The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
Nucleons & their structure
Atomic Nucleus
Nucleons & their structure
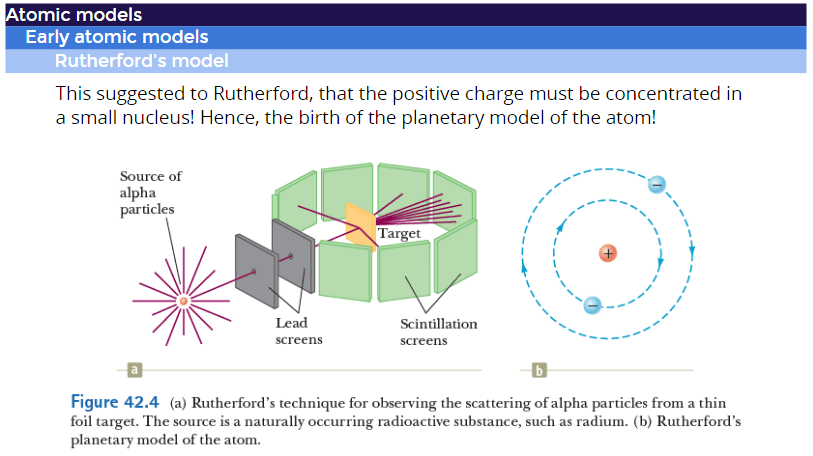
Rutherford
Once upon a time ...
Atomic Nucleus
Nucleons & their structure
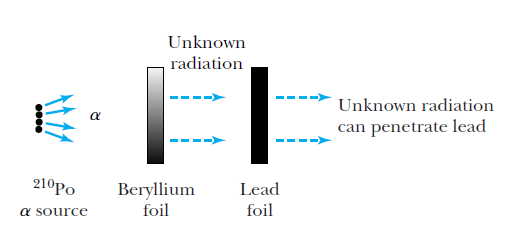
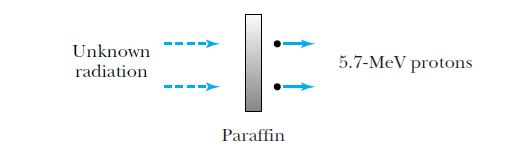
Discovery of the neutron (1932)

James Chadwick
Chadwick suggested the radiation was a neutral particle
of about the same mass as a proton.
Atomic Nucleus
Size of the nucleus
Atomic nuclei are bound states of protons + neutrons
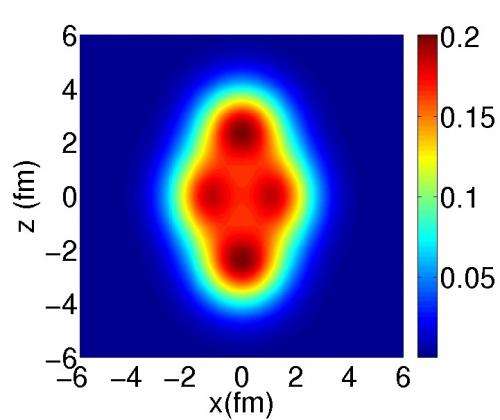
Probability density for the presence of neutrons and protons predicted for the neon-20 nucleus. It can be seen that this is not homogeneous: the neutrons and protons are distributed in clusters. © Jean-Paul Ebran/CEA
Nucleons & their structure

