Diving into the Python call stack
Nikhil Marathe
signal.signal(
signal.SIGSEGV,
handler
)
def handler(...):
# collect informationDropbox

C
int *p = NULL;
...
*p = 42;☠️
signal.signal(
signal.SIGSEGV,
handler
)
def handler(...):
# collect informationDropbox
Dropbox
Crashpad
Python exception traceback
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "run.py", line 16, in <module>
main()
File "run.py", line 14, in main
foo()
File "run.py", line 11, in foo
bar()
File "run.py", line 8, in bar
baz()
File "run.py", line 4, in baz
raise Exception("Hi there")
Exception: Hi there#0 0x00007f9026e263a3 in __select_nocancel () at ../sysdeps/unix/syscall-template.S:84
#1 0x000057da6483182e in pysleep (secs=<optimized out>) at ../Modules/timemodule.c:1408
#2 time_sleep () at ../Modules/timemodule.c:231
…
#12 call_function (oparg=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512450) at ../Python/ceval.c:4745
#13 PyEval_EvalFrameEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:3251
#14 0x000057da6478193f in fast_function (nk=<optimized out>, na=<optimized out>, n=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512580,
func=<optimized out>) at ../Python/ceval.c:4818
#15 call_function (oparg=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512580) at ../Python/ceval.c:4745
#16 PyEval_EvalFrameEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:3251
#17 0x000057da64786286 in _PyEval_EvalCodeWithName () at ../Python/ceval.c:4033
#18 0x000057da64786f9f in PyEval_EvalCodeEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:4054
#19 PyEval_EvalCode (co=<optimized out>, globals=<optimized out>, locals=<optimized out>) at ../Python/ceval.c:777
#20 0x000057da648548f2 in run_mod () at ../Python/pythonrun.c:976
#21 0x000057da64856e1d in PyRun_FileExFlags () at ../Python/pythonrun.c:929
#22 0x000057da648575be in PyRun_SimpleFileExFlags () at ../Python/pythonrun.c:396
#23 0x000057da648854d7 in run_file (p_cf=0x7ffdb15127f0, filename=0x57da65cca260 L"dummy.py", fp=0x57da65d30780)
at ../Modules/main.c:318
#24 Py_Main () at ../Modules/main.c:768
#25 0x000057da64715c01 in main () at ../Programs/python.c:65
#26 0x00007f9026d652e1 in __libc_start_main (main=0x57da64715b20 <main>, argc=2, argv=0x7ffdb1512a08, init=<optimized out>,
fini=<optimized out>, rtld_fini=<optimized out>, stack_end=0x7ffdb15129f8) at ../csu/libc-start.c:291
#27 0x000057da6481f1ba in _start ()Crash report
Dropbox
Crashpad
SnapshotMac::CapturePythonStacks(
ProcessInfo& info
)
{
process_info.ReadMemory(0xee44ffdd);
...
}# dummy.py
def baz():
time.sleep(100)
def bar():
baz()
def foo():
bar()
def main():
foo()
main()#0 __select_nocancel ()
#1 pysleep
#2 time_sleep
#3 call_function
#4 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#5 fast_function
#6 call_function
#7 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#8 fast_function
#9 call_function
#10 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#11 fast_function
#12 call_function
#13 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#14 fast_function
#15 call_function
#16 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#17 _PyEval_EvalCodeWithName
#18 PyEval_EvalCodeEx
#19 PyEval_EvalCode
# dummy.py
def baz():
time.sleep(100)
def bar():
baz()
def foo():
bar()
def main():
foo()
main()#0 __select_nocancel ()
#1 pysleep
#2 time_sleep
#3 call_function
#4 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#5 fast_function
#6 call_function
#7 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#8 fast_function
#9 call_function
#10 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#11 fast_function
#12 call_function
#13 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#14 fast_function
#15 call_function
#16 PyEval_EvalFrameEx
#17 _PyEval_EvalCodeWithName
#18 PyEval_EvalCodeEx
#19 PyEval_EvalCode
Frame evaluation
def PyEval_EvalFrameEx(frame):
code = f.f_code
while True:
op = next_instruction()
if op == LOAD_FAST:
...
elif op == BINARY_ADD:
...
elif op == CALL_FUNCTION:
...
def call_function(...):
fast_function()
def fast_function():
t = PyThreadState_GET()
f = PyFrameObject()
f.f_back = t.frame
t.frame = f
...
