Loops and Arrays
On keeping things tight
Quick review
-
What types of conditionals do you know?
-
When to use a conditional?
-
How many cases a switch can have?
- if(4==5) { print("4");} prints what?

Contents
-
Loops
-
Arrays
-
2D arrays (matrices)
-
Looping through arrays
-
Summary
-
Quiz
Bad joke
of the day
A programmer is sent to the grocery store with instructions to "buy butter and see whether they have eggs, if they do, then buy 10."
Returning with 10 butters, the programmer says, "they had eggs."
The need for loops
static void main (String[] arguments) {
print("Car #1");
print("Car #2");
print("Car #3");
} What if we had 200 cars?
(get it?)
How loops help?

- Execute similar code multiple times
- Less code duplication
- Iterate over collections
While loop
static void main (String[] arguments) {
int i = 1;
while(i <= 200) {
print("Car #" + i);
i++;
}
} Counting with care
Make sure your loop will finish
while(CONDITION) {
STATEMENTS;
}For loop
static void main (String[] arguments) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 200; i++) {
print("Car #" + i);
}
}
for(INITIALIZATION; CONDITION; UPDATE;) {
STATEMENTS;
}When you know the number of loops
How to stop early?
public static void main (String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 200; i++) {
if(i == 10) {
break;
}
print("Car #" + i);
}
}break terminates the loop
How to skip one iteration?
public static void main (String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 200; i++) {
if(i == 10) {
continue;
}
print("Car #" + i);
}
}continue skips an iteration
Questions?
Break (10 min)

Why arrays?
public static void main (String[] args) {
String car1 = "Nissan Micra";
String car2 = "Peugeot 206";
String car3 = "Smart for two";
print(car1);
print(car2);
print(car3);
}Array?
- Indexed list of values
- Can be of any type - int, String, double etc...
- All elements must be of the same type
Common gotchas
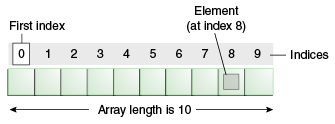
- First index: zero
- Last index: length - 1
How to create one?
To create array of given size use the operator new
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] cars = new String[5];
print(cars);
}Array initialization
Curly braces can be used to initialize an array.
ONLY when you declare the variable!
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] cars = {"Nissan Micra", "Peugeot 206"};
print(cars);
}Accessing arrays
Access an element from array using the [ ] operator
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] cars = {"Nissan Micra", "Peugeot 206"};
print(cars[0]);
}What happens when we try to access cars[2] ?
Does the size matter?
Each array has a built-in length variable that contains the size of the array
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] cars = {"Nissan Micra", "Peugeot 206"};
print(cars.length);
}2D Array or Matrix
Grid of rows and columns

2D Array or Matrix (2)
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[][] cars = {
{"Micra", "350Z", "Primera"},
{"206", "306", "406"}};
print(cars);
// Alternative
String[][] cars1 = new String[2][3];
cars1[0][0] = "Micra";
}Initialize
Another
way
Looping through an array
Or how to combine arrays and loops
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] cars = {"Nissan Micra", "Peugeot 206"};
for(int i = 0; i < cars.length; i++) {
print(cars[i]);
}
}Math Wars is back
Questions?

Summary
- Loops can execute a piece of code multiple times
- Use break to stop a loop prematurely
- Use continue to skip the current loop iteration
- Arrays are collection of items
- You can examine array contents with loops
Daily quiz
http://wp.me/P67zDd-19

Questions?
Homework or not
Thank you :)
Lecture 4 - Loops and Arrays
By naughtyspirit
Lecture 4 - Loops and Arrays
- 454



