WEB DEVELOPMENT
(Zero-Hero)
[School]
Course Outline
Day 1
- General Theory
- Table
- Form
- Styles
- Group styles
Day 2
- Javascript Intro
- Conditional & Functions
- Libraries
General Theory
HTML
Hyper text markup language


Basic Structure
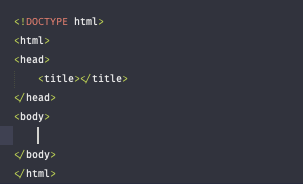
Syntax
The syntax for a single HTML tag is an opening angle bracket (<) followed by the element name and closed with the closing angle bracket (>).
HTML element
Closing tag
An HTML closing tag is used to denote the end of an HTML element. The syntax for a closing tag is a left angle bracket (<) followed by a forward slash (/) then the element name and a right angle bracket to close (>).
The content of an HTML element is the information between the opening and closing tags of an element. In the above example the element content is “Codecademy is the best!”.
Document type declaration
The document type declaration <!DOCTYPE html> is required as the first line of an HTML document. The doctype declaration is an instruction to the browser about what type of document to expect and which version of HTML is being used, in this case it’s HTML5.
HTML element
The Head element
The <head> element contains general information about an HTML page that isn’t displayed on the page itself. This information is called metadata and includes things like the title of the HTML document and links to stylesheets.
Title element
The <title> element contains a text that defines the title of an HTML document. The title is displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab in which the HTML page is displayed. The <title> element can only be contained inside a document’s <head> element.
The <html> element, the root of an HTML document, should be added after the doctype declaration. All content/structure for an HTML document should be contained between the opening and closing <html> tags.
Body
We create the <body> element by using the opening and closing <body> tags. Web browsers will render any content inside the <body> tags. The <body> element should contain all content meant to be rendered to a web page. There can be one <body> element per HTML document.
Elements
Heading Element
HTML can use six different levels of heading elements. The heading elements are ordered from highest level (<h1>) to lowest level (<h6>).
Div Element
Paragraph Element
Paragraph elements, <p>, contain and display blocks of text.
Span element
The <span> element is an inline container for text and can be used to group text for styling purposes. However, as <span> is a generic container to separate pieces of text from a larger body of text, its use should be avoided if a more semantic element is available.
The <div> element is used as a container that divides an HTML document into sections and is short for “division”. <div> elements can contain flow content such as headings, paragraphs, links, images, etc.
Emphasis element
The emphasis element, <em>, emphasizes text and browsers will usually italicize the emphasized text by default.
Strong element
The <strong> element highlights important, serious, or urgent text and browsers will normally render this highlighted text in bold by default.
Line Break element
The line break element, <br>, will create a line break in text and is especially useful where division of text is required, like in an address. The line break element requires only an opening tag and must not have a closing tag.
The anchor element, <a>, is used to create hyperlinks in an HTML document. The hyperlinks can point to other webpages, files on the same server, a location on the same page, or any other URL via the hyperlink reference attribute, href. The href determines the location the anchor element points to.
Anchor Element
List Element
List item elements (<li>) create list items in ordered lists (<ol>) and unordered lists (<ul>). List items must be added to ordered and unordered lists using the <li> element.
Image Element
HTML image (<img>) elements embed images in documents. The src attribute contains the image URL and is mandatory. <img> is an empty element and should not have a closing tag.
Video Element
The <video> element embeds a media player into an HTML document for video playback. The src attribute will contain the URL to the video. Adding the controls attribute will display video controls in the media player.
Practical
Part 1
HTML Part2 - Table Element
Table
Table Element
The HTML <table> element is used to represent a two-dimensional table made from rows and columns. The <table> element will contain all table data cells within said rows and columns.
Row Element
Table body Element
The table body element, <tbody>, is a semantic element that will contain all table data other than table heading and table footer content. If used, <tbody> will contain all table row (<tr>) elements, and indicates that <tr> elements make up the body of the table. <table> cannot have both <tbody> and <tr> as direct children.
Table row elements, <tr>, are used to add rows to a table before adding table data and table headings.
Table Data Element
A table data element (<td>) can be nested inside a table row element (<tr>) to add a cell of data to a table.
Table head element
The table head element, <thead>, defines the headings of table columns encapsulated in table rows.
