Create parametric 3D fusion reactor CAD models
Paramak
J. Shimwell, J. Billingsley, R Delaporte-Mathurin, D. Morbey, M. Bluteau, P. Shriwise, A. Davis
This work was funded by the RCUK Energy Programme
[Grant number EP/P012450/1]



Motivation - automation
Diagram / sketch / idea
Manual CAD model creation via GUI
CAD model geometry created
Manual CAD model cleaning via GUI
Analysis


Motivation - speed at scale
Model complexity
CSG models
Lines of code
CAD Shapes
CAD Components


Decompose existing models
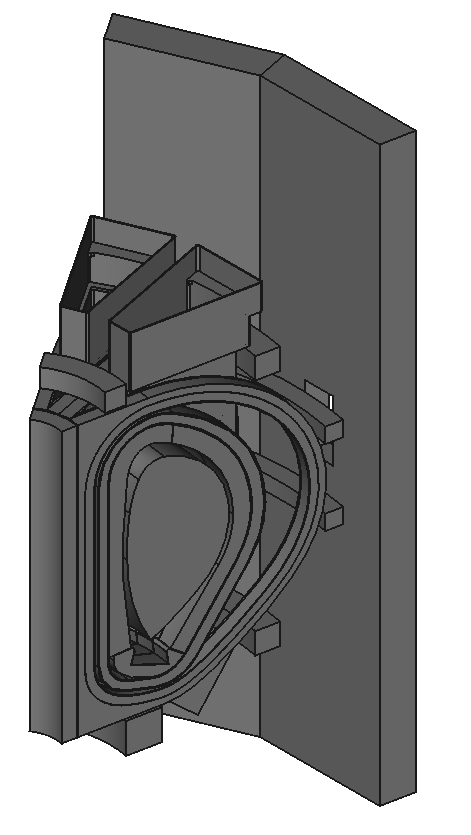

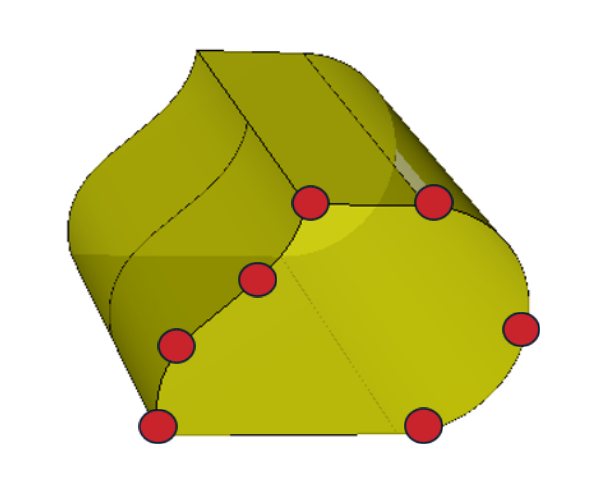
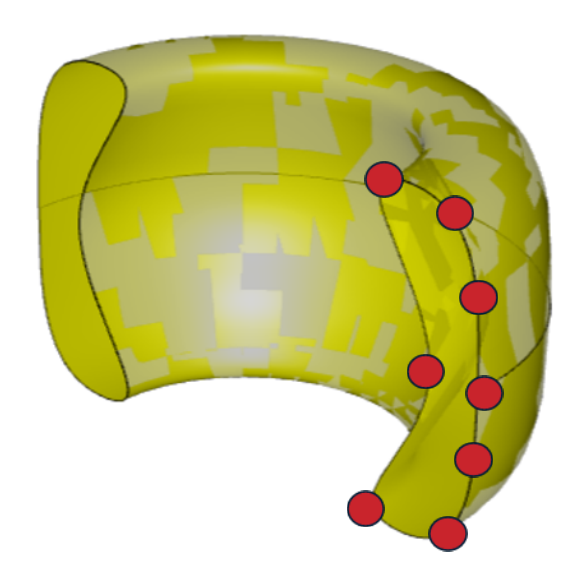
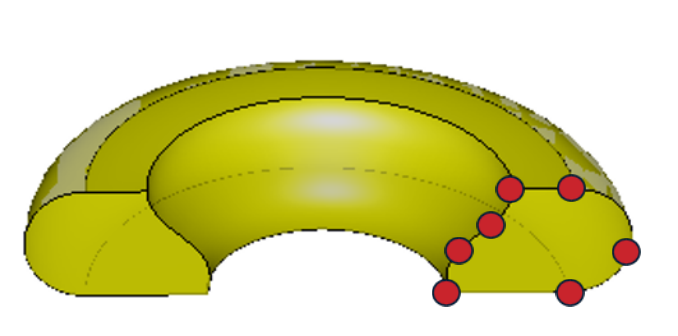
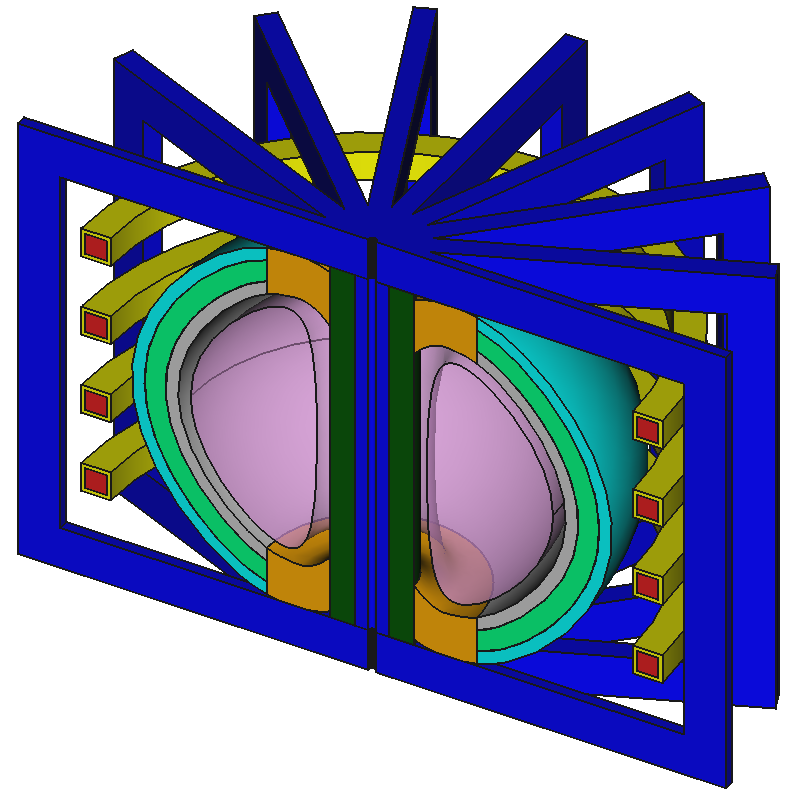
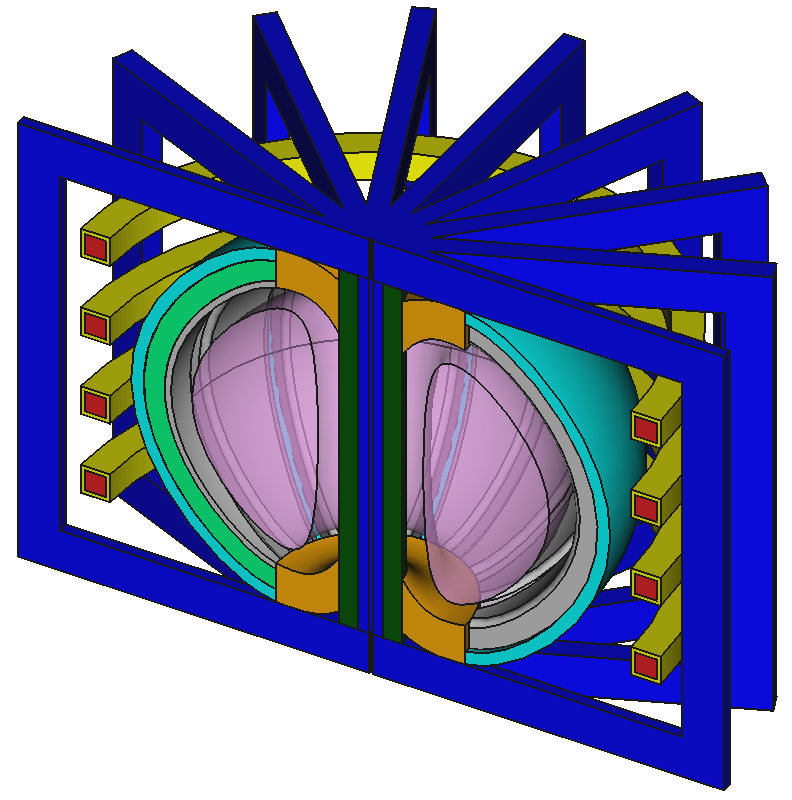
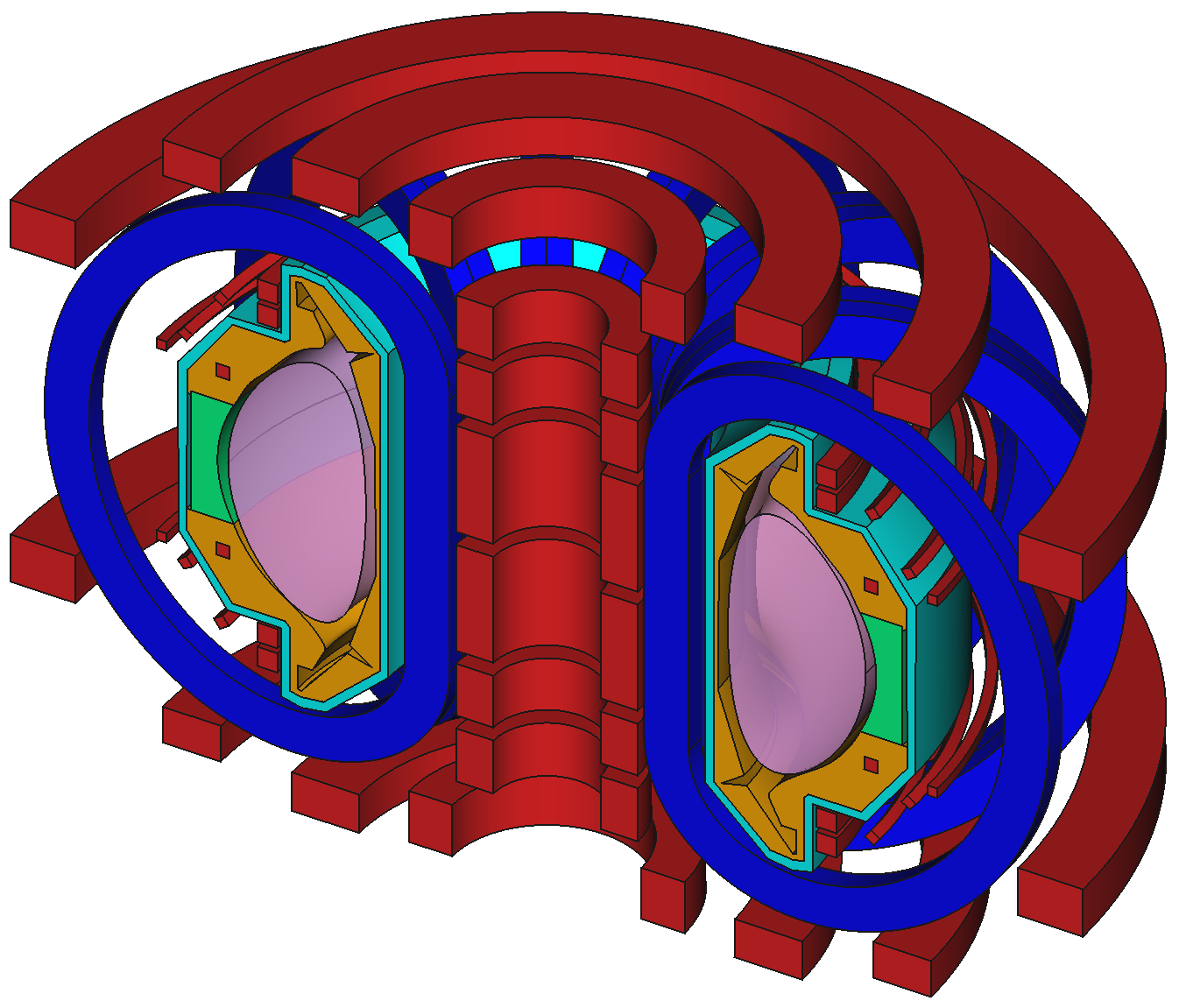
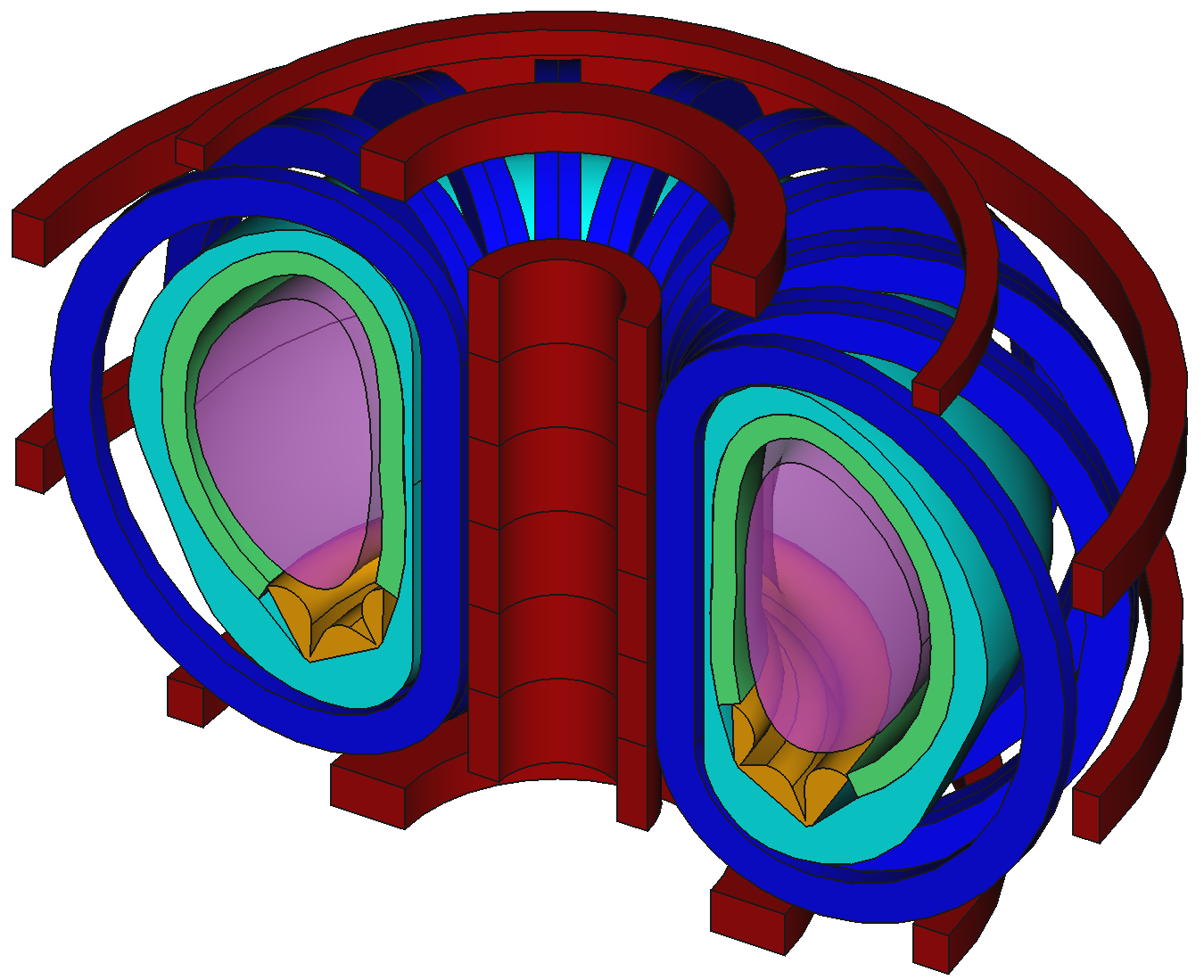
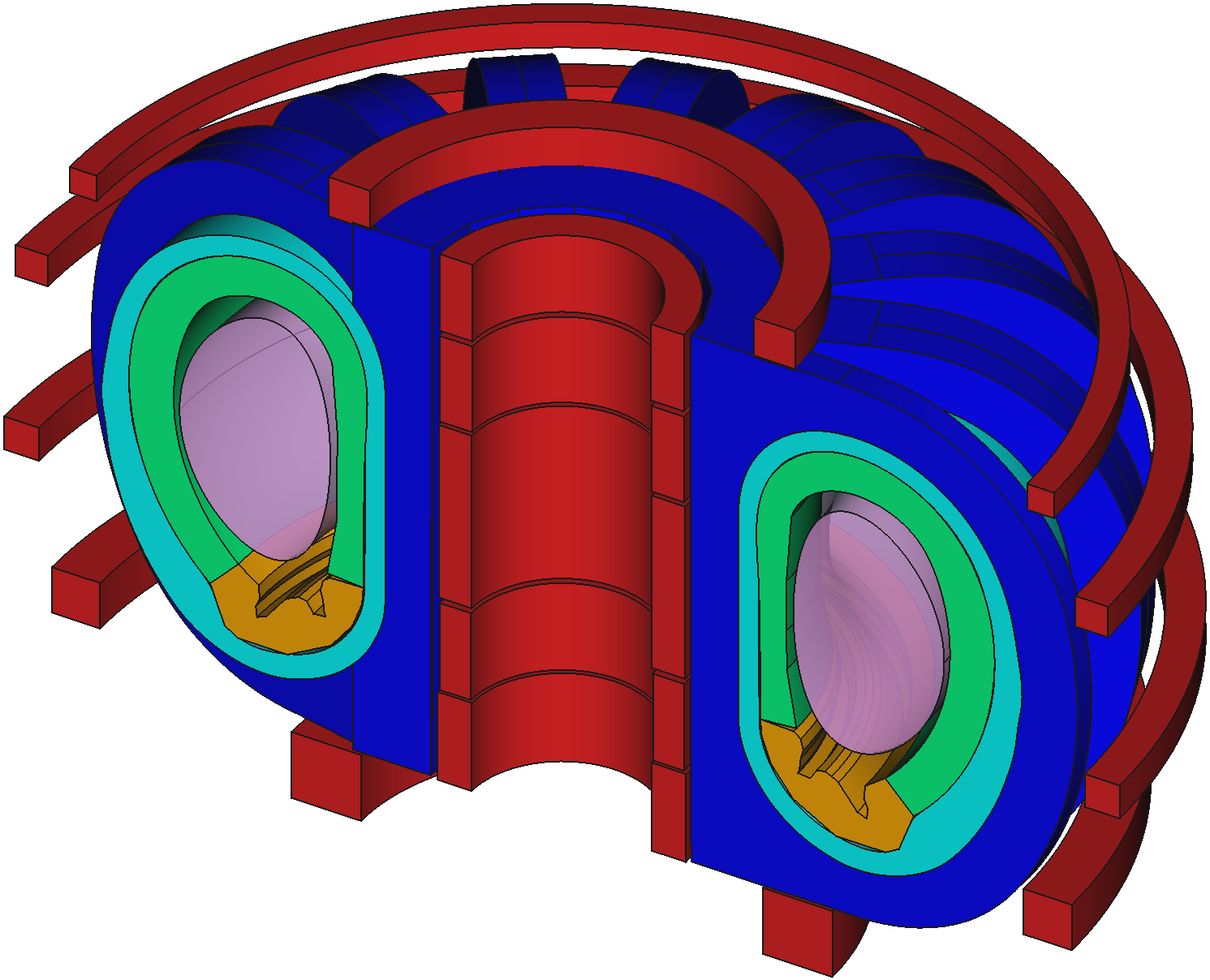
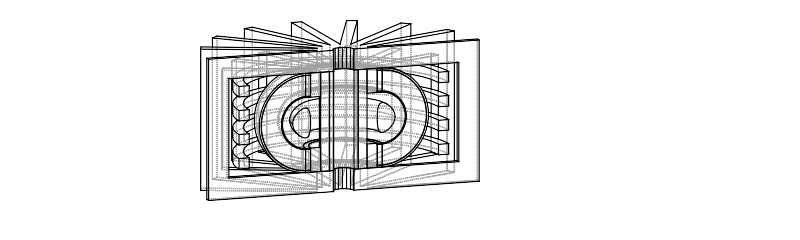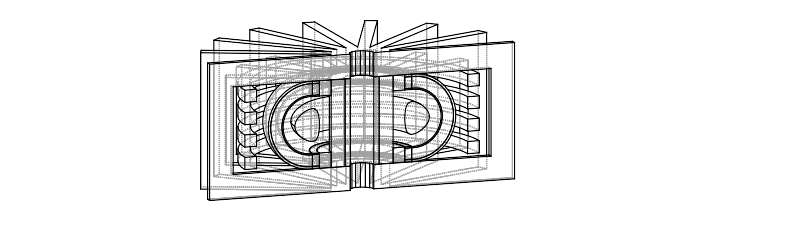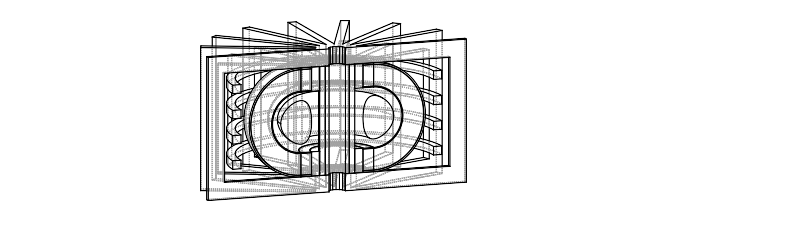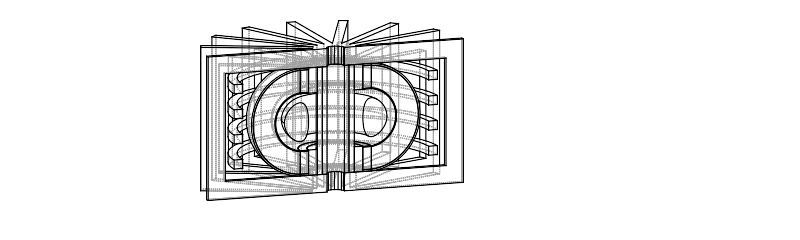
Example CAD model based on EU-DEMO


