Classes and Objects
Further examination
Quick review
-
What is the difference between class and object?
-
Which are the components of a class?
-
What is the difference between private and public?
- How to initialize some fields of an object at the moment of it's creation?

Weekly Quiz (10 min)

Homework
Contents
-
this keyword
-
Composition
-
References & values
-
Comparing objects
-
Enum types
-
static keyword
Wacky Racer
Bad joke
of the day

this keyword
public class Car {
private int topSpeed;
Car() {
topSpeed = 100;
}
public setTopSpeed(int topSpeed) {
topSpeed = topSpeed
}
public int getTopSpeed() {
return topSpeed;
}
}Car bmw = new Car();
int speed = bmw.getTopSpeed();What is the value of speed?
Car bmw = new Car();
bmw.setTopSpeed(200);
int speed = bmw.getTopSpeed();100
What is the value of speed?
100
this keyword(2)
public class Car {
private int topSpeed;
public setTopSpeed(int topSpeed) {
this.topSpeed = topSpeed
}
public int getTopSpeed(int topSpeed) {
return topSpeed;
}
}- Represents the current instance of the class in which it appears (means "my object")
- Clarifies scope
this keyword(3)
public class Car {
private int topSpeed;
Car() {
topSpeed = 100;
}
public setTopSpeed(int topSpeed) {
this.topSpeed = topSpeed
}
public int getTopSpeed() {
return topSpeed;
}
}Car bmw = new Car();
int speed = bmw.getTopSpeed();What is the value of speed?
Car bmw = new Car();
bmw.setTopSpeed(200);
int speed = bmw.getTopSpeed();100
What is the value of speed?
200
Composition
- A way to combine simple objects or data types into more complex ones
- "has a" relationship - car "has a" driver
Until now:
public class Car {
...
private String driver;
...
}What if every driver has not only name but points?
Composition(2)
What if every driver has not only name but points?
One way:
public class Car {
...
private String driver;
private int driverPoints;
...
}What if in the future we decide to add age, category, number of games played...?
Composition(3)
Separate driver as a new class
public class Driver {
private String name;
private int points;
public Driver(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void setPoints(int points) {
this.points = points;
}
}Composition(4)
Change driver type in class Car
public class Car {
private Driver driver;
