Innovation -and other- Models
Models
A workable and testable description of a more complex system, and/or its simplified representation. Models can depict theories, processes, practices, phenomena, and/or patterns. They are used to enable analysis and comparison, and/or facilitate communication among agents as well as the use of technologies and knowledge. Models often include standards and measurement indicators that are based on data.
Examples
Communication
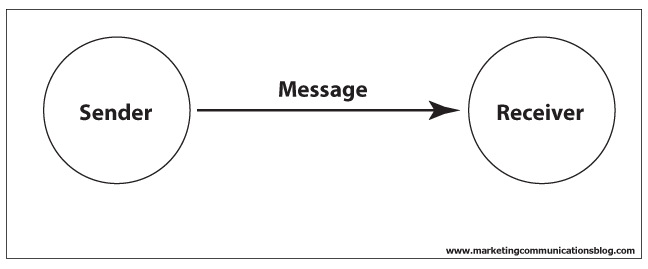
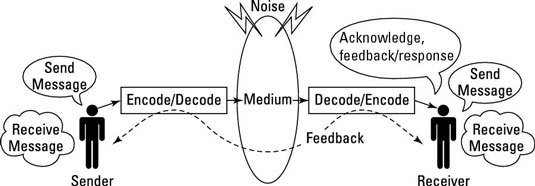
Examples
Geography
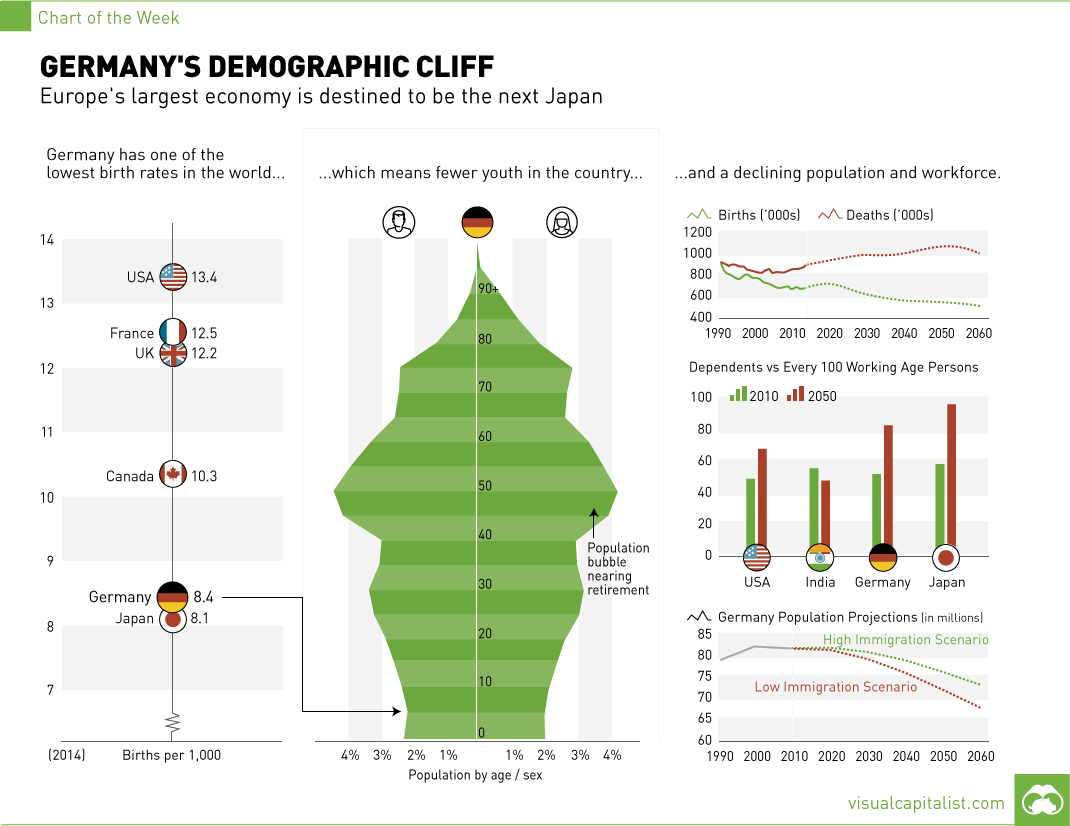
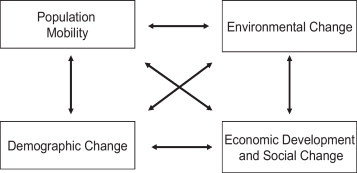
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.09.008
Examples
Innovation management