Method

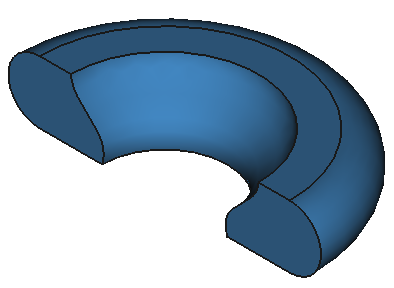
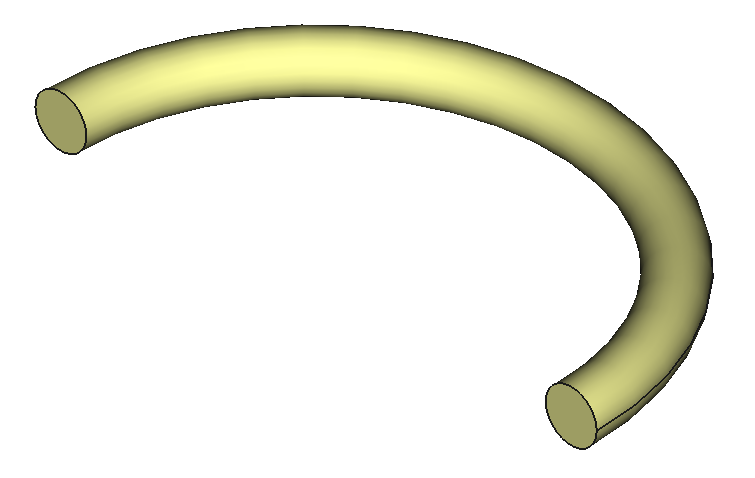
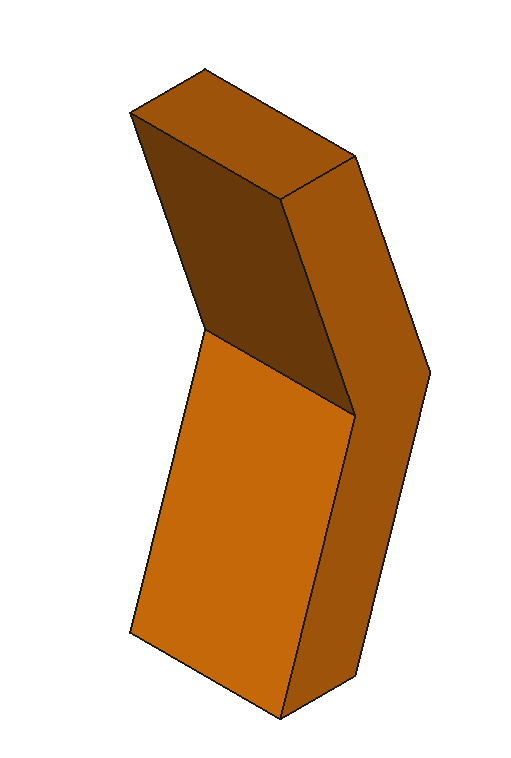

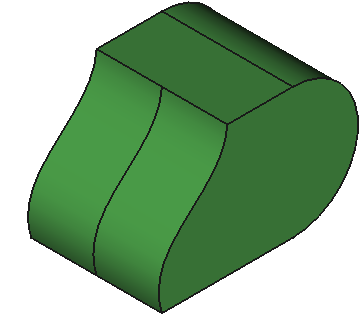
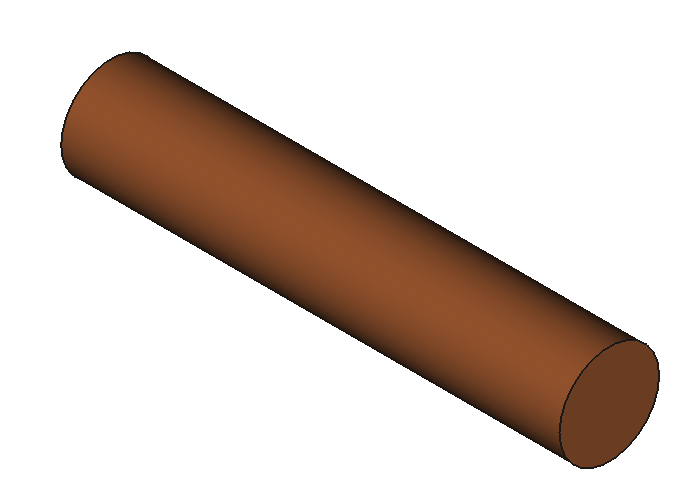
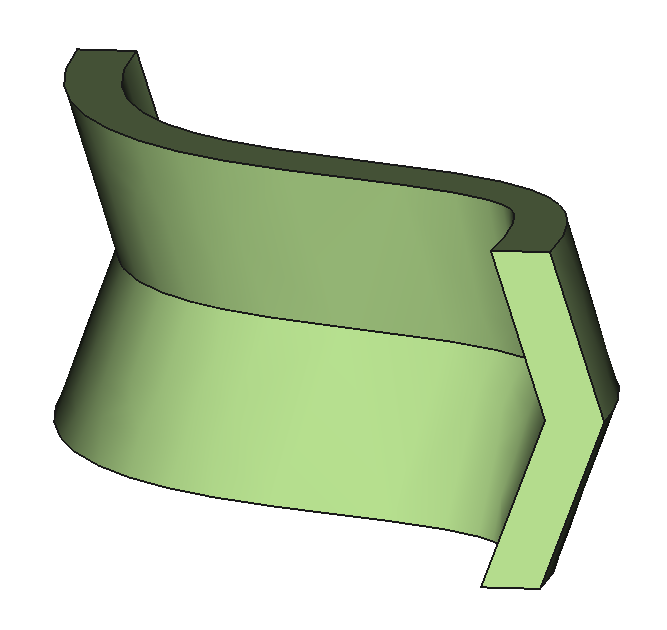

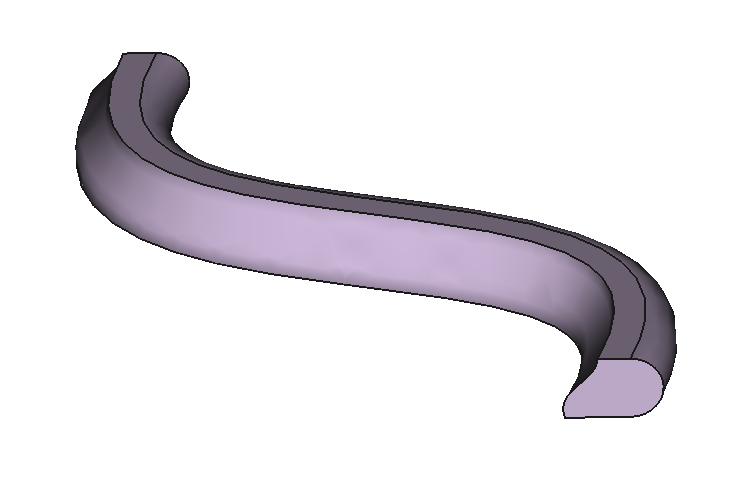
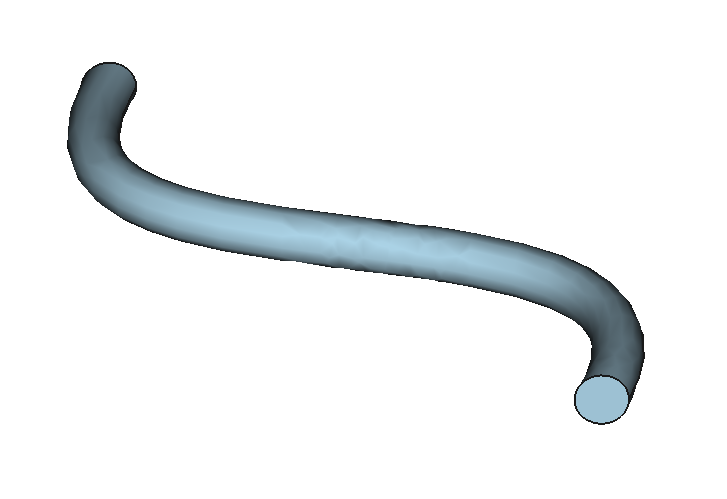
12 Shapes

