Talk more about Git
Git 起源故事
這要先從 Linux 講起...
1991 年
- Linus Torvalds 建立了開源的 Linux
(2002年前都是他人工在合併 Linux 程式碼)
2002 年
- Linux 開始用 BitKeeper 做版本控制
2005 年
- Andrew 試圖破解 BitKeeper 的協議,於是 Linux 無法再使用 BitKeeper


Linus Torvalds 開發出了 Git
(順道一提,GitHub 網站 2007 年開發,2008年上線)
使用 Git 背後的事
當我們用 git init or git clone 來建立 git repo
其實是在資料夾內創建 .git 檔
讓 Git 開始對這個目錄進行版本控制
.git 紀錄了所有 git 操作的資訊
.git 目錄內容
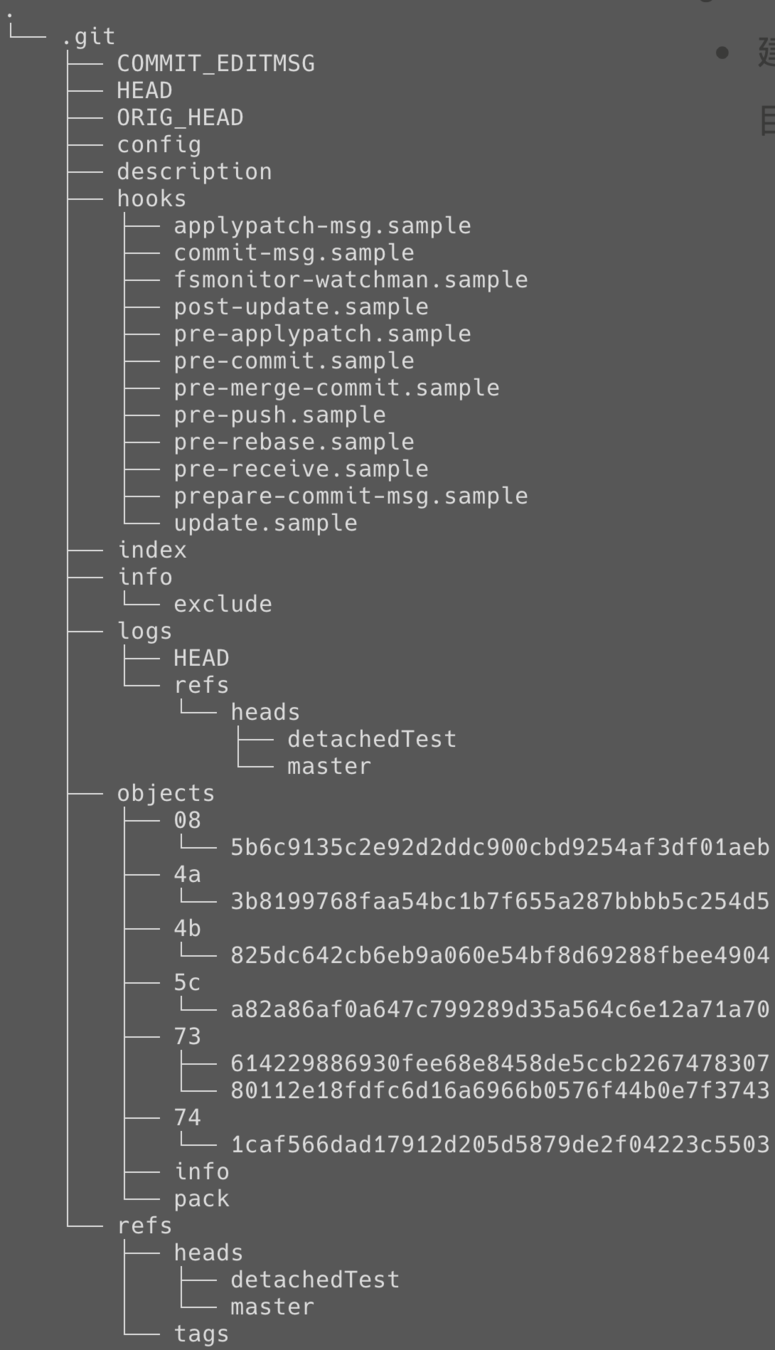
設定檔
倉庫
branch's reference
(name to SHA-1)
當前位置
HEAD & refs 演變史(SHA-1形式)
.git/config
- core:核心設定
- remote:
