SQL Queries II
Objetives

Filter Data

GROUP BY

-- Structure
SELECT fields
FROM table_name
GROUP BY field
SELECT COUNT(week_id)
FROM days
GROUP BY week_id;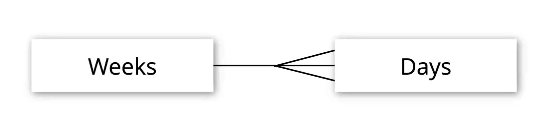
GROUP BY
Example using SQLBOLT

SELECT
director,
count(title) AS titles
FROM movies
GROUP BY director;HAVING

-- Structure
SELECT fields
FROM table_name
GROUP BY field
HAVING condition
SELECT count(week_id)
FROM days
GROUP BY week_id
HAVING count(week_id) > 2
HAVING
Example using SQLBOLT

SELECT
director,
count(title) AS titles
FROM movies
GROUP BY director
HAVING movies > 1HAVING & WHERE

SELECT
director,
count(title) AS titles
FROM movies
WHERE NOT director = "Pete Docter"
GROUP BY director
HAVING movies > 1Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database.


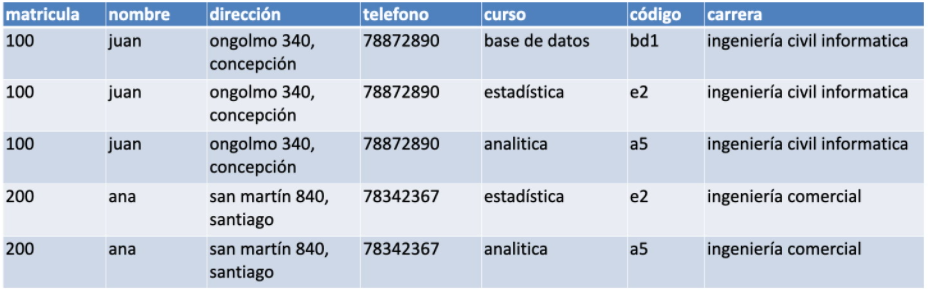
First Normal Form (1FN)

-
Remove repeated groups from individual tables.
-
Create a separate table for each set of related data.
-
Identify each set of related data with a primary key
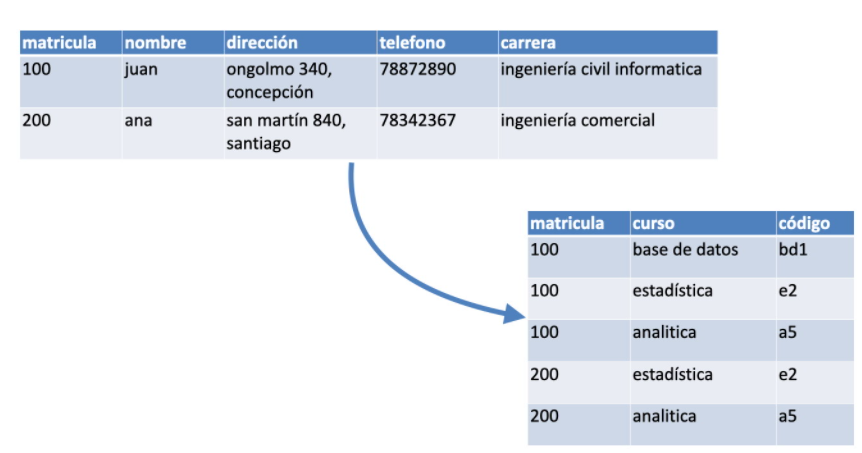
Second Normal Form (2FN)

-
Create separate tables for sets of values that apply to multiple records.
-
Relate these tables with a foreign key.
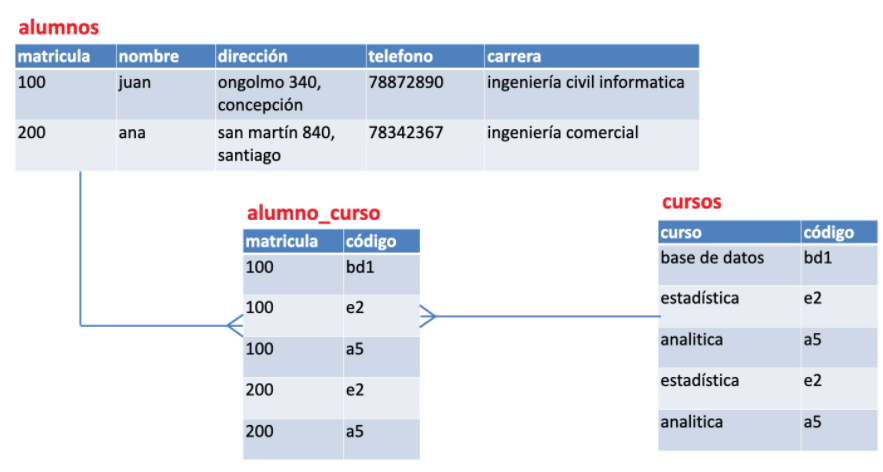
Third Normal Form (3FN)

-
Delete the fields that do not depend on the key.
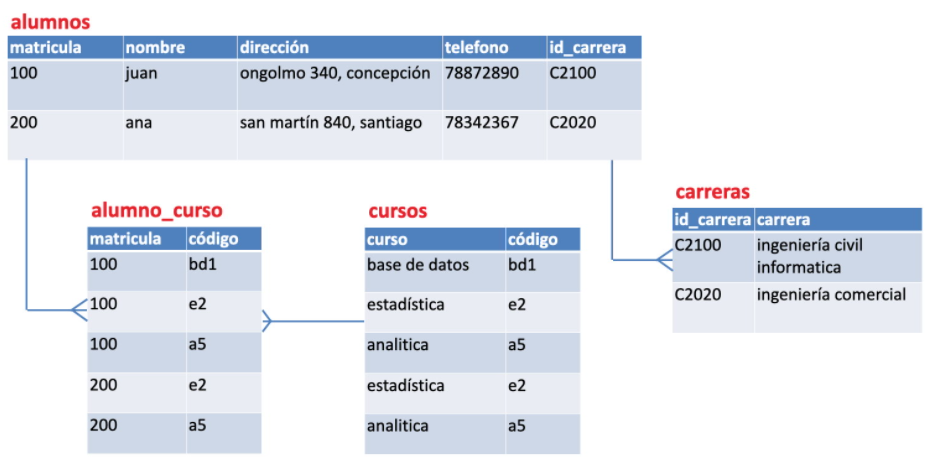
Clauses to query data from multiple tables

JOINS

SQL Queries 2
By Paulo Tijero
SQL Queries 2
- 52