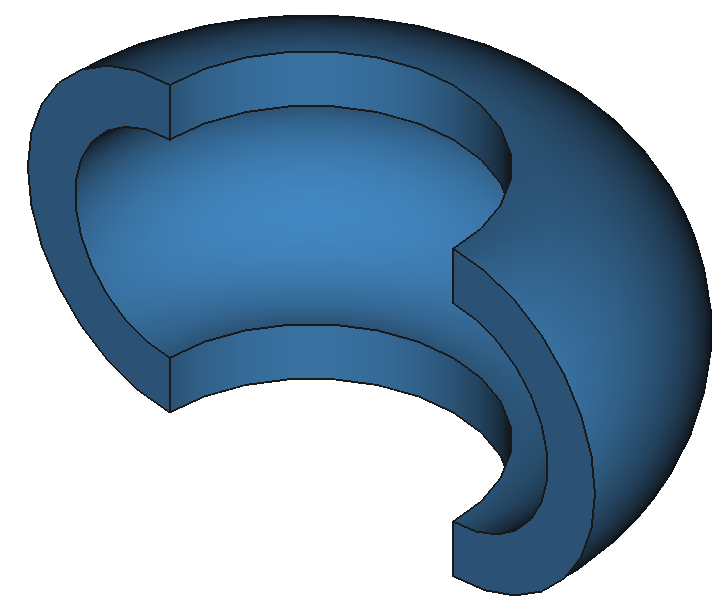
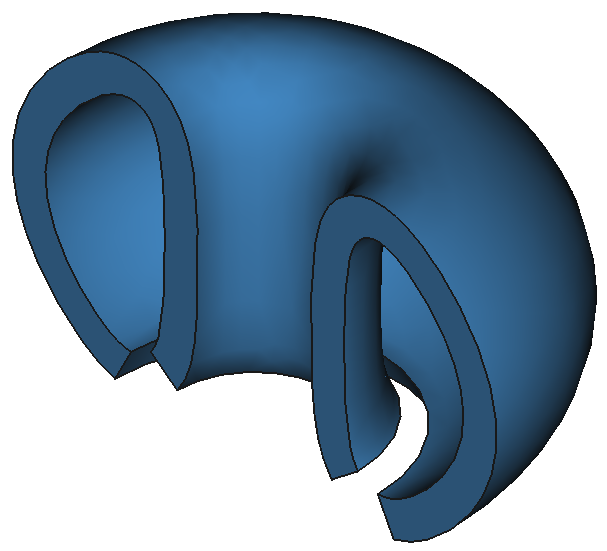
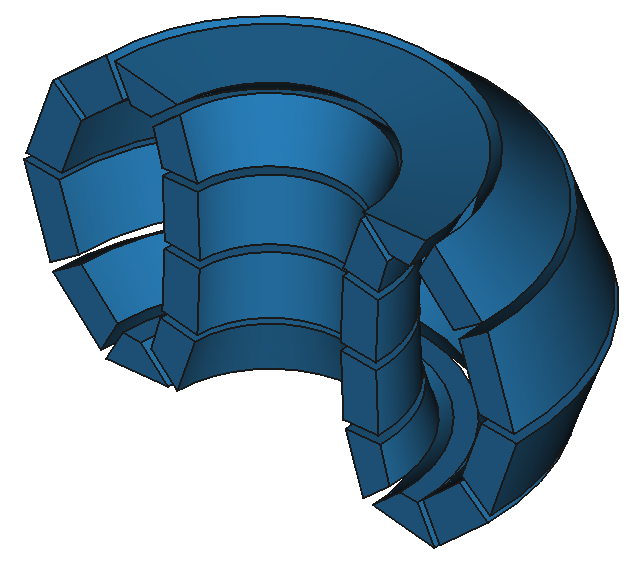
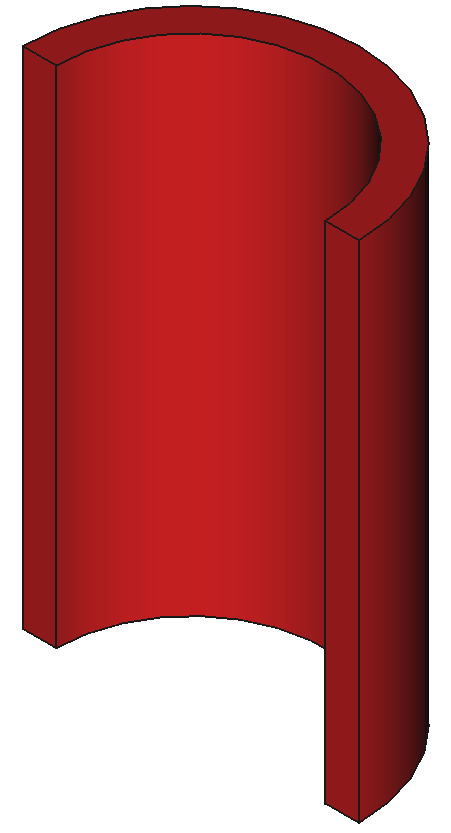
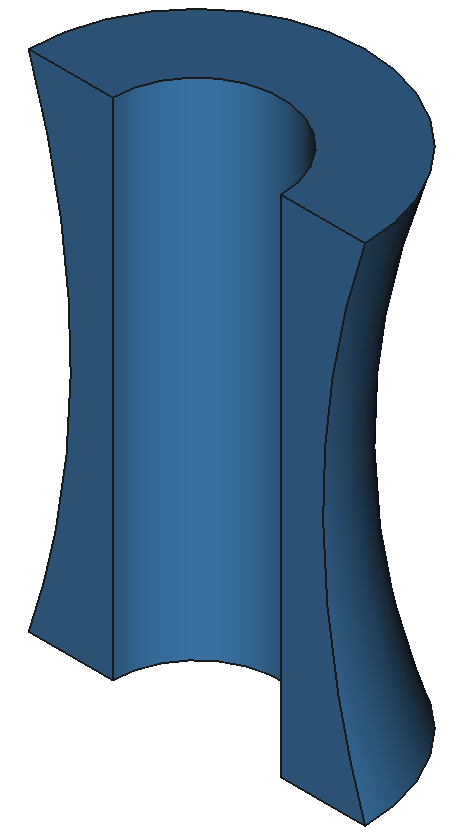
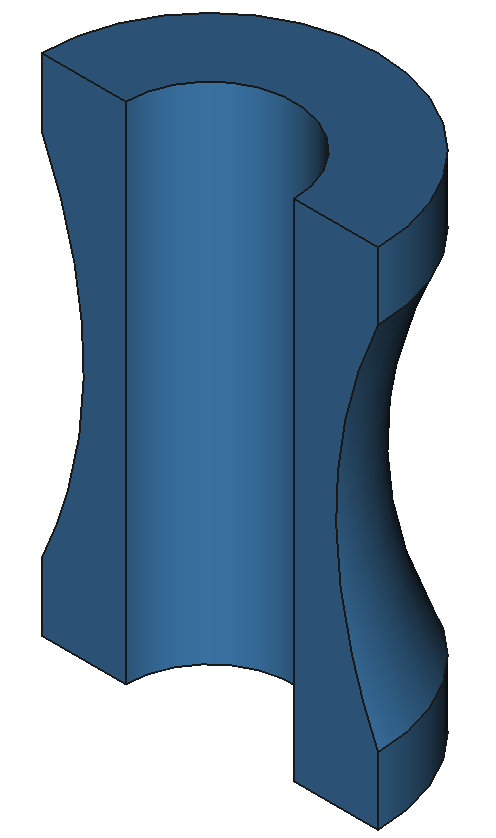
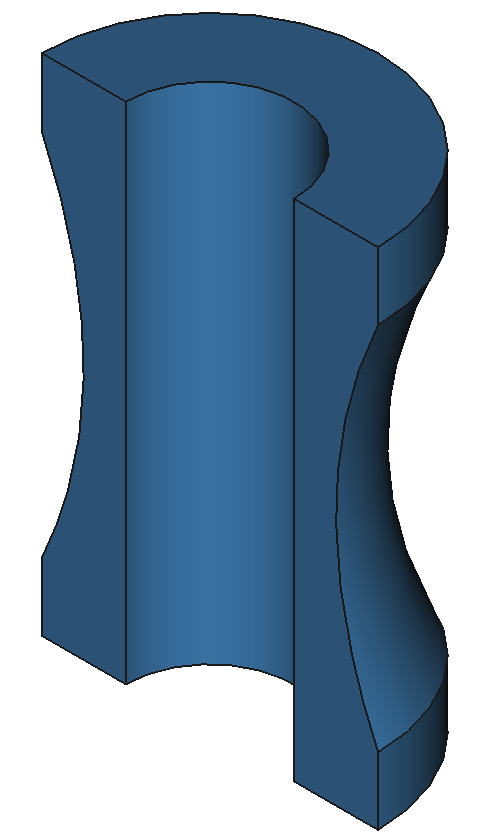
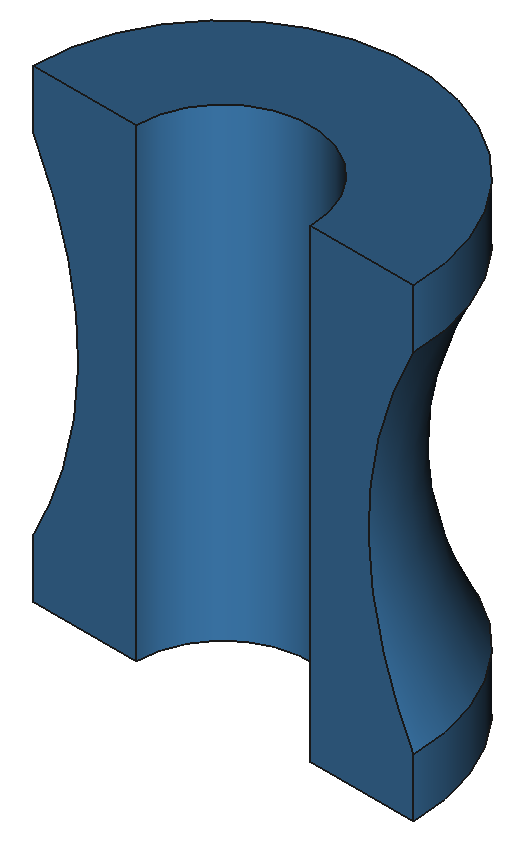
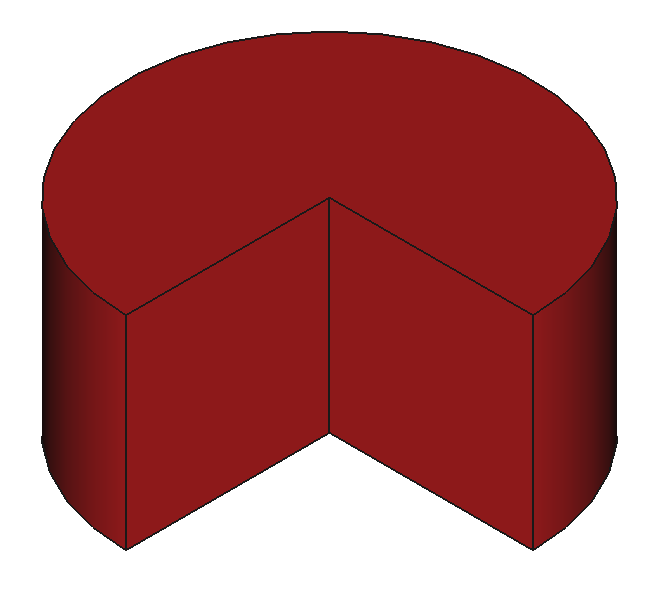
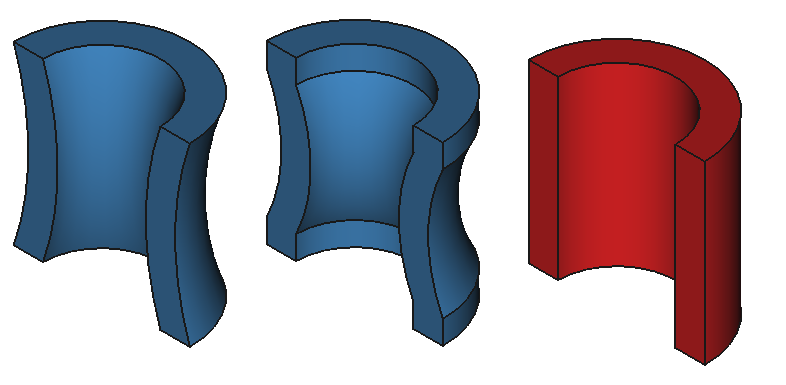
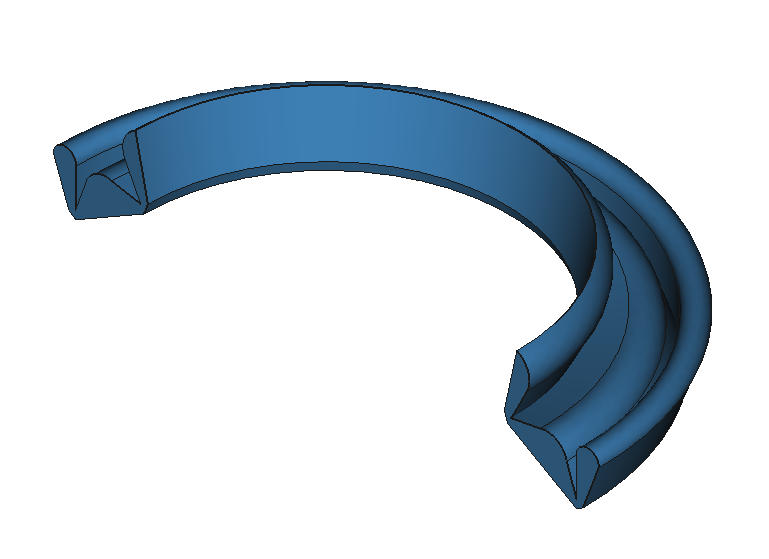
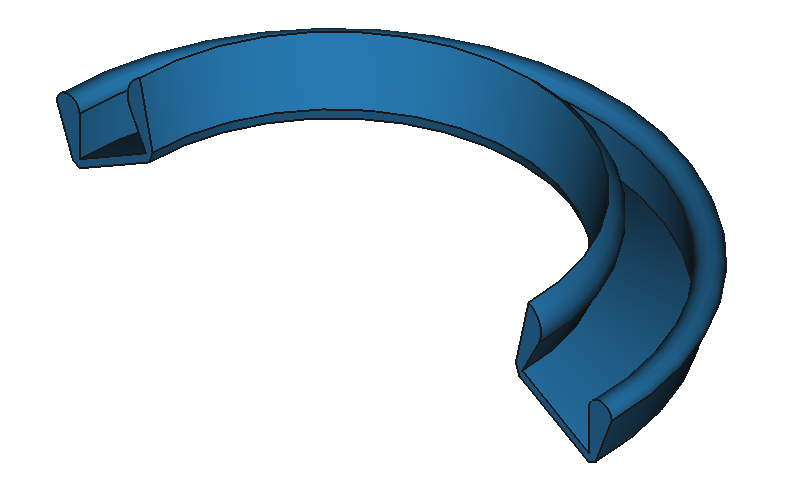
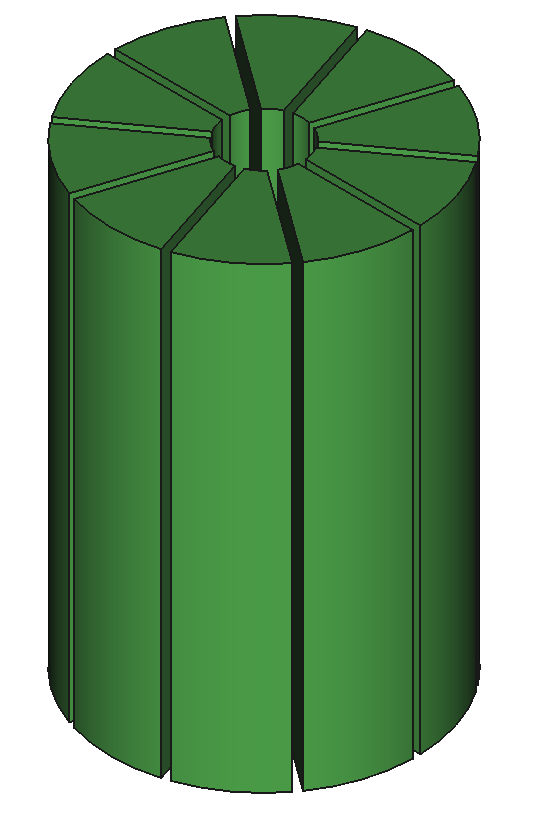
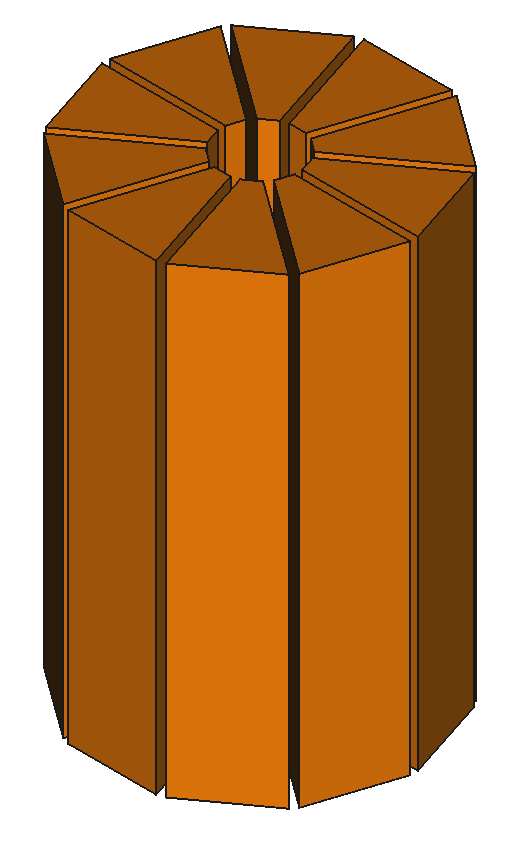
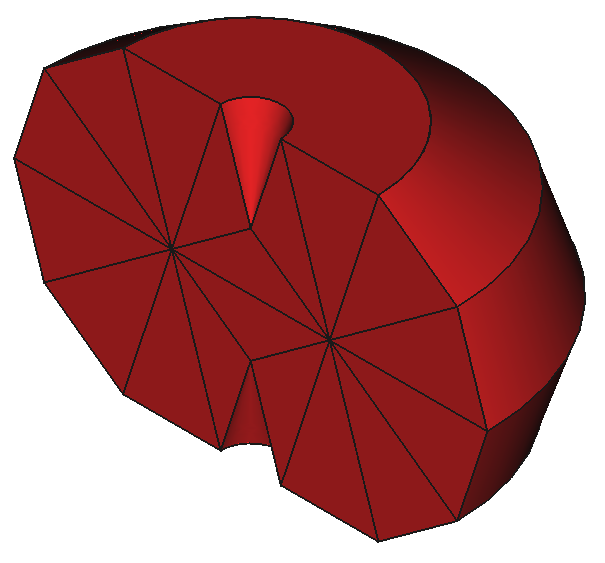
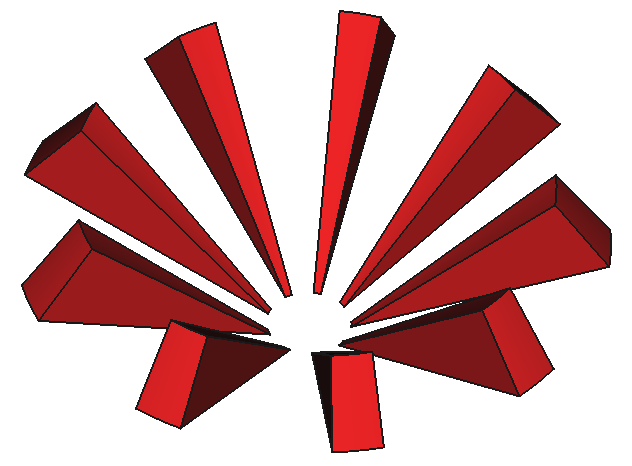
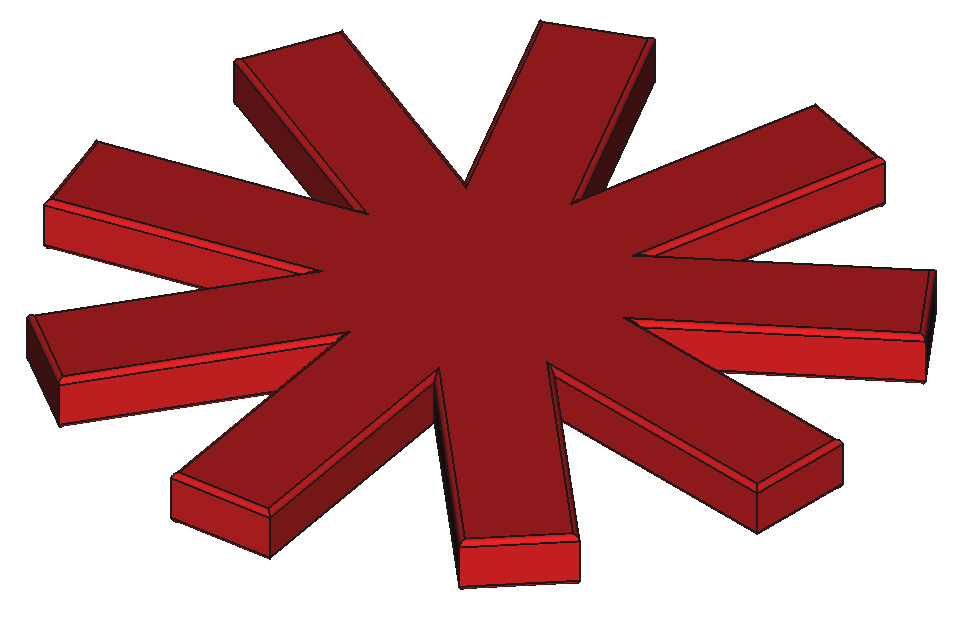
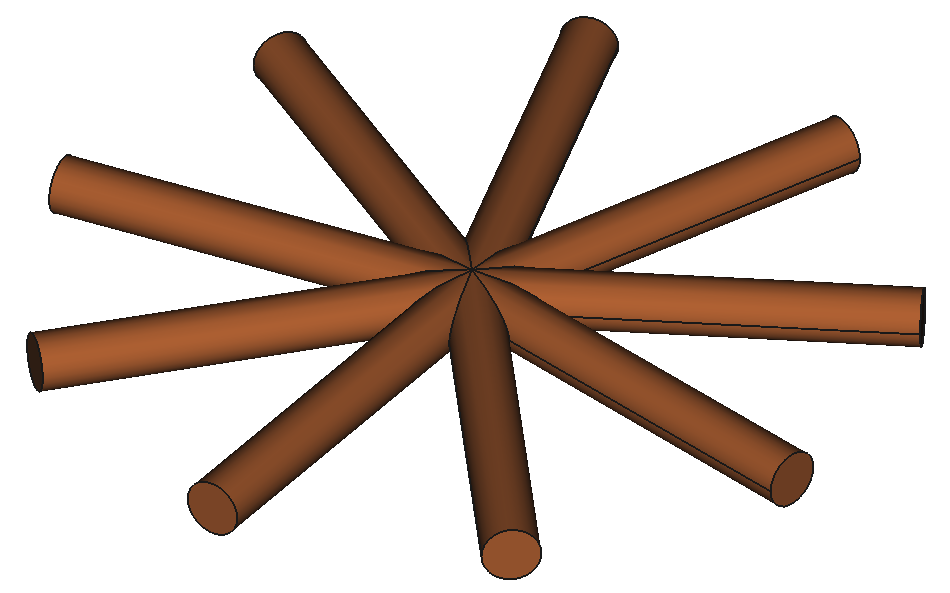
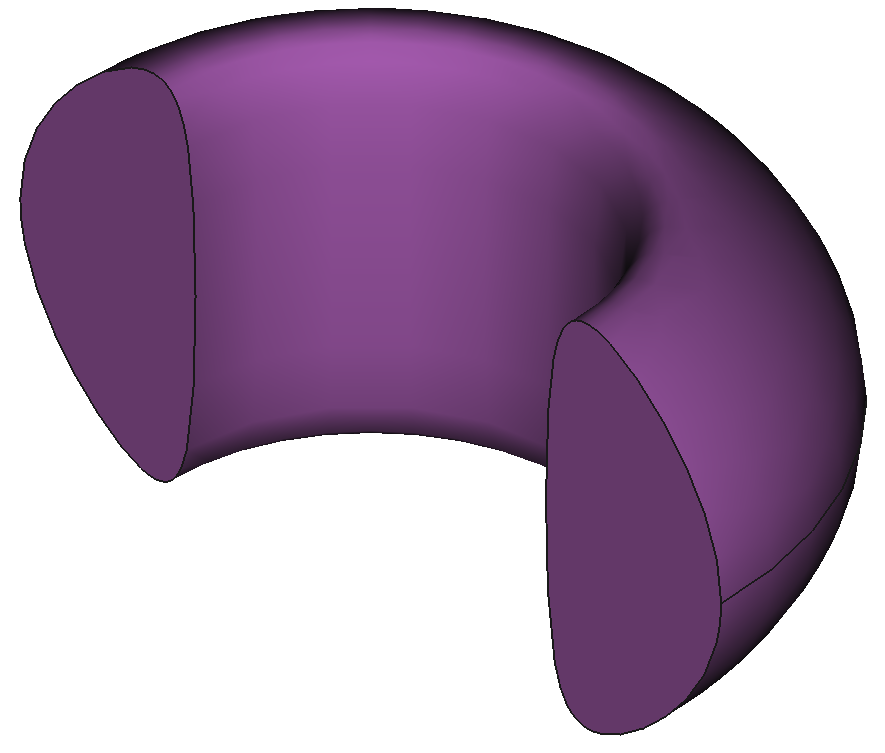
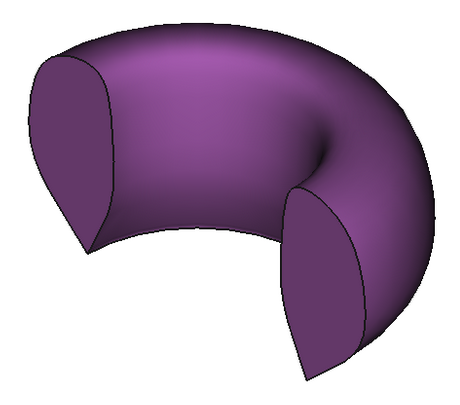
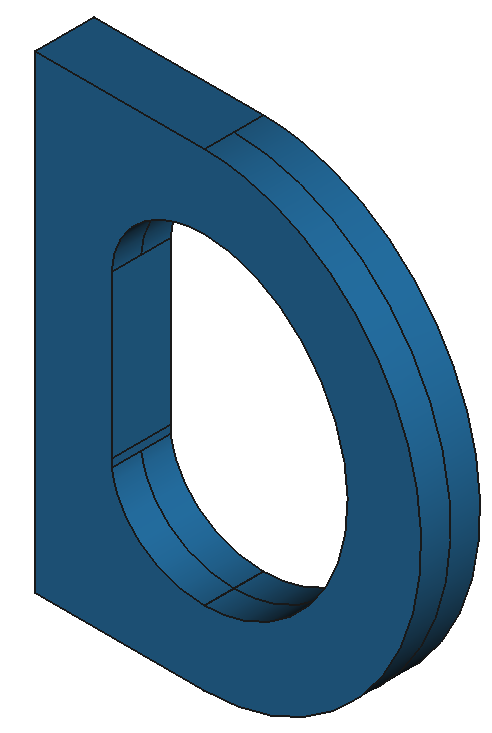
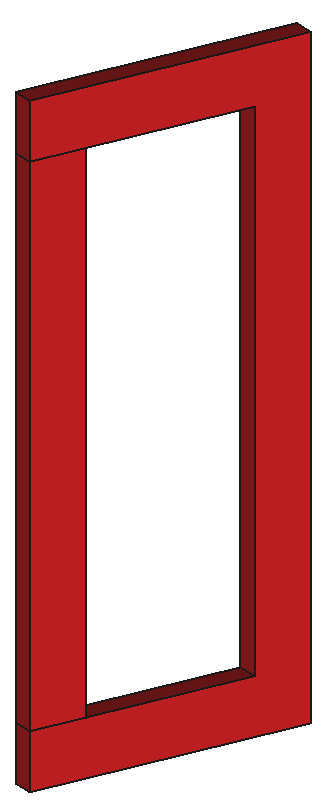
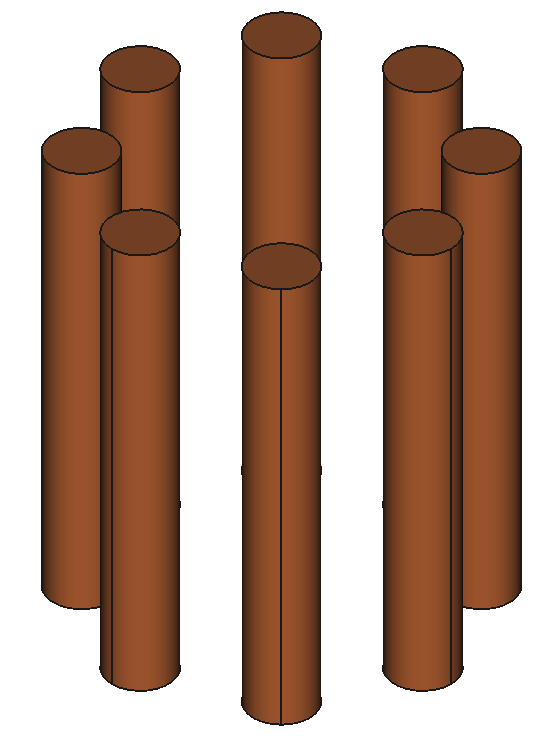
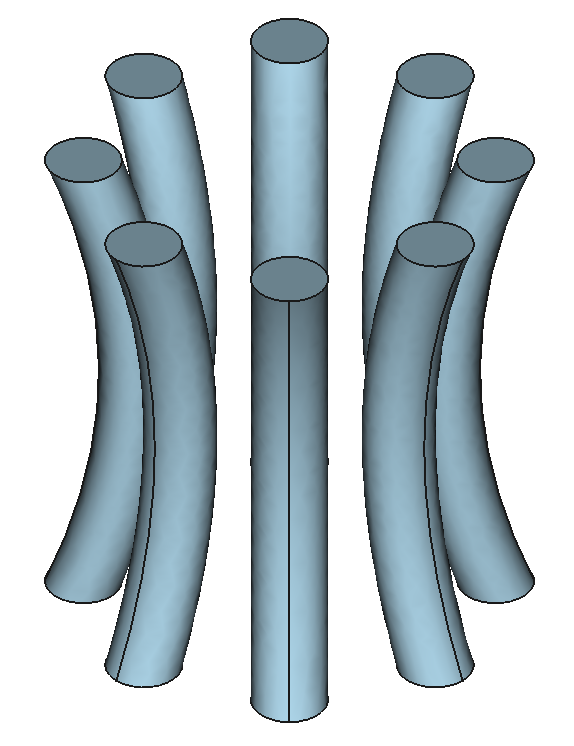
37
Components
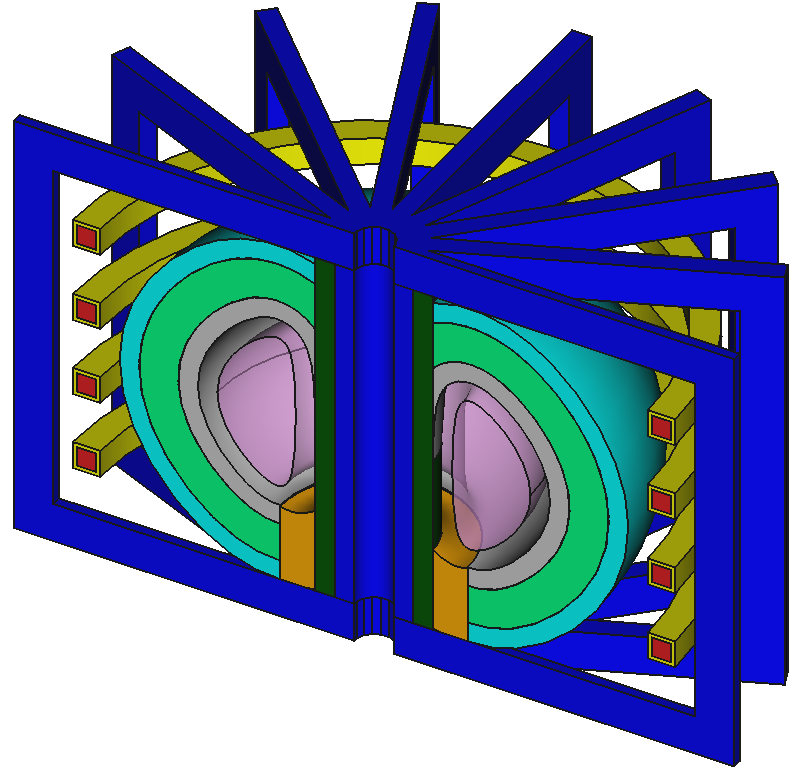
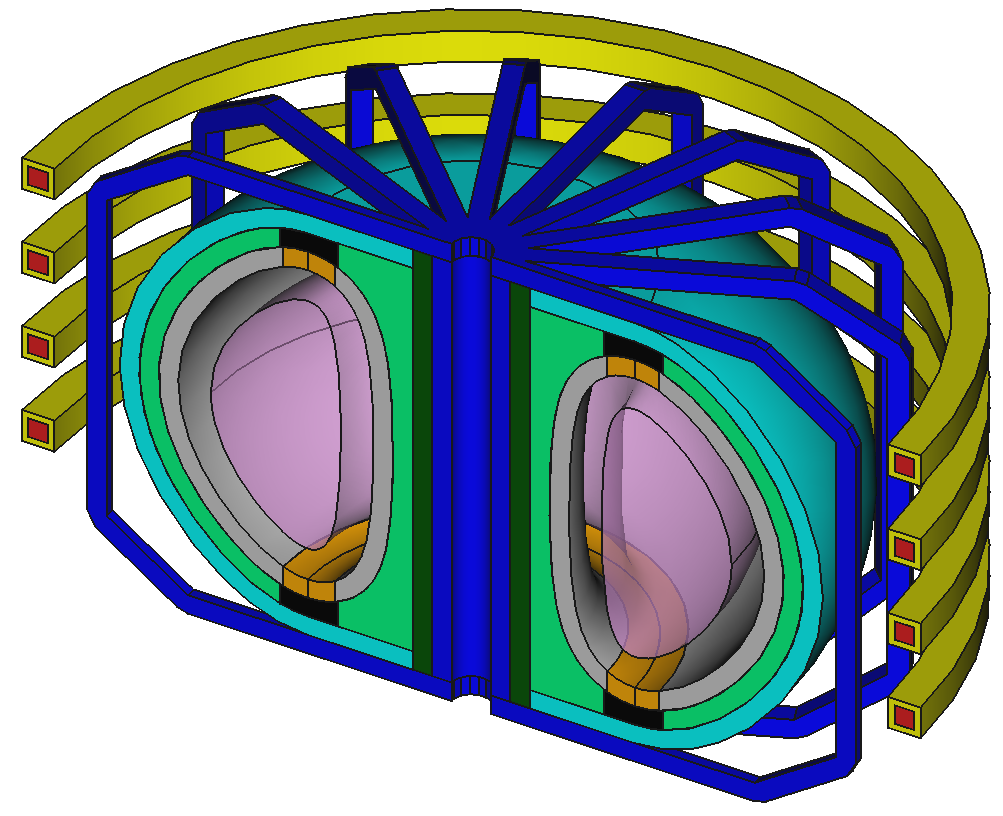
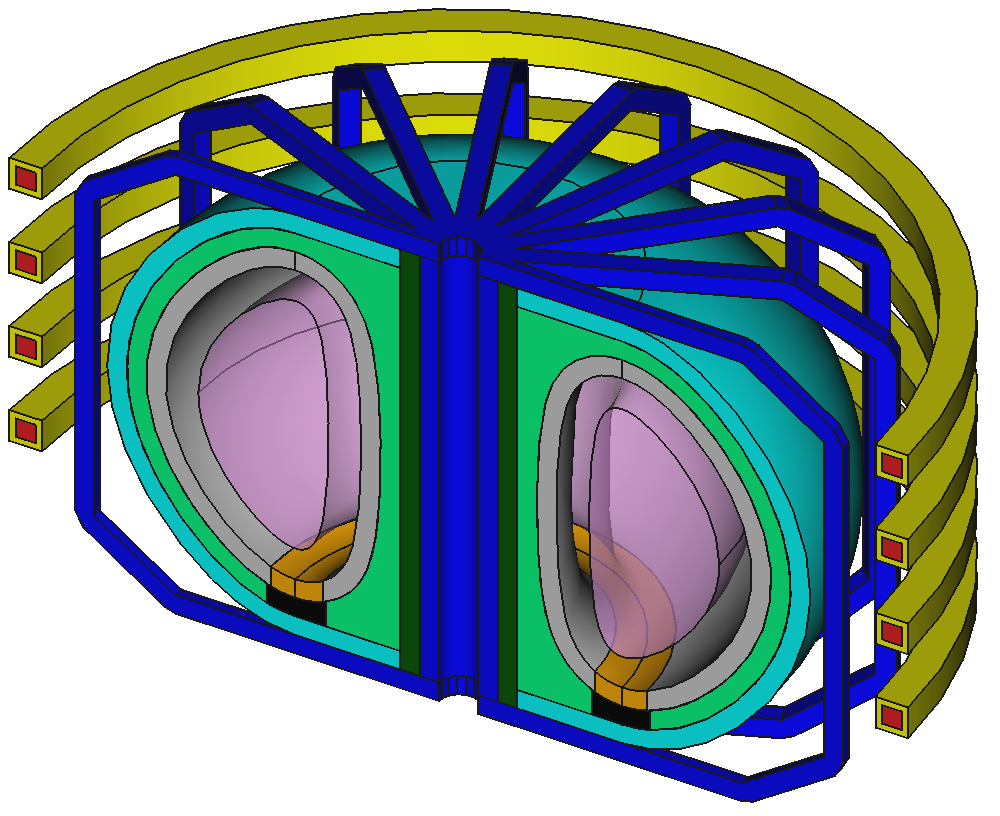
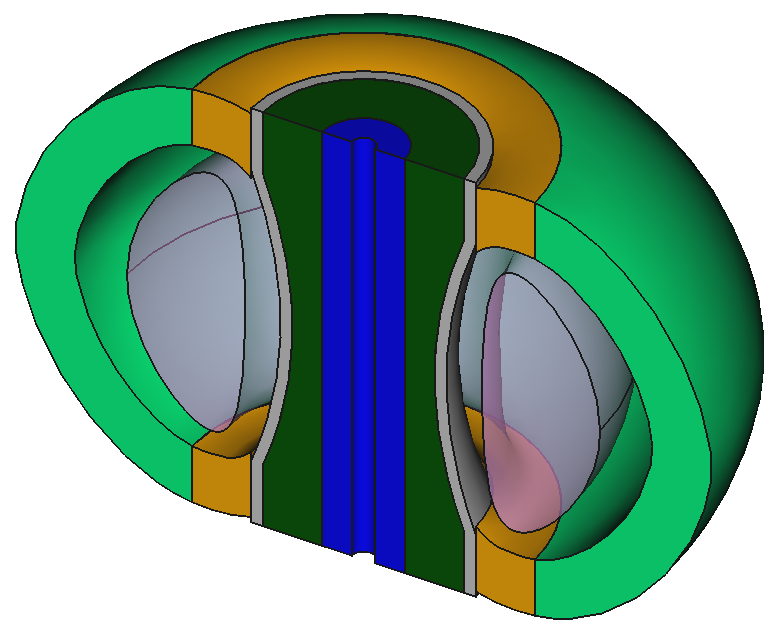
9
Reactors