遠端(GitHub) & fetch - branch 資訊
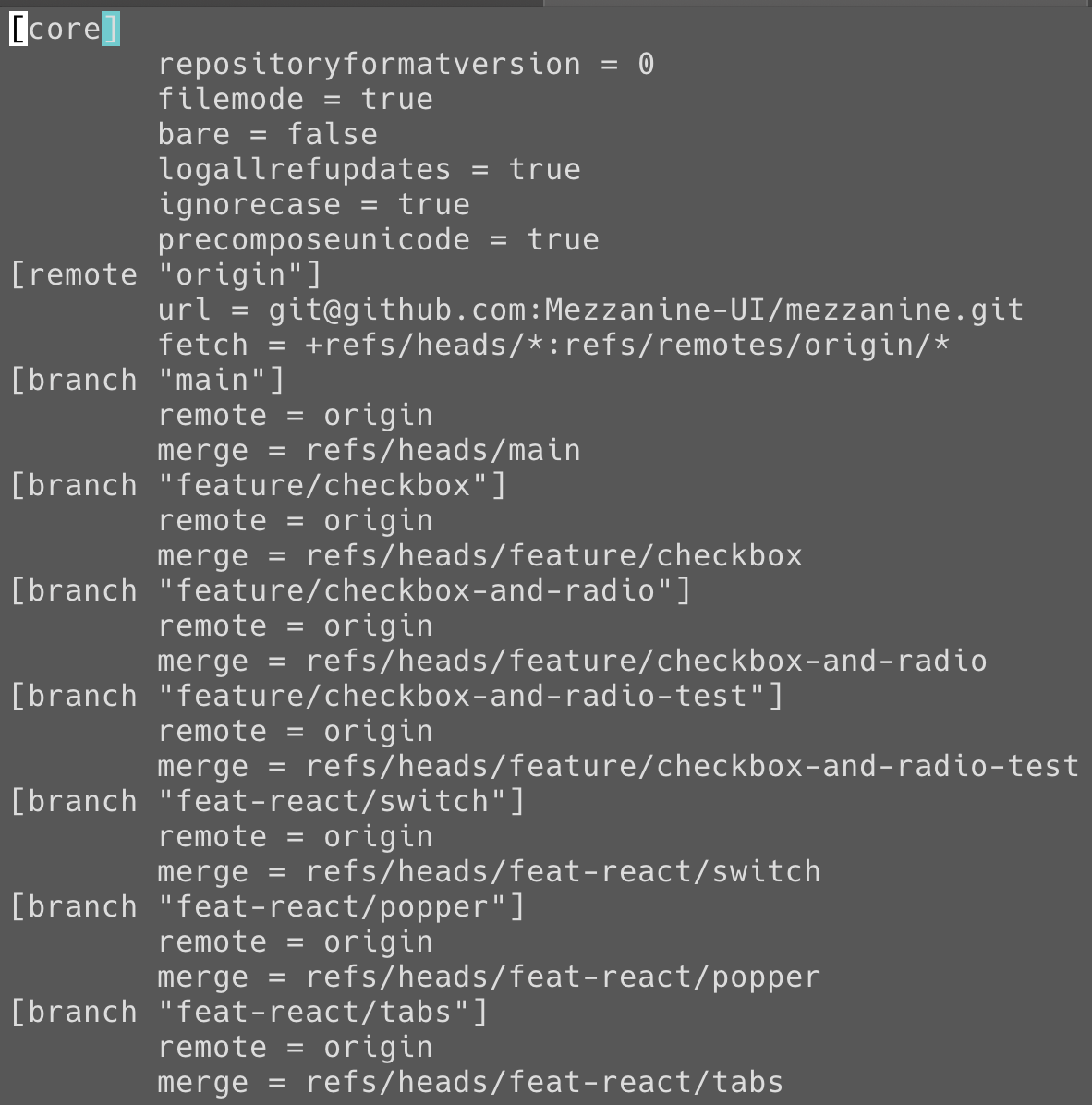
用 git config -e 查看
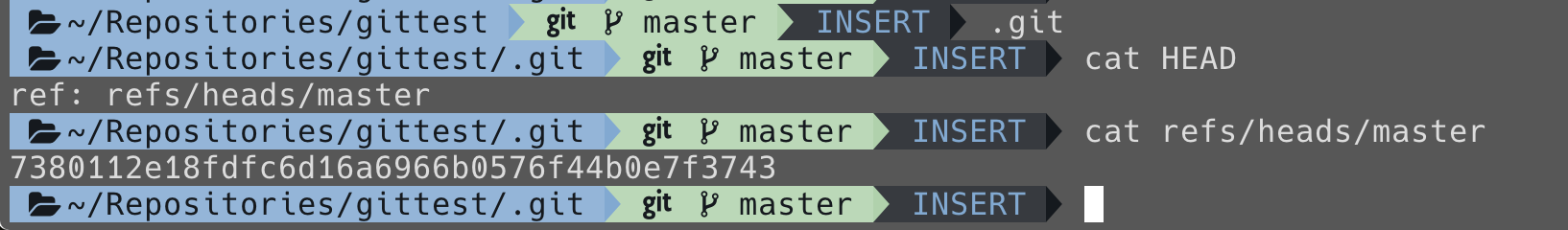
.git/refs
儲存 SHA-1 值 對應到的 branch name ( reference )

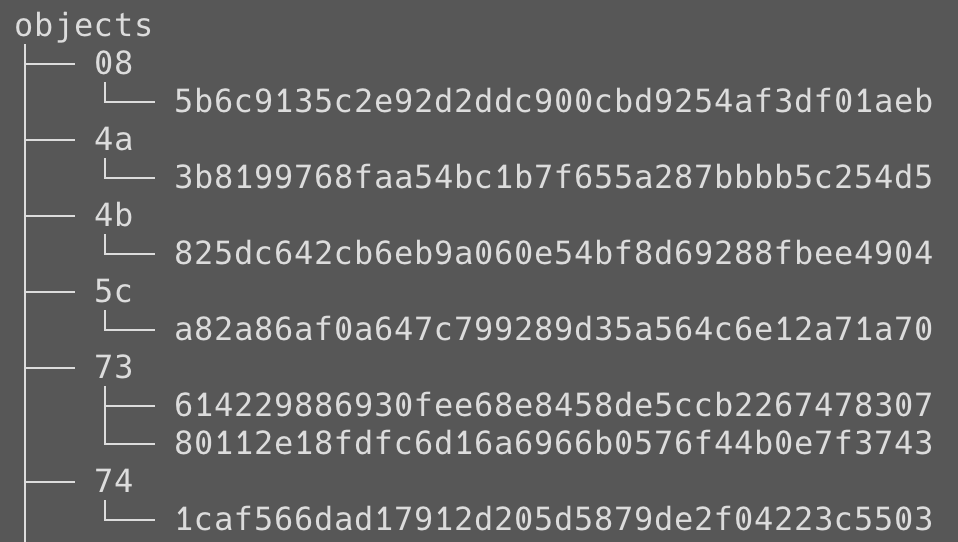
.git/objects
四種物件:
- Blob 物件:存檔案內容
- Tree 物件:存資料夾
- Commit 物件:整合了 tree 和 blob 型別,儲存了當前的所有變化
- Tag 物件:存 Annotated Tag
儲存資料的主要地方
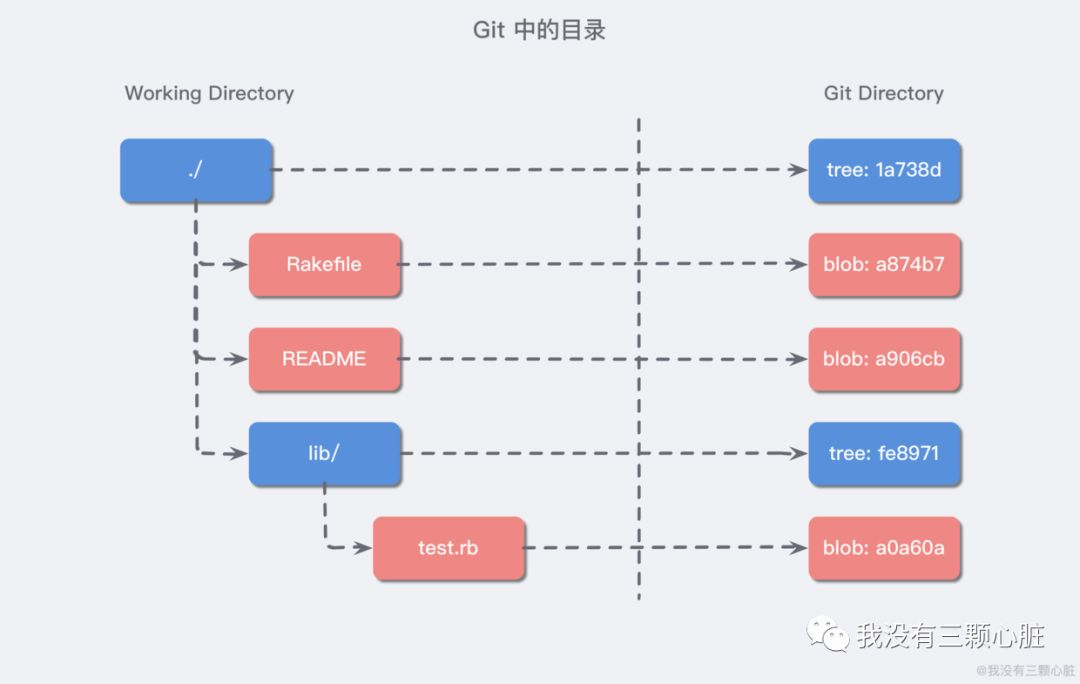

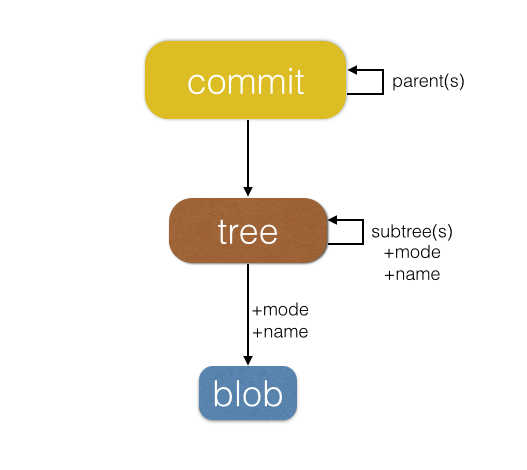
平常 commit 的 hash 值也就是從 .git/objects 拿的
所以..
Git 會按照上述的方式把紀錄存在 .git
Commit 是透過 SHA-1 演算法 產出的 40 字元
Branch, Tag, HEAD 等也都是同樣的格式
