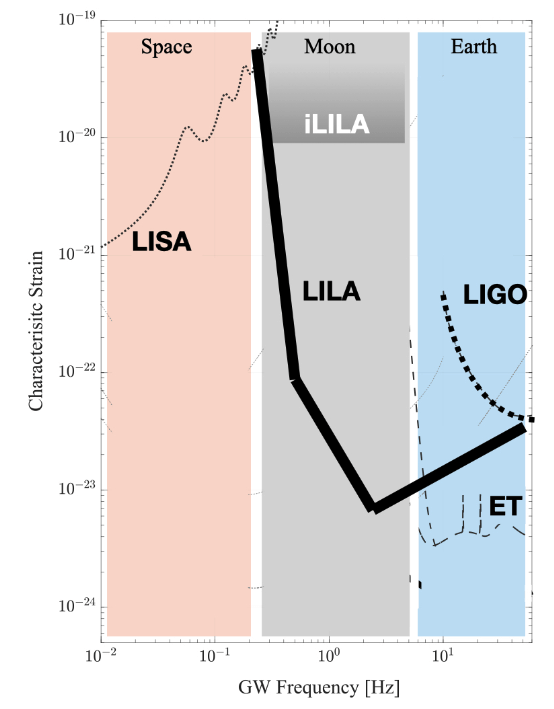
Lunar Gravitational Wave Observatories
- The Lunar Gravitational-wave Antenna (LGWA) (Parameswaran et al. 2024)
- Seismometer
- Laser Interferometer Lunar Antenna (LILA):
- LIGO-like suspension system


Methods