Base parametric Shapes()
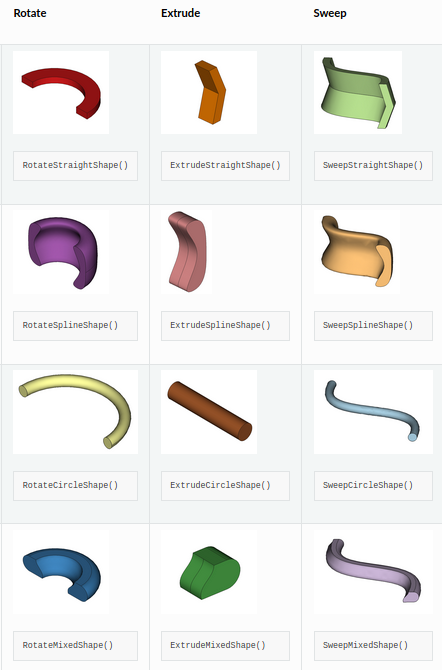
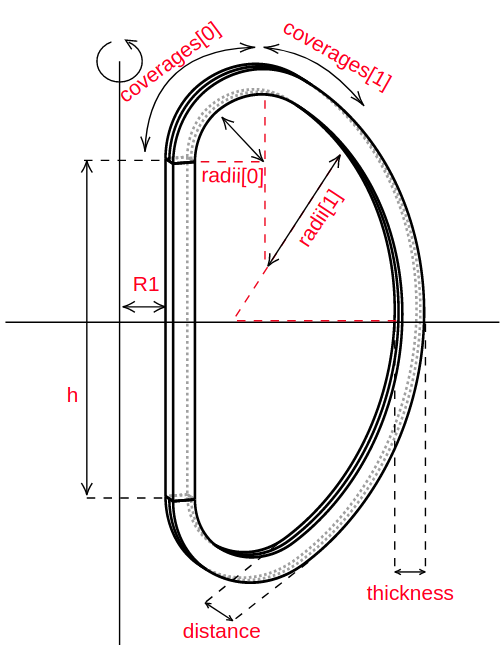
- Shapes require the user to provide points / coordinates to make a 3D geometry.
- A rotate, extrude or sweep operation is applied to the points
- Boolean operations such as cut, union, intersection are supported
- Repeating patterns around an axis are supported


Components from Shapes
import paramak
height = 700
blanket_rear = 400
blanket_front = 300
blanket_mid_point = 350
blanket = paramak.RotateMixedShape(
rotation_angle=180,
points=[
(blanket_rear, height / 2.0, "straight"),
(blanket_rear, -height / 2.0, "straight"),
(blanket_front, -height / 2.0, "spline"),
(blanket_mid_point, 0, "spline"),
(blanket_front, height / 2.0, "straight"),
]
)
blanket.export_stp('"blanket.stp")
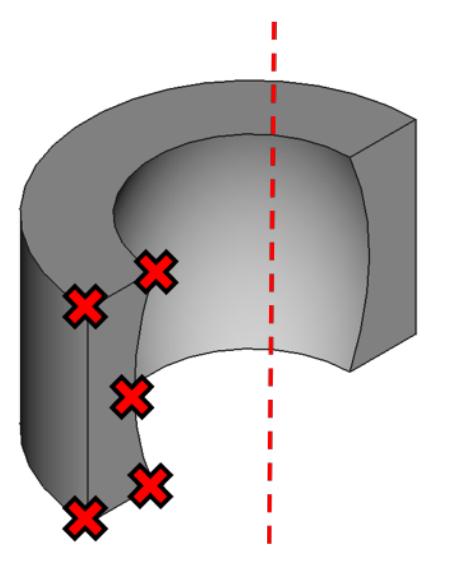
import paramak
blanket = paramak.RotateMixedShape(
rotation_angle=180,
points=[
(538, 305, "straight"),
(538, -305, "straight"),
(322, -305, "spline"),
(470, 0, "spline"),
(322, 305, "straight"),
]
)
blanket.export_stp("blanket.stp")
CAD from points
CAD from parameters


Simple Parametric Compents
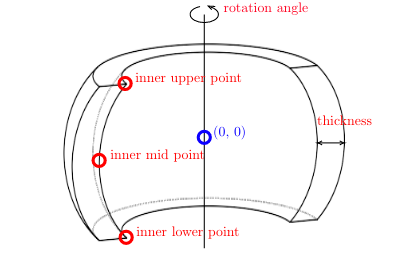
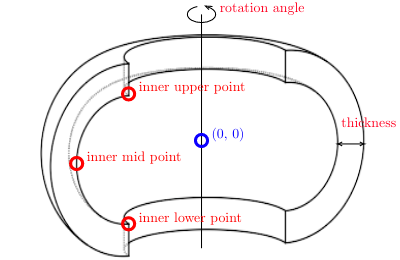
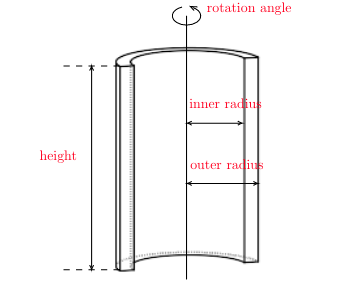
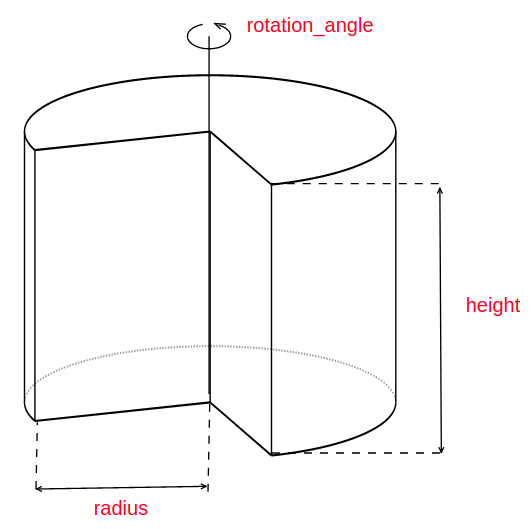
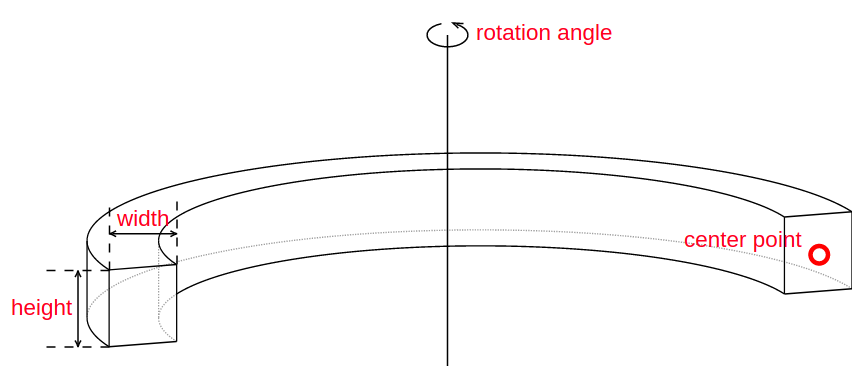
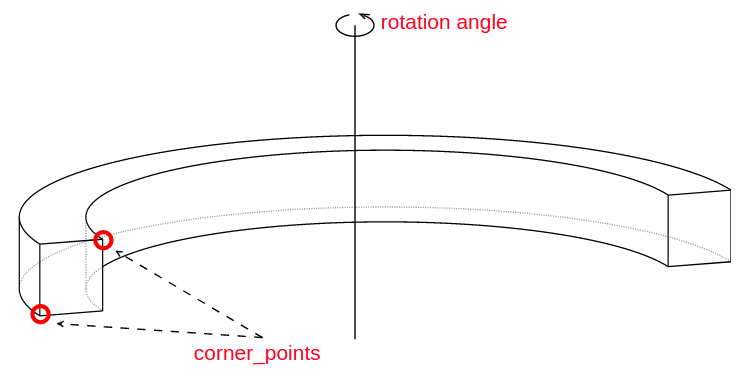
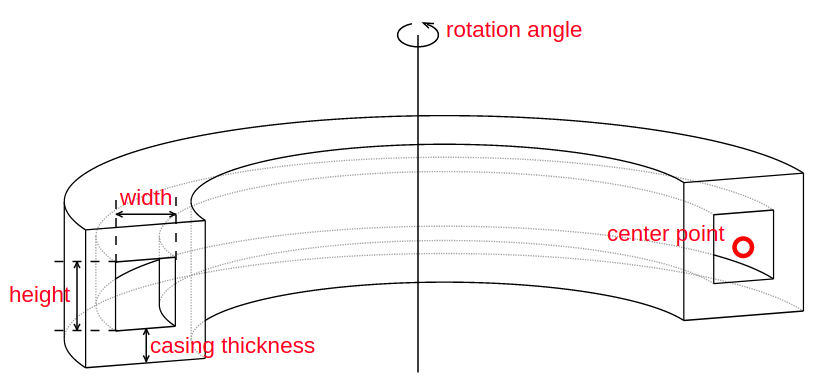
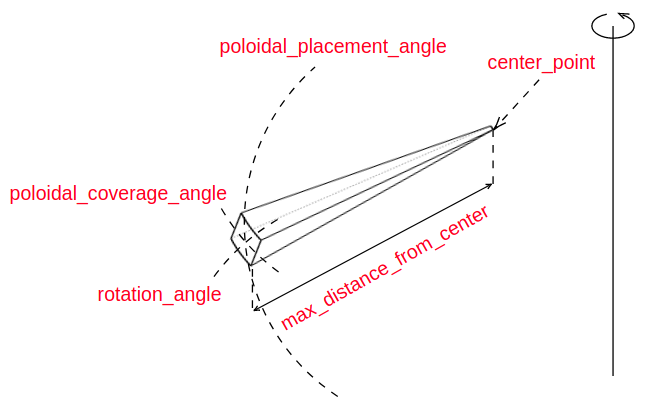
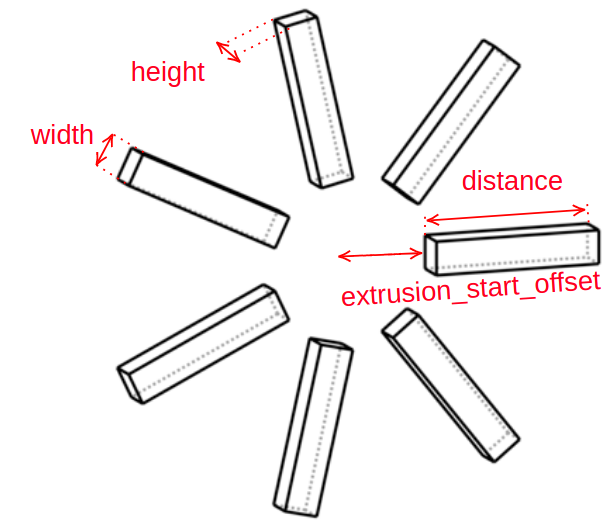
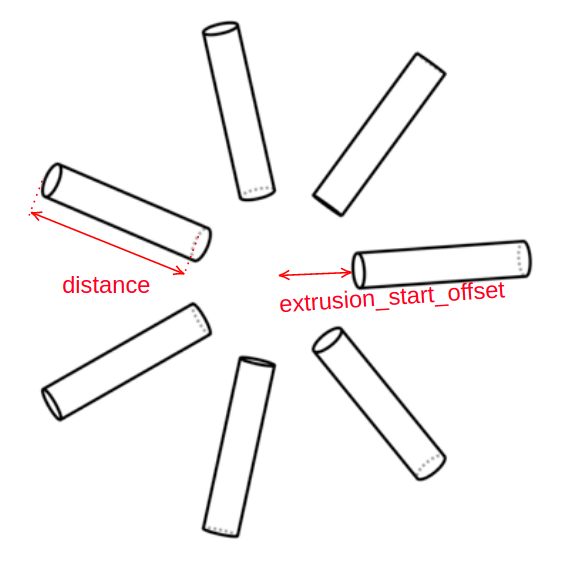

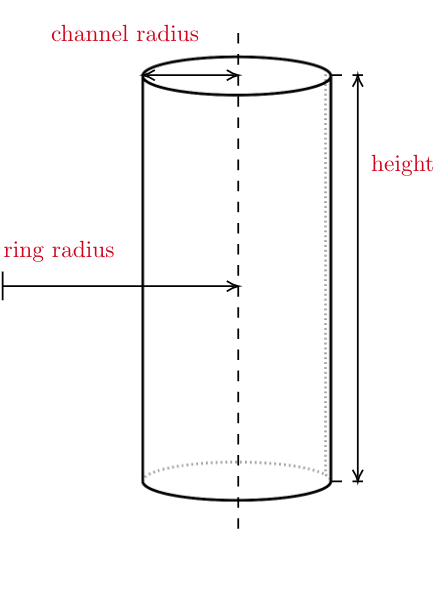
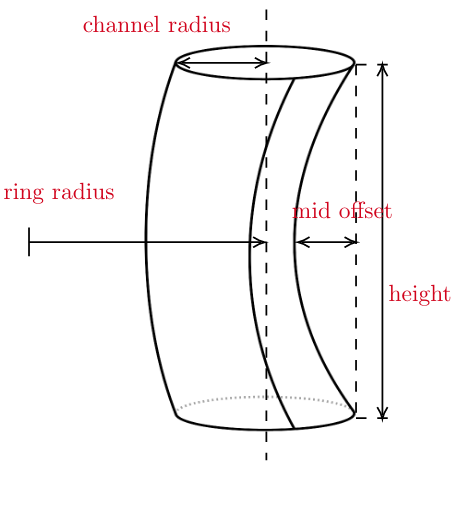
All instances of Shape classes with encoded design rules for generating the points needed