因此,只要有 commit 就不會找不回來
(除非 detached 或 Git 自動回收)
只要內容有變,SHA-1 出來的值都會變
也就是說,我們永遠都是在新增 commit 訊息
小統整
使用 Git
操作 .git 裡的檔案
HEAD
當前位置(一個指標)
.git
都是以 SHA-1 處理出來的 40 字元
(commit, branch, HEAD, logs ...)
Commit
紀錄每次的變更(tree+blob)
tree
儲存 資料夾
blob
儲存 資料
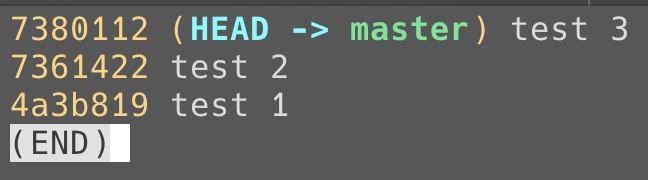
commits & HEAD 切換紀錄
logs
Detached HEAD
HEAD & Branch 不同步
正常情況:HEAD會 指向 Branch,Branch 指向其最新 Commit
情境:
- git checkout 直接跳到某個 commit
- Rebase 的過程
:Rebase 完就好了
直接跳到某個 commit 的情況
情境:
- 想砍掉幾個 commit 從過去某個 commit 開始重寫
- 想去到丟失的 commit
解法:
- 跳過去後在那裡直接開一個新 branch
