React and friends
Nick Mosher
Topics
React - Frontend framework
Redux - App state management
React Router - URL navigation
Immutable.js - Immutable data structures
Webpack - JS dependency management
Using Bootstrap and React
Environment and Tools
Node.js/npm - JS package manager
IntelliJ Ultimate - IDE/Editor
Git/Github - Version control
React
Traditional Web
HTML - Structure
Javascript - Behavior
CSS - Style
React
JSX - Structure and Behavior
CSS - Style
HTML is static by nature.
Many frameworks/tools use templating to solve this.
React moves structure responsibility into JS for flexibility.
Sample Code
Get the sample code for this seminar
# Get sample code
git clone https://github.com/nicholastmosher/react-boilerplate.git
cd react-boilerplate
git checkout -b base-sample react-base
# Install dependencies and run
npm install
npm run devComponents
Functional Components
Class Components
- Have no local state
- Rely solely on props for content
- Have no means to access lifecycle methods
- Have access to local state as well as props
- Can override lifecycle methods
const UserListElement = (props) => (
<div>
<h1>{props.user.name}</h1>
<p>{props.user.bio}</p>
</div>
);class AddUserView extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = { name: '', bio: '' };
}
handleName = (e) => this.setState({name: e.target.value});
handleBio = (e) => this.setState({bio: e.target.value});
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text"
value={this.state.name}
onChange={this.handleName}>Name</input>
<input type="text"
value={this.state.bio}
onChange={this.handleBio}>Bio</input>
</div>
);
}
}Props
Props (properties) are passed from parent
components to their children
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
const ContactsView = (props) => (
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Phone number</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>{props.user.name}</td>
<td>{props.user.phone}</td>
<td>{props.user.email}</td>
</tr>
</table>
);
let myUser = { name: "John",
phone: "555-555-5555",
email: "john@example.com" };
render(
<ContactsView user={myUser}/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
ECMAScript 6 Stuff
Arrow functions
// Arrow functions
const expressionFunction = (args) => "Evaluates to this string with args " + args;
const statementFunction = (args) => { console.log("Executes this statement with args " + args); };
// Similar to:
var myFunc = function (args) { console.log("Executes this statement with args " + args); }Destructuring
let user = { name: 'Johnny Appleseed',
phone: '123-456-7890' };
const printUserDetails = ({ name, phone }) => {
console.log("User name: " + name + ", phone: " + phone);
};
printUserDetails(user);Property value shorthand
let name = 'Johnny Appleseed';
let phone = '123-456-7890';
let user = {
name, // Equivalent to 'name: name'
phone // Equivalent to 'phone: phone'
};className
React "className" becomes html "class"
import React from 'react';
const FriendList = (props) => (
<ul className="list-group">
<li className="list-group-item">Alice</li>
<li className="list-group-item">Bob</li>
<li className="list-group-item">Cathy</li>
</ul>
);Component using Bootstrap classes
classNames
A handy tool for dynamically assigning classes
# Install 'classnames' and add to package.json
$ npm install --save classnamesimport React, { Component } from 'react';
import classNames from 'classnames';
class NameForm extends Component {
constructor() { super(); this.state = { nameText: '' }; }
handleInput = (e) => this.setState({ nameText: e.target.value });
validName = () => !!this.state.nameText; // Valid if not blank
render() {
return (
<div className={classNames('form-group', { 'has-danger': !this.validName() })}>
<label className="form-control-label">Enter Name:</label>
<input type="text" className="form-control"
value={this.state.nameText} onChange={this.handleInput}/>
</div>
);
}
}Redux
Redux is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps.
- redux.js.org
Three Principles
Single source of truth
The state of your whole application is stored in an object tree within a single store.
State is read-only
The only way to change the state is to emit an action, an object describing what happened.
Changes are made with pure functions
To specify how the state tree is transformed by actions, you write pure reducers.
- redux.js.org
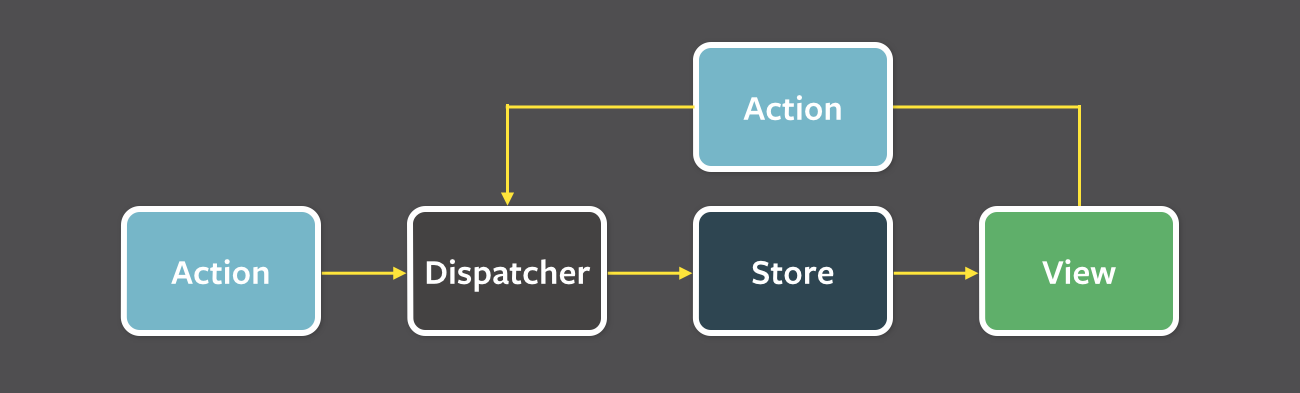
Inspired by Flux
https://facebook.github.io/flux/docs/in-depth-overview.html
The Dispatcher queues actions as they arrive
The Store uses reducers to combine the current state and an action to arrive at a new state
Sample Code
Checkout the code for redux
# Get sample code
git checkout -b redux-sample with-redux
# Install dependencies and run
npm install
npm run devActions
Plain javascript objects that describe a change to the state
// src/js/constants/AppActionTypes.js
export const AppActionTypes = {
SAY_HELLO: 'SAY_HELLO',
};
// src/js/actions/AppActions.js
import { AppActionTypes } from '../constants/AppActionTypes';
export const sayHello = (name) => ({ type: AppActionTypes.SAY_HELLO, name });Actions are "dispatched", causing reducer executions
Reducers
Pure functions of the form (state, action) => state
// src/js/reducers/AppReducer.js
import { Map } from 'immutable';
import { AppActionTypes } from '../constants/AppActionTypes';
const initialState = Map({ greetee: 'John' });
const AppReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch(action.type) {
case AppActionTypes.SAY_HELLO:
return state.set('greetee', action.name);
default:
return state;
}
};
export default AppReducer;Using Redux with React
We need access to state and actions within components, so we map the state and dispatch into props.
