Rotational Dynamics
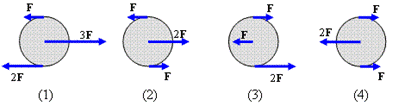
Which of the following objects is experiencing the largest angular acceleration due to the shown forces?
A series of wrenches of different lengths are used on a hexagonal bolt as shown in the figure. Which combination of wrench length and applied force produces the greatest torque on the bolt?
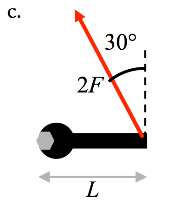



d
A CD can be thought of as a uniform solid disk, with mass of 20 g and a radius of 6.0 cm. When the CD is inserted into a player, a +0.005 Nm torque from the motor accelerates the CD from rest to an angular velocity of 20 rad/s.
a) Calculate the angular acceleration of the CD.
b) How many revolutions does the disk make as it accelerates from rest to 20 rad/s
A weightlifter accidently puts uneven weights on the bar. If the weight on the left side is 400 N, and the weight on the right side is 600 N, calculate the upward forces the weightlifter must apply with his left and right arms in order to keep the bar in equilibrium. The weight of the bar itself is 100N, and can be assumed to act at its midpoint.

A diver whose mass is 56kg is poised at the end of a 4.0m diving board, which is bolted down at the other end. The board has a negligible mass and is supported by a fulcrum, 1.6m from the bolt. Find the forces that the fulcrum and the bolt exert on the board in equilibrium.

Sit down with your feet on the ground on a chair that rotates. Lift one of your legs such that it is unbent (straightened out). Using the other leg, begin to rotate yourself by pushing on the ground. Stop using your leg to push the ground but allow the chair to rotate and slow down until it stops. Suppose that (from the moment you stop pushing) the chair completes 1.5 revolutions in 8 seconds before it completely stops. Assume that the acceleration of the chair is constant throughout its motion.
- To answer some of the following questions, you will need to know or assume how far your extended foot is from the axis of rotation, i.e. the length of your leg. Record that here: _________
- Calculate the angular acceleration of the chair.
- Estimate the tangential speed of your extended foot just at the moment you stop pushing with your other leg.
- Estimate the magnitude of the total linear acceleration of your extended foot just at the moment you stop pushing with your other leg.
Sit down with your feet on the ground on a chair that rotates. Lift one of your legs such that it is unbent (straightened out). Using the other leg, begin to rotate yourself by pushing on the ground. Stop using your leg to push the ground but allow the chair to rotate and slow down until it stops. Suppose that (from the moment you stop pushing) the chair completes 1.5 revolutions in 8 seconds before it completely stops. Assume that the acceleration of the chair is constant throughout its motion.
- To answer some of the following questions, you will need to know or assume how far your extended foot is from the axis of rotation, i.e. the length of your leg. Record that here: _________
- Calculate the angular acceleration of the chair.
- Estimate the tangential speed of your extended foot just at the moment you stop pushing with your other leg.
- Estimate the magnitude of the total linear acceleration of your extended foot just at the moment you stop pushing with your other leg.
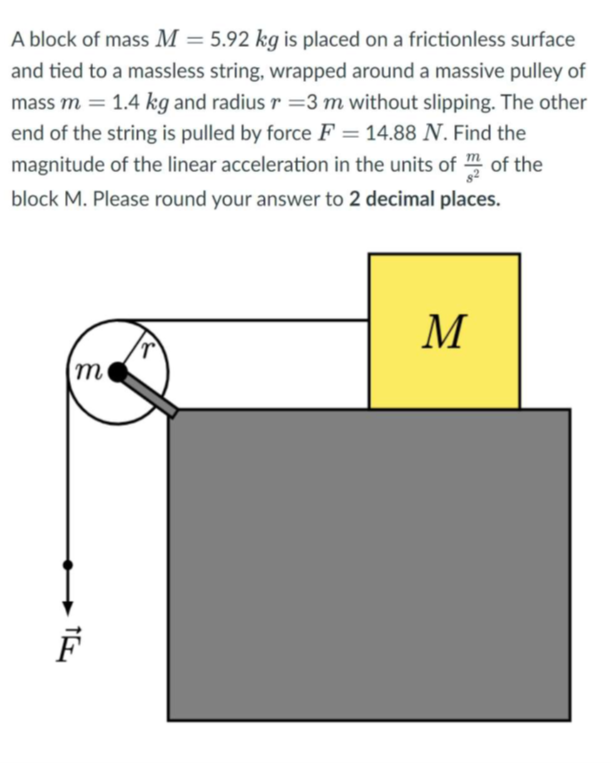
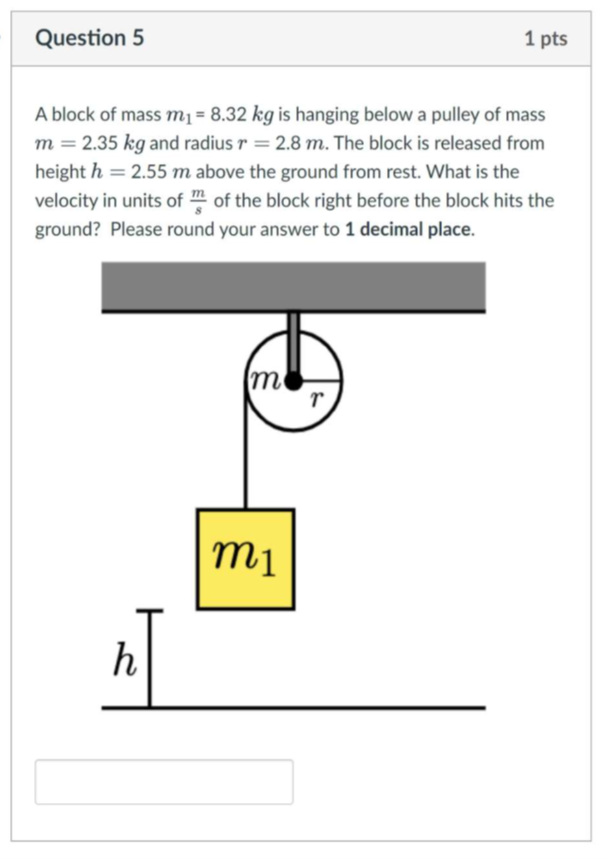
rotational dynamics
By omoussa
rotational dynamics
- 138