Table footer element
The table footer element, <tfoot>, uses table rows to give footer content or to summarize content at the end of a table.
Table Heading element
The table heading element, <th>, is used to add titles to rows and columns of a table and must be enclosed in a table row element (<tr>).
Colspan attribute
The colspan attribute on a table header (<th>) or table data (<td>) element indicates how many columns that particular cell should span within the table. The colspan value is set to 1 by default and will take any positive integer between 1 and 1000.
Rowspan attribute
Similar to colspan, the rowspan attribute on a table header or table data element indicates how many rows that particular cell should span within the table. The rowspan value is set to 1 by default and will take any positive integer.
Practical
Part 2
HTML Part3 - Form Element
Forms
Form Element
The HTML <form> element is used to collect and send information to an external source.
<form> can contain various input elements. When a user submits the form, information in these input elements is passed to the source which is named in the action attribute of the form.
Input Element
Label Element
Input type
The HTML <input> element is used to render a variety of input fields on a webpage including text fields, checkboxes, buttons, etc. <input> element have a type attribute that determines how it gets rendered to a page.
The example code block will create a text input field and a checkbox input field on a webpage. The value of the <input>‘s name and value attribute of the element are sent as a key-value pair when the form is submitted.
The HTML <label> element provides identification for a specific <input> based on matching values of the <input>‘s id attribute and the <label>‘s for attribute. By default, clicking on the <label> will focus the field of the related <input>.
- text
-password
-number
-range
-checkbox
-radio
-select
-datalist
-textarea
-submit
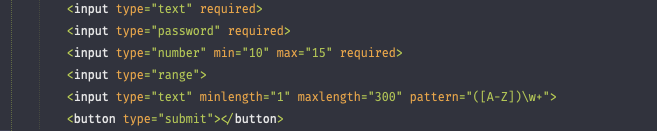
Validators
- required (all)
- min, max (number)
- minlength, maxlength (text)
- pattern (text)
Practical
Part 3
HTML Part4 - General Attributes and styling
Attributes
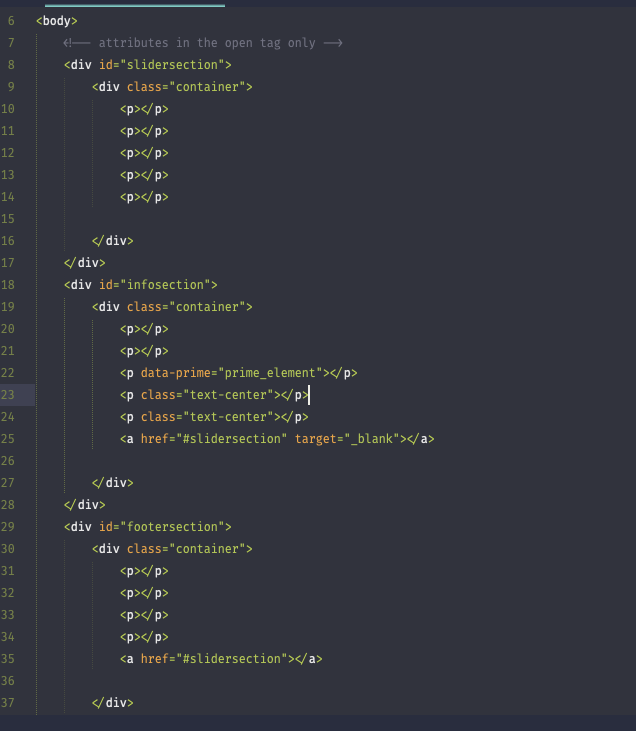
HTML attribute
HTML attributes are values we can use on the opening tag of an element to configure the element or change the element’s default behavior.
Target attribute
The target attribute on an anchor (<a>) element specifies where a hyperlink should be opened. For example, a target value of "_blank" will tell the browser to open the hyperlink in a new tab in modern browsers, or in a new window in older browsers or if the browser has had settings changed to open hyperlinks in a new window.
Unique ID attribute
In HTML, specific and unique id attributes can be assigned to different elements in order to differentiate between them. When needed, the id value can be called upon by CSS and Javascript to manipulate, format, and perform specific instructions on that element and that element only. Valid id attributes can only contain capital letters (A-Z), lowercase letters (a-z), hyphens (-), underscores (_), colons (:), and periods (.).