public Driver getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(Driver driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
}Break (10 min)

References & Values
Primitives vs References
-
Primitives types are default Java types
- int, double, boolean, char, float ...
- The actual values are stored in the variable
-
Reference types are arrays and objects
- String, int[], Car, ...
References & Values(2)
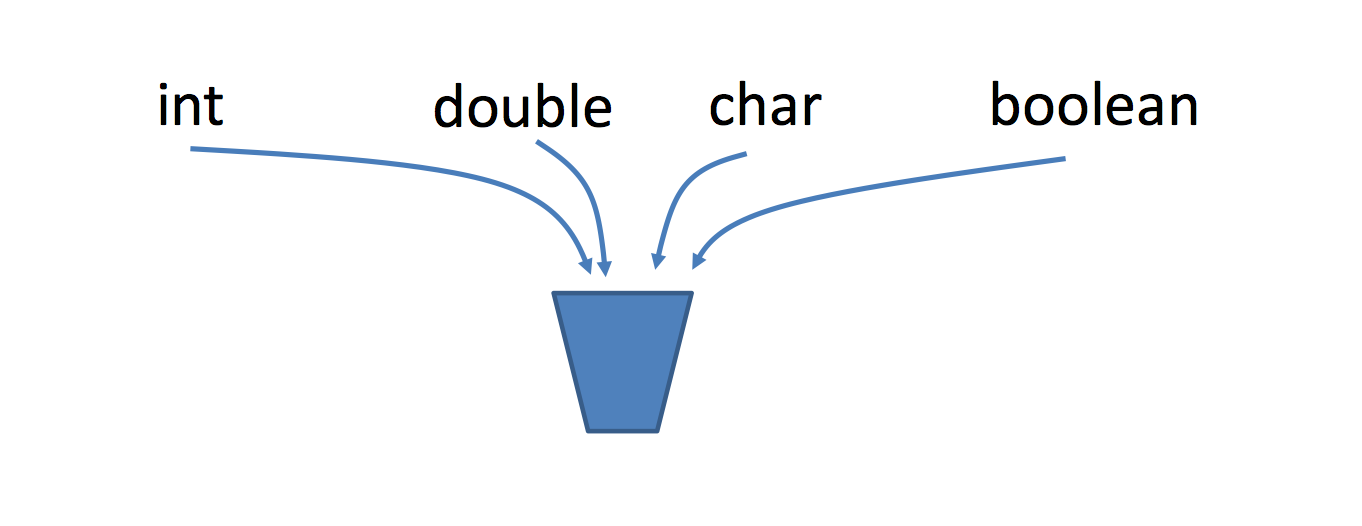
How Java stores primitives
- Variables are like fixed size cups
- Primitives are small enough that they just fit into the cup
References & Values(3)
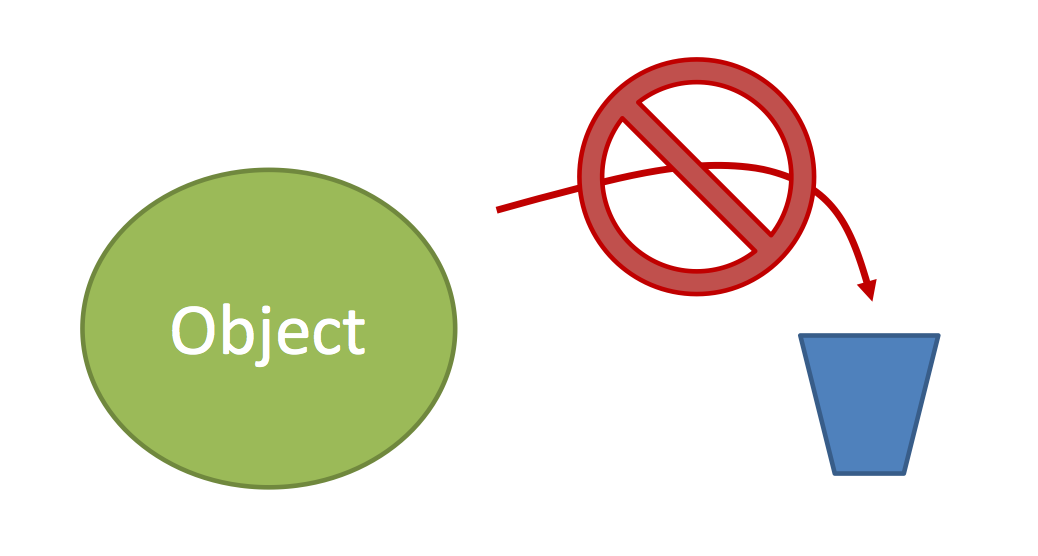
How Java stores objects
- Objects are too big to fit in a variable
- Stored somewhere else
- Variable stores a number(address) that locates the object
References & Values(4)
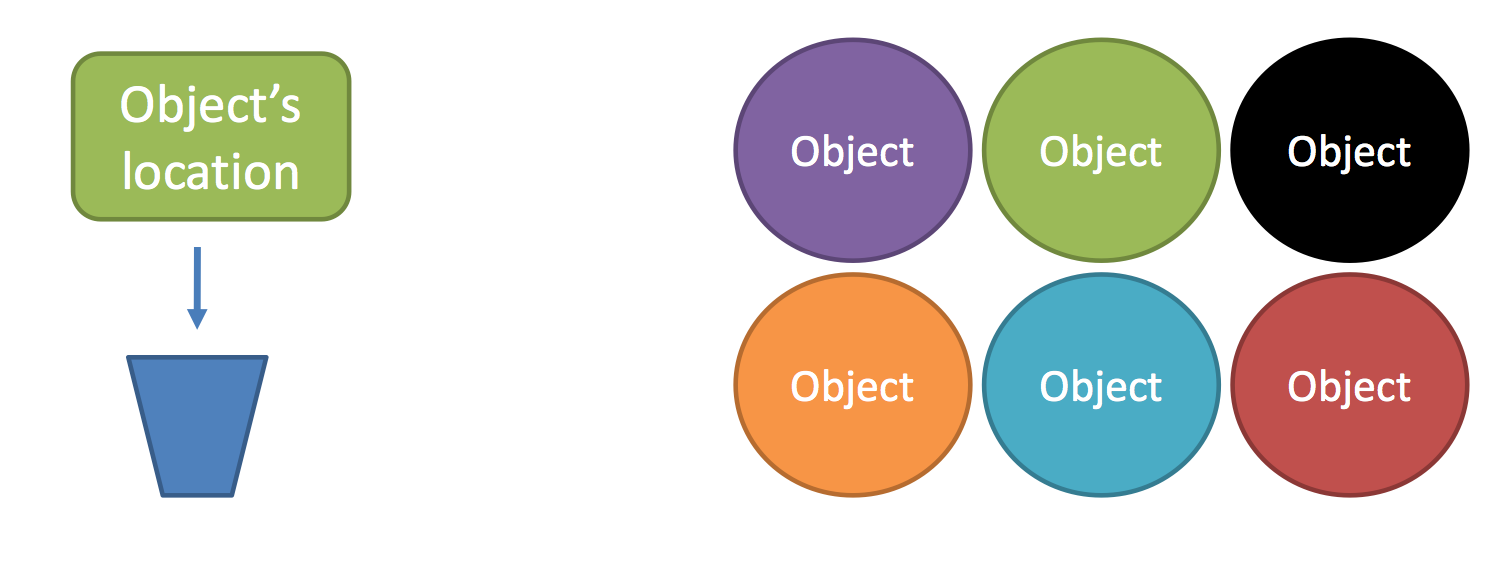
References
- The object's location is called a reference
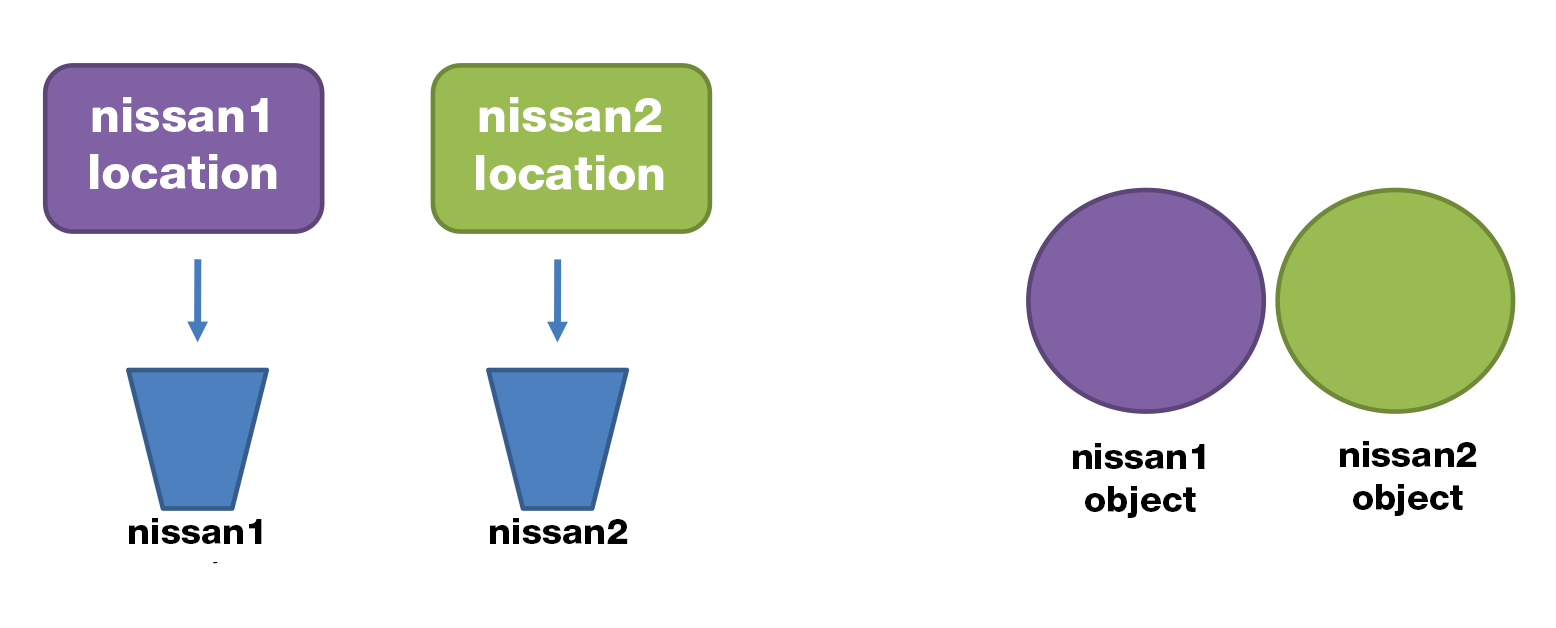
Comparing objects
- == compares the references
NO
Car nissan1 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
Car nissan2 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");Does nissan1 == nissan2 ?