:git branch $branchName $commitID
branch 只是一個 ref,幫斷頭的 commit (or 孤兒 Commit)建立新 ref 的概念
比較:git checkout vs git reset
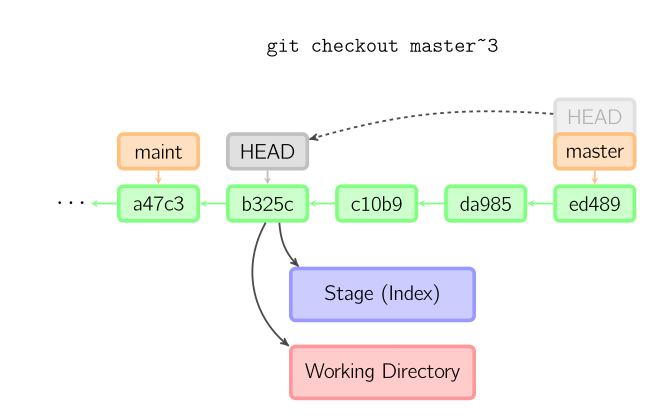
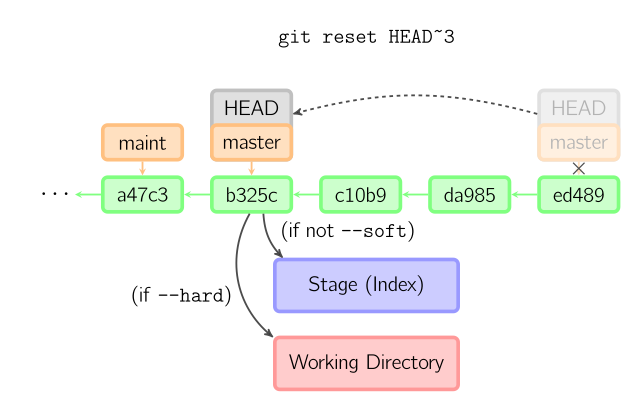
checkout : 移動 HEAD
reset:同時移動HEAD和master
--soft:暫存區的會保留
--mixed(default):暫存會清空
--hard:放棄本地所有變更
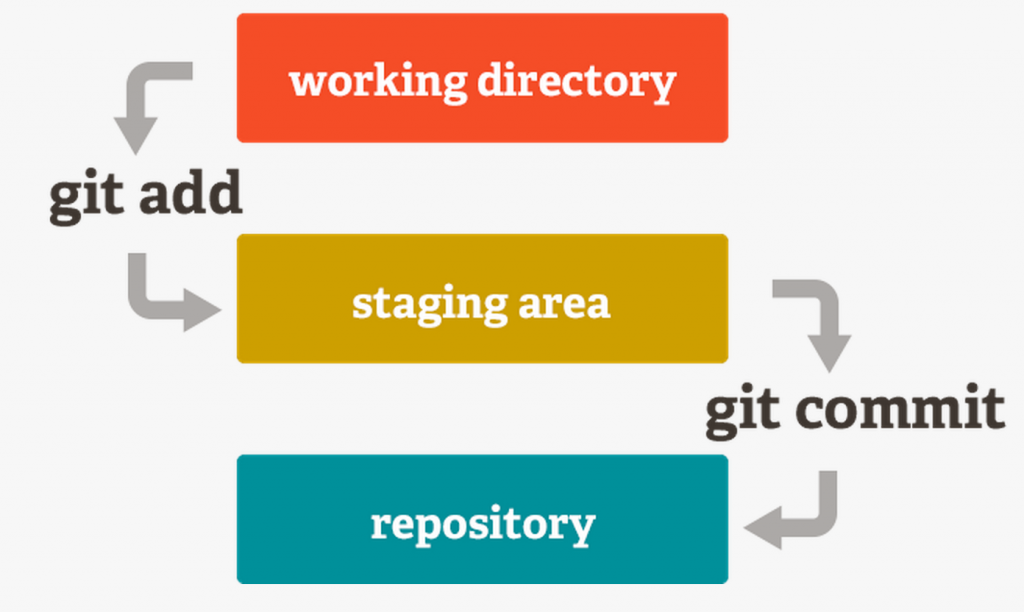
Next Step: commit
Next Step:add
Next Step:NO next step 😢
再比較:HEAD vs ORIG_HEAD vs Reflog
HEAD : 當前位置(一個指標)
ORIG_HEAD :上一次危險操作前的 HEAD 位置
Reflog : 紀錄 HEAD 每個變更紀錄(後面會再提到)
(危險操作:merge, reset, rebase 等會更動歷史的)
開發上常用的指令組合&情境
