Networking
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
- Take pulses of light, electricity, or radio and translate to 1's and 0's.
- Pass received data up to data link layer
- Take binary data-link info and turn to pulses
Communication Media
- The channel or system through which a sender transmits a message to the receiver
- Example: Sound waves through air when we talk
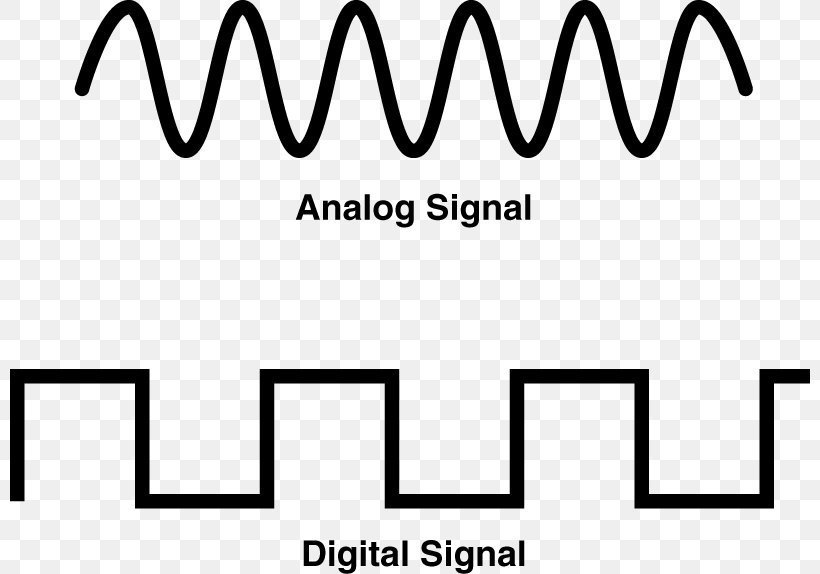
Communication Media
- Digital - Specific values. Often 1 or 0
- Analog - Continuously variable

Medium types
- Electricity over a wire
- Radio waves (wi-fi, mobile, satellite/dish)
- Light via fiber optics (or IR remote)
Digital Over a Wire
- Electricity on - 1, off - 0
- Electricity pos - 1, neg - 0
Signal Issues
- Electricity through a wire creates a magnetic field
- The causes loss, and smoothing of signal, called attenuation
- Magnetic fields create signal in the wire, called noise or interference



Text
Text
Balanced Line
Differential Signaling
Twisted Pair (TP)

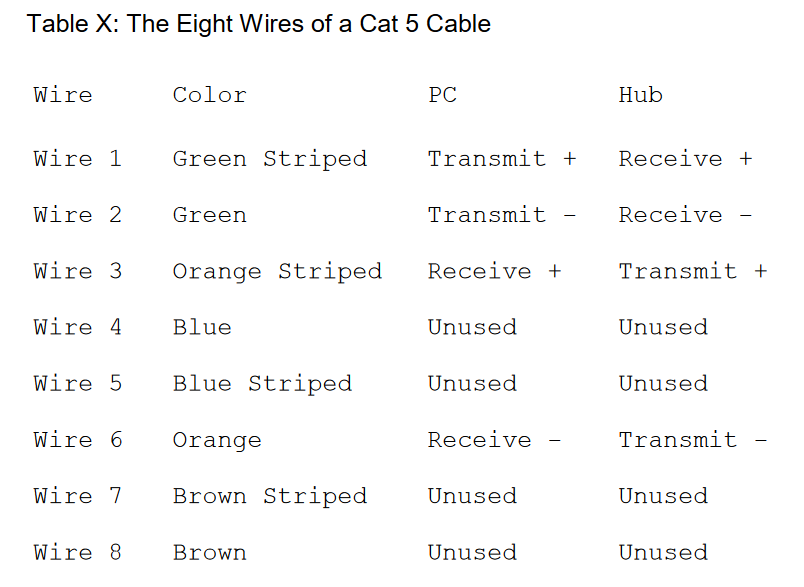
Cable Standards
- 8 wires in a cable
- Cat 5 - 100 Mbps
- Cat 5e - 1 Gbps
- Cat 6 - 10 Gbps
- Connectors are called RJ45 connectors
- (Old phones used RJ11 - 4 wires)
Wire types
- Solid wire transmits a better signal, but stiff
- Stranded wire is more flexible
- Shielded cable has foil around it
Coaxial Cable (Coax)


Radio

1040 KHz (1.04 MHz) - AM Radio
90.1 MHz - FM radio
2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz Wi-Fi
700 MHz 4G Phone
850 MHz, 24 GHz 5G Phone
Frequencies
- Data amount
- Higher frequency - more data
- Higher frequency - more data
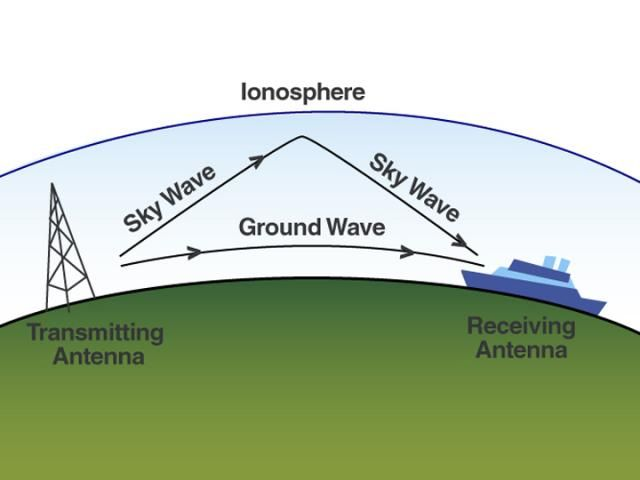
- Radio wave propagation - easier to block
- Lower frequency - bends with Earth, passes through things
- High frequency, straight line, easy to block
- Lower frequency - bends with Earth, passes through things
- Electromagnetic spectrum
- United States Spectrum Allocation Chart
- United States Spectrum Allocation Chart

