Understanding Drupal 8 Plugins System

About Me?
- Full stack Developer at Srijan Technologies PVT LTD
- Working with Drupal 6, 7 and 8
- I also love Javascript and CSS
- Hobbyist photographer, biker and runner

@msankhala @MutantMahesh @msankhala

Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of Drupal 7
- Object Oriented Programming concepts

Disclaimer
- I am not a Drupal 8 expert, but i'll try my best to explain D8 plugin system

What's in the talk
- What were plugins in Drupal 7
- What is Plugin in Drupal 8 ?
- Advantage of using plugins
- PSR-4, Annotation, Dependency injection, Service Container
- What all the things to think about when you think about Plugins?
- Available plugins in Drupal 8
- How to create plugin (Demo)
- How to create your custom plugin type. (Demo)

What were plugins in Drupal 7
- In Drupal 7 core there was nothing like plugins.
- Plugins were introduced by contributed module like Ctools, Views, panels etc
- These plugins helps you to create reusable custom functionality.
- Other module need to rely on these contributed module to develop something like plugin

<?php
/**
* Implements hook_ctools_plugin_directory().
*/
function MY_MODULE_ctools_plugin_directory($owner, $plugin_type) {
if ($owner == 'panels' && $plugin_type == 'YOUR-PLUGIN-TYPE') {
return "plugins/$plugin_type";
}
}
// YOUR-PLUGIN-TYPE
1. content_type
2. access(visibility rules)
3. context
4. relationships
5. arguments D7 declare your own ctools plugin

D7 ctools content type plugin
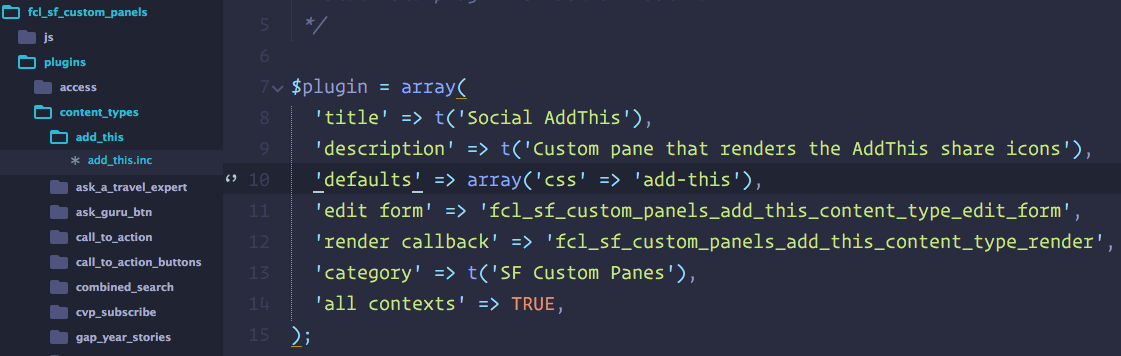

D7 ctools access plugin
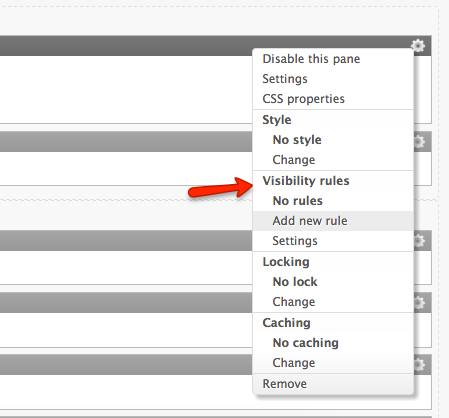

Drupal 7 panels plugins

- row
- display
- display_extender
- style
- argument default
- argument validator
- access
- query
- cache
- pager
- exposed_form
- localization.
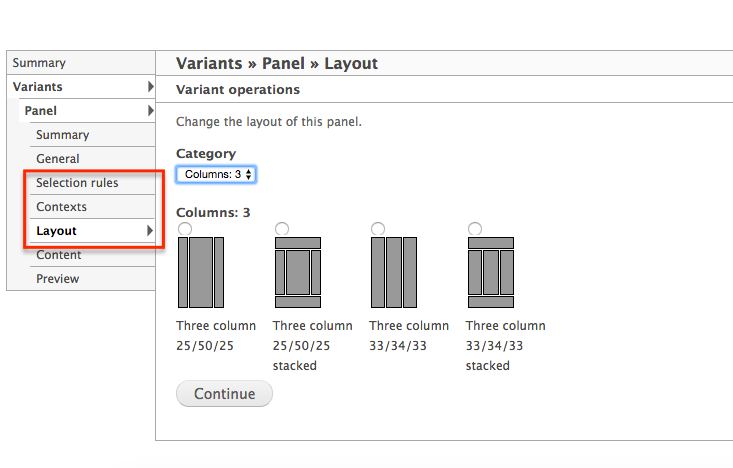
Drupal 7 views plugins