PyEval_EvalFrameEx(f)
del fdef PyEval_EvalFrameEx(f):
code = f.f_code
while True:
op = next_instruction()
if op == CALL_FUNCTION:
call_function(...)
t.frame = f.f_backFrame evaluation
* Actual implementation in C in pyeval.c
typedef struct _ts {
struct _ts *prev;
struct _ts *next;
PyInterpreterState *interp;
struct _frame *frame;
...
long thread_id;
...
} PyThreadState;Thread information
typedef struct _is {
...
struct _ts *tstate_head;
} PyInterpreterState;Interpreter state
MainThread
Thread 1
Thread 2
typedef struct _frame {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
...
struct _frame *f_back;
/* several fields here */
} PyFrameObject;Frame Information
baz
bar
foo
main
thread state
The whole enchilada
typedef struct _frame {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
struct _frame *f_back;
PyCodeObject *f_code;
PyObject *f_builtins;
PyObject *f_globals;
PyObject *f_locals;
PyObject **f_valuestack;
PyObject **f_stacktop;
PyObject *f_trace;
PyObject *f_exc_type, *f_exc_value, *f_exc_traceback;
PyObject *f_gen;
int f_lasti;
int f_lineno;
int f_iblock;
char f_executing;
PyTryBlock f_blockstack[CO_MAXBLOCKS];
PyObject *f_localsplus[1];
} PyFrameObject;typedef struct _frame {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
/* lots of properties elided */
struct _frame *f_back;
PyCodeObject *f_code;
PyObject **f_valuestack;
int f_lasti;
PyObject *f_localsplus[1];
} PyFrameObject;A simplified frame
Frame evaluation
def callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + loc
def caller():
callee(7)
caller()∅
∅
Rest of frame
f_back
...
caller frame
stack pointer
f_valuestack
tstate->frame
<module>
Frame evaluation
fl[0]
fl[1]
Rest of frame
f_back
...
caller frame
callee function object
7
number object
stack pointer
f_valuestack
tstate->frame
<module>
def callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + loc
def caller():
callee(7)
caller()>>> dis.dis(caller)
# edited for clarity
LOAD_GLOBAL callee
LOAD_CONST 7
CALL_FUNCTIONcallee
7
Rest of frame
...
caller frame
stack pointer
f_valuestack
∅
∅
Rest of frame
f_back
...
callee frame
f_valuestack ; stack pointer
∅
∅
f_executing = False
tstate->frame
* PyFrame_New is responsible for setup
f_executing = False
callee
7
Rest of frame
...
caller frame
stack pointer
f_valuestack
7
∅
Rest of frame
f_back
...
callee frame
f_valuestack ; stack pointer
∅
∅
f_executing = False
* fast_function copies arguments
f_executing = False
tstate->frame
7
∅
Rest of frame
...
callee frame
f_valuestack ; stack pointer
5
∅
>>> dis.dis(callee)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (5)
3 STORE_FAST 1 (loc)
3 6 LOAD_FAST 0 (arg)
9 LOAD_FAST 1 (loc)
12 BINARY_ADD
13 RETURN_VALUEf_executing = True
* we are in PyEval_EvalFrameEx now
def callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + loc7
5
Rest of frame
...
callee frame
f_valuestack ; stack pointer
∅
∅
>>> dis.dis(callee)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (5)
3 STORE_FAST 1 (loc)
3 6 LOAD_FAST 0 (arg)
9 LOAD_FAST 1 (loc)
12 BINARY_ADD
13 RETURN_VALUEf_executing = True
* we are in PyEval_EvalFrameEx now
def callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + loc7
5
Rest of frame
...
