Variational Quantum Linear Solver for Multiphysics Problems
Mostafa Atallah
Cairo University
\frac{\partial^2 T}{\partial x^2} = 0
The Heat Equation
T_{i+1} - 2T_{i}+ T_{i-1} = 0
apply FDM
\begin{pmatrix}
-2 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\
0 & -2 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\
1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\
0 & 1 & 0 & -2 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0\\
0 & 0 & 1 & 1 & -2 & 0 & 1 & 0\\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1\\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & -2 & 0\\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & -2
\end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix}
T_{0} \\
T_{1} \\
T_{2} \\
T_{3} \\
T_{4} \\
T_{5} \\
T_{6} \\
T_{7}
\end{pmatrix}
=\begin{pmatrix}
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0
\end{pmatrix}
A x = b
A = 2 \left( I -0.125\; X_0 X_1 X_2 + 0.125 \; X_0 Y_1 Y_2 + 0.125 \; Y_0 X_1 Y_2 - 0.125 \; Y_0 Y_1 X_2 - 0.25 \; X_1 X_2 - 0.25 \; Y_1 Y_2 - 0.5 \; X_2 \right)
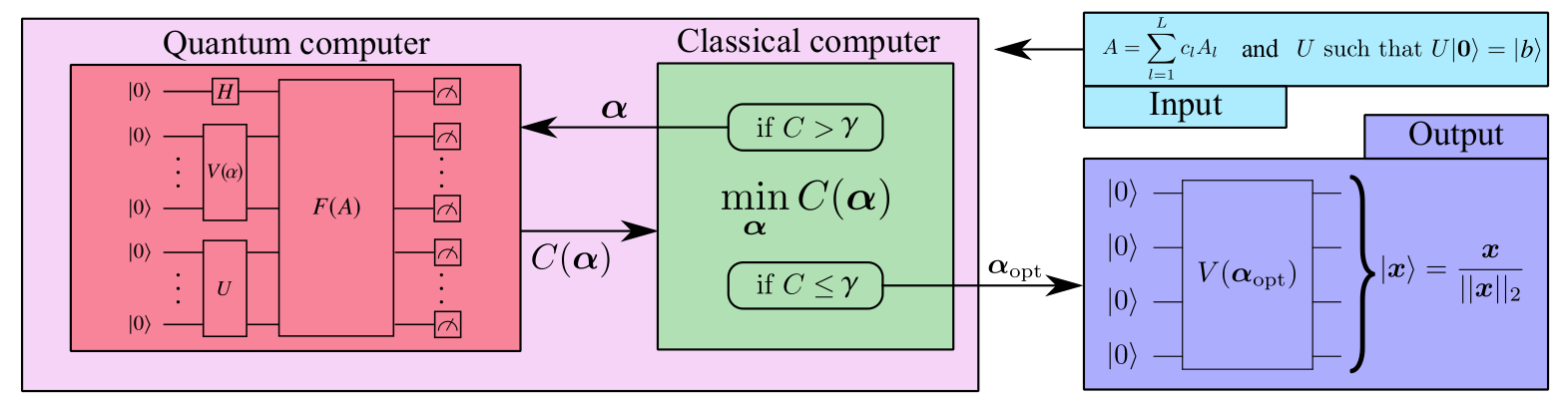
VQLS
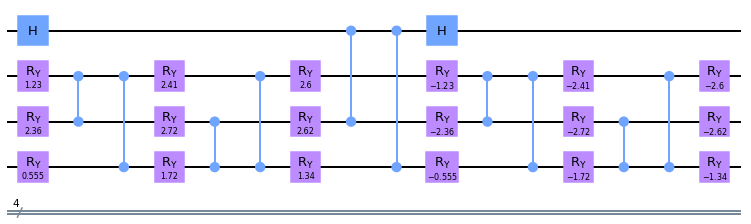
R_y(\alpha_i) = \mathbf{e}^{-\imath \; \alpha_i Y / 2}
C = 1 - \frac{| \left < b | \Phi \right >|^2}{ \left < \Phi|\Phi \right >}
\left<\Phi|\Phi \right> = \sum_{m, n} c_m^* c_n \left < 0 | V^\dagger A_m^\dagger A_n V |0 \right >
|\left < b | \Phi \right > |^2 = \sum_{m, n} c_m^* c_n \left < 0 | V^\dagger A_m^\dagger U |0 \right > \left < 0 | U^\dagger A_n V |0 \right >
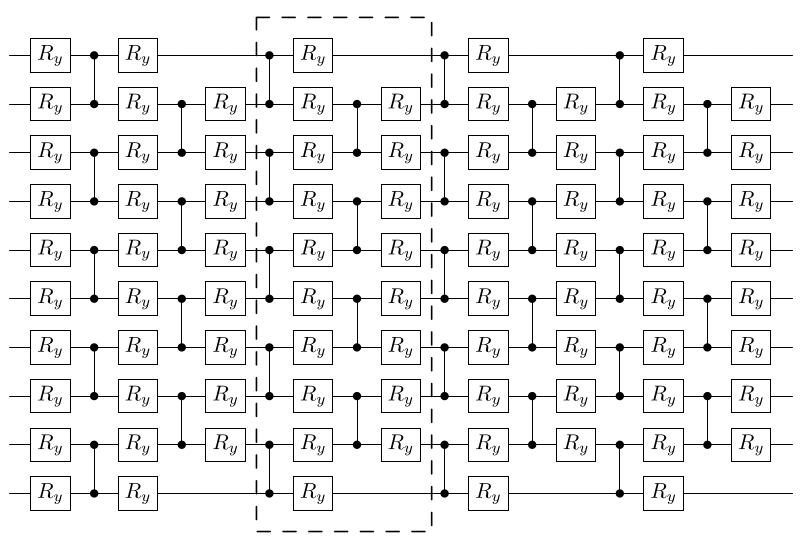
V(\alpha)
Hadamard Test
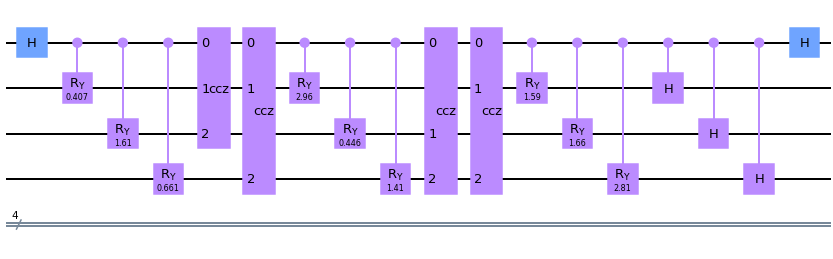
Hadamard Test
CCZ = MCMT(ctrl=2, target=1, U=Z)
Results (so far)
- Problem: 8 x 8 matrix (most of its elements are zeros)
- Number of Qubits: 3 (working qubits) + 1 (control qubit of the Hadamard test)
- Circuit Depth: 18
- Backend: Aer Simulator
- Number of Shots: 10,000
- Optimizer: COBYLA
- Min Cost: 0.116
- Max Overlap: 0.737
problem
FDM
FEM
Matrix Decomposition
VQLS
solution
HHL
Summary
Possible outcomes of the mentorship:
- Study and analyze the performance of the Variational Quantum Linear Solver (VQLS) in general
- Solve some Multiphysics problems such as the Heat equation, etc. using VQLS.
- Execute the results using Qiskit on both a simulator and a device.
Solving Multiphysics Problems on quantum computers
By Mostafa Ataallah
Solving Multiphysics Problems on quantum computers
- 60

