
What is Cassandra?
- Distributed Database
- Open Source
- No single point of failure
- Highly Scalable
- Tunable Consistency
Why pick Cassandra?
- High availability
- Store massive amounts of data
- Handle high volume of reads or writes
- Easily integrate with analytics/search/etc
Who uses Cassandra?
Tons of people... some have listed themselves here:
http://planetcassandra.org/companies/
- Netflix
- Microsoft
- CERN
- NASA
- Call of Duty
- ... TONS more.....
How does it work?
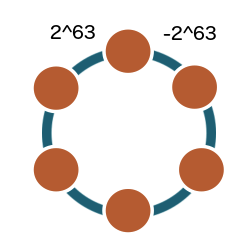
- This is a cluster
- composed of peer-to-peer nodes (the dots)
- A "node" is an instance of Cassandra
- The "ring" is a range of token values from -2^63 to 2^63
- (out of scope: racks, data centers)
Change the Cluster
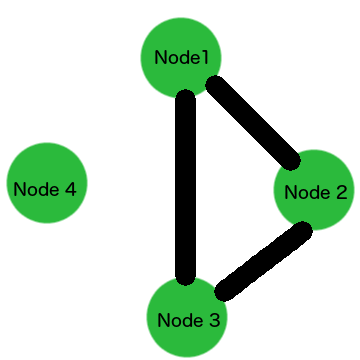
->
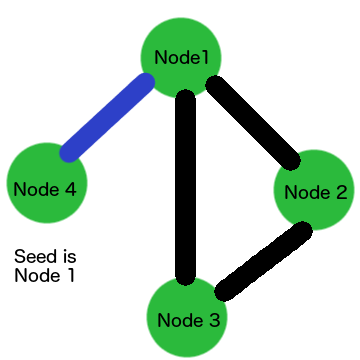
Change the Cluster
Cool Bits
- "Seed nodes" are just regular nodes that you (the ops person) knows about.
- No "special" node
- The topology and node liveliness are determined via gossip protocol, not a central authority.
Read/Write
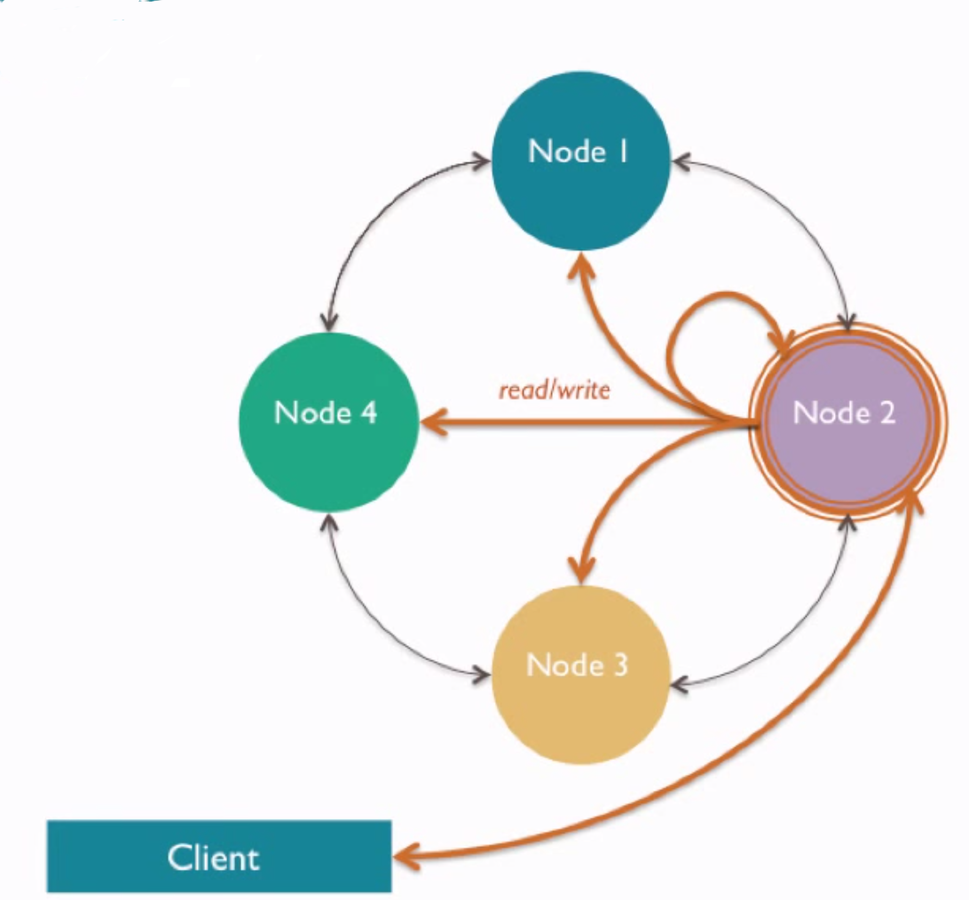
Coordinator
- Client picks *any* node to talk to
- Any node can be a coordinator
- If a node goes down, just move on to the next one.