Drupal 7 views plugins


Drupal 7 views plugins directory

What is plugin in D8
- Plugin is a reusable functionality encapsulated in a class which implements one or more specific interfaces.
- Evolved from ctools and Views plugins but implementation is different.
- Plugins replaces _info hooks and few other implementation hooks.
- Example: hook_block_info() and hook_block_view(), _configure(), _save() replaced by Block plugins.

What is plugin in D8
- Plugins system is a drupal specific design pattern to solve a recurring problem of developing reusable functionality with different configuration in different context.
- A module can contain multiple plugins of different type.
- Plugin is implemented as a class.
- All the plugins are implemented as classes but not all classes are plugins.

Plugin Manager and IDs

- Every plugin has a type, which is responsible for its own type of functionality.
- Every plugin type has a manager - registered as a service (available from the container) and used to find and instantiate the desired plugin instance(s)
- Each plugin has an ID, which may be in its definition, or generated as a derivative
- For a given plugin ID one single class will be used for all plugin instances using that plugin ID
- A plugin instance is specified by the combination of plugin ID and its configuration values, potentially coming from a ConfigEntity
Advantage of using Plugins

- Definition + implementation at one place
- Plugins are lazy loaded
- Code is unified
- Plugins are extensible
- Plugins are consistent
- interchangeable within plugin types
- Reusable across different projects
Few concepts used in Drupal 8 core

- PSR-0 / PSR-4
- Annotation
- Dependency Injection
- Service Container
PSR-0 / PSR-4

- PSR stands for Php Standard Recommendation
- This basically defines two rules:
- All classes should be under namespace and fully qualified namespace should be in format Vendor/NameSpace/ClassName
- Directory structure must match namespace for class.
http://www.php-fig.org/faqs
http://www.php-fig.org/psr/psr-4/
PSR-0 vs PSR-4

- PSR-0 had some backwards compatibility features for PEAR-style classnames that PSR-4 dropped.
- PSR-4 does not force you to have the whole namespace as a directory structure, but only the part following the anchor point.
-
Acme\Foo\ namespace is anchored in src/ then PSR-0 will look for Acme\Foo\Bar class in src/Acme/Foo/Bar.php
- While in PSR-4 it will look for it in src/Bar.php
http://www.php-fig.org/faqs
http://www.php-fig.org/psr/psr-4/
class under namespace according to PSR-4

<?php
/**
* @file
* Contains \Drupal\search\Plugin\Block\SearchBlock.
*/
namespace Drupal\search\Plugin\Block;
use Drupal\Core\Access\AccessResult;
use Drupal\Core\Session\AccountInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Block\BlockBase;
/**
* Provides a 'Search form' block.
*
* @Block(
* id = "search_form_block",
* admin_label = @Translation("Search form"),
* category = @Translation("Forms")
* )
*/
class SearchBlock extends BlockBase {
}- Annotations are meta-data that can be embedded in source code.
- Annotation extends the PHP reflection API.
- Annotation let you examine and modify structure and behaviour of object at runtime.

Annotation
<?php
/**
* Simple Demo class to show php reflection class.
*/
class DCampHyderabad {
public $location;
function __construct() {
$this->location = 'IIIT';
}
function getLocation() {
return $this->location;
}
}
$ref = new \ReflectionClass('DCampHyderabad');
echo $ref->getDocComment() . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL;
print_r($ref->getMethods());
PHP Reflection API example:

// Output:
/**
* Simple Demo class to show php reflection class.
*/
Array
(
[0] => ReflectionMethod Object
(
[name] => __construct
[class] => DCampHyderabad
)
[1] => ReflectionMethod Object
(
[name] => getLocation
[class] => DCampHyderabad
)
)
Dependency Injection

Its 'D' in SOLID rule / Inversion of Control
class ShoppingCart {
protected $mailer;
function __construct()
{
$this->mailer = new Mailer();
}
}
class ShoppingCart {
protected $mailer;
function __construct($mailer)
{
$this->foo = $mailer;
}
}
$mailer = new Mailer();
$cart = new ShoppingCart($mailer);Service Container

