How Do You Know About Networking?
Lecturer: Иo1lz
About Me
I have a lot of names so whatever you call, since I know that you are calling me then I will give you a response.
As my depiction to myself, I'm just a lazy and normal person, nothing special, nothing amazing, just interesting in a little much area.
If you want to know me more, you can check my own blog
Outline
- What is Internet?
- The Structure You Never Care
- Communicate with Protocol
What is Internet?
How to describe Internet?
Nuts-and-Bolts

Services
- In Internet jargon, all of devices are called hosts or end system
- Based on hardware and software
- "an infrastructure that provides services to applications"
Nuts-and-Bolts
- End systems are connected together by a network of communication links and packet switches.
- End systems access the Internet through Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
- End systems run protocols that control
the sending and receiving of information.

PACKET?


Services
- The applications are said to be distributed applications, since they involve multiple end systems that exchange data with each other.






LAN
Local Area Network





WAN
Wide Area Network




















The Structure You Never Care
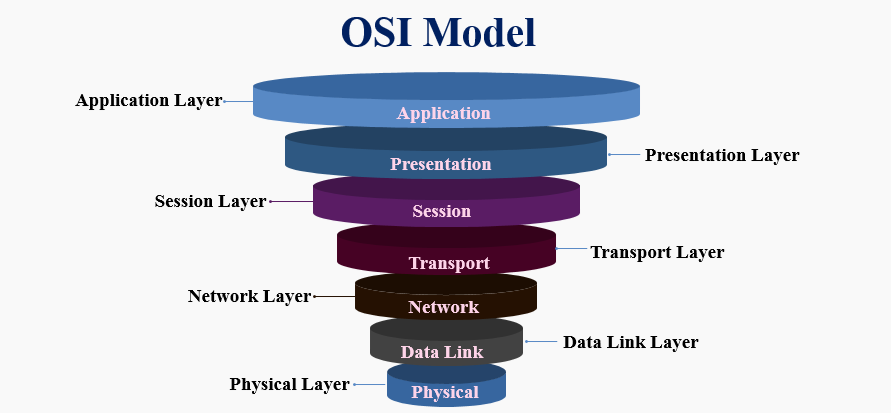
OSI Model
| Application | High-level APIs |
|---|---|
| Presentation | Translation of data between a networking service and application |
| Session | Managing communication sessions |
| Transport | Reliable transmission of data segments between points on a network |
| Network | Structuring and managing a multi-node network |
| Data Link | Reliable transmission of data frames between 2 nodes connected |
| Physical | Transmission and reception of raw bit streams |

TCP/IP Model
| Application | The applications make use of the services provided by the underlying lower |
|---|---|
| Transport | Performs host-to-host communications on the networks separated by routers |
| Internet | Exchanges datagrams across network boundaries |
| Link | Defines the networking methods within the scope of the local network link on which hosts communcate without intervening routers. |
Relationship Between Hosts
Client/Server


Server
Client
Request
Response
Peer-to-Peer


Host
Host
Request / Response
Communicate with Protocol
Protocol
A system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity.

IP
The principle communication protocol in the Internet.
the task
Deliver the packets from the source host to the destination host
based on
IP Address
(in packet's header)
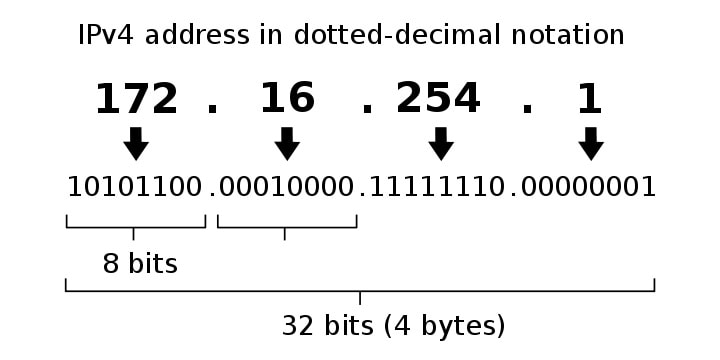
2 versions of IP address: IPv4, IPv6
IPv4
IPv6
XXX . XXX . XXX . XXX
XXXX : XXXX : XXXX : XXXX : XXXX : XXXX : XXXX : XXXX
IPv4
Public IP Address
| A | 0~127 | for research agency or large business |
|---|---|---|
| B | 128~191 | for medium business or educational agency |
| C | 192~223 | for small business or ISPs |
Private IP Address
| 10.0.0.0/8 | 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 | |
|---|---|---|
| 172.16.0.0/12 | 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 | |
| 192.168.0.0/16 | 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 | |
| 127.0.0.1 | 127.0.0.1 | localhost |
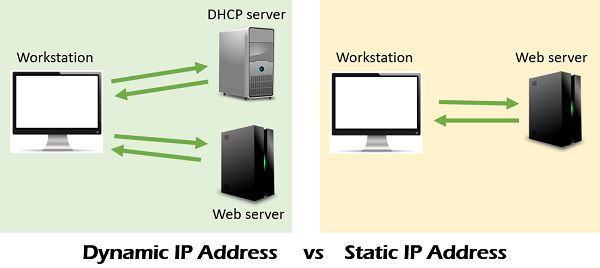
Static IP Address
Dynamic IP Address
- Staying the same, which means the IP address would never change.
- Constantly change which get the IP address through DHCP.
| Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 80 | HTTP | Used in World Wide Web(www) |
| 443 | HTTPS | HTTP Over TLS / SSL |
| 20 | FTP | Data Transfer |
| 21 | FTP | Command Control |
| 22 | SSH | Secure Login |
| 25 | SMTP | Email Routing |
TCP / UDP
- In the Transfer Layer which provide host-to-host communication services for applications.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP(User Datagram Protocol)
| TCP | UDP |
|---|---|
| Connection-oriented | Connectless |
| Less data in single packet | More data in single packet |
| More header information | Less header information |
References
- OSI Model - Wikipedia
- Internet Protocol Suite - Wikipedia
- "Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach, 7th", Kurose Ross
- Introduction to Internet
Thanks for Listening
How Do You Know About Networking?
By Иo1lz
How Do You Know About Networking?
- 271