react-redux provides the 'connect' function to help
// AppContainer.js
import React from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { sayHello } from '../actions/AppActions';
const AppContainer = (props) => (
<div>
<h1>Hello, {props.name}!</h1>
<button onClick={() => props.greet('Bob')}>Bob</button>
<button onClick={() => props.greet('Ann')}>Ann</button>
</div>
);
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
name: state.AppReducer.get('greetee'),
});
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
greet: (name) => dispatch(sayHello(name)),
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps)(AppContainer);// AppActions.js
import AppActionTypes from '../constants/AppActionTypes';
export const sayHello = (name) =>
({ type: AppActionTypes.SAY_HELLO, name });
// AppReducer.js
import { Map } from 'immutable';
import AppActionTypes from '../constants/AppActionTypes';
const initialState = Map({ greetee: 'John' });
const AppReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch(action.type) {
case AppActionTypes.SAY_HELLO:
return state.set('greetee', action.name);
default:
return state;
}
};
export default AppReducer;Middleware
Middlewares influence the behavior of the dispatch
Dispatched actions flow through middlewares before reaching reducers
Common middlewares include redux-logger and redux-thunk
More middleware details: http://redux.js.org/docs/advanced/Middleware.html
Configuring Middleware
Middlewares are configured at store creation
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import { createLogger } from 'redux-logger';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from '../reducers/index';
const configureStore = () => (
createStore(
rootReducer,
compose(
applyMiddleware(
createLogger({
level: 'info',
collapsed: true
}),
thunk,
)
)
)
);
export default configureStore;Redux Thunk
Middleware that enables dispatching functions
Useful for chaining other actions or making asynchronous calls
// actions/SomeActions.js
import $ from 'jquery';
import SomeActionTypes from '../constants/SomeActionTypes';
export const insertData = (data) => ({ type: SomeActionTypes.INSERT_DATA, data });
export const queryEndpoint = server => dispatch => {
$.ajax({
url: server.host + '/api/some/endpoint',
method: 'GET',
accepts: 'application/json',
contentType: 'application/json',
beforeSend: xhr => xhr.setRequestHeader('Authorization', 'Basic ' + btoa('user:password')),
error: jqXHR => console.log('Ajax module error: ' + jqXHR.status),
}).done(data => {
dispatch(insertData(data['entries']));
});
};React Router
React Router is a collection of navigational components that compose declaratively with your application.
- reacttraining.com/react-router
Routes
Act as an on/off switch for rendering components
If the URL includes "path", the component renders
import React from 'react';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import NavigationView from '../views/NavigationView';
import SplashScreenView from '../views/SplashScreenView';
import DashboardView from '../views/DashboardView';
const AppContainer = (props) => (
<div>
<Route path="/" component={NavigationView} />
<Route exact path="/" component={SplashScreenView} />
<Route path="/dashboard" component={DashboardView} />
</div>
);
export default AppContainer;Redirect
A component that redirects the URL when it's rendered
Must have "to" prop, optional "from" prop
import React from 'react';
import { Route, Redirect } from 'react-router-dom';
import DashboardView from '../views/DashboardView';
const AppContainer = (props) => (
<div>
<Redirect from="/" to="/dashboard"/>
<Route path="/dashboard" component={DashboardView}/>
</div>
);Redirect Trick
Since a redirect only fires when it's rendered,
we can do some interesting things
import React from 'react';
import { Redirect } from 'react-router-dom';
/**
* Redirects from 'from' to 'to' if 'condition' is true.
*/
const RedirectOrRender = ({ condition, from, to, children }) => (
(condition ? <Redirect from={from} to={to} /> : children)
);
export default RedirectOrRender;URL Parameters
Routes can extract parameters from the URL.
import React from 'react';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
const URLView = (props) => (
<h2>{props.match.params.myParameter}</h2>
);
const AppContainer = (props) => (
<div>
<h1>Hello, React Router!</h1>
<Route path="/:myParameter" component={URLView} />
</div>
);
export default AppContainer;Sample App
Setup
# Download and install starter files
git clone https://github.com/nicholastmosher/react-boilerplate.git
cd react-boilerplate
git checkout todo-sample
npm install
# Run starter app (on localhost:8080)
npm run devReact, Redux, and Router
By Nick Mosher
React, Redux, and Router
- 693



