Laravel 5 Middleware
Follow along:
slides.com/phillipsharring/laravel-5-middleware
Laravel 5 Middleware
Phillip Harrington
PHP Developer for 20 Years
Cisco Systems, Inc., Walt Disney Corporation,
Johnson & Johnson, and many others
phillipharrington.com
@phillipsharring
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Learning@Cisco
CX Training
+ external learners
High Touch Delivery
training and course material
What We'll Cover
- What's Laravel?
- What's Middleware?
- Middleware in Laravel
- How to make it
- What to do with it
- How to test it
Then We'll Have Q&A
Look for the
"Deep Dive" icon
dive down when you see this

You got it
Cool
1. What's
Laravel?
Laravel
"The PHP Framework
For Web Artisans"
laravel.com
Laravel
- Easy To Learn
- Well documented
- Laracasts
- An ecosystem of tools and platforms
- Artisan
- Forge & Envoyer
- Packages, packages, packages
- A great community of developers
- Blogs, Podcast, Newsletters, etc.

Laravel Quickstart
- Create New Application
-
Use Laravel Installer
- OR Use Composer Create Project
-
Create A Route
- Edit
routes.php - Create A Function
- OR Create A Controller
- Use Artisan
- Make A View
Use Laravel Installer
$ composer global require "laravel/installer"
$ laravel new middleware-demo
OR Use Composer
Create Project
$ composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel middleware-demo-2
Create A Route
app/Http/routes.php
<?php
Route::get('hello-world', {something goes here});
Create A Function
app/Http/routes.php
<?php
Route::get('hello-world', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
});
Voila!
OR Create A Controller
Use Artisan
$ php artisan make:controller MyController
Modify The Route
app/Http/routes.php
<?php
Route::get('hello-world', 'MyController@hello');
The Controller
app/Http/Controllers/MyController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Http\Requests;
class MyController extends Controller
{
public function hello()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}
}
Voila Again!

Use A View
...Edit The Controller
app/Http/Controllers/MyController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Http\Requests;
class MyController extends Controller
{
public function hello()
{
return view('hello');
}
}
Make A View
resources/views/hello.blade.php
<h2>Hello, world!</h2>
Voila Yet Again!

More...
- Use Models to store and retrieve data
- Create Restful Resources
- Use Layouts
- Much, much more
2. What's
Middleware?
"Middleware is a terribly nebulous term."
Middleware
- Software in the Middle of Two Things
- Software "glue"
-
The "dash" in "client-server" or
the "to" in "peer to peer" - Communicate between two
completely incompatible systems
Such as connecting an E-Commerce
website to an ERP system - Connects two applications
and passes data between them
3. Laravel &
Middleware
Middleware
Connects two applications
and passes data between them
Laravel's Middleware
Connects two
layers of the application
and passes data between them
-
Request
-
Response
Laravel's Middleware
Connects two
layers of the application
and passes data between them
-
Request
- Response
place to modify these
Laravel
Lifecycle
Laravel Lifecycle
-
Request
- Router
-
Application
- Controllers, Models, Views, etc.
-
Response

Laravel Lifecycle
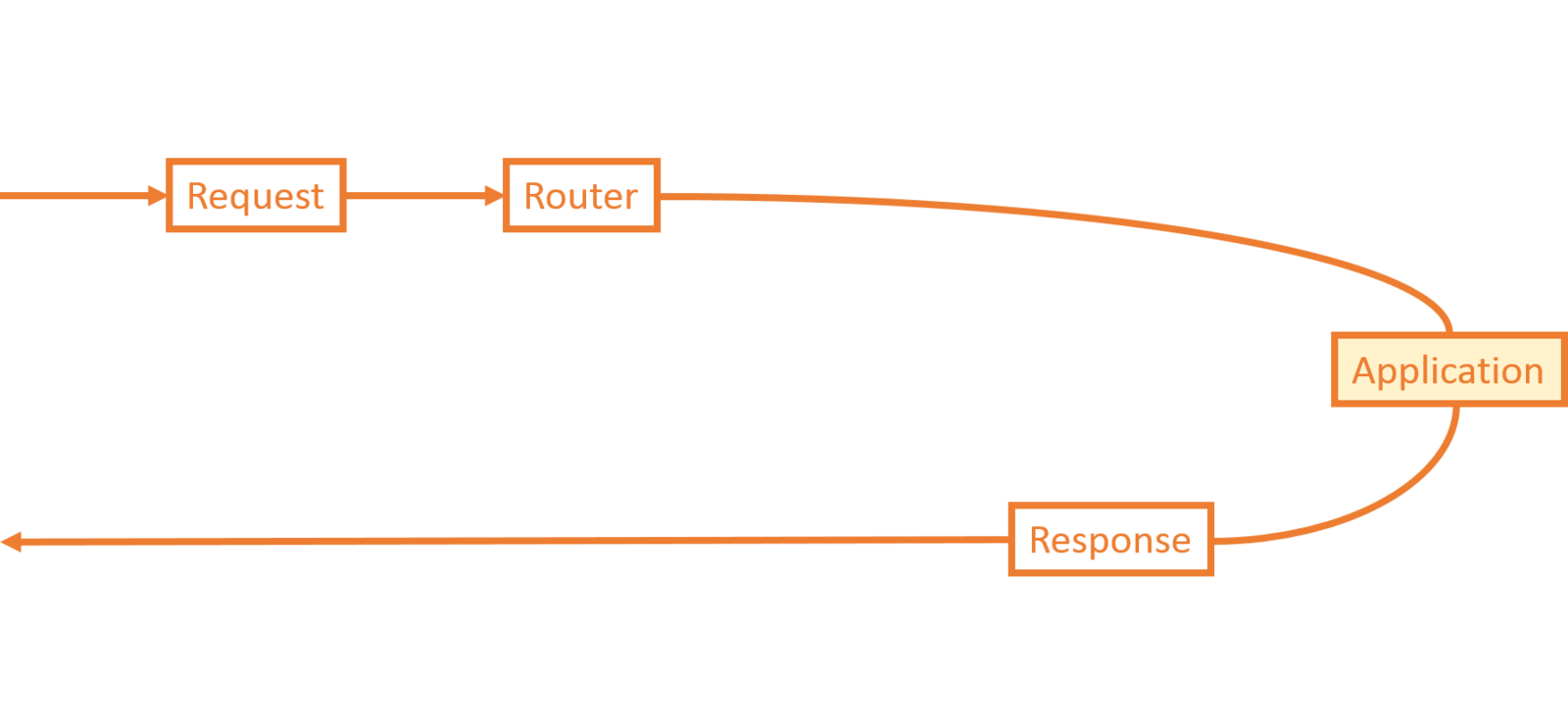
Laravel Lifecycle