More complex Components
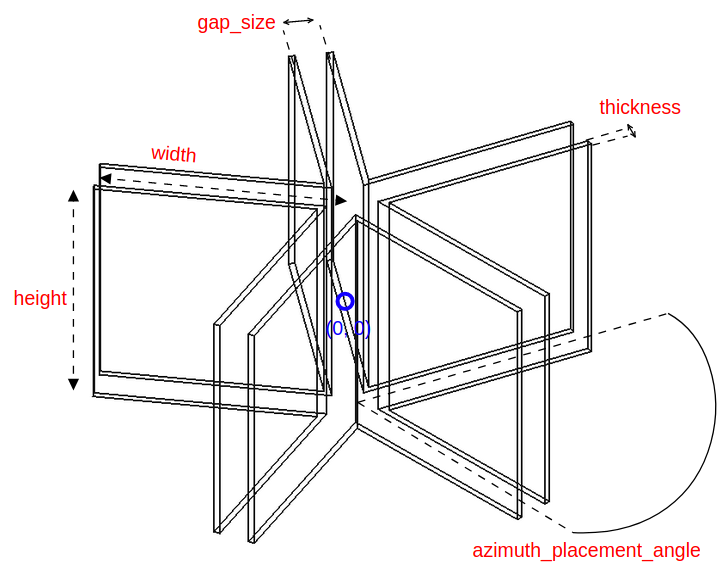
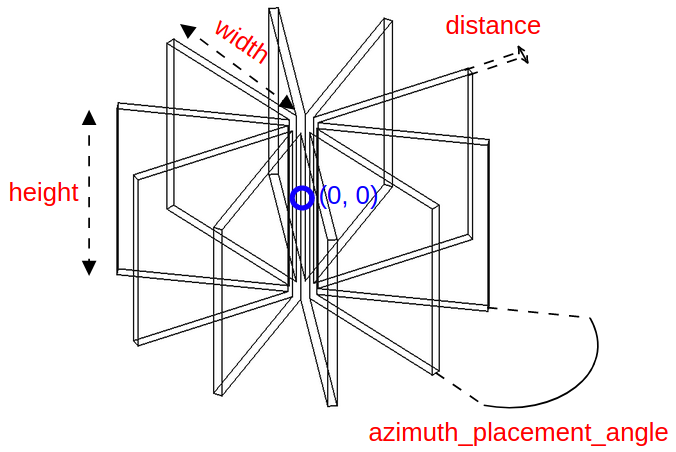
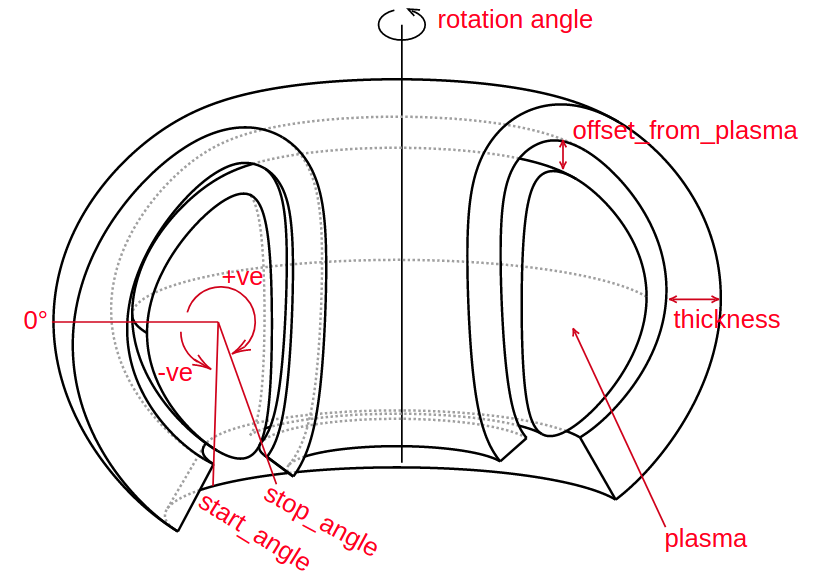
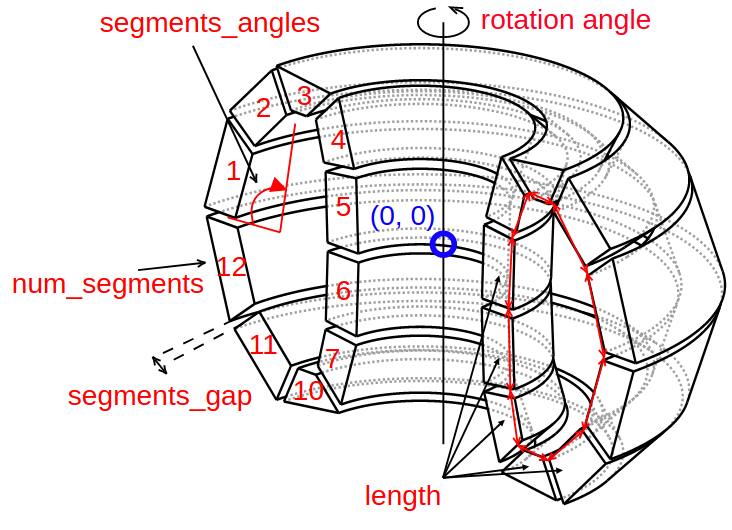
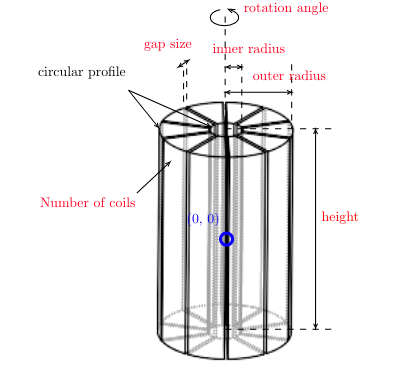
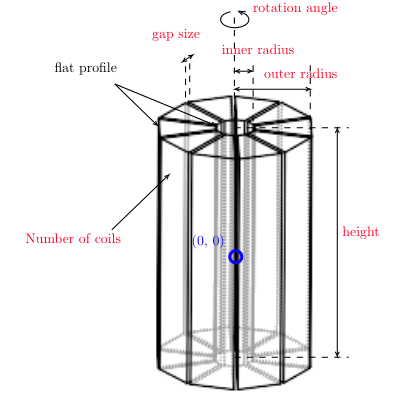
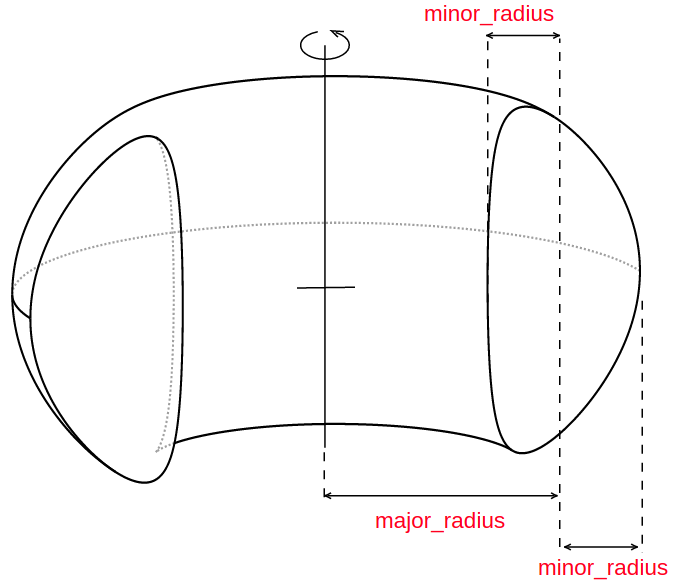
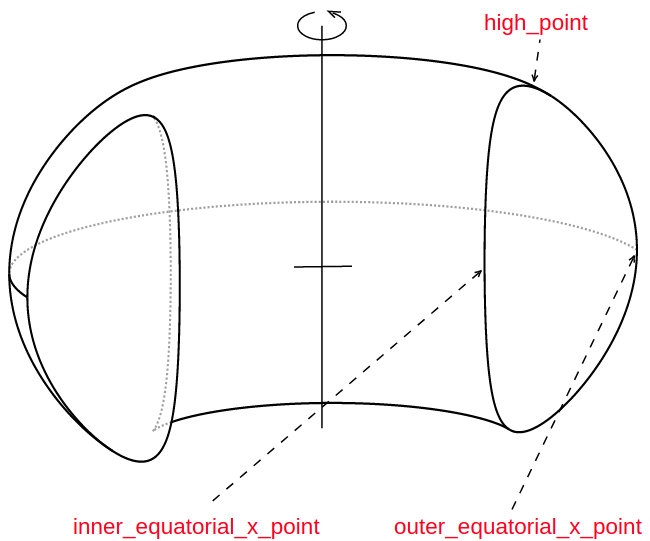
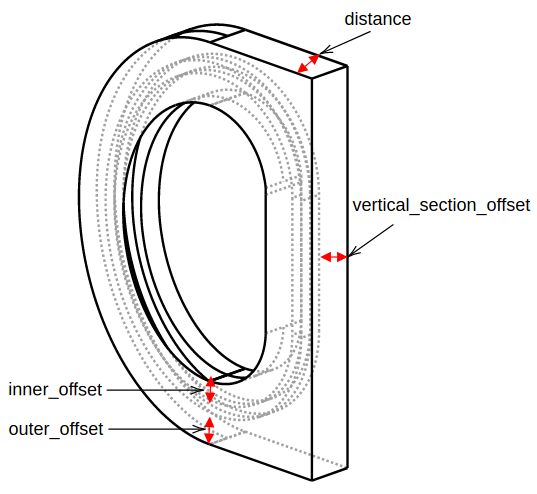
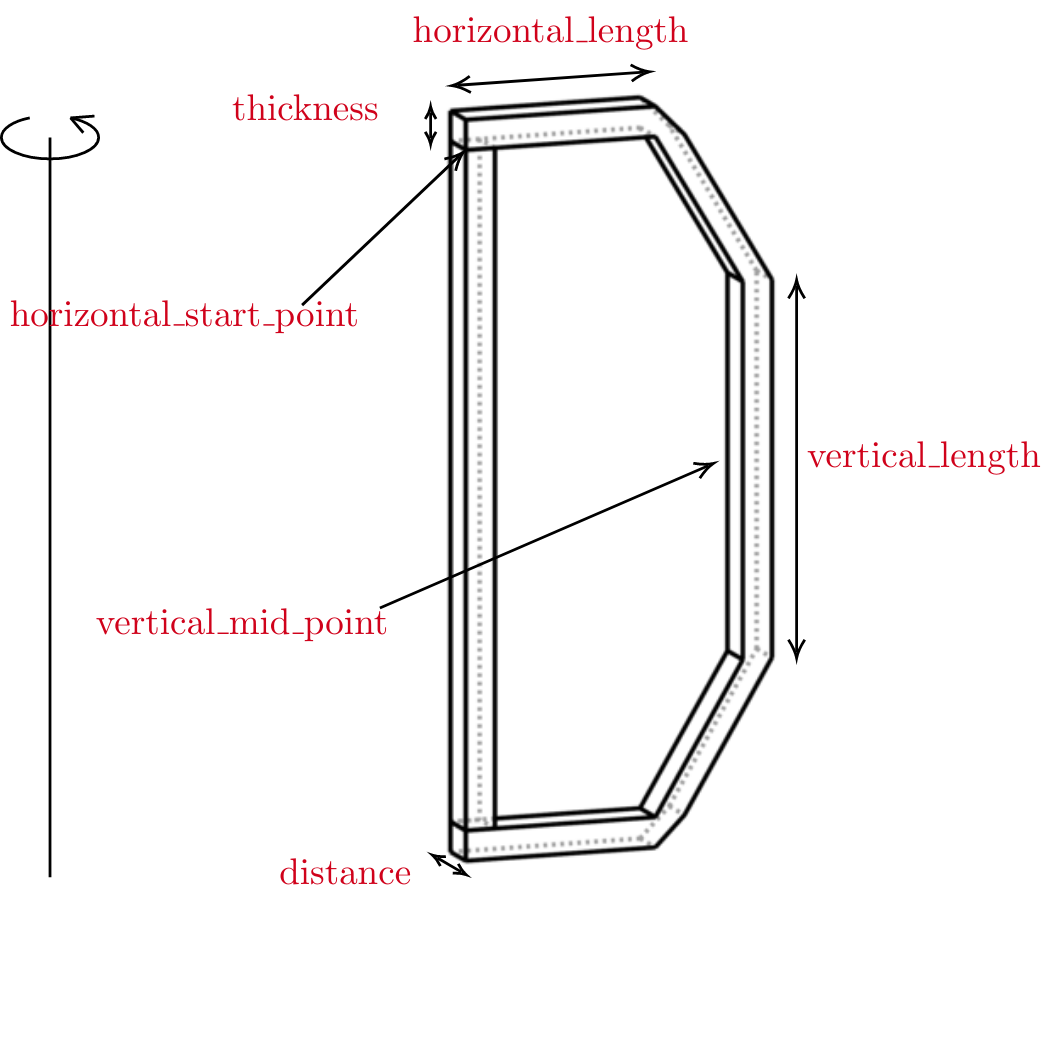
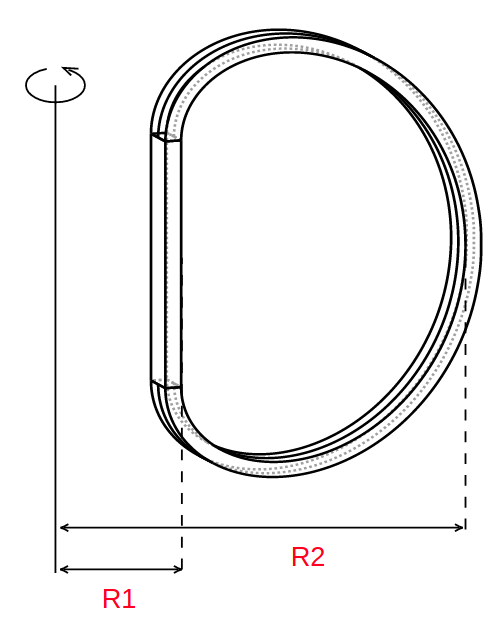
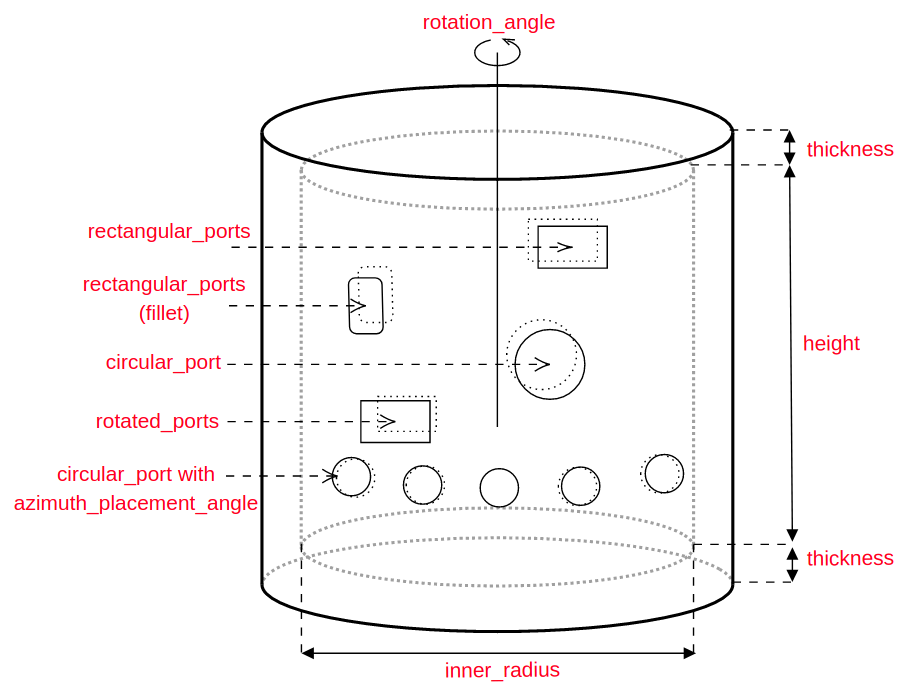
All instances of Shape classes with encoded design rules for generating the points needed


Parametric Components()



































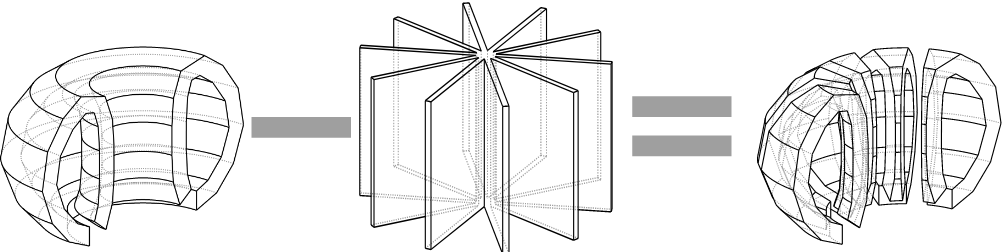
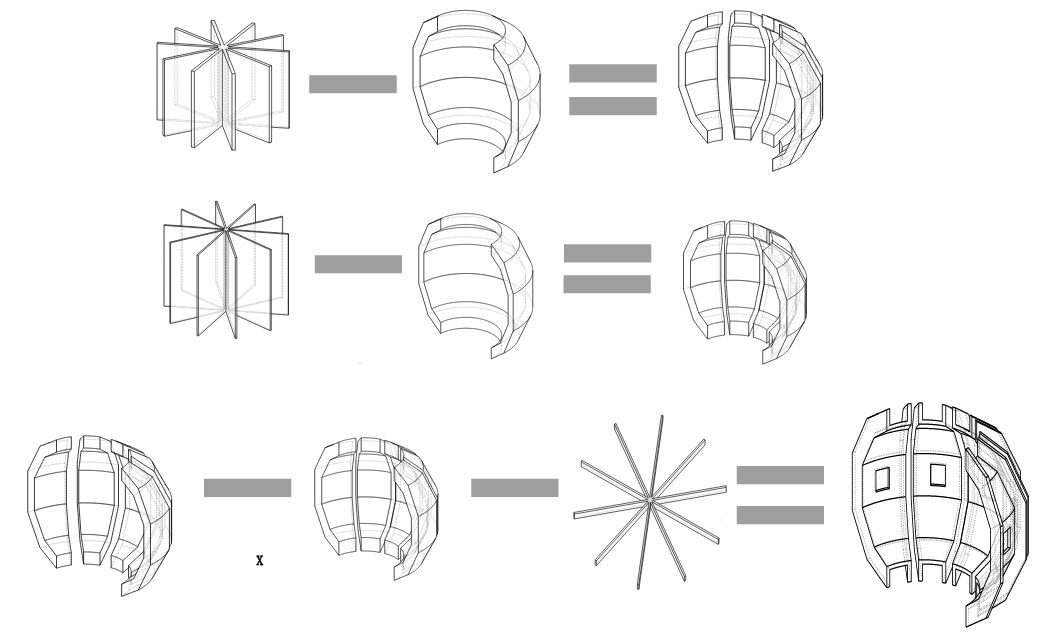

Parameters CAD geometry DAGMC h5m OpenMC simulation
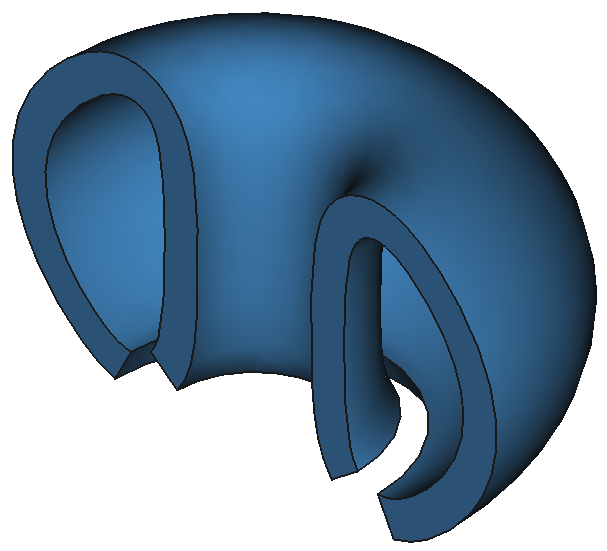