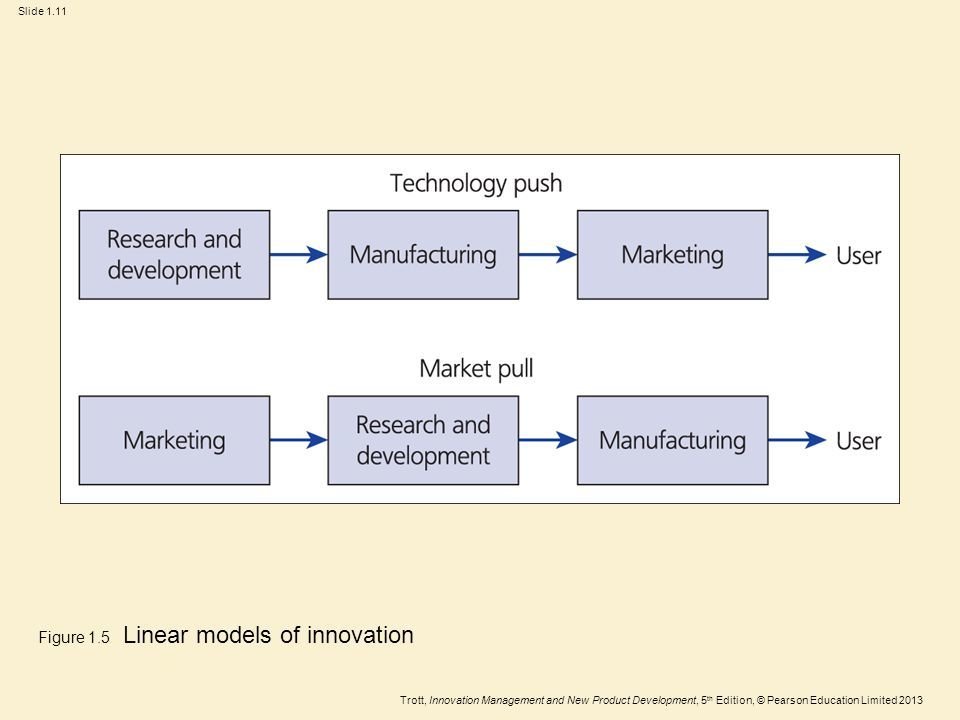
Why are models an important way of distilling information?
Evolution of IM models
- Linear
- Coupled/interactive
- Network - Externalities and knowledge management matter
- Open innovation (Chesbrough, 2003)
- Business Model Innovation (BMI)
Closed vs. open innovation models
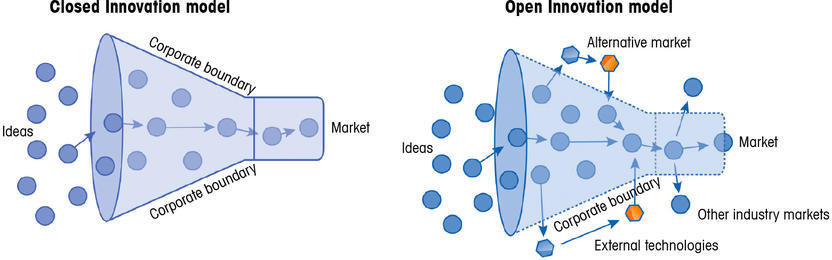
Source: http://q-more.chemeurope.com/html
Open innovation models
- GE project
- CocaCola Freestyle Dispenser Machines (and App)
- (intermediary) 99designs
- Threadless designs
- Userfarm
-Ideasbrewery/Heineken
-(public) The Green Challenge
Chesbrough, H. (2003). Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology. Harvard Business School Press.
General Electric
Co-creation for better appliances