The spatial extension of a typical nucleus is ~ fm
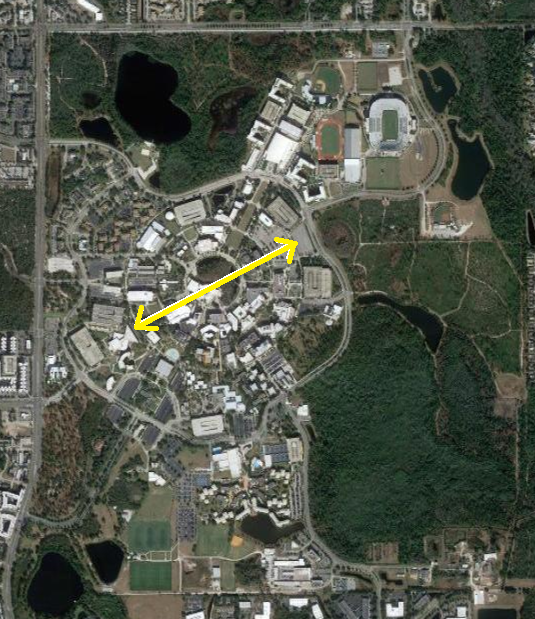
The comparative spatial extension of the atomic nucleus to the spatial extension of the electronic cloud in an atom is of the same order as the ratio of the size of your thumb compared to the size of UCF campus.
Atomic Nucleus
Underlying structure
Atomic nuclei are bound states of protons + neutrons
Probability density for the presence of neutrons and protons predicted for the neon-20 nucleus. It can be seen that this is not homogeneous: the neutrons and protons are distributed in clusters. © Jean-Paul Ebran/CEA
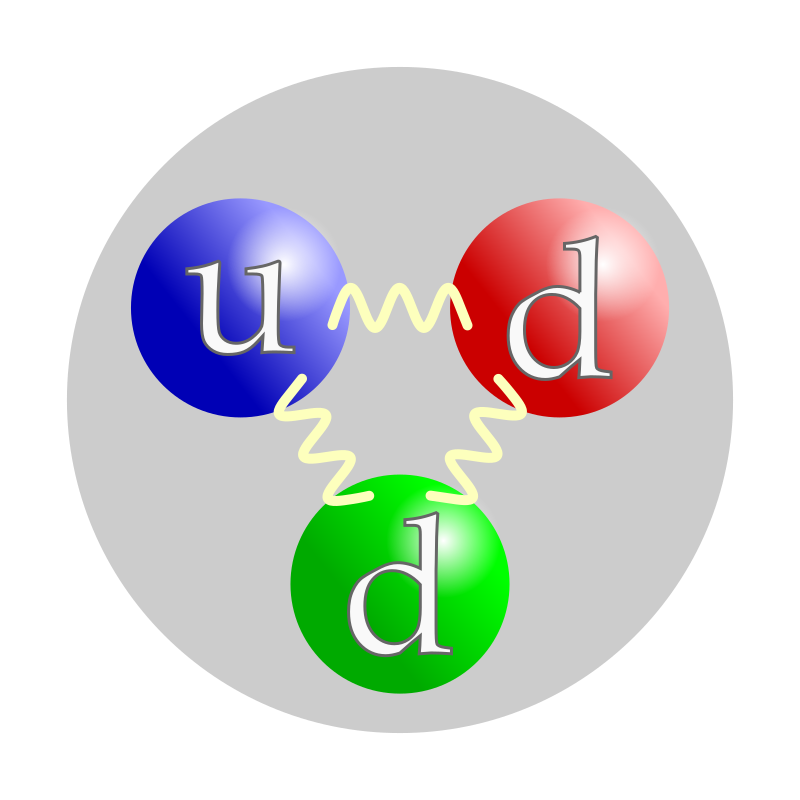
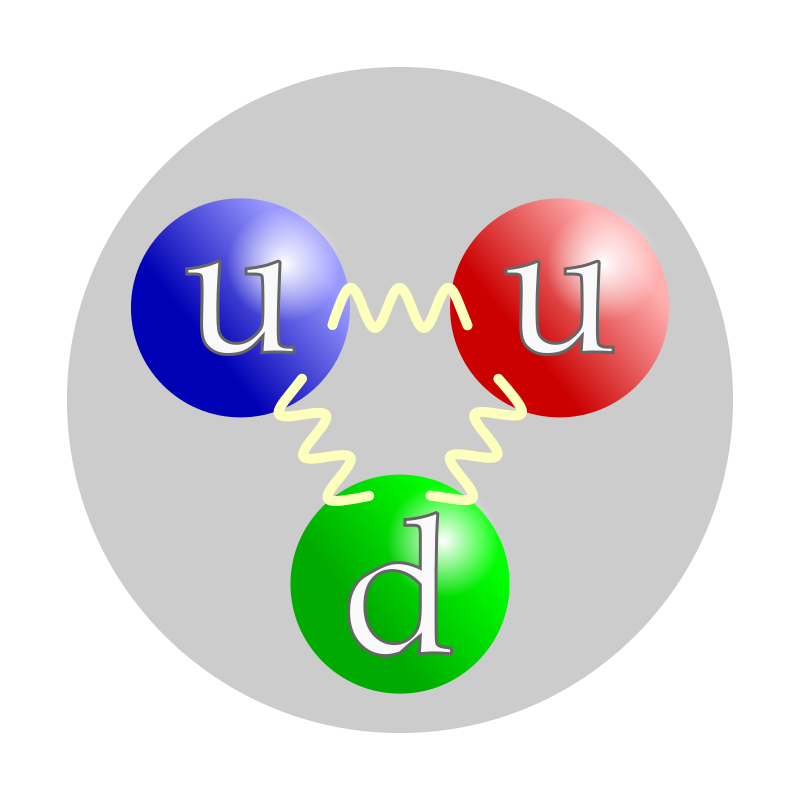
protons & neutrons
have internal structure
Nucleons & their structure
proton



neutron



Atomic Nucleus
Underlying structure


of Elementary Particles





Nucleons & their structure
The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
The variety of nuclei
Definitions
Isotope:
Atoms with same Z but different A
Nuclide:
A nuclear species with a given Z, N, and A
Isotone:
Atoms with same N but different A
Isobar:
Atoms with same A but different combination of Z and N

Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides

The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides

The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides
The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Binding energy
Naively, we might think that the mass of each nucleus is the sum of the masses of the constituents:
The difference is known as the binding energy
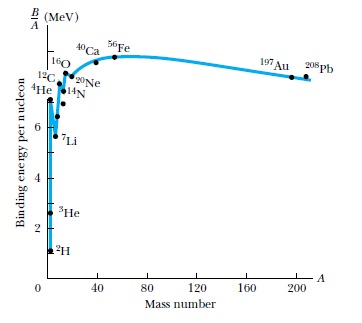
But when the masses are measured, we find a discrepancy (~ 0.1%)
The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
3D chart of the nuclides
The variety of nuclei
The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Atomic Nucleus
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Radioactive decay
Alpha-decay
Beta-decay
Gamma-decay
Atomic Nucleus
Beta decay

Beta-decay

Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Atomic Nucleus
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Radioactive decay chains
...
...
Atomic Nucleus
Nuclear Fission
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions

Atomic Nucleus
Nuclear Fission
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei.
The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay.
The fission process can be either induced by a collision, or spontaneous.

Induced fission of Uranium 235
Atomic Nucleus
Nuclear Fission
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions

Atomic Nucleus
Fusion
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei, combine to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons).
The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy.
A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than iron-56 or nickel-62 will generally release energy.
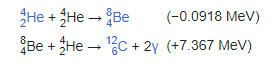
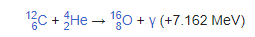
Atomic Nucleus
The origin story
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions



per 10,000 atoms in the universe
Atomic Nucleus
The origin story
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions

Atomic Nucleus
Origin Story
Radioactivity & other Nuclear Reactions
Utterly captivating! One of the best presentations on the topic!
Nuclear Physics
By omoussa
Nuclear Physics
- 226