Example parametric Reactors






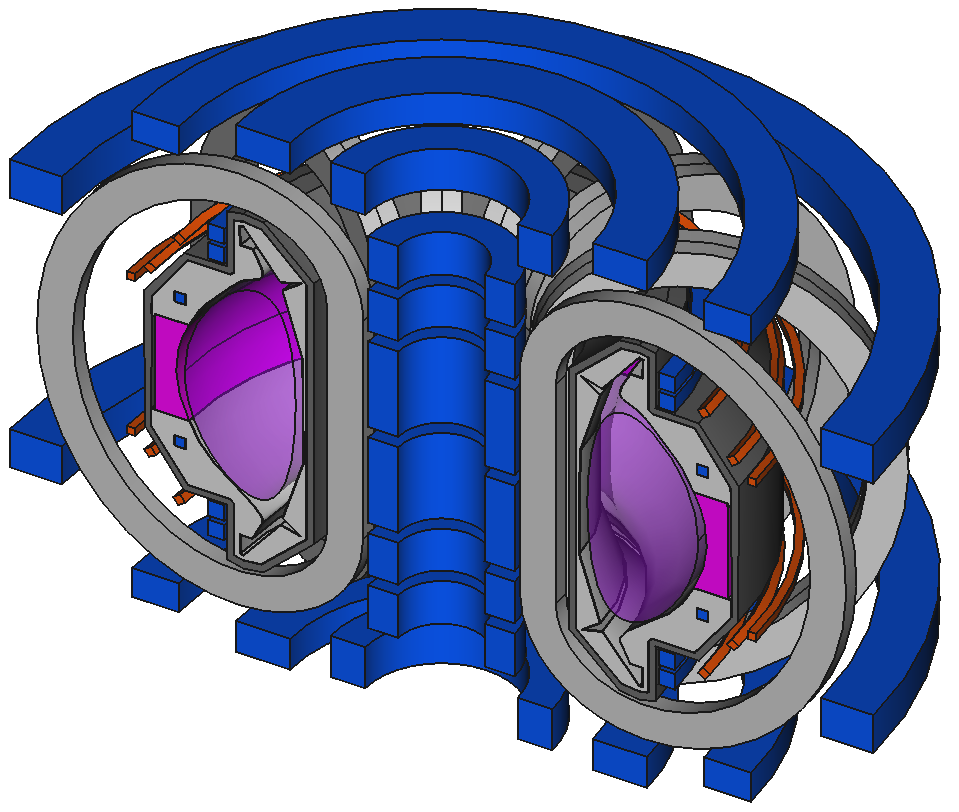


import paramak
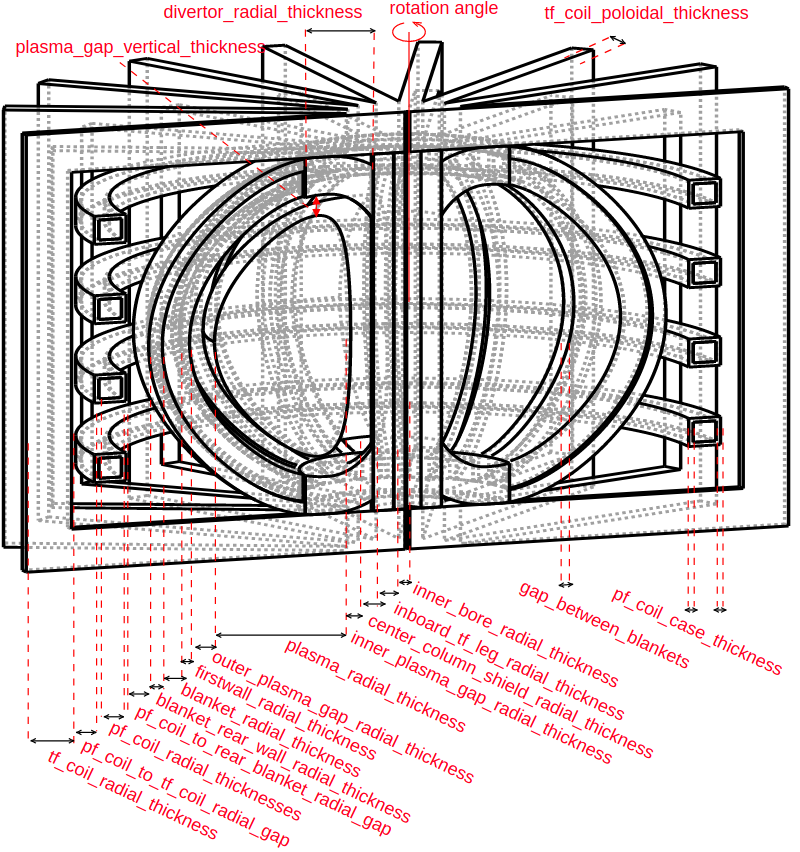
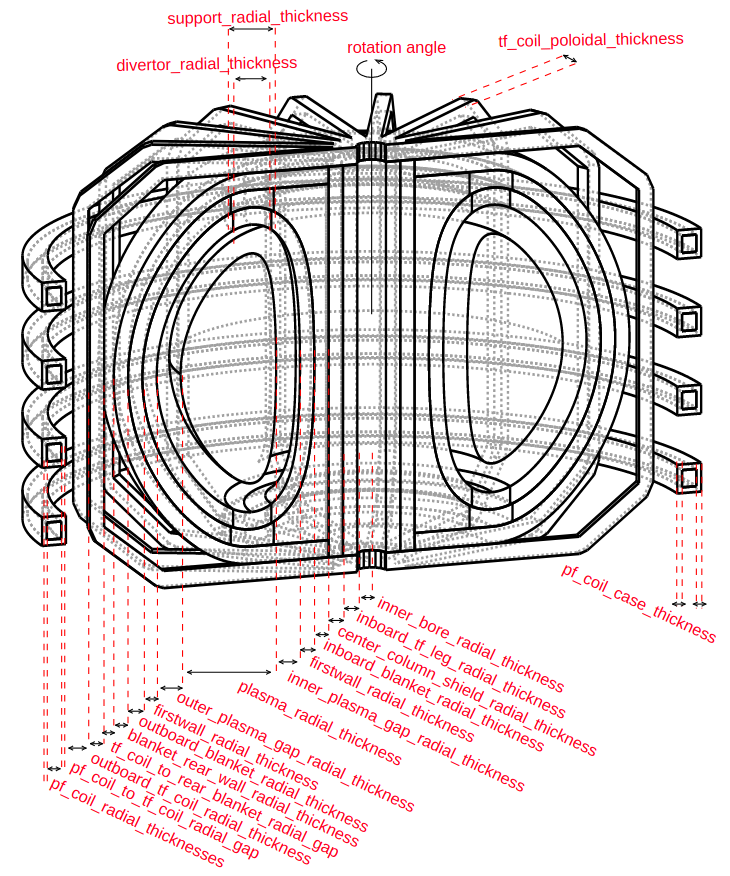
my_reactor = paramak.BallReactor(
inner_bore_radial_thickness=10,
inboard_tf_leg_radial_thickness=30,
center_column_shield_radial_thickness=60,
divertor_radial_thickness=150,
inner_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=30,
plasma_radial_thickness=300,
outer_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=30,
firstwall_radial_thickness=30,
blanket_radial_thickness=50,
blanket_rear_wall_radial_thickness=30,
elongation=2,
triangularity=0.55,
number_of_tf_coils=16,
rotation_angle=180,
pf_coil_radial_thicknesses=[50, 50, 50, 50],
pf_coil_vertical_thicknesses=[50, 50, 50, 50],
pf_coil_to_rear_blanket_radial_gap=50,
pf_coil_to_tf_coil_radial_gap=50,
outboard_tf_coil_radial_thickness=100,
outboard_tf_coil_poloidal_thickness=50
)import paramak
my_reactor = paramak.SubmersionTokamak(
inner_bore_radial_thickness=30,
inboard_tf_leg_radial_thickness=30,
center_column_shield_radial_thickness=30,
divertor_radial_thickness=80,
inner_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
plasma_radial_thickness=200,
outer_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
firstwall_radial_thickness=30,
blanket_rear_wall_radial_thickness=30,
number_of_tf_coils=16,
rotation_angle=180,
support_radial_thickness=90,
inboard_blanket_radial_thickness=30,
outboard_blanket_radial_thickness=30,
elongation=2.00,
triangularity=0.50,
pf_coil_radial_thicknesses=[30, 30, 30, 30],
pf_coil_vertical_thicknesses=[30, 30, 30, 30],
pf_coil_to_tf_coil_radial_gap=50,
outboard_tf_coil_radial_thickness=30,
outboard_tf_coil_poloidal_thickness=30,
tf_coil_to_rear_blanket_radial_gap=20,
)

Decompose existing models
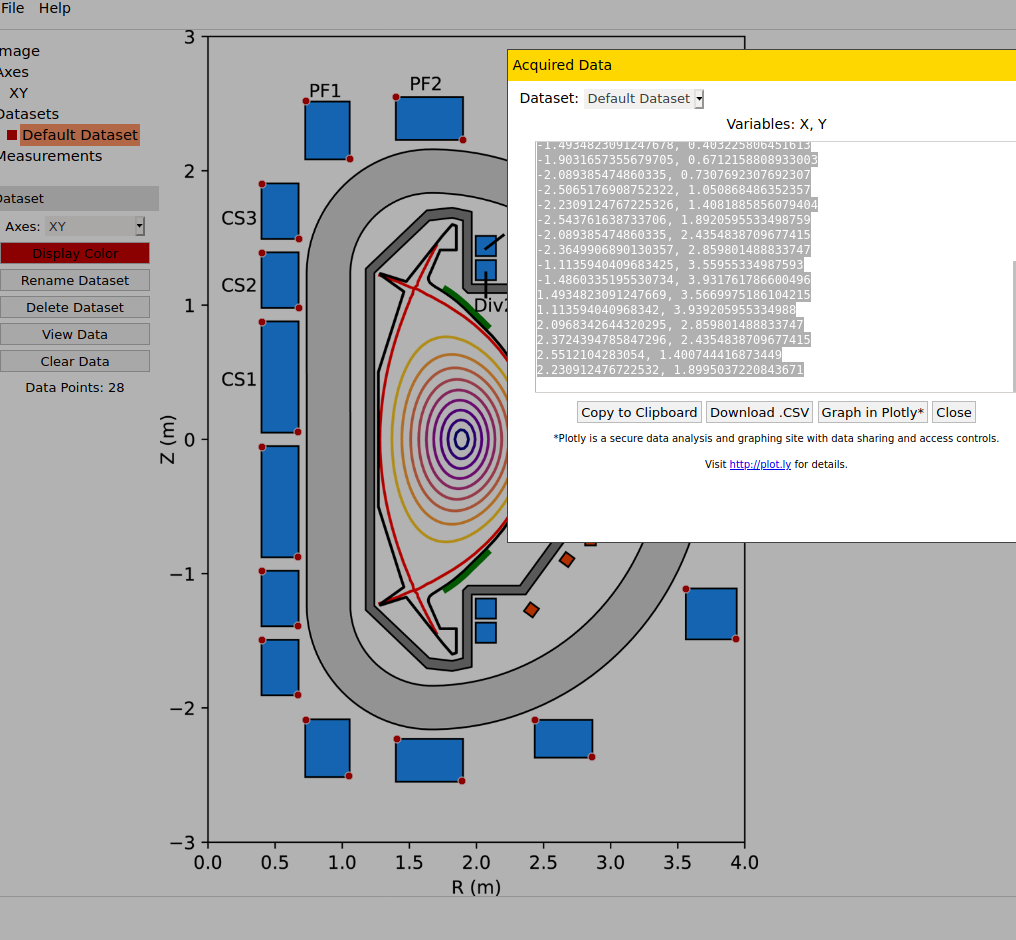
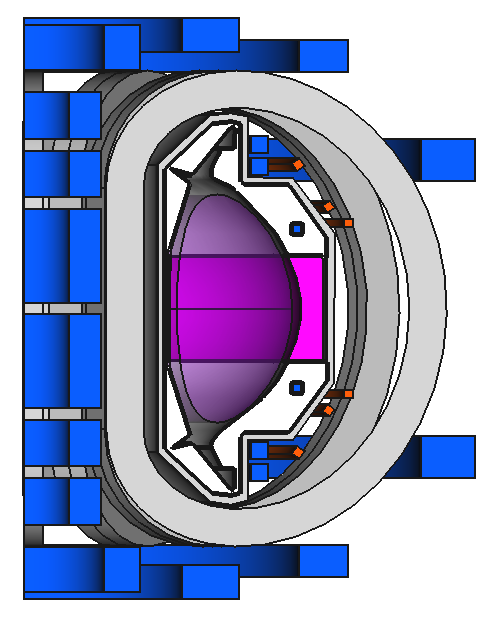
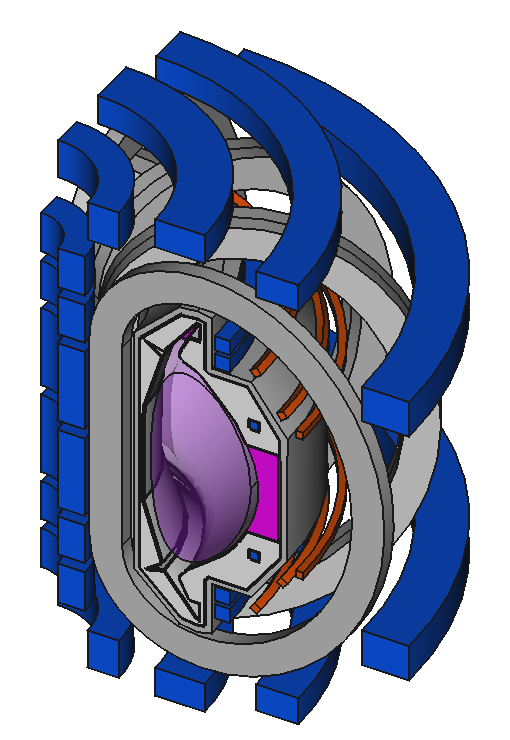
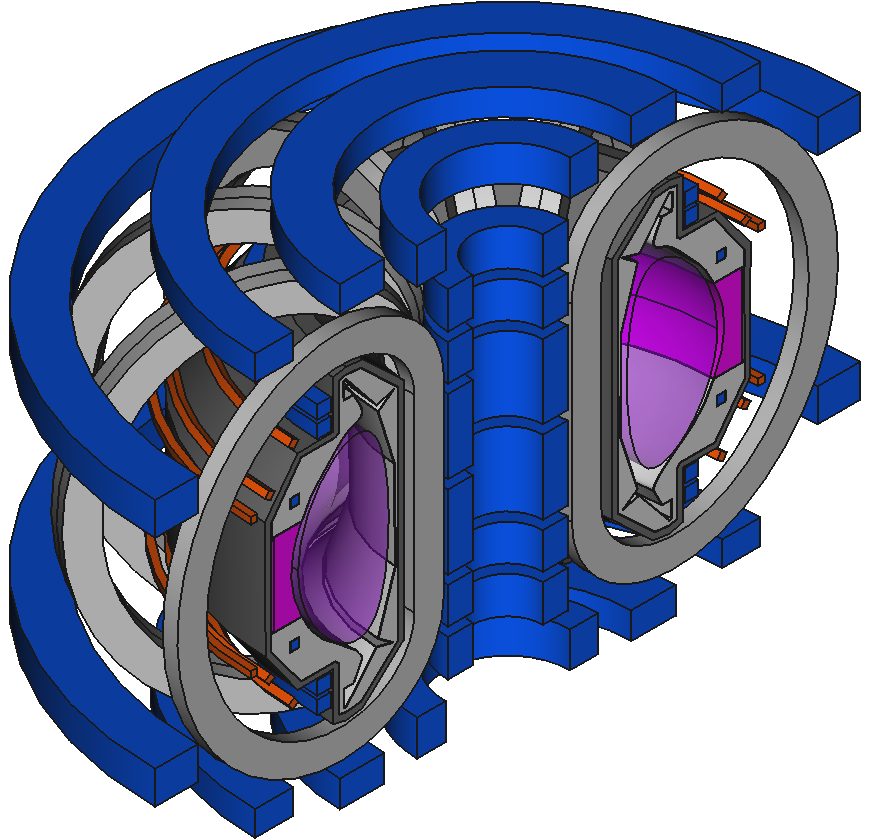
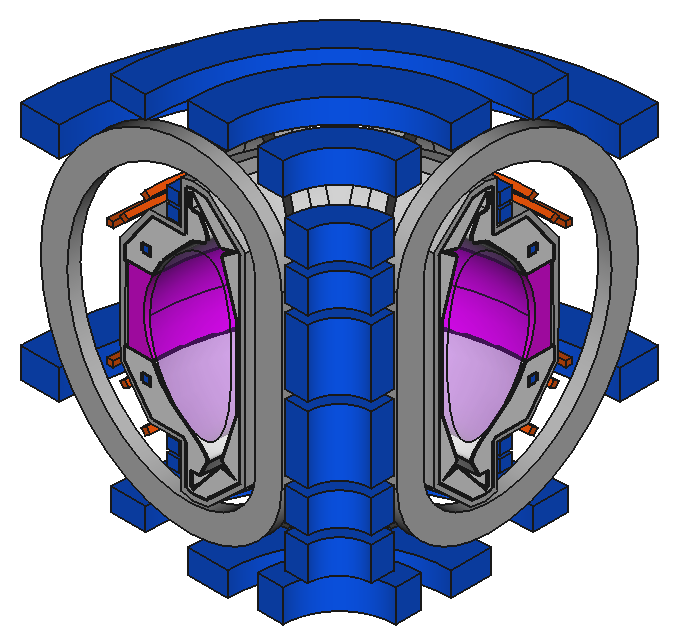
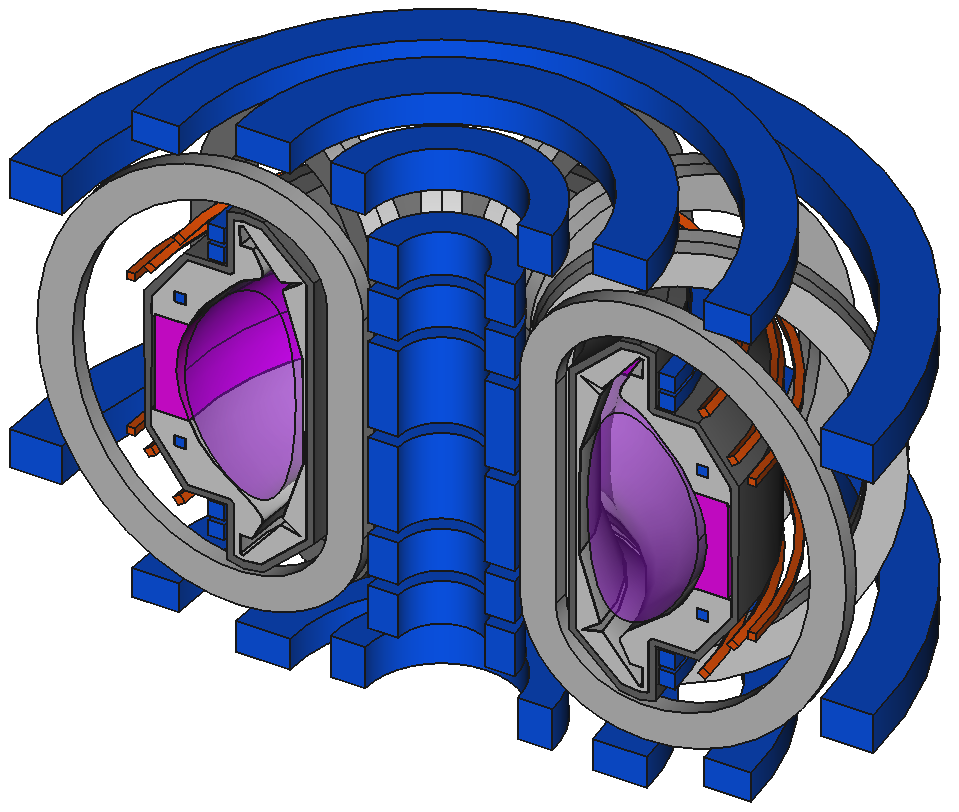
Image source Overview of the SPARC tokamak. Journal of Plasma Physics, 86(5), 865860502. doi:10.1017/S0022377820001257


Progress
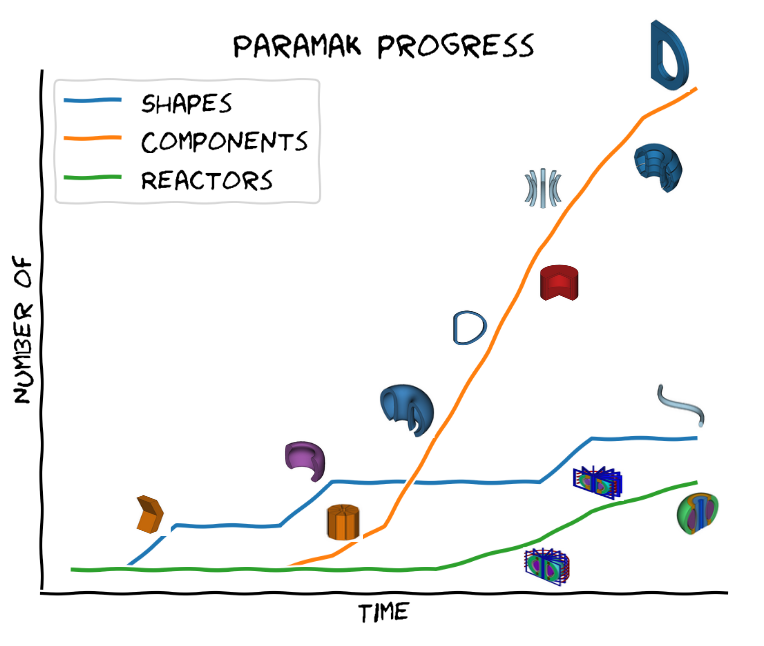
Rough estimate of how we have built up the number of parametric shapes, parametric components and parametric reactors over time.
12
33
6


Neutronics Support
Geometry output formats:
- stp
- stl
- h5m
- vtk
Automatic conversion of geometry into DAGMC based neutronics geometry
(h5m file)
import paramak
# # makes the 3d geometry from input parameters
my_reactor = paramak.BallReactor(
inner_bore_radial_thickness=50,
inboard_tf_leg_radial_thickness=200,
center_column_shield_radial_thickness=50,
divertor_radial_thickness=50,
inner_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
plasma_radial_thickness=100,
outer_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
firstwall_radial_thickness=1,
blanket_radial_thickness=100,
blanket_rear_wall_radial_thickness=10,
elongation=2,
triangularity=0.55,
number_of_tf_coils=16,
rotation_angle=360,
)
my_reactor.export_stp()
my_reactor.export_stl()
my_reactor.export_h5m(method='pymoab')
my_reactor.export_h5m(method='trelis')
my_reactor.export_vtk()


Neutronics Support
Addition of:
- materials,
- tallies,
- source
to combine with the neutronics geometry to make a neutronics model
import paramak
# # makes the 3d geometry from input parameters
my_reactor = paramak.BallReactor(
inner_bore_radial_thickness=50,
inboard_tf_leg_radial_thickness=200,
center_column_shield_radial_thickness=50,
divertor_radial_thickness=50,
inner_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
plasma_radial_thickness=100,
outer_plasma_gap_radial_thickness=50,
firstwall_radial_thickness=1,
blanket_radial_thickness=100,
blanket_rear_wall_radial_thickness=10,
elongation=2,
triangularity=0.55,
number_of_tf_coils=16,
rotation_angle=360,
)
# makes the neutronics model from the geometry and materials
neutronics_model = paramak.NeutronicsModel(
geometry=my_reactor,
materials={
'inboard_tf_coils_mat': 'eurofer',
'center_column_shield_mat': 'eurofer',
'divertor_mat': 'eurofer',
'firstwall_mat': 'eurofer',
'blanket_rear_wall_mat': 'eurofer',
'blanket_mat': 'Li4SiO4'},
cell_tallies=['TBR', 'heating'],
simulation_batches=5,
simulation_particles_per_batch=1e4,
)
neutronics_model.simulate()