callee frame
f_valuestack
7
5
stack pointer
>>> dis.dis(callee)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (5)
3 STORE_FAST 1 (loc)
3 6 LOAD_FAST 0 (arg)
9 LOAD_FAST 1 (loc)
12 BINARY_ADD
13 RETURN_VALUEdef callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + locf_executing = True
7
5
Rest of frame
...
callee frame
f_valuestack
12
5
stack pointer
>>> dis.dis(callee)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (5)
3 STORE_FAST 1 (loc)
3 6 LOAD_FAST 0 (arg)
9 LOAD_FAST 1 (loc)
12 BINARY_ADD
13 RETURN_VALUEdef callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + locf_executing = True
7
5
Rest of frame
...
callee frame
f_valuestack;
stack pointer
5
12
12
to caller
>>> dis.dis(callee)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (5)
3 STORE_FAST 1 (loc)
3 6 LOAD_FAST 0 (arg)
9 LOAD_FAST 1 (loc)
12 BINARY_ADD
13 RETURN_VALUEdef callee(arg):
loc = 5
return arg + locf_executing = False
Accessing frames in Python


def print_stack():
for tid, frame in sys._current_frames().items():
# skip this frame
frame = frame.f_back
while frame:
code = frame.f_code
print("File {}, line {}, in {}".format(
code.co_filename,
frame.f_lineno,
code.co_name,
))
frame = frame.f_back
def bar():
print_stack()
def foo():
bar()
def main():
foo()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Accessing frames in Python
File dummy.py, line 17, in bar
File dummy.py, line 20, in foo
File dummy.py, line 23, in main
File dummy.py, line 26, in <module>Crash reporting
Where should we start?
It's just code!
/* pystate.c */
static int autoTLSkey = 0;autoTLSkey = 5;typedef struct _ts {
thread_id = 1
} PyThreadState;0x4455667a
PyThreadState*Thread 1
autoTLSkey = 5;typedef struct _ts {
thread_id = 2
} PyThreadState;0x4455667c
PyThreadState*Thread 2
Retrieving thread states
/* pystate.c */
__attribute__((section ("key_section")))
static int autoTLSkey = 0;Extracting frame information
typedef struct {
...
int co_firstlineno;
...
PyObject *co_filename;
PyObject *co_name;
PyObject *co_lnotab;
...
} PyCodeObject;typedef struct _frame {
...
struct _frame *f_back;
PyCodeObject *f_code;
...
int f_lasti;
...
} PyFrameObject;co_filename and co_name are Python strings
co_firstlineno + co_lnotab + f_lasti allow us to resolve line numbers. See cpython/Objects/lnotab_notes.txt
#0 0x00007f9026e263a3 in __select_nocancel () at ../sysdeps/unix/syscall-template.S:84
#1 0x000057da6483182e in pysleep (secs=<optimized out>) at ../Modules/timemodule.c:1408
#2 time_sleep () at ../Modules/timemodule.c:231
…
#12 call_function (oparg=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512450) at ../Python/ceval.c:4745
#13 PyEval_EvalFrameEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:3251
#14 0x000057da6478193f in fast_function (nk=<optimized out>, na=<optimized out>, n=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512580,
func=<optimized out>) at ../Python/ceval.c:4818
#15 call_function (oparg=<optimized out>, pp_stack=0x7ffdb1512580) at ../Python/ceval.c:4745
#16 PyEval_EvalFrameEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:3251
#17 0x000057da64786286 in _PyEval_EvalCodeWithName () at ../Python/ceval.c:4033
#18 0x000057da64786f9f in PyEval_EvalCodeEx () at ../Python/ceval.c:4054
#19 PyEval_EvalCode (co=<optimized out>, globals=<optimized out>, locals=<optimized out>) at ../Python/ceval.c:777File "run.py", line 16, in <module>
File "run.py", line 14, in main
File "run.py", line 11, in foo
File "run.py", line 8, in bar
File "run.py", line 4, in bazWin!
Recap
- The Python interpreter stores a list of threads as PyThreadStates.
- Each PyThreadState keeps track of the top of its stack.
- The stack is just a linked list of PyFrameObjects.