Comparing objects(2)
Car nissan1 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
Car nissan2 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");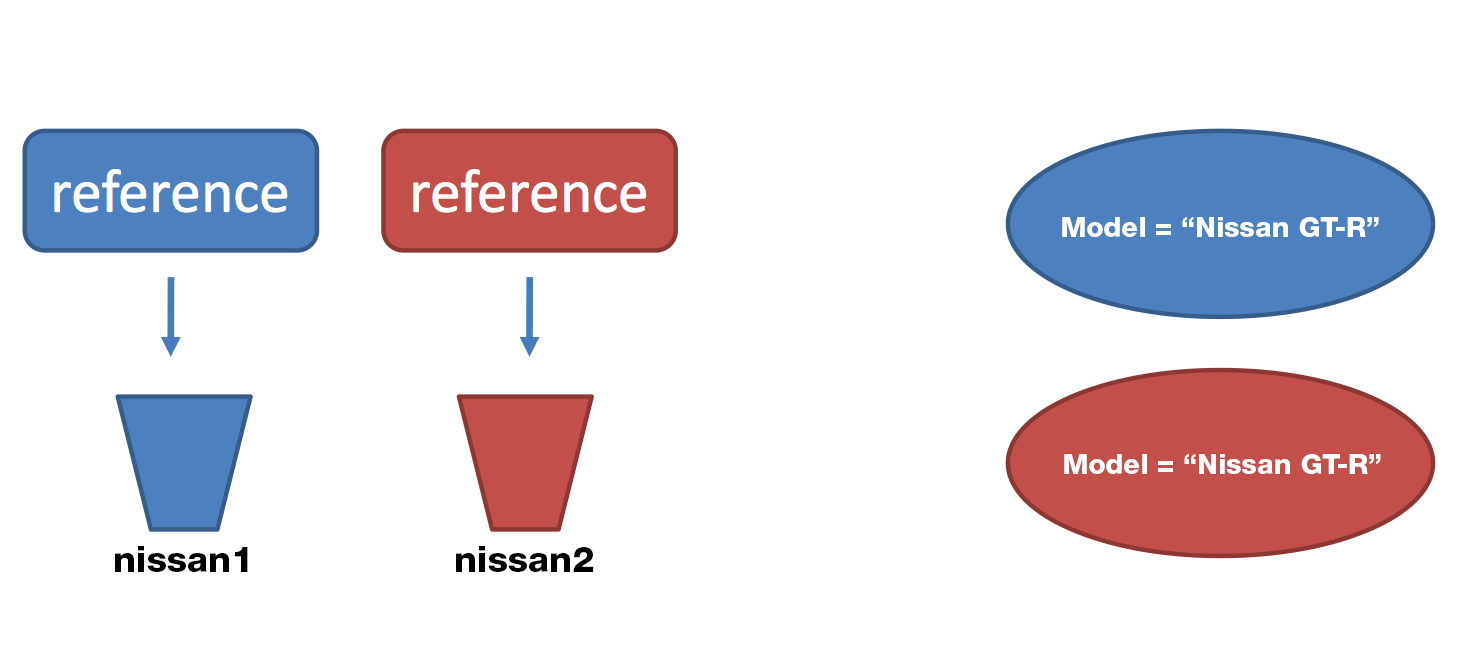
Comparing objects(3)
Car nissan1 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
Car nissan2 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
nissan1 = nissan2;- Using = updates the reference
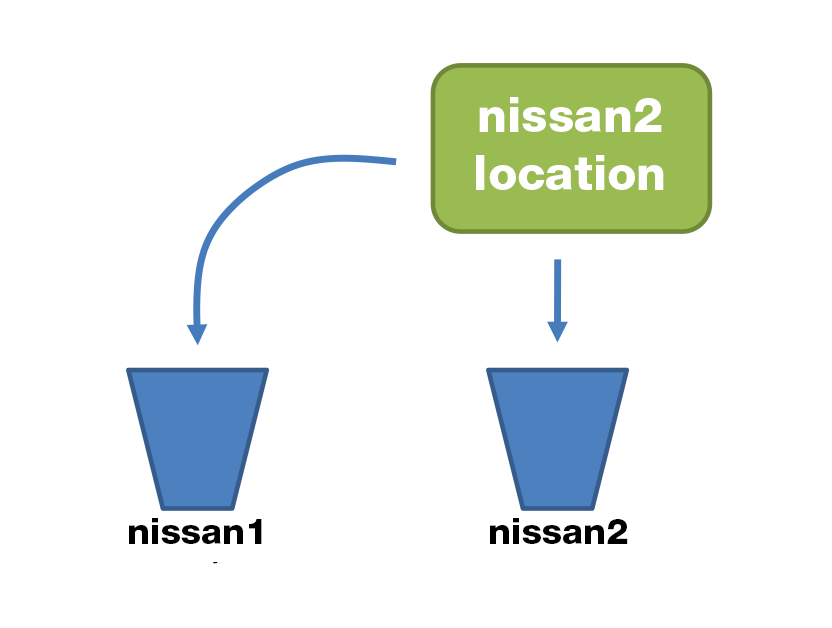
->
Comparing objects(4)
Car nissan1 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
Car nissan2 = new Car("Nissan GT-R");
nissan1 = nissan2;Does nissan1 == nissan2 ?
YES
- About equals() - in the next lectures
Enum Types
- An enum type is a special data type that enables for a variable to be a set of predefined constants
- Often used for comparisons
Examples:
- Days of the week - SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY
- Compass directions - NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, WEST
Enum Types(2)
- Definition - using the enum keyword
- Values are often written with capital letters
public enum Day {
SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY,
THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY
}Usage example:
Day day1 = Day.MONDAY;
Day day2 = Day.TUESDAY;Enum Types(3)
Day day1 = Day.MONDAY;
Day day2 = Day.TUESDAY;
Day day3 = Day.MONDAY;Comparison
Does day1 == day2 ?
NO
Does day1 == day3 ?
YES
Enum Types(4)
- Enums are often used for comparison in switch statement
switch (day) {
case MONDAY:
...
break;
case FRIDAY:
...
break;
case SATURDAY: case SUNDAY:
...
break;
default:
...
break;
}Enum Types(5)