Service container are responsible for instantiating classes with all its dependency.
# core/modules/search/search.services.yml
search.search_page_repository:
class: Drupal\search\SearchPageRepository
arguments: ['@config.factory', '@entity.manager']/* Service Container */
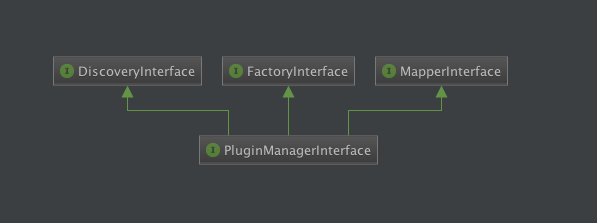
$instance = \Drupal::service('search.search_page_repository');Drupal 8 Plugins System components

Plugin Manager
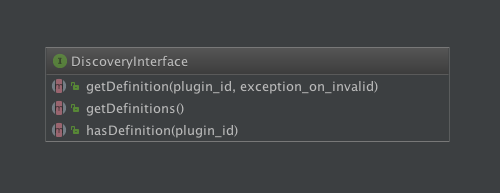
Discovery
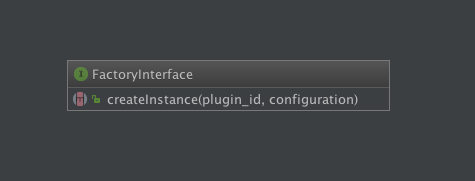
Factory
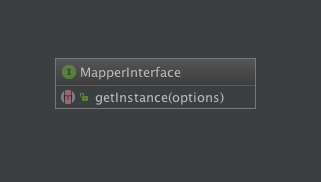
Mapper
DiscoveryInterface

FactoryInterface

MapperInterface

Drupal 8 Plugins System components

$pluginManager->getDefination();
// $this->discovery->getDefination();
$pluginManager->createInstance(plugin_id, configuration);
// $this->factory->createInstance(plugin_id, configuration);
$pluginManager->getInstance(options);
// $this->mapper->getInstance(options);Available Plugins in Drupal 8

- Block
- Field
- FieldWidget
- FieldFormatter
- TextFilter
- Action
- Menus
- Validation
- ImageEffect
and many more.....
Plugins Discovery in core

- YAML based: MenuLink, LocalTask, LocalAction, ContextualLink
- Annotation, some config, but no config entity: ImageToolkit, Archiver
- Annotation and config entity (many) including: Block, ViewsDisplay, ImageEffect, SearchPlugin
- Not a pure Plugin but uses Annotation discovery: Entity (Node, User, etc.)
Plugins Discovery in core

MyPluginManager::discovery = new AnnotatedClassDiscovery(‘Plugin/Block’, $namespaces,
'Drupal\block\Annotation\Block');
Annotated Plugin Discovery
Hook Based Plugins Discovery
MyPluginManager::discovery = new HookDiscovery($this->moduleHandler, 'block_info');
YAML Based Plugin Discovery
MyPluginManager::discovery = new YamlDiscovery('blocks',
$module_handler->getModuleDirectories());Static Plugin Discovery
MyPluginManager::discovery = new StaticDiscovery();
Plugin Factories in core

return new $plugin_class($configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition);
The Default Factory
The Container Factory
return $plugin_class::create(\Drupal::getContainer(), $configuration, $plugin_id,
$plugin_definition);What all the things to think about when you think about Plugins?
- What is my plugin type. (In most cases D8 core plugin type)
- What is my plugin annotation class. (In most case D8 core plugin annotation)
- Which discovery class i am going to use for my plugin discovery (AnnotatedClassDiscovery)
- Which factory class i am going to use for my plugin instantiation. (ContainerFactory)
- Is my plugin going to have derivative.

How to create D8 Plugin / Custom Plugin Type
Demo

Resources
Unraveling the Drupal 8 Plugin System
https://drupalize.me/blog/201409/unravelling-drupal-8-plugin-system
Plugin API overview
https://www.drupal.org/docs/8/api/plugin-api/plugin-api-overview
Drupal 8 Plugin System - Helior Colorado
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2o5uY-iOoMo
Peter Wolanin: Drupal 8, where did the code go? From info hook to plugin

Questions
Find me on Twitter @MutantMahesh
Understanding Drupal 8 Plugins system
By Mahesh Sankhala
Understanding Drupal 8 Plugins system
Session presented at DrupalCamp Hyderabad 2017 about Understanding Drupal 8 Plugins System.
- 1,202