Use cases - parameter studies
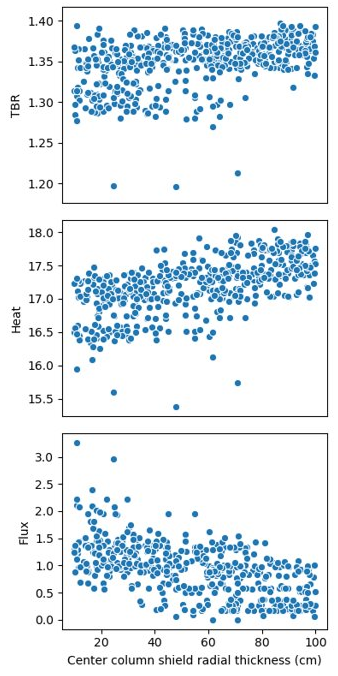
Carrying out a multi dimensional parameter study can be achieved with relatively low user effort


Software practices employed

Automated static code analysis with code-inspector.com



Automated docker build and distribution to dockerhub

Testing with Circle CI and Github Actions

Code coverage


Automated PyPi updating


Online Documentation


Summary
Automated geometry can help speed up the current
design process for pre-conceptual design
Documentation
https://paramak.readthedocs.io
Source code
https://github.com/ukaea/paramak
Package Distribution
https://pypi.org/project/paramak/
Environment Distribution
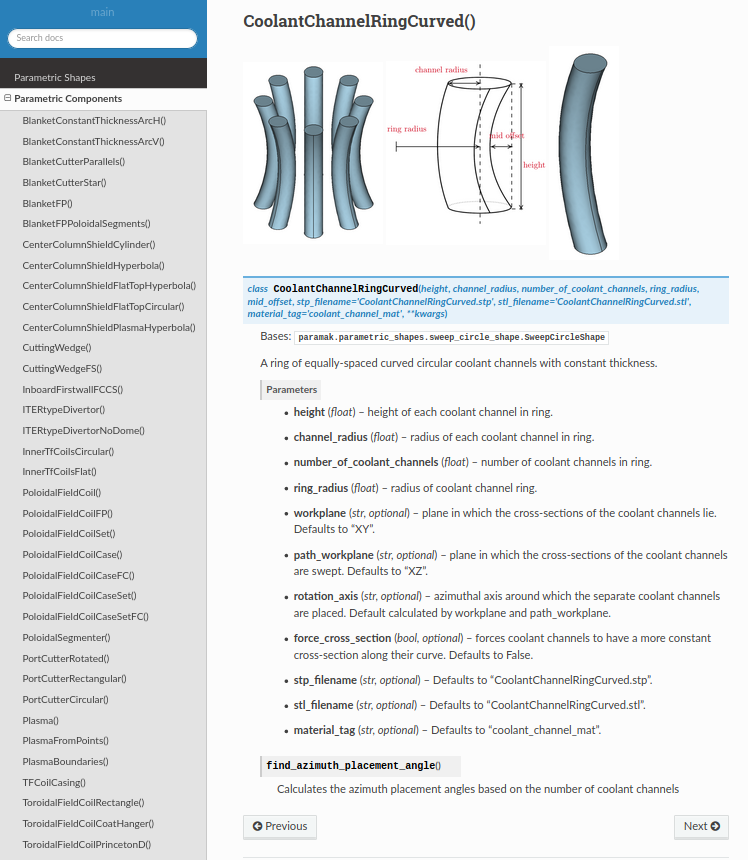
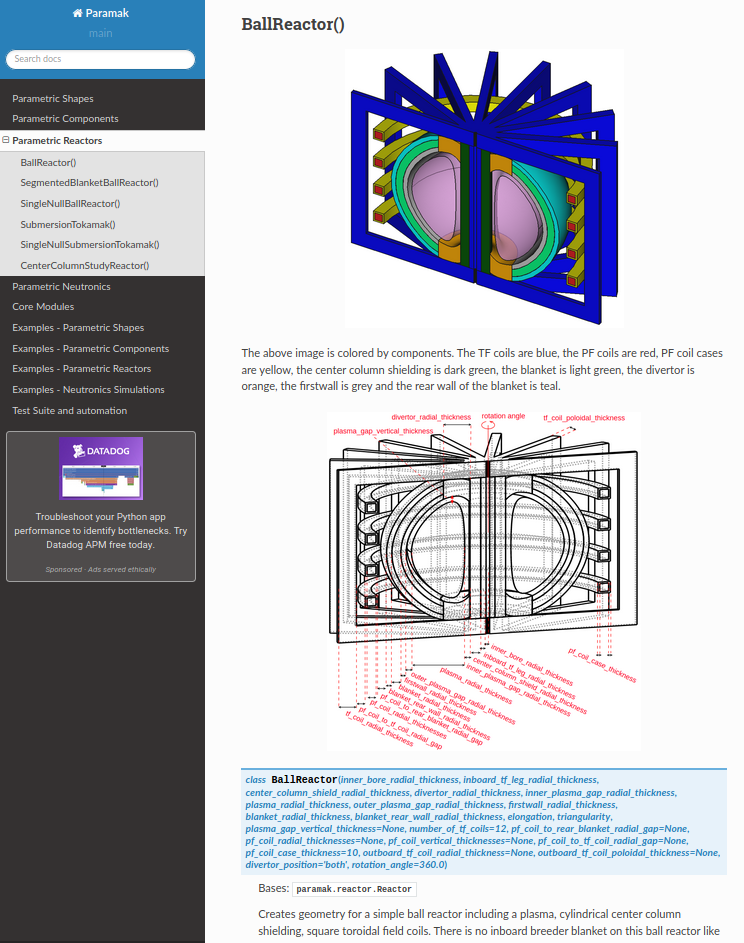
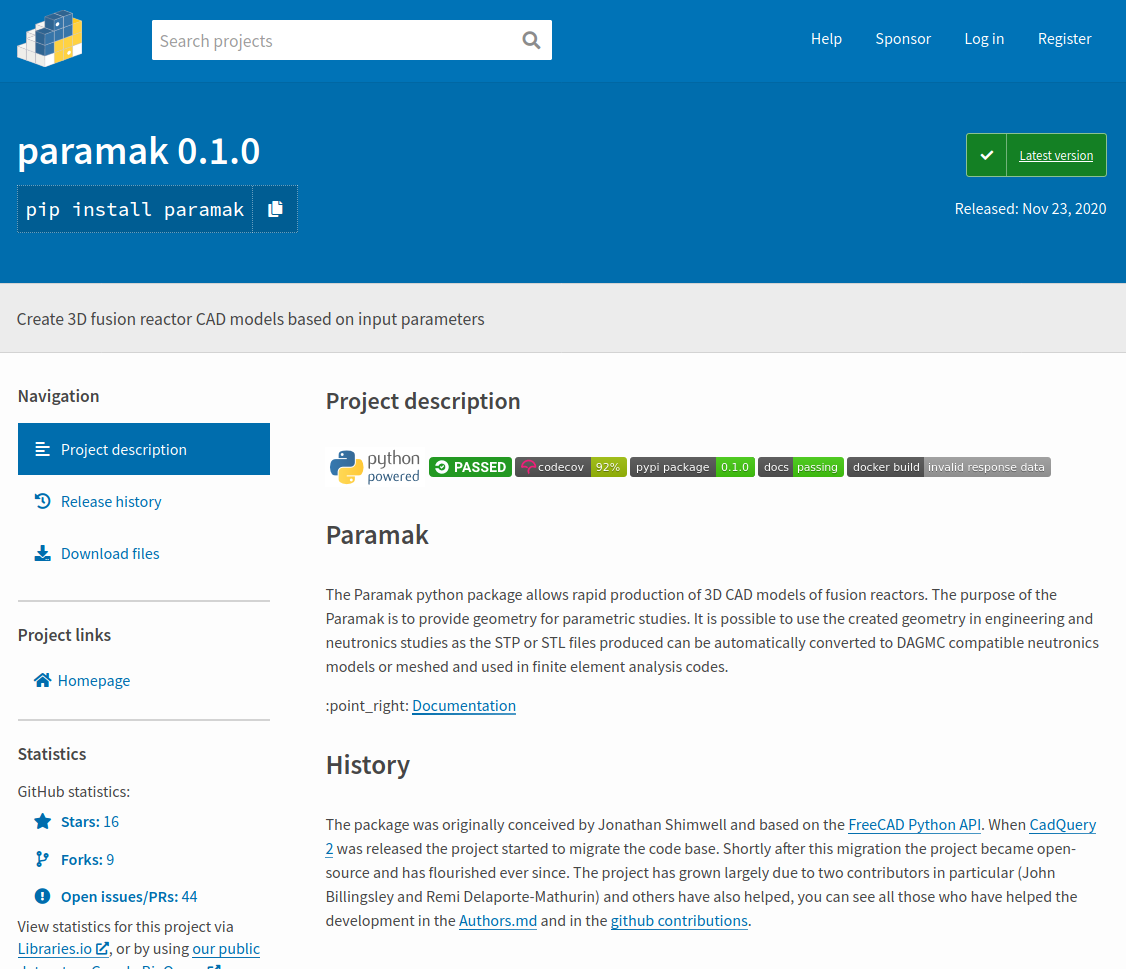


Software review
RSE review prior to going opensource (M. Bluteau)
Provision of review document






PullRequest.com review after v0.2 release


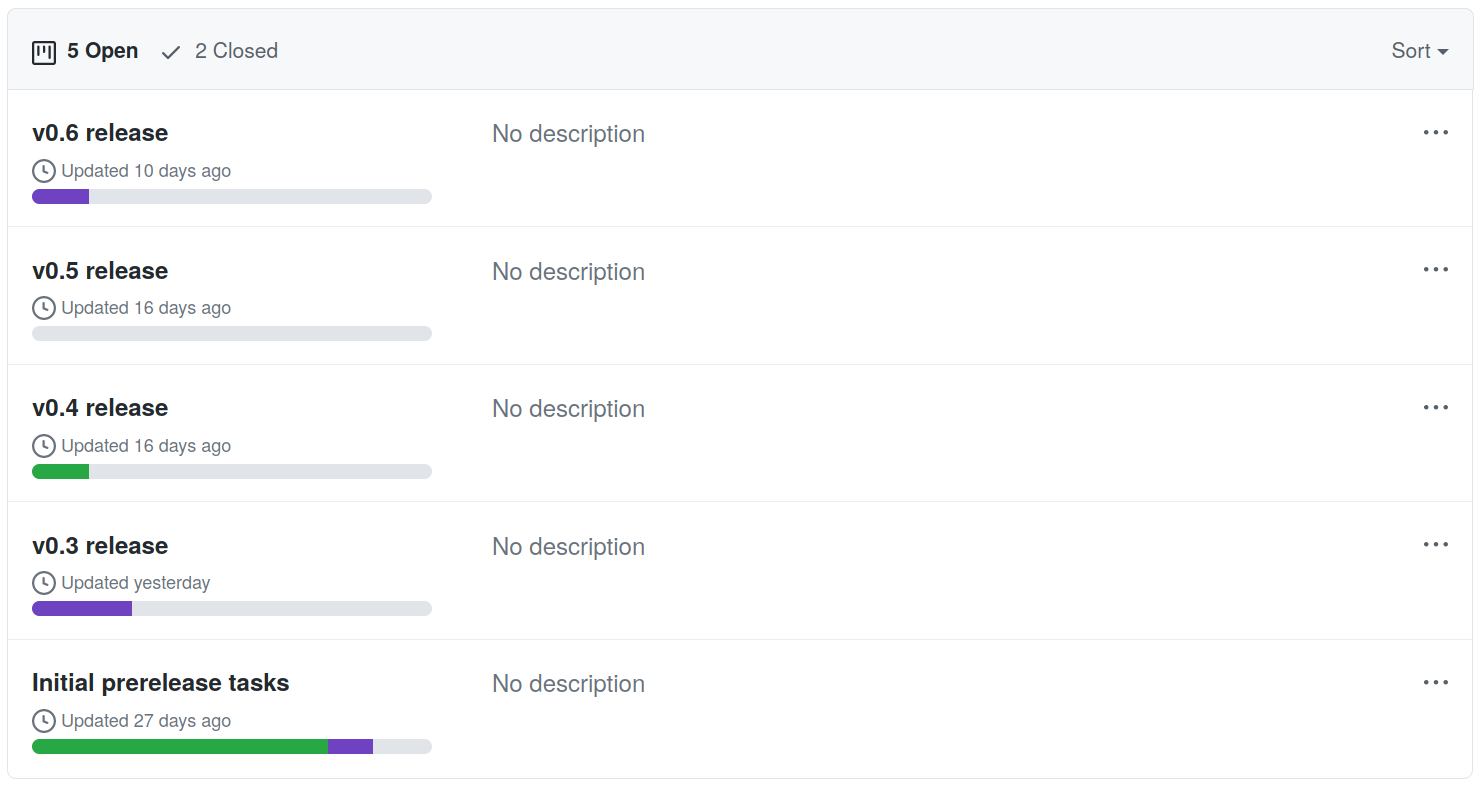
Agile (working progress)
- Regular meet ups between the core developers
- Project boards to track progress
- Discussion with customers, define the product
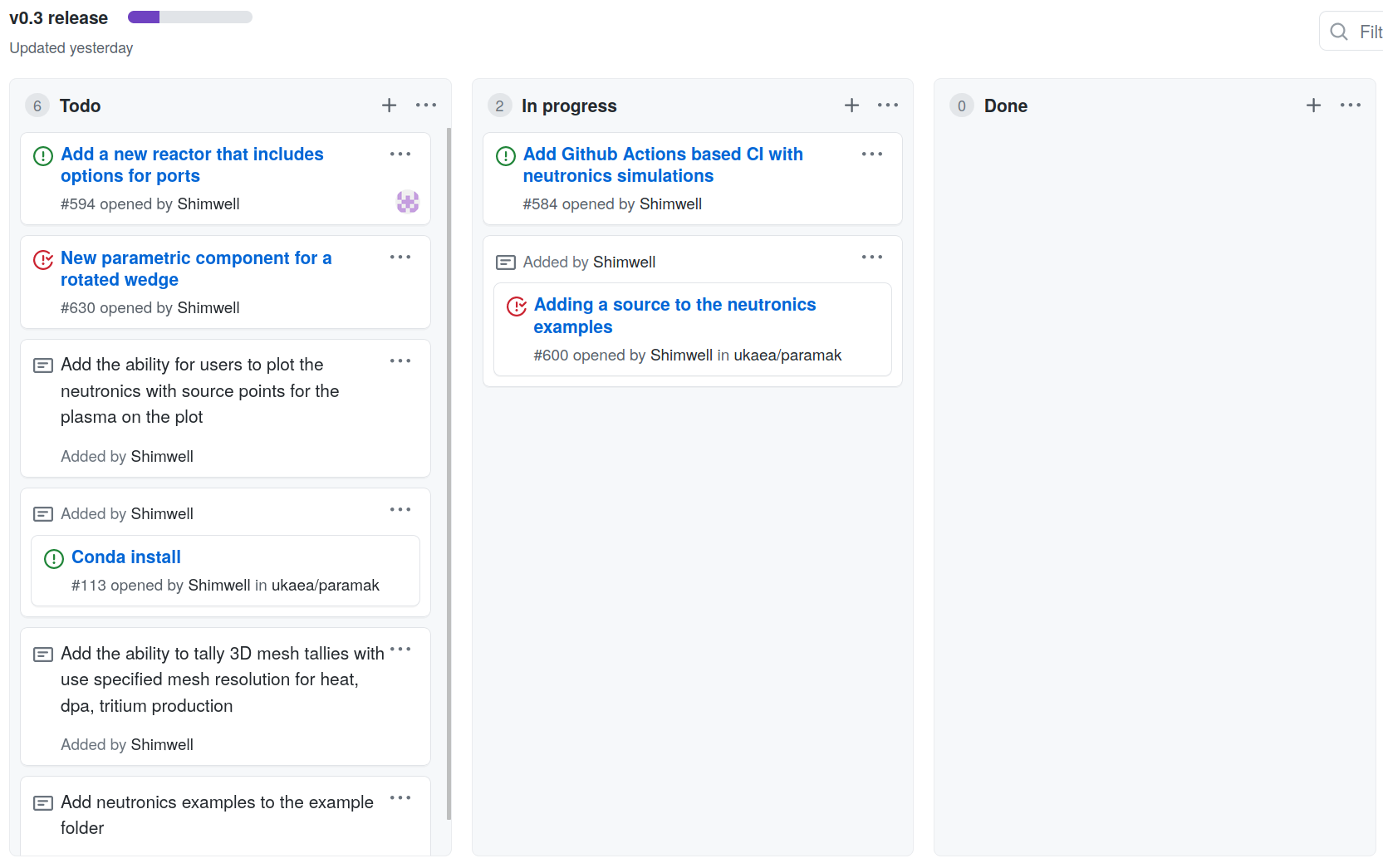
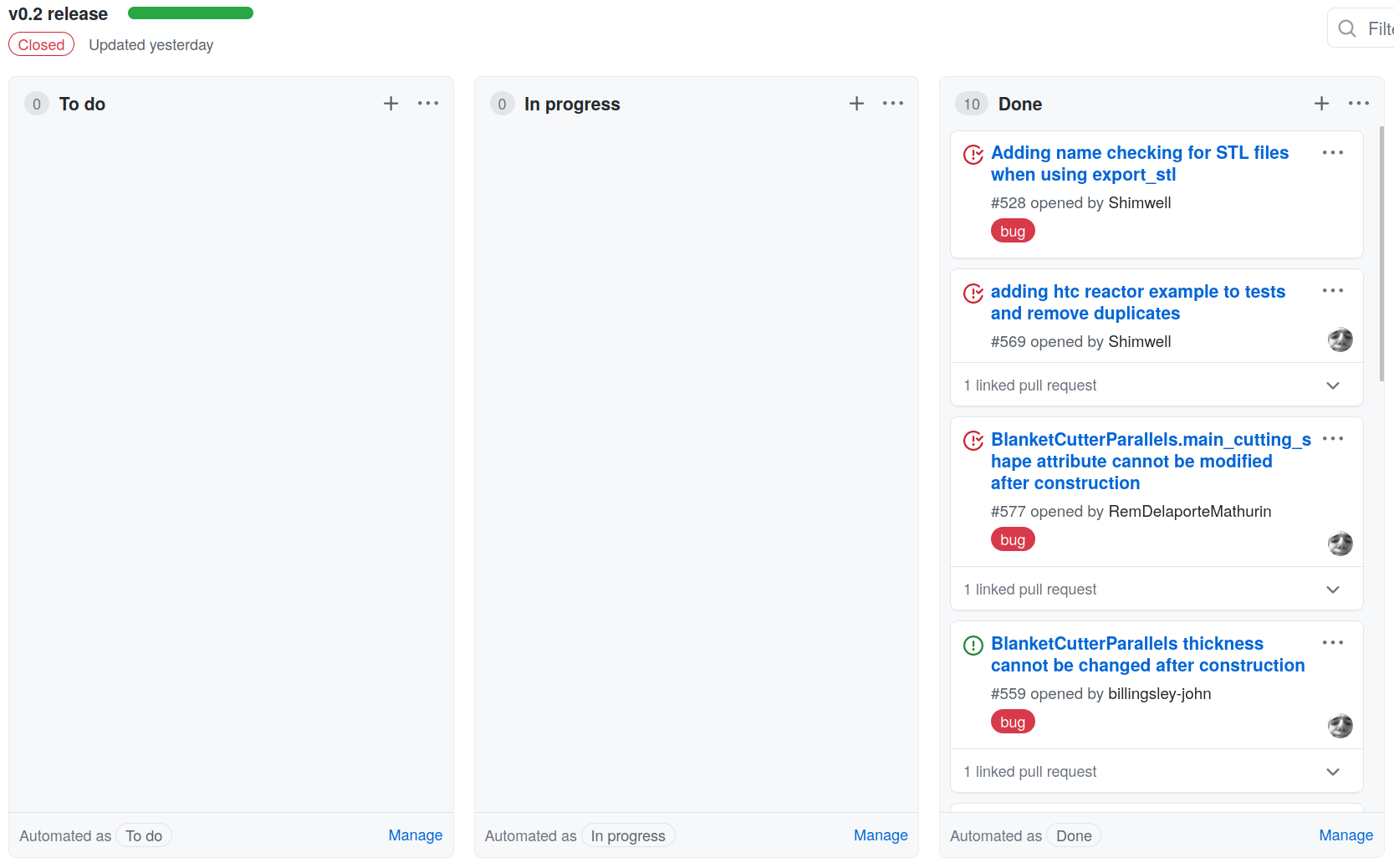
- Deliver MVP and then iterate.


