ERD & DDL
Objetives

ERD
(Entity Relationship Diagram)

Entities

-
An entity can be a single thing, person, place, or object, data can be stored about such entities.
-
Only those things about which data will be captured or stored is considered an entity.
-
If you aren't going to capture data about something, there's no point in creating an entity in a database.
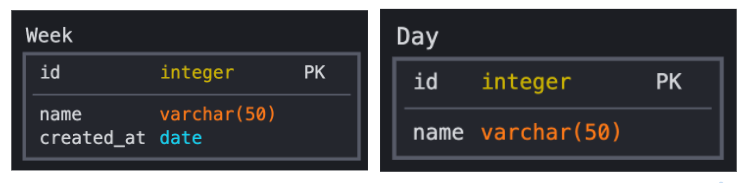
Attributes

-
An attribute is a property that describes a particular entity.
Relationships

-
Association between two entities.
-
Each relationship has a verb. This describes what kind of relationship connects the objects.
-
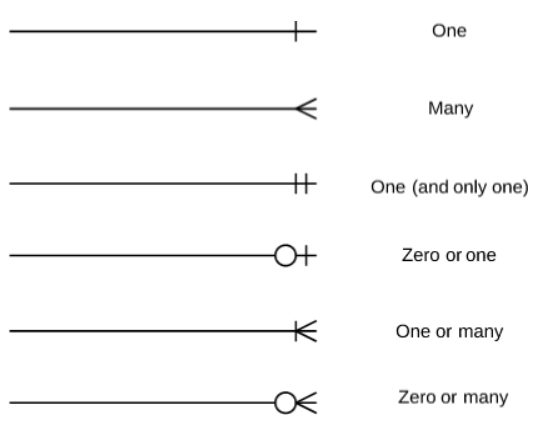
Shows the cardinality -the maximum number of times that an instance of an entity can be associated with instances of the related entity-.
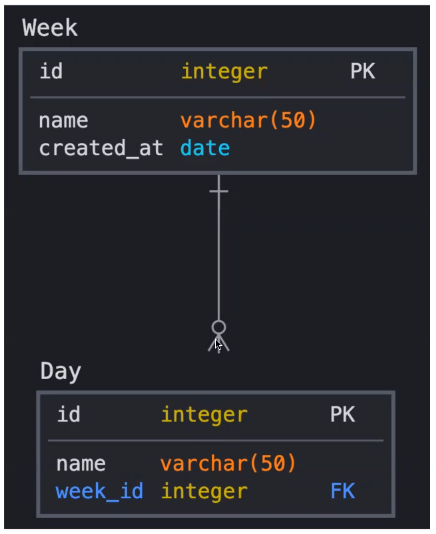
Notation

-
Crow's foot notation is often recognized as the most intuitive style, some use OMT, IDEF, Bachman, or UML notation.
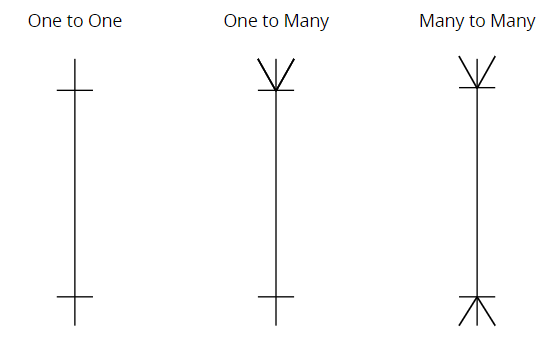
Cardinality & Ordinality

-
Cardinality refers to the maximum number of times an instance in one entity can relate to instances of another entity.
-
Ordinality, on the other hand, is the minimum number of times an instance in one entity can be associated with an instance in the related entity.

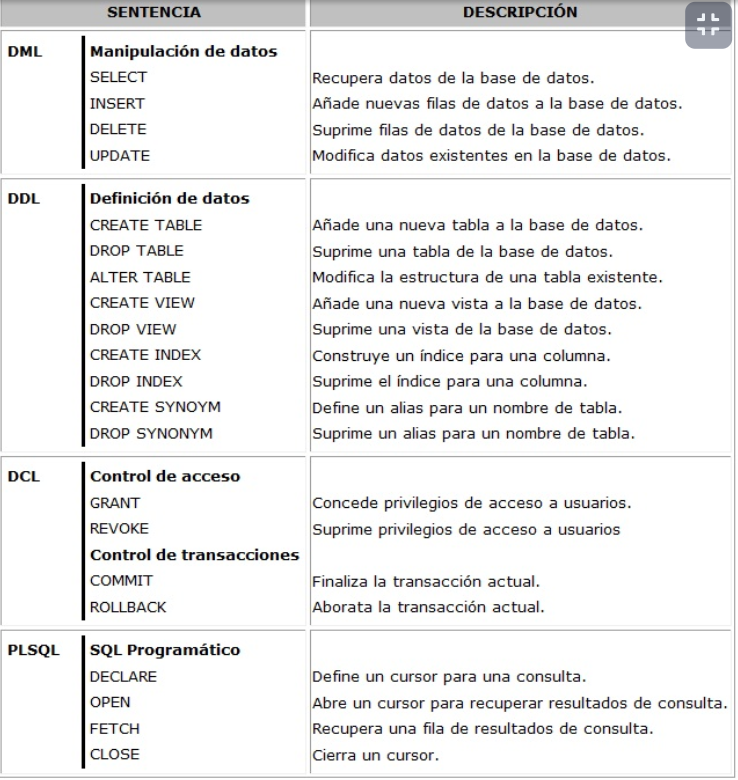
DDL
(Data Definition Language)

Data Types
INTEGER, NUMERIC, SERIAL,
CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT,
DATETIME, DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMPTZ, BOOLEAN,
JSON

Constraints
NOT NULL, UNIQUE,
PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY,
CHECK (field comparison)

CREATE

-- Structure to create DB
CREATE DATABASE db_name;
-- Structure to create a table
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name (
column1 datatype(length) column_contraint,
column2 datatype(length) column_contraint,
column3 datatype(length) column_contraint,
table_constraints
);ALTER

ALTER TABLE table_name action;
# Actions
# Rename table
RENAME TO new_table_name;
# Add column
ADD COLUMN column_name datatype column_constraint;
# Drop column
DROP COLUMN column_name;
# Rename column
RENAME COLUMN column_name
TO new_column_name;
# Default set/drop default
ALTER COLUMN column_name
[SET DEFAULT value | DROP DEFAULT];
# Default set/drop not null
ALTER COLUMN column_name
[SET NOT NULL| DROP NOT NULL];
# Add check validation
ADD CHECK validation;
# Add check validation
ADD CHECK validation;
# Add constraint rules
ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name constraint_definition;INSERT

INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …)
VALUES (value1, value2, …)
RETURNING *;
INSERT INTO table_name (column_list)
VALUES
(value_list_1),
(value_list_2),
...
(value_list_n)
RETURNING *;ERD & DDL
By Paulo Tijero
ERD & DDL
- 60