Text
Text
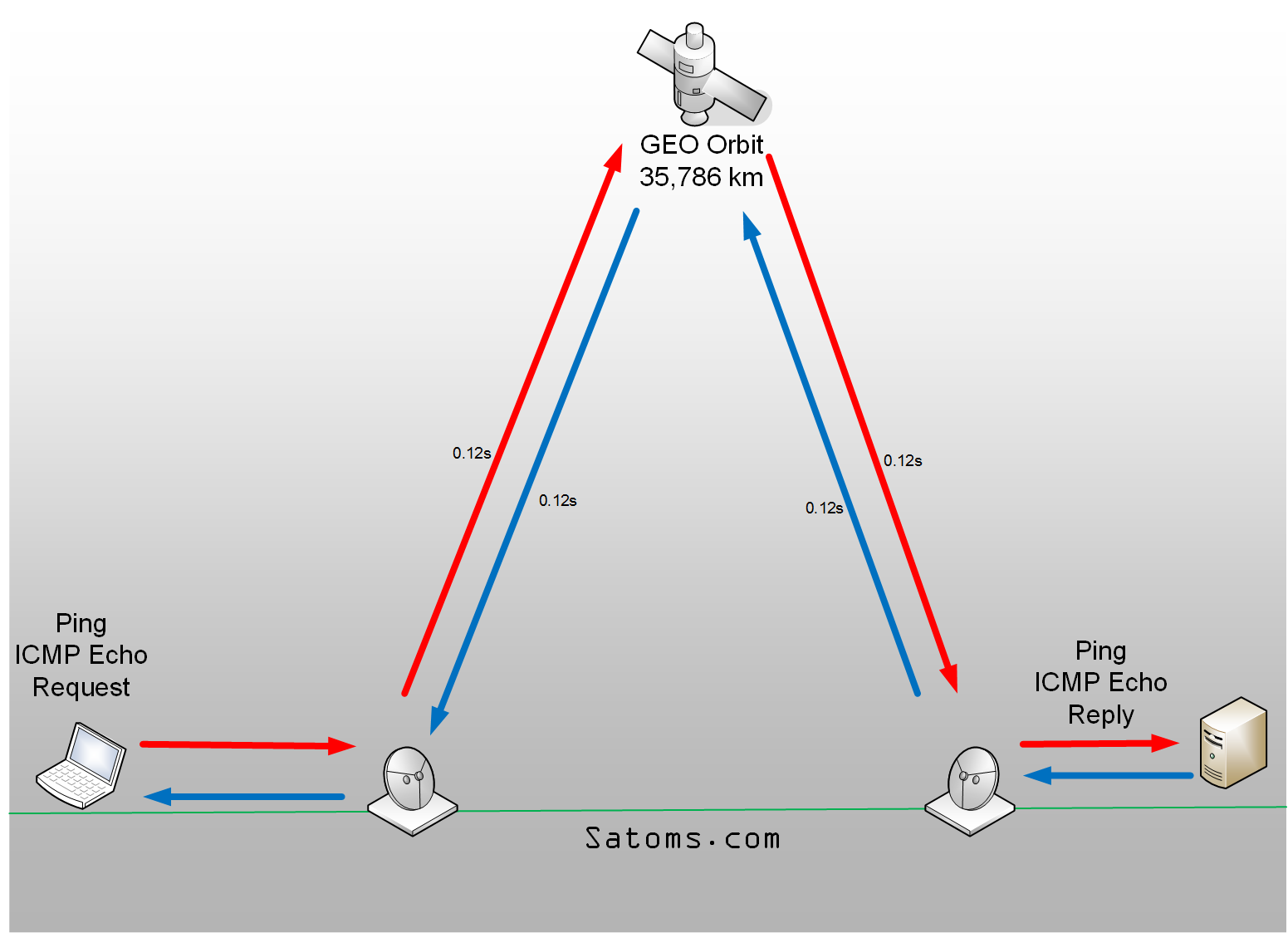

Starlink in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
35 ms vs 500 ms
Transmission Types
- Simplex - One way - broadcast
- Half-duplex - Two ways, can't talk and listen at the same time - CB
- Full duplex - Talk and listen at the same time. Requires two channels/frequencies.
Modulation
- Modulation - take one signal and put on a different medium.
- Demodulation - take a signal off the medium and convert it back
- Modem - Modulator / Demodulator - Very common term from 90's when we used modems to modulate/demodulate binary data onto audio phone lines. Less common term now as they are often combined with routers and wi-fi devices.
Radio modulation types
- CW (Morse code)
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- Single Side Band
- Frequency Modulation (FM)





Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)

Pulse Width Modulation

Text
Serial Clock (SCLK)

Networking - Physical Layer
By Paul Craven
Networking - Physical Layer
- 1,063