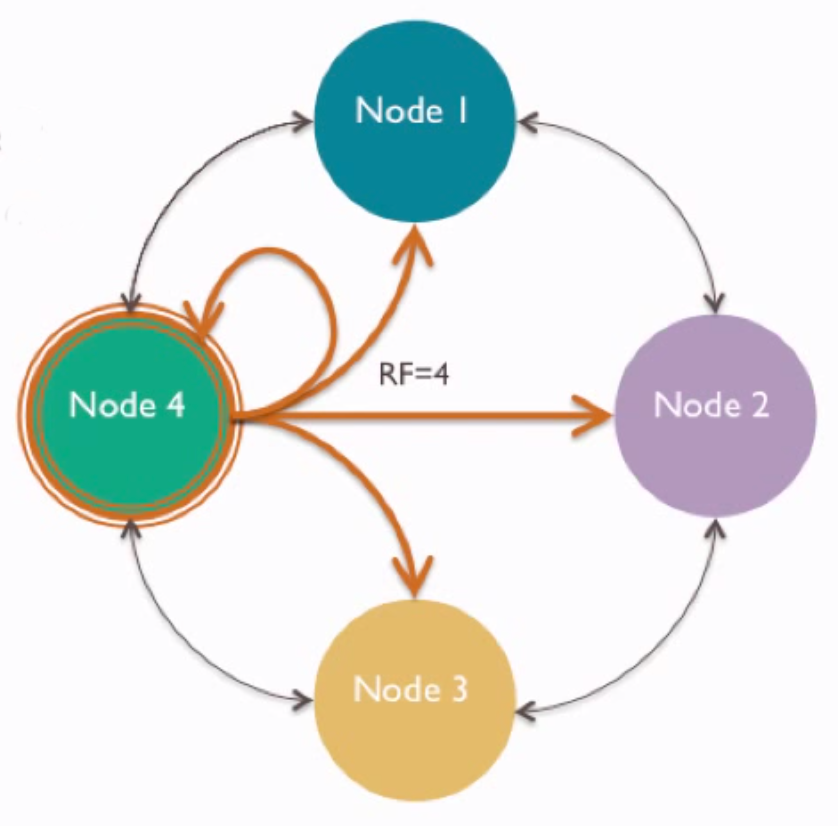
Write Replication
Writes can be Replicated
- The number of nodes that store a write is called the Replication Factor "RF"
- You can write to every node in a cluster.
- You can control where writes are stored with a replication strategy.
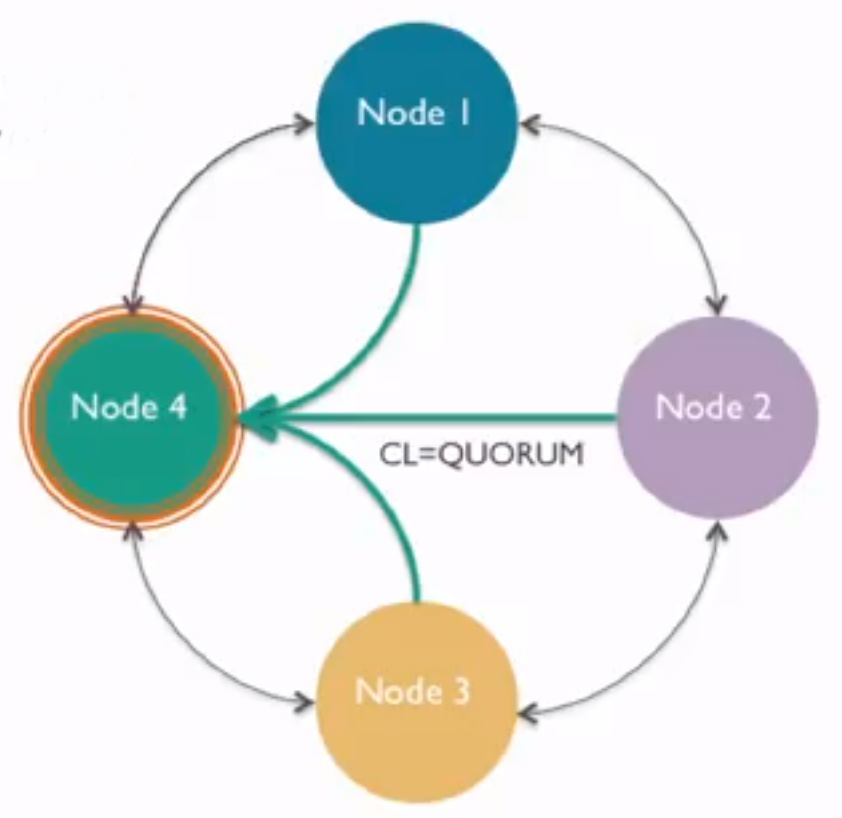
Client Consistency
Cassandra offers tunable consistency
- CL is the number of nodes that must acknowledge a client request.
- Varying CL helps achieve differing availability or performance goals.
- Common CLs: 1, Quorum, ALL
Learn More
https://academy.datastax.com/
Intro To Cassandra
By Philip Doctor
Intro To Cassandra
What is Cassandra? When to use it?
- 1,487