Using enum for car color in Wacky Racers - green, red, blue, yellow
public enum CarColor {
Yellow, Green, Red, Blue
}public class Car {
...
private CarColor color;
public void setCarColor(CarColor color) {
this.color = color;
}
public CarColor getCarColor() {
return color;
}
...
}static keyword
-
Applies to fields and methods
-
Means the field/method
-
Is defined for the class declaration
-
Is not unique for each instance
-
static field
public class Driver {
...
public static int numOfDrivers = 0;
...
}Driver driver1 = new Driver();
Driver driver2 = new Driver();
driver1.numOfDrivers = 4;What is the value of the field numOfDrivers on driver1?
4
What is the value of the field numOfDrivers on driver2?
4
static method
public class Driver {
...
private static int numOfDrivers = 0;
...
public static int getNumOfDrivers() {
return numOfDrivers;
}
}Call a static method:
...
int driversNum = Driver.getNumOfDrivers();
...What is the value of driversNum?
0
static keyword(2)
public class Driver {
...
private static int numOfDrivers = 0;
...
public Driver() {
numOfDrivers++;
}
...
public static int getNumOfDrivers() {
return numOfDrivers;
}
}Where to increment numOfDrivers?
In the constructor
Summary
- this keyword - means "my object"
- Composition - one object has other objects
- Object variables are references
- == of objects compares their references
- enums - special data types for predefined variables
- static - same for all instances of a class
Daily quiz

Questions?
Thank you :)
Lecture 7 - Classes and Objects - Further examinatio
By naughtyspirit
Lecture 7 - Classes and Objects - Further examinatio
- 488