- Evolve WDs with masses 1.3 to 1.4 M⊙
- 4 years before merging:
- Roche-lobe: Lower Mass Fills Roche Lobe
- Contact: a = R1+R2
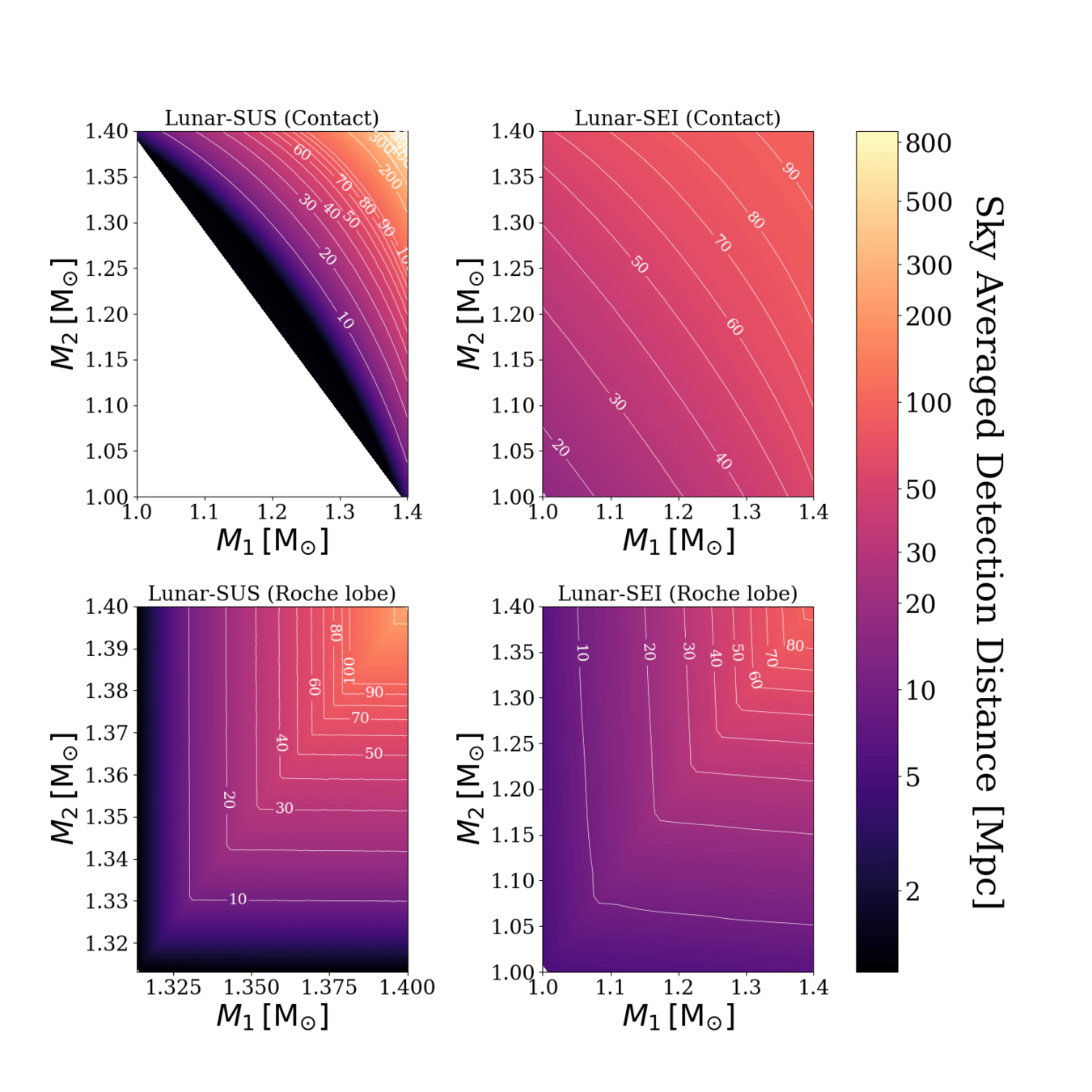
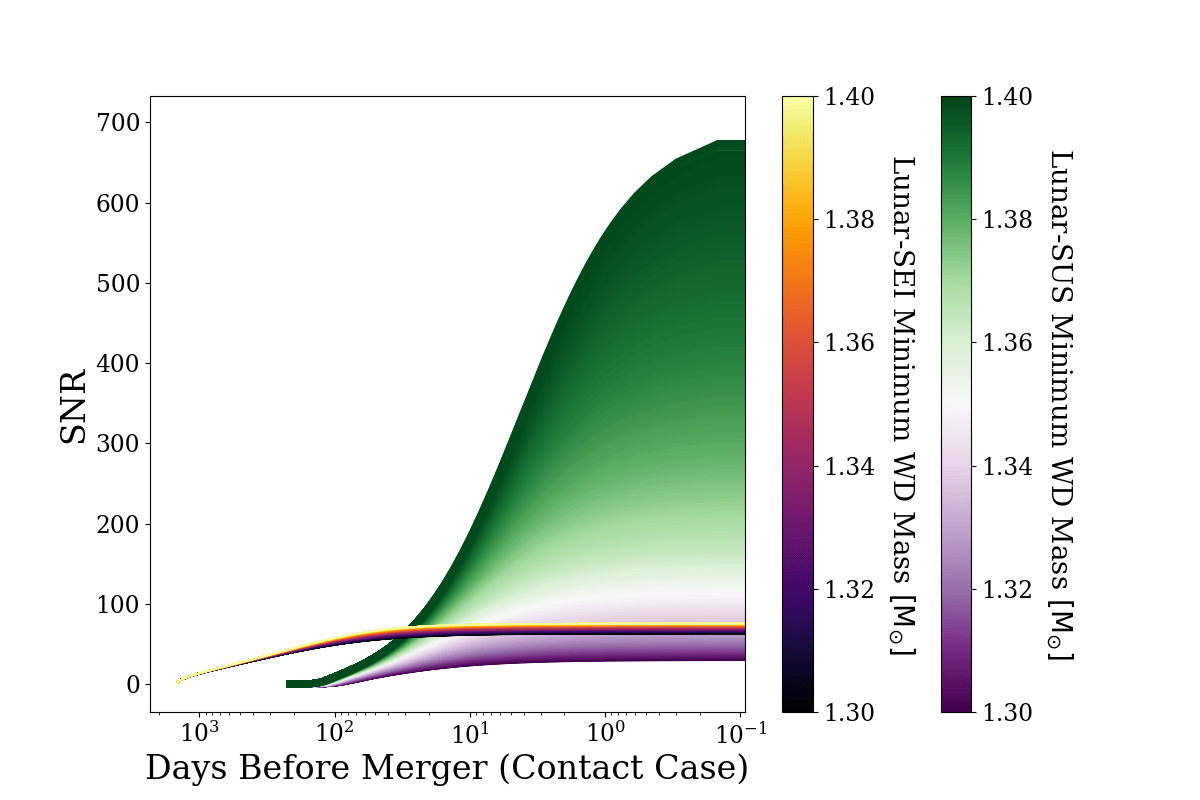
- Calculate SNR for LGWA and Gravitational-Wave Lunar