- A PyFrameObject is the basic unit of bytecode evaluation
- Each frame uses its own stack to perform code execution.
- We can leverage interpreter internals to improve the quality of software we ship and make users and developers happy!*
*but it could break any time!
Related work
- Useful for profiling
- in-process profiling with cooperation from Python using sys.setprofile is possible, but
- requires modifying and restarting the program
- has high overhead
- pyflame and py-spy are out of process, sampling profilers that use similar techniques to extract frame information
- Can execute code inside the interpreter to retrieve thread states. No modifications required.
How they look
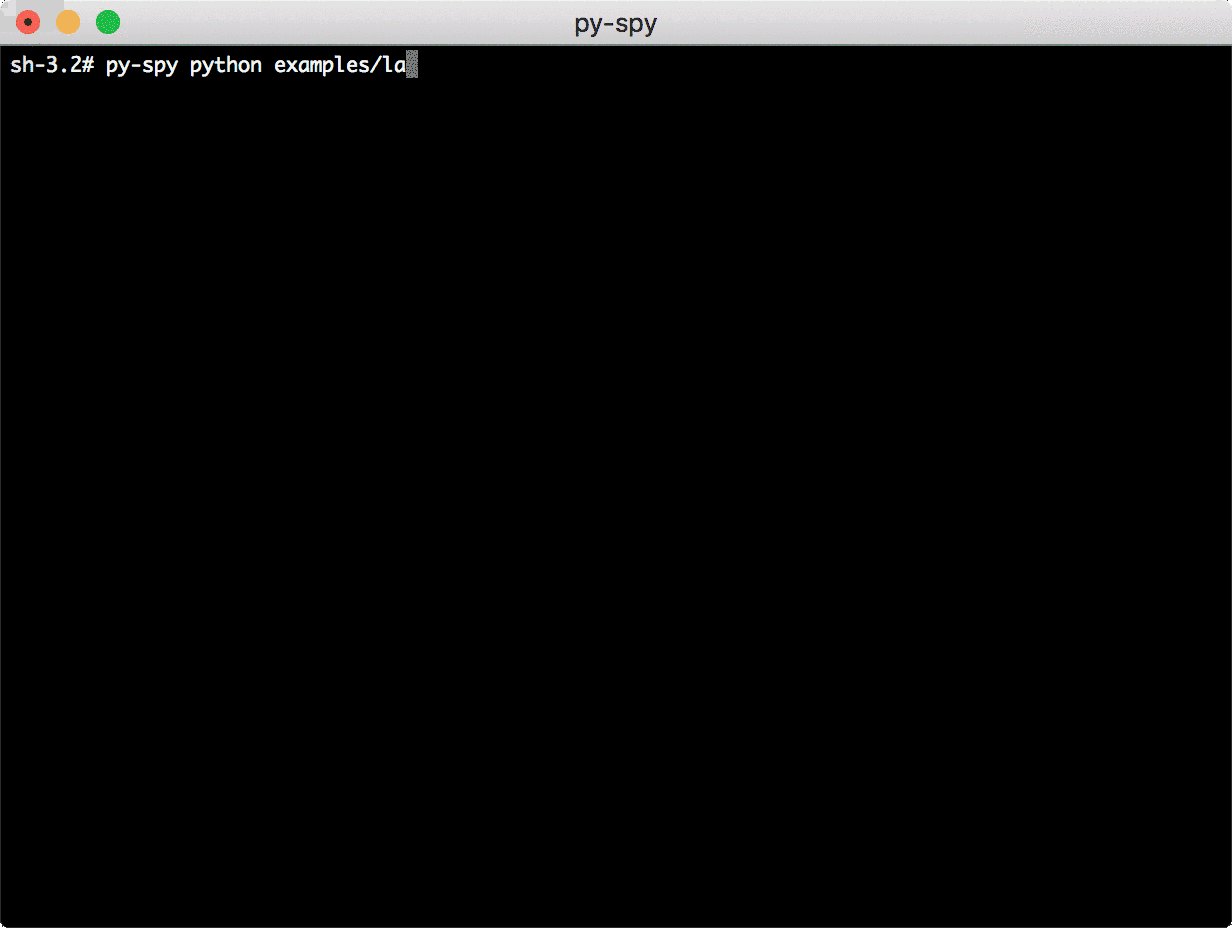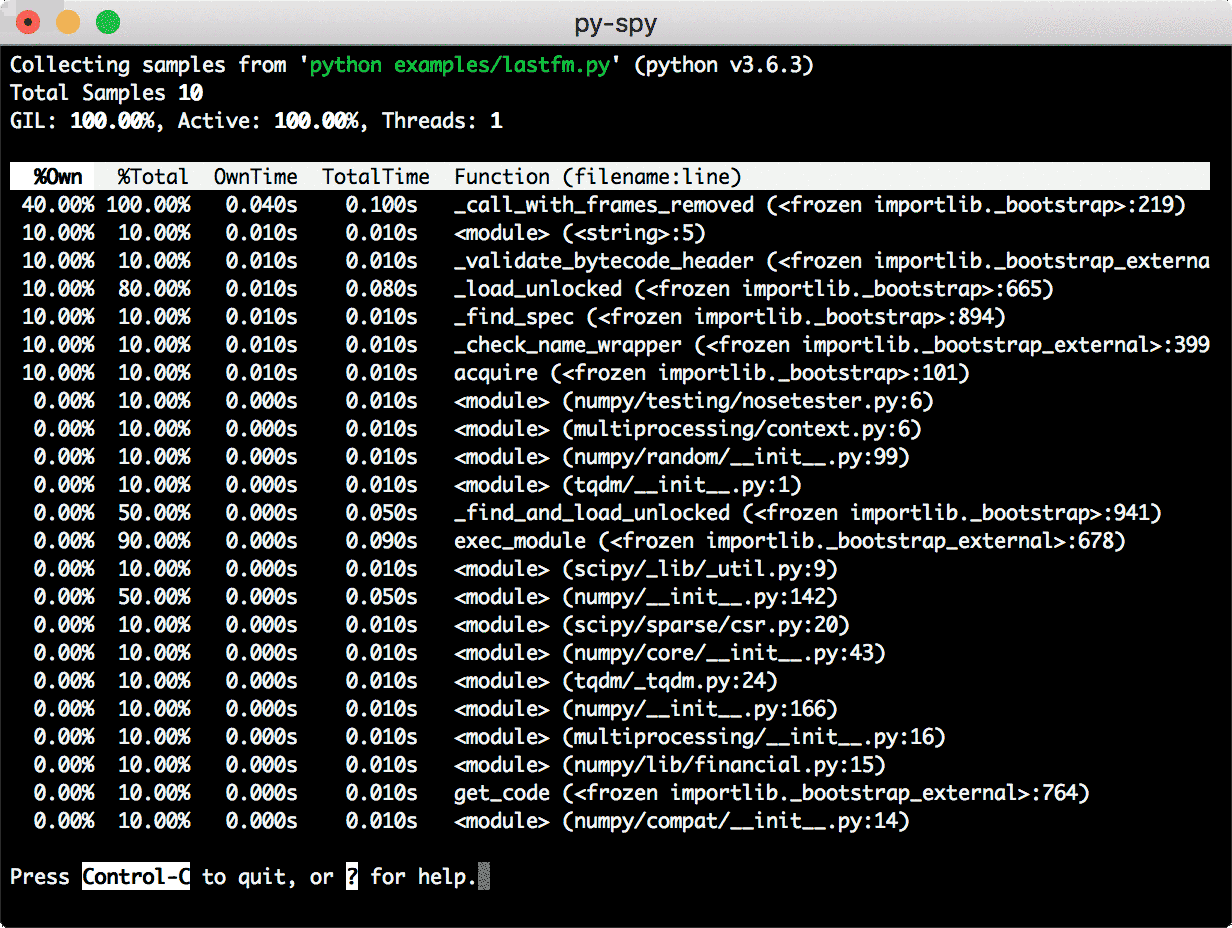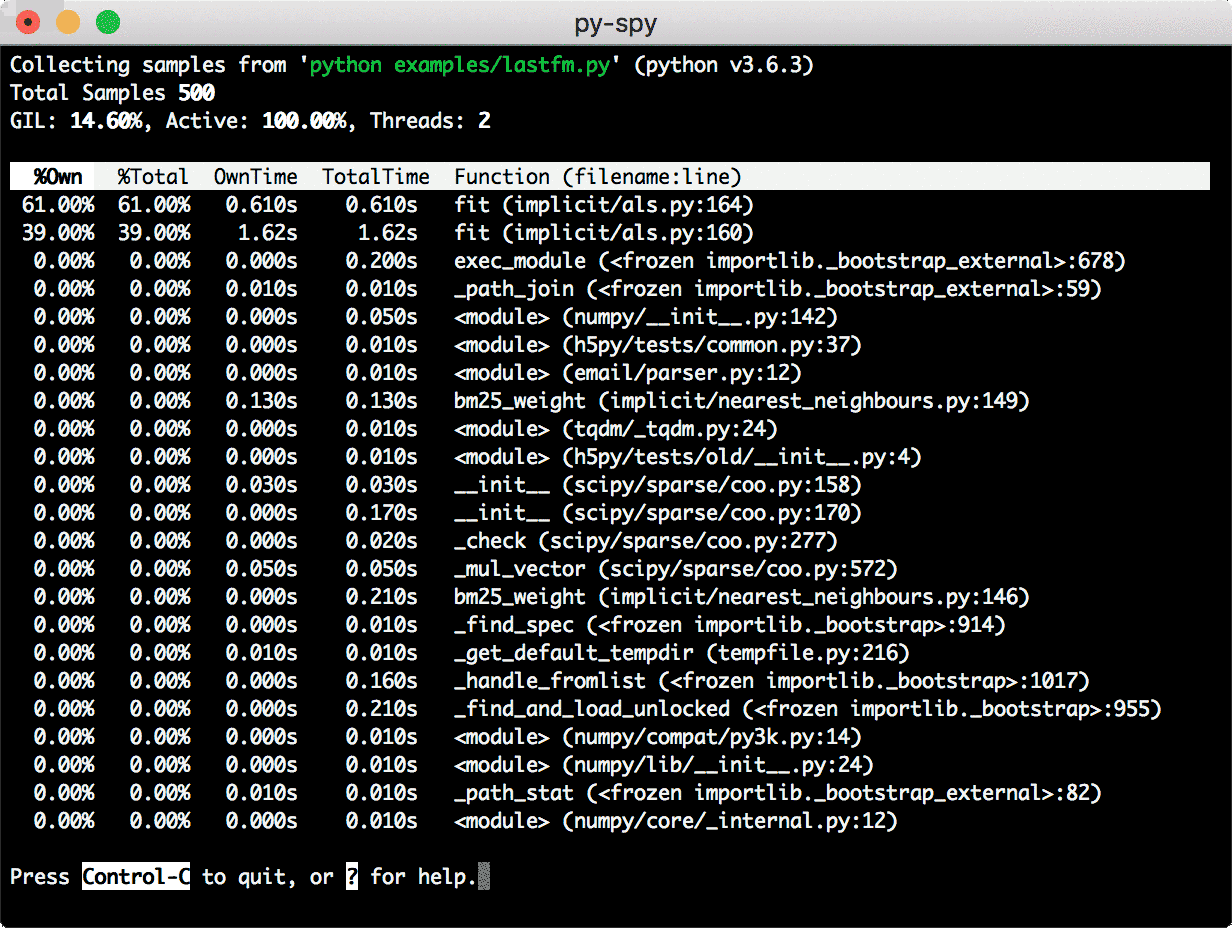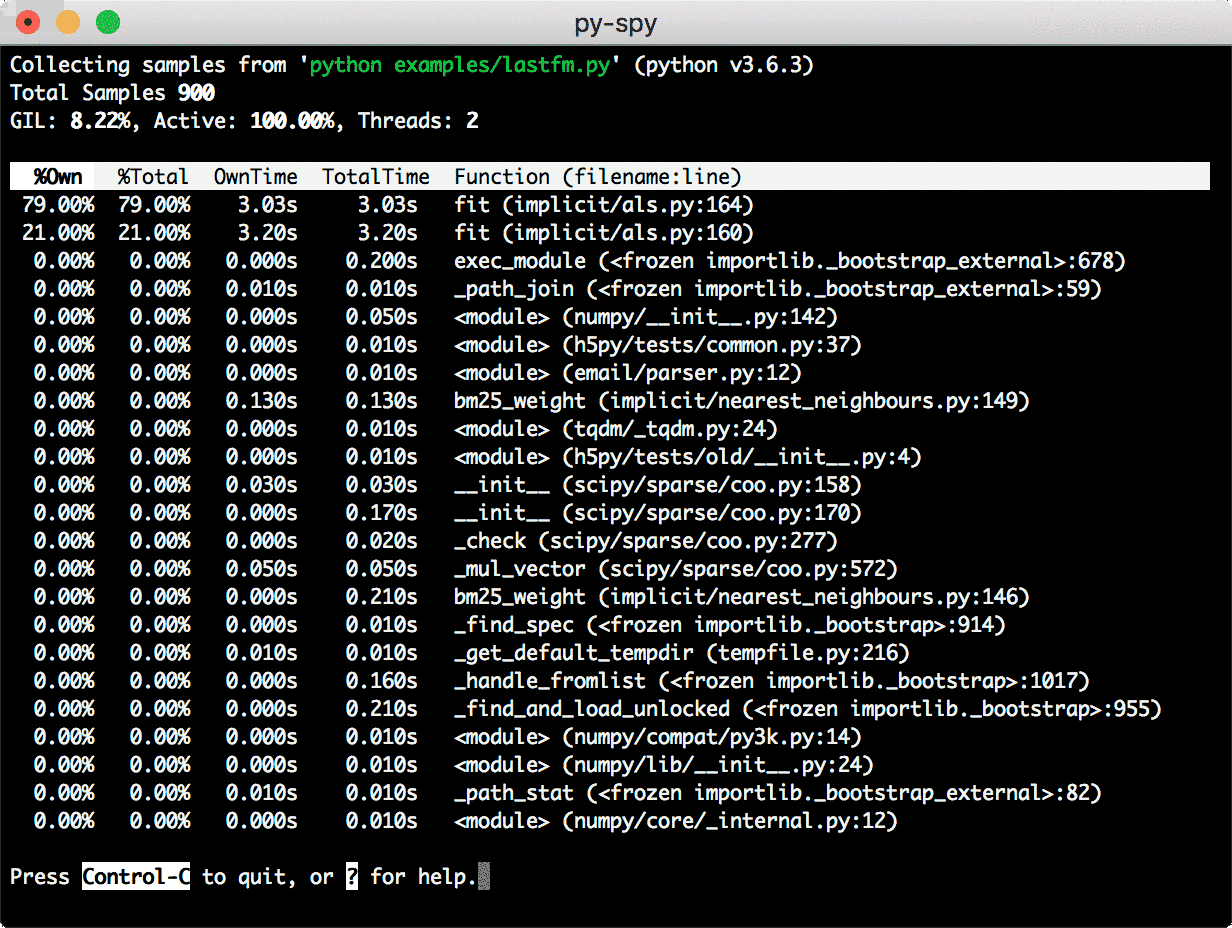

Images courtesy py-spy and pyflame marketing!
-
Python source code, in particular:
Include/{frameobject.h, pystate.h}
Objects/{frameobject.c}
Python/{pystate.c, ceval.c} - James Bennett - A Bit about Bytes: Understanding Python Bytecode - PyCon 2018
- Crashpad design and overview
- Sampling profilers: pyflame and py-spy
Resources
Questions?
http://nikhilism.com
nsm.nikhil@gmail.com
Diving into Python Call Stacks
By Nikhil Marathe
Diving into Python Call Stacks
This talk was presented at PyGotham 2018 on October 6.
- 5,168