Source: https://firstbuild.com/products/opal/
Coca Cola
Freestyle dispensers and Apps
source: www.coca-colafreestyle.com/


99designs
Freelancing design (brokerage)
source: www.99designs.com


Threadless
Crowdsourcing design
source: www.threadless.com


Userfarm
Vertical video. Crowdsourcing
source: https://www.userfarm.com/en
Heineken
Ideasbrewery project. User research and innovation hub
source: https://www.theheinekencompany.com
Greenchallenge
Global scale sustainable entrepreneurship
source: http://greenchallenge.info/ sponsors of the lauch of the http://www.physee.eu/

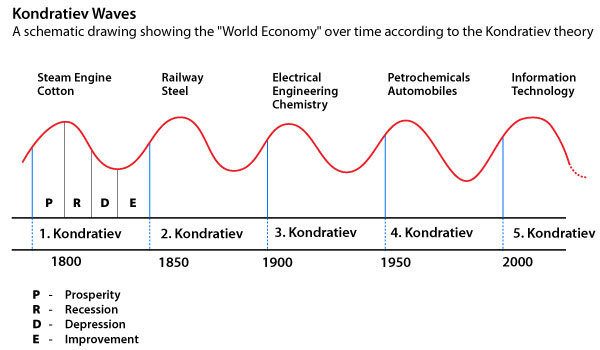
Druker's sources of innovation
Schumpeter's key shifting factors raising innovation opportunities
Context
Systems and strategies that support and seek to promote economic growth
Capitalism (free market economies)
Subtitle
Innovation opportunities
- Unexpected events
- Incongruities
- Need to make processes more effective
- Structural changes of an industry
- Demographics
- Changes in perceptions
- New knowledge
- Analogy, convergence and TRANSFER
What affects diffusion?
1. Relative advantage




2. Compatibility

3. Complexity
4. Trialability

5. Observability

Technology transfer
When this became a key component in IM strategies?
Technology transfer and National Innovation Systems (NIS)
Technology transfer
became a key component in IM strategies by the sixth generation of innovation models when the context became as important as the organization itself
Triple Helix marks the begining
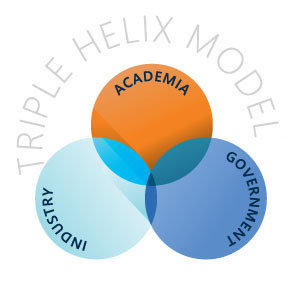
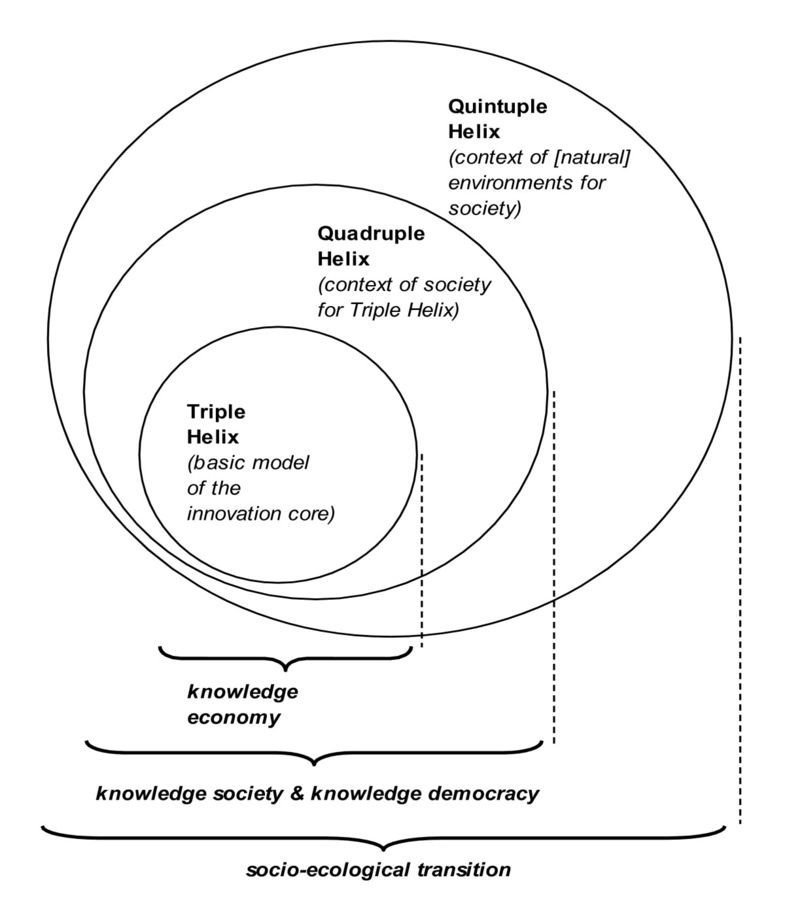
Status of the Helix as for now
Text
Text
Source: Carayannis et al., 2012
Status of the Helix as for now

Text
Status of the Helix as for now
Smart Cities
Technology parks
Innovation Districts
They allow engagement and connections
Models are everywhere, they are a language useful to learn
Models simplify complexity
data-wisdom
Model thinking + computational thinking
Analytical tools of the times. They allow the efficient use of data
Models assist decision making
Design and strategy
Models
By mtalyc
Models
- 492