Observatory for Cosmology (GLOC) as a LILA proxy

Wagg et al. (2022)
Dupletsa et al. (2023)
Strain
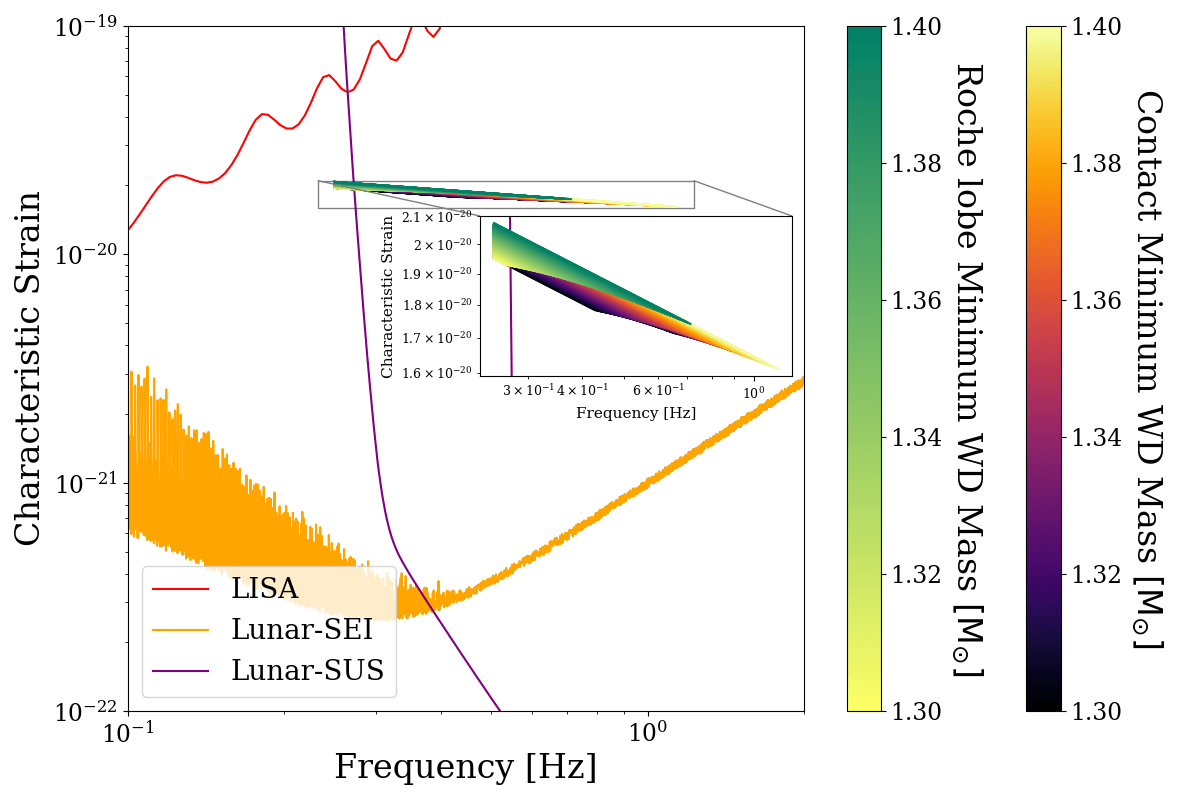
Horizon Distance
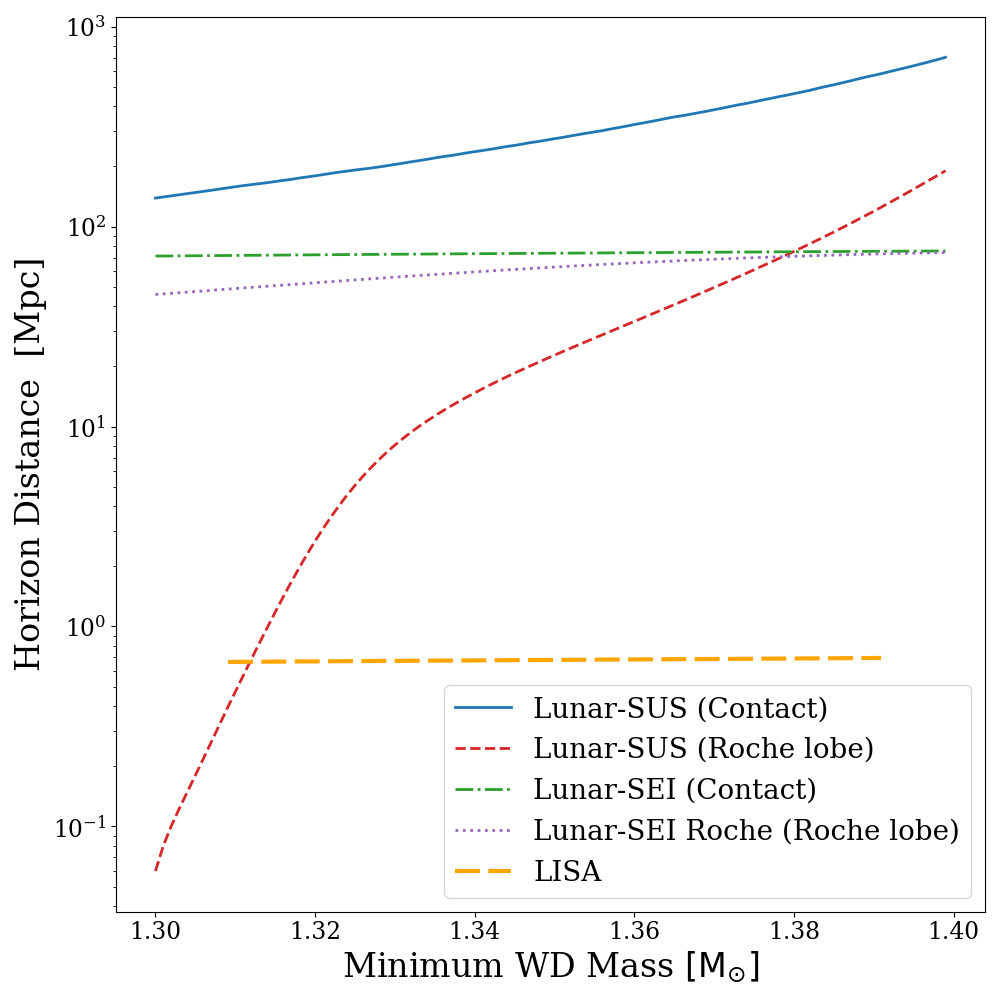
Horizon Distance
Early Alert at 10 Mpc
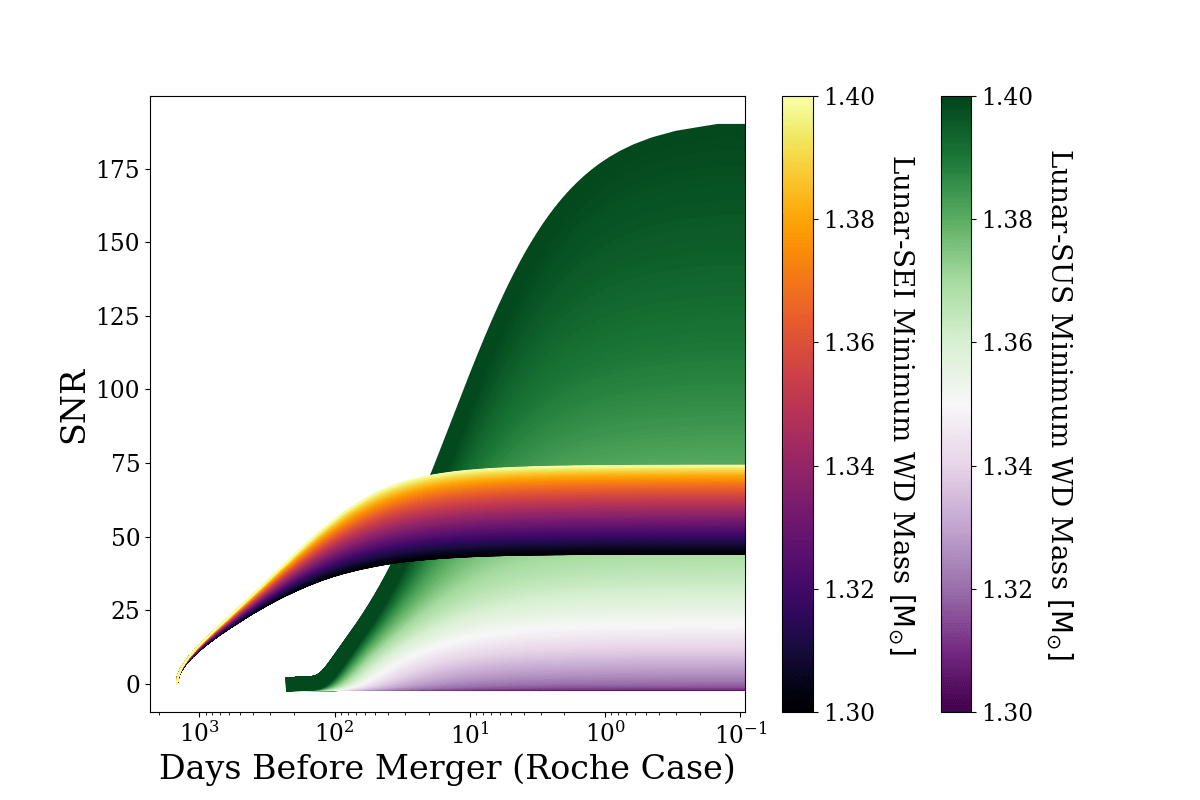
Early Alert at 10 Mpc
GWs from the Moon
- GW freq. between LISA and LIGO
- Massive WDs merger at Mpc distances
- Weeks of Early Alert
- Multi-Messenger Astrophysics
- WDs + NS
- WDs + Primordial BHs
LILAAAS
By mmarcano22
LILAAAS
- 177