Class attribute
The class is an attribute which specifies one or more class names for an HTML element.The class attribute can be used on any HTML element. The class name can be used by CSS and JavaScript to perform certain tasks for elements with the specified class name.
Style attribute
The style attribute specifies an inline style for an element.
Practical
Part - 4
HTML Part5 - Grouped Attributes / Class styling / CSS
Practical
Part - 5
Happy Meal
Intro to javascript
Variables
Whenever there’s a need to use a piece of data, variables are a good solution. A variable contains data that can be used in the program.

- const
- let
Datatype
- String
- Numbers
- Booleans
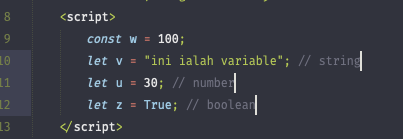
Debugging & Comments

Practical
Part - 1
Conditional
&
Functions
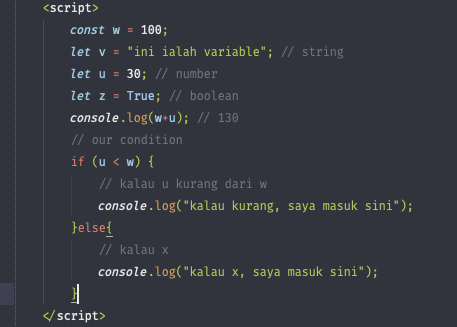
Conditional
Control flow is the order in which statements are executed in a program. Control structures such as conditionals allow for control flow to be altered during the execution of a program. In JavaScript, the default control flow is for statements to be read and executed in order from left-to-right, top-to-bottom in a program file.
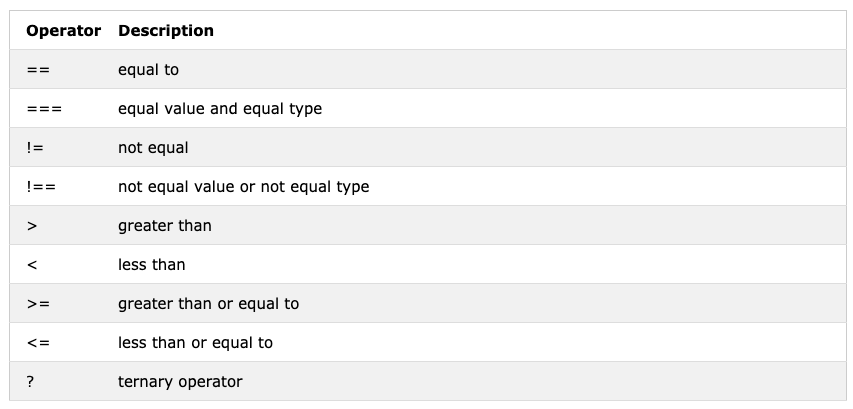
Operators
Logical Expression that will return the boolean result of true and false.
Functions
Functions are one of the fundamental building blocks in JavaScript. A function is a reusable set of statements to perform a task or calculate a value. Functions can be passed one or more values and can return a value at the end of their execution. In order to use a function, you must define it somewhere in the scope where you wish to call it.
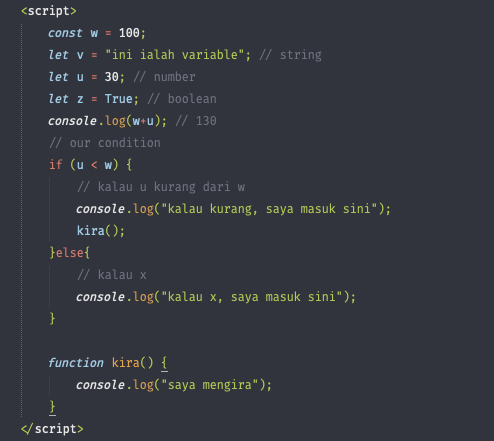
Practical
Part - 2
Libraries
Happy Meal
Refferences
- Html, css, js documentations from https://www.codecademy.com , https://www.geeksforgeeks.org , https://www.w3schools.com
- Building own calculator https://medium.freecodecamp.org/how-to-build-an-html-calculator-app-from-scratch-using-javascript-4454b8714b98
Trainer
- Firdaus (Full Stack Engineer)
- Arif (Software Change Manager)
Web Dev School
By nexxa
Web Dev School
school - web dev
- 306



