Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Overview
Just like the roots of a tree or the foundations of a house, some of the most important components of a structure are not the most glamorous or apparent, but nevertheless they are integral!
In this module, we will focus on foundational ideas in the science of astronomy -- namely, what do we mean by science? and what exactly is the science of astronomy?
We will also highlight the numerical aspect of the science of astronomy, and in particular when it comes to the relationship between space & time!
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Contents
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
What is Astronomy?
Astronomy is ...
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method
Science is a human activity, and as such, it evolves alongside all other human activities, which can be summarized in one word: "culture."
Science overlaps philosophy, history, art, engineering .. etc.
As is typical in the introduction of any new topic, we are going to learn the most basic features, and then you are encouraged to dig as deep as you like :)
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method
Read Section 1.2
par3
When they are first ...
...hypotheses in astronomy.
Pay attention to the passages in the indicated paragraphs.
par1
Science is not merely ...
...to further testing.
par4
A hypothesis must ...
...description of nature.
par8
Much of Astronomy is ...
...cosmic past.
par10
The self-correcting...
... modified hypothesis.
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method
The Scientific Method: Steps, Examples, Tips, and Exercise
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method
This is one of my favorite videos about the scientific methods!
It's densely packed, so you might want to pause every few minutes to remind yourself that what we came for is how is science made?
Also, @8:35 he makes an incorrect statement about Einstein's theories of relativity, but it is not critical to the main story about how science advances.
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method
Let's clarify some terms.
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method - the philosophy of science
For those more philosophically inclined
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method - the history of science
For those more historically inclined
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
The scientific method - more resources

Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Numbers in Astronomy
Scientific Notation
scientific notation at 5:41
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
On the importance of the proper use of units.


I recall an incident from back in 1999 ...

When NASA lost a spacecraft!





Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Numbers in Astronomy
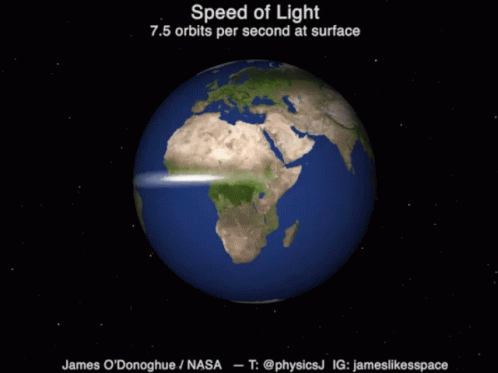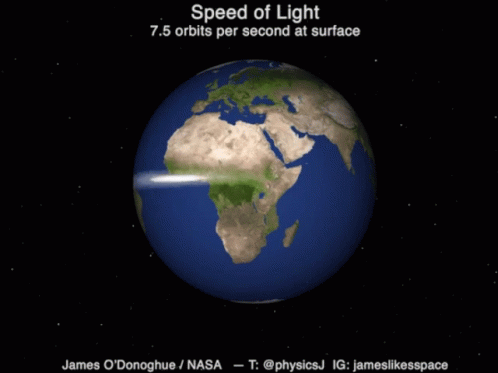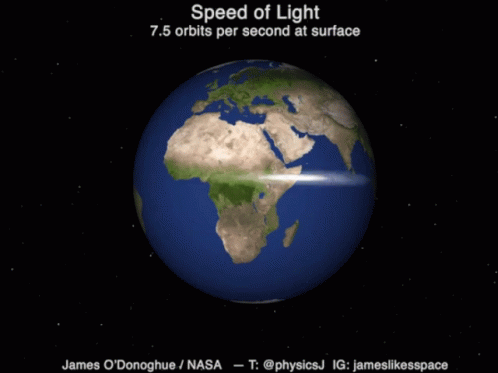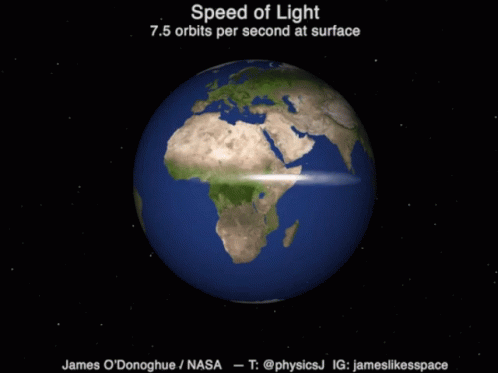
Speed of light
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Numbers in Astronomy

Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Numbers in Astronomy
Example 1.2 --
How many kilometers are there in a ...
Light-second?
Light-minute?
Light-year?
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
What you see has already happened

Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
Consequences of light travel-time
A consequence of the finite speed of light is that what we currently see is light that has left the object a while ago, and the further the object, the longer light had to travel and therefore by the time light arrives, we see the object as it was in its past!
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour - Earth
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour - Earth and its Moon
Earth is a
nearly spherical planet
~ 13,000 km in diameter.
The moon is about a quarter of Earth's size;
~ 3476 km in diameter.
Our nearest astronomical neighbor is Earth’s satellite, commonly called the Moon.
< The distance from Earth to the Moon is Approximately 384,000 km >
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour -- the Solar System
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour -- the Solar System
What is a planet?
Earth is only one of eight planets that revolve around the Sun. These planets, along with their moons and swarms of smaller bodies such as dwarf planets, make up the solar system
How far is the sun?
How big is the sun?
How long does it take for earth to orbit the sun?
What is an astronomical unit?
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour -- the Galaxy
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour - how far?
Earth to ....
| The Moon | 384,000 km | 3.8*10^8 m |
| The Sun | 1 a.u. = 150,000,000 km | 1.5*10^10 m |
| Nearest Star | 4.3 light-years | 4*10^16 m |
| Center of Milky Way | 30,000 light-years | 2.8*10^20 m |
| Nearest (small) Galaxy | 70,000 light-years | 6.6*10^20 m |
| Nearest (large) Galaxy | 2 million light-years | 2*10^22 m |
| The Big Bang | 46 billion light-years | 4.4*10^26 m |
Introduction to Astronomy
The science of Astronomy
A quick tour - from the very small to the very large
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above
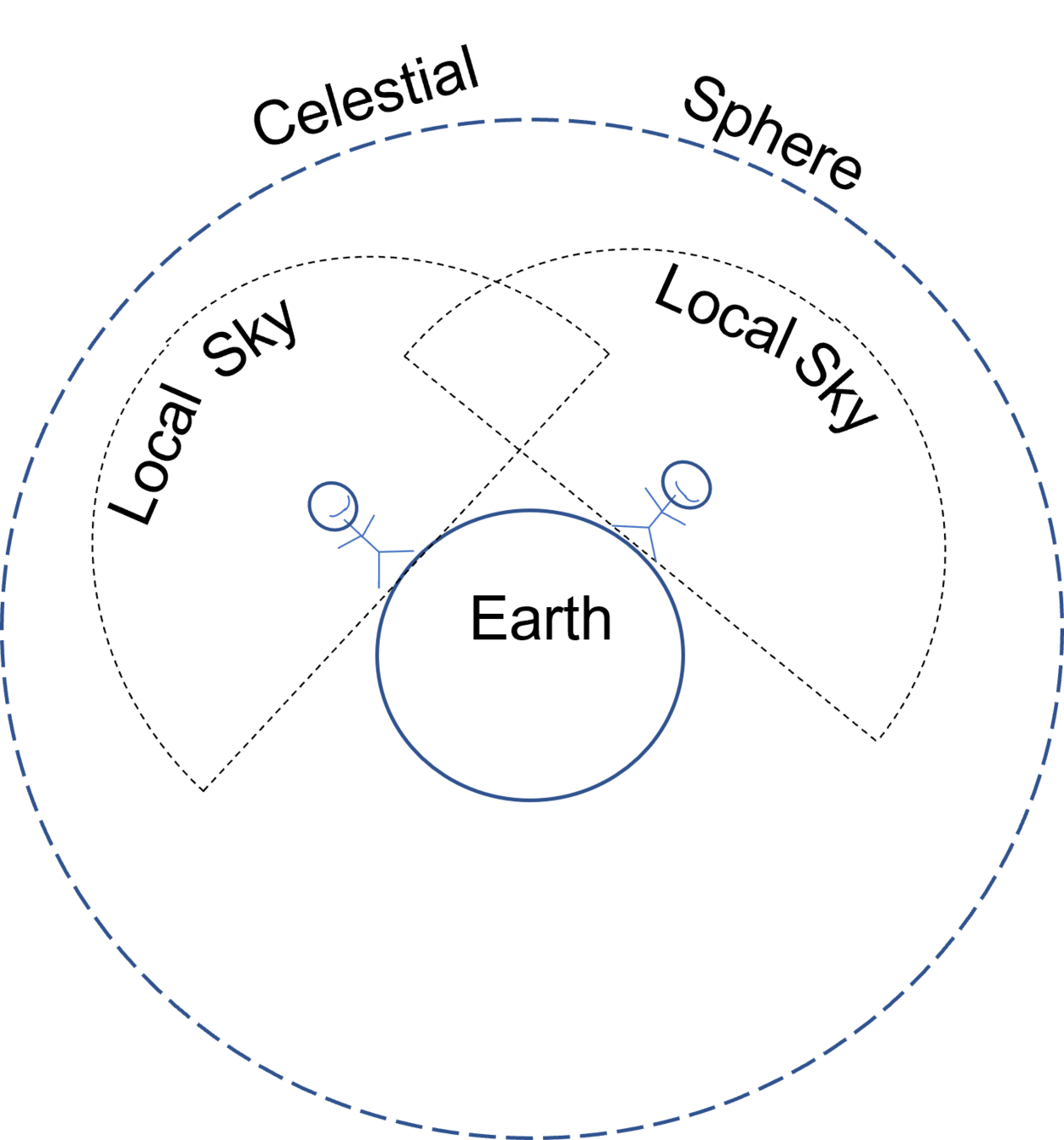
Your local sky is a portion of the celestial sphere
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above
From your perspective, stars appear to rise and set on a rotating celestial sphere.
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above
Alternatively, this can be seen as a consequence of the rotation of Earth around its axis.
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above

Alternatively, this can be seen as a consequence of the rotation of Earth around its axis.
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above

Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
The sky above
Explain the following phenomena ...
- Night
- Succession of night and day
- The change in the Sun's location on the celestial sphere relative to the stars
- The seasons
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
Geocentric vs Heliocentric models
Introduction to Astronomy
Observing the sky
Key Terms
AST - Intro
By omoussa
AST - Intro
- 235