Automated - software review
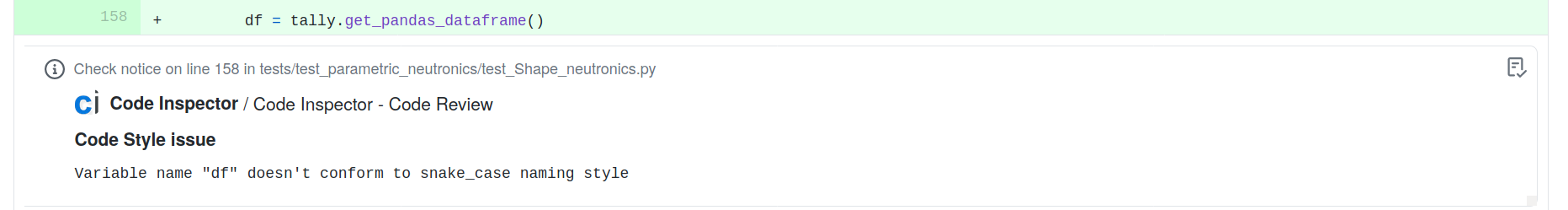
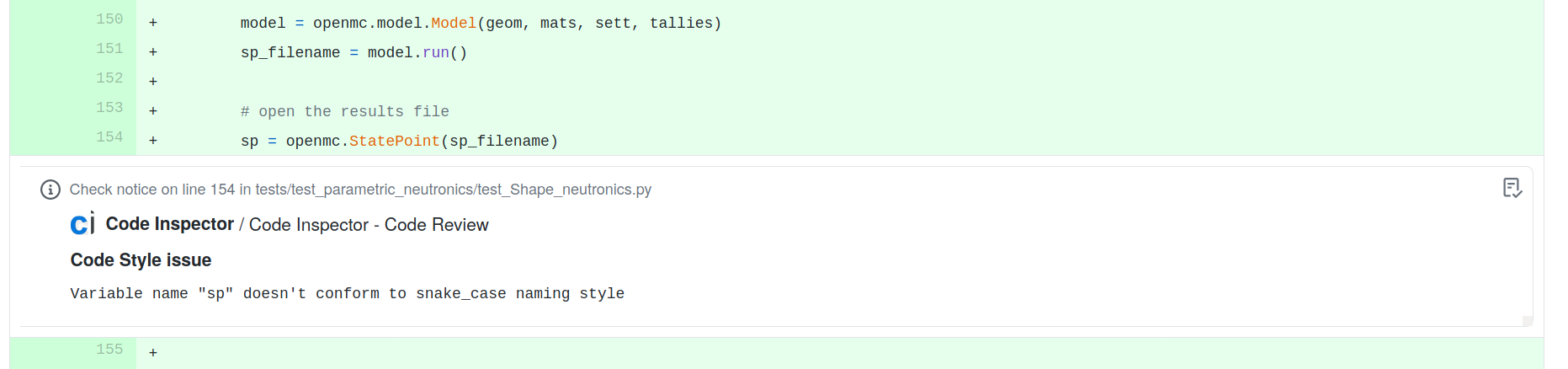
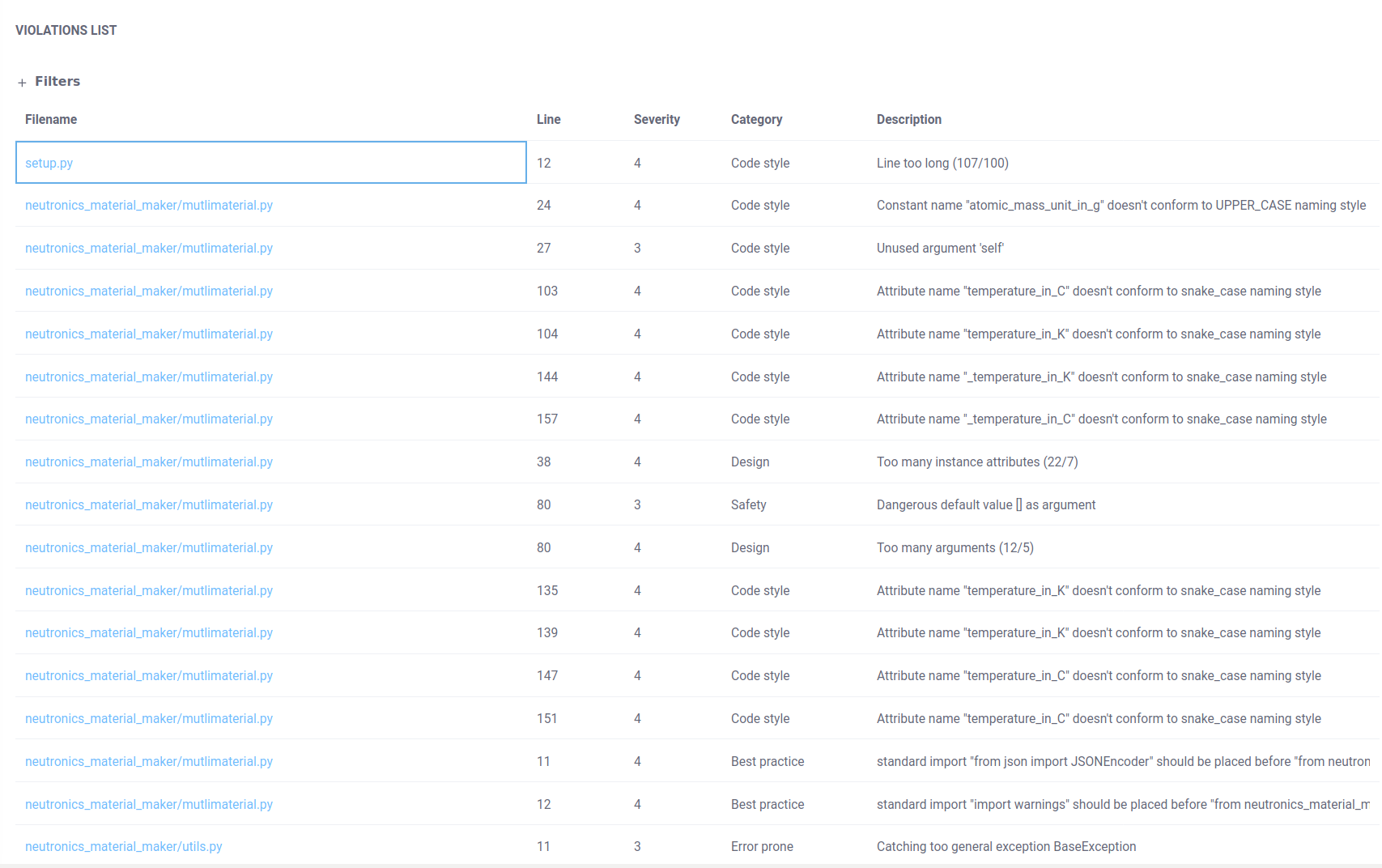
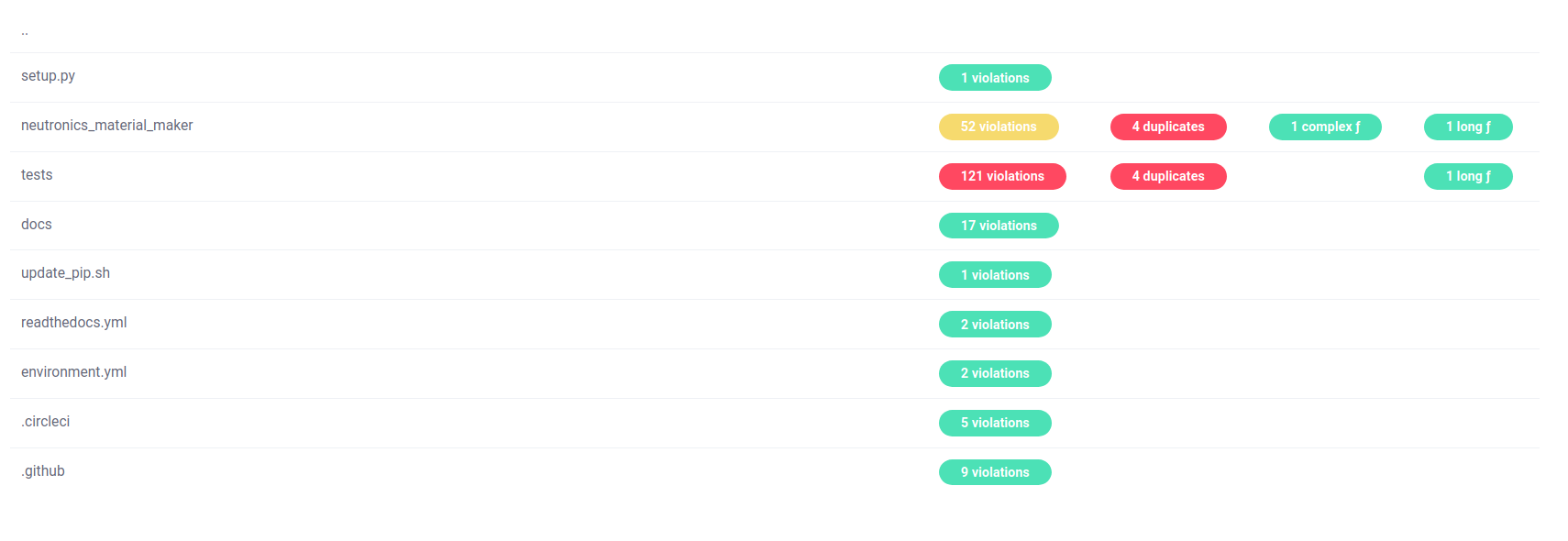
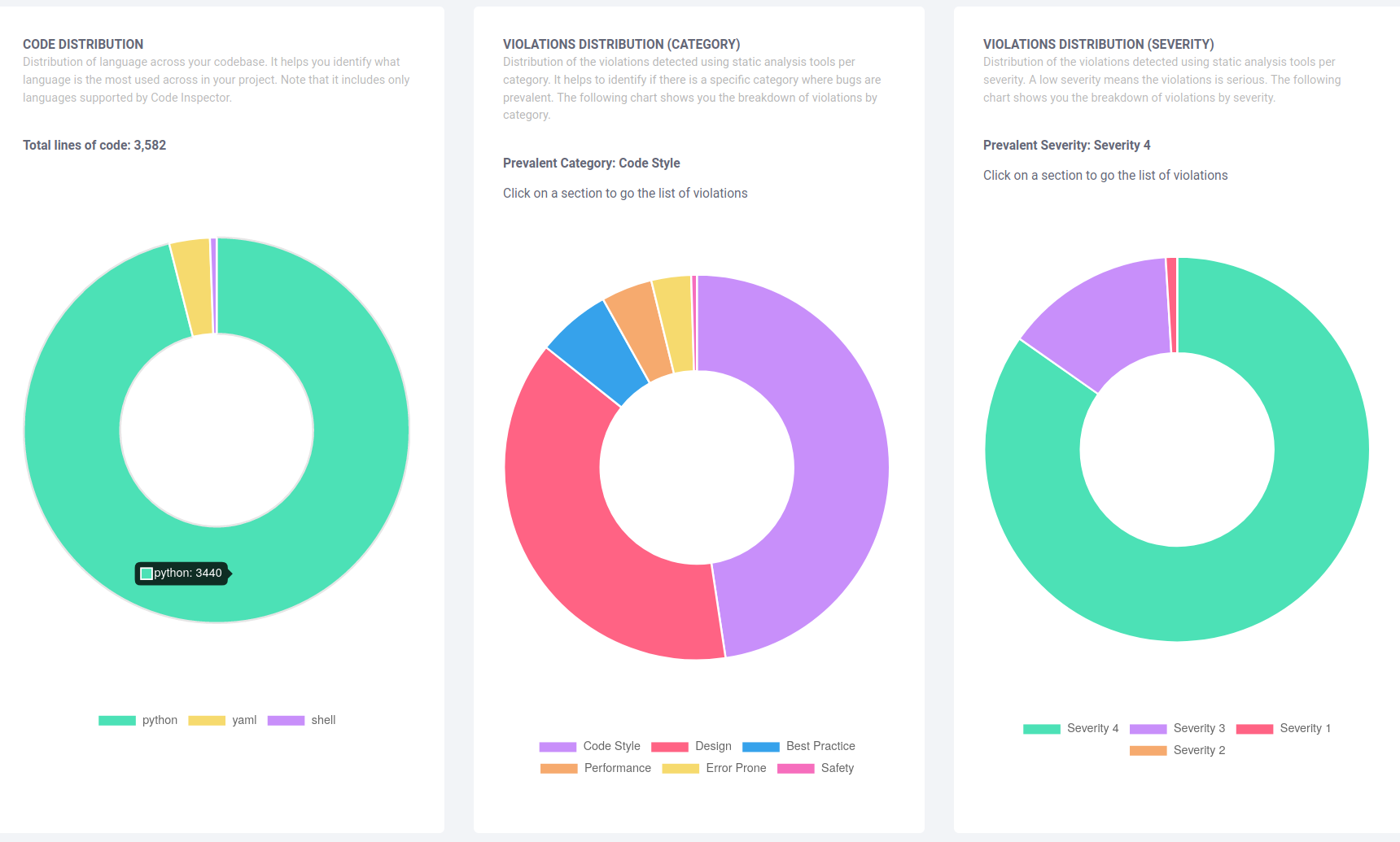
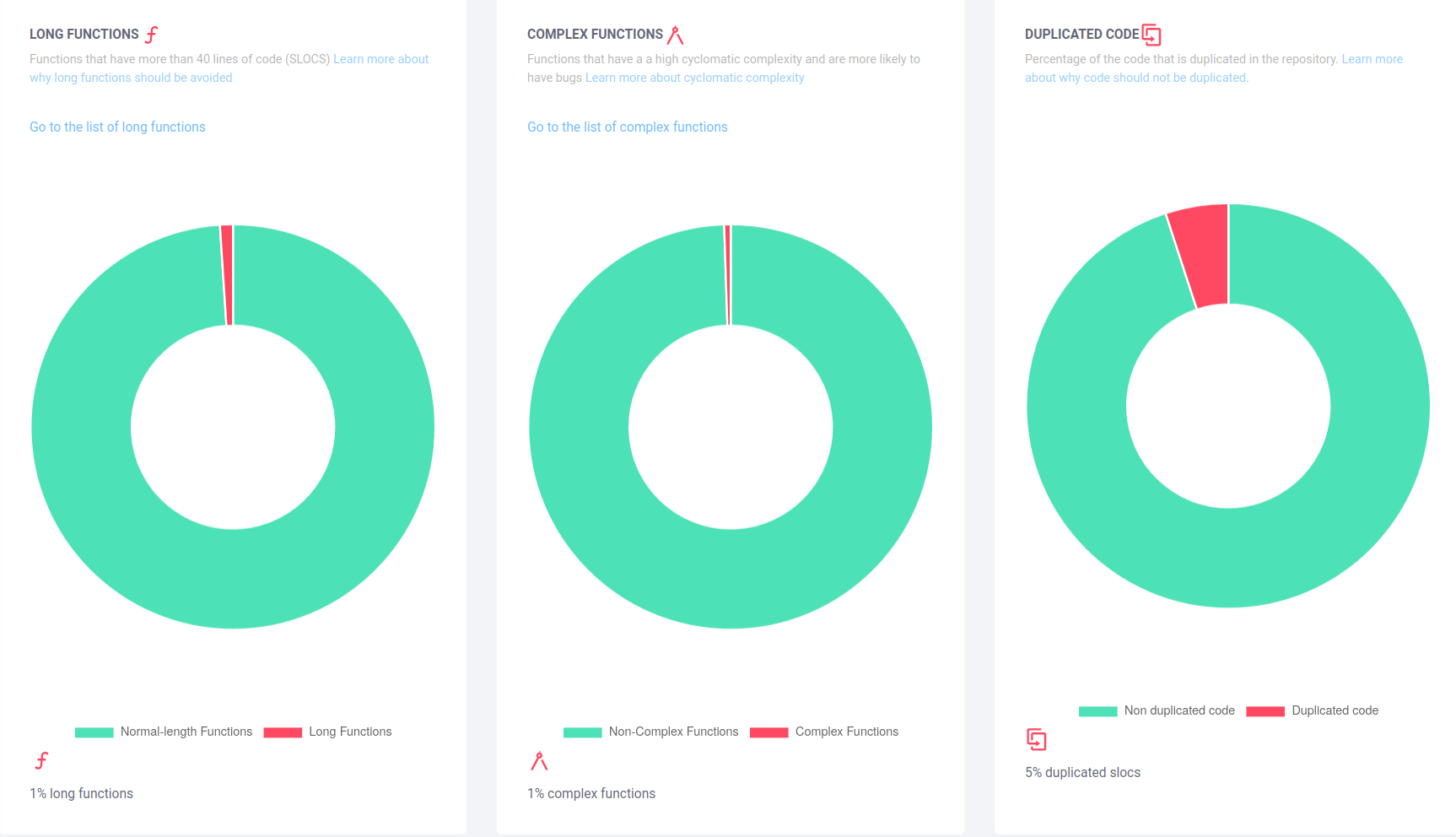
www.code-inspector.com


Preparing for compute
OpenMC: A state-of-the-art Monte Carlo code for research and development
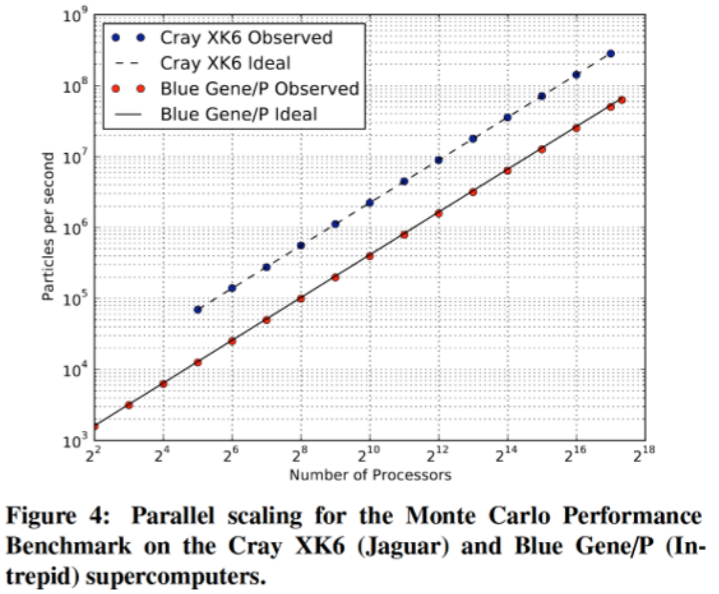
Dimensional reduction removes some variables but the number of simulations require to explore the parameter space is stilll quite large.



Speeding up the neutronics workflow
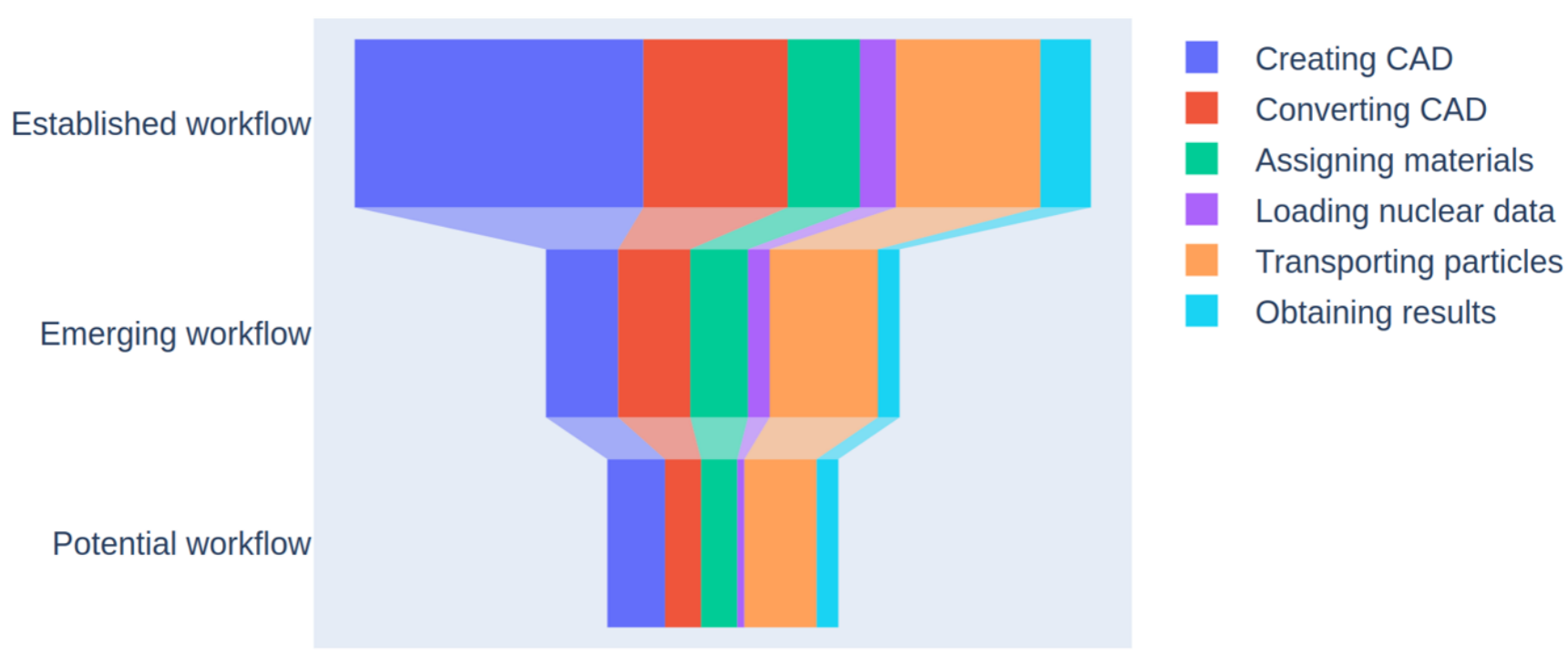
Paramak
By neutronics_workshop
Paramak
Create parametric 3D fusion reactor CAD models
- 437