修改 commit 紀錄的三種方式
情境:剛 commit 完就發現有東西沒存到、有空格、錯字等等
- rebase i + squash → 把 commit 壓到上一個裡面
- reset + commit → 拆掉重新 commit
- add + commit --amend --no-edit
git commit --amend (-m):幫 commit 改名
--no-edit : 不編輯 commit 訊息
→ amend 限用於追加檔案到「最近一次」 commit
git rebase
功能:根據 rebase 的 branch 重新定義分支的參考基準
情境:開發過程中,主要的 / 有依賴的 branch 有改動時

git rebase -i 編輯模式
# p, pick = use commit
# r, reword = use commit, but edit the commit message
# e, edit = use commit, but stop for amending
# s, squash = use commit, but meld into previous commit
# f, fixup = like "squash", but discard this commit's log message
# x, exec = run command (the rest of the line) using shell
# d, drop = remove commit使用情境:開PR前或是上版前的 commit 整理
常用的指令組合:
- 把多個 commit 合併成 一個 commit:squash
- 一個 commit 分割成多個 commit:edit + git reset HEAD^ 再分次 commit
- 在某些 commit 之間再新增新的 commit: rebase 後新增檔案&commit 後再 git rebase --continue
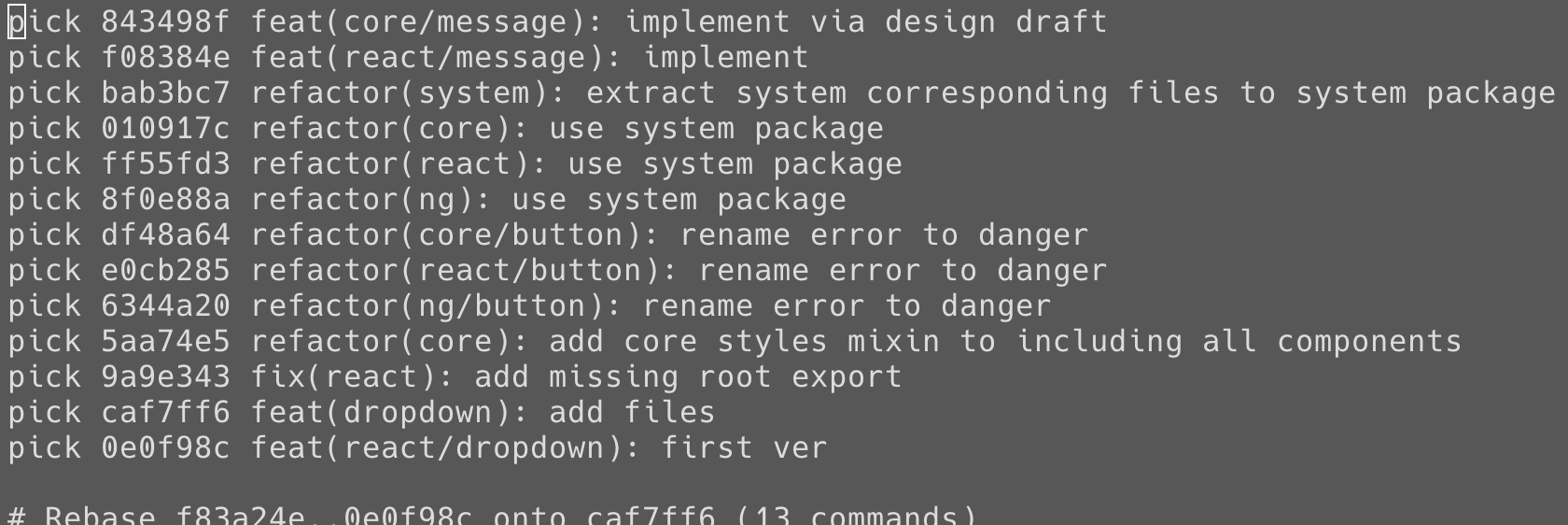
舉例:Mezzanine UI
Git Reflog
再用 git reset $commitID --hard 回去
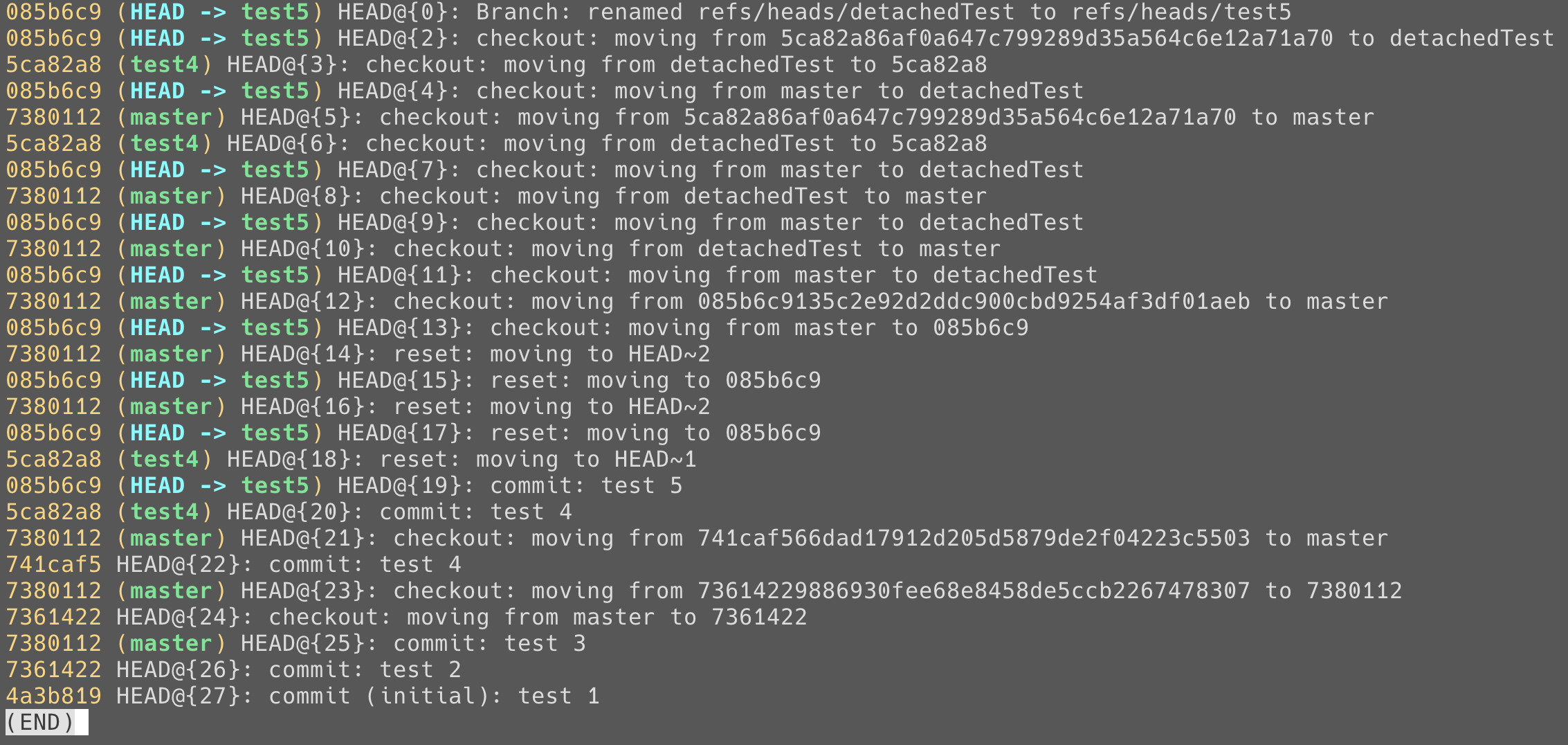
可查看 HEAD 切換的紀錄 和 所在的 commit SHA-1值
透過 git reflog 查找所有變更紀錄
情境:若不記得 commit 又不小心 reset --hard的話
其餘還有一些指令會整理在 HackMD 共筆裡
一些想法
1. 開PR前善用 git rebase 同步 和 整理 commit
3. 善用 git-cz 產出有格式的 commit msg
2. 開專案時也建立 commit msg style
Branch 通常 merge 完會刪除所以應該還好(?)
Reference
https://www.mdeditor.tw/pl/2wWV/zh-tw
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66506485
https://titangene.github.io/article/git-tag-object.html
https://dotblogs.com.tw/wasichris/2016/04/29/225157
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/964876/head-and-orig-head-in-git
https://gitbook.tw/
其他推薦網站:
Git
By parkerhiphop
Git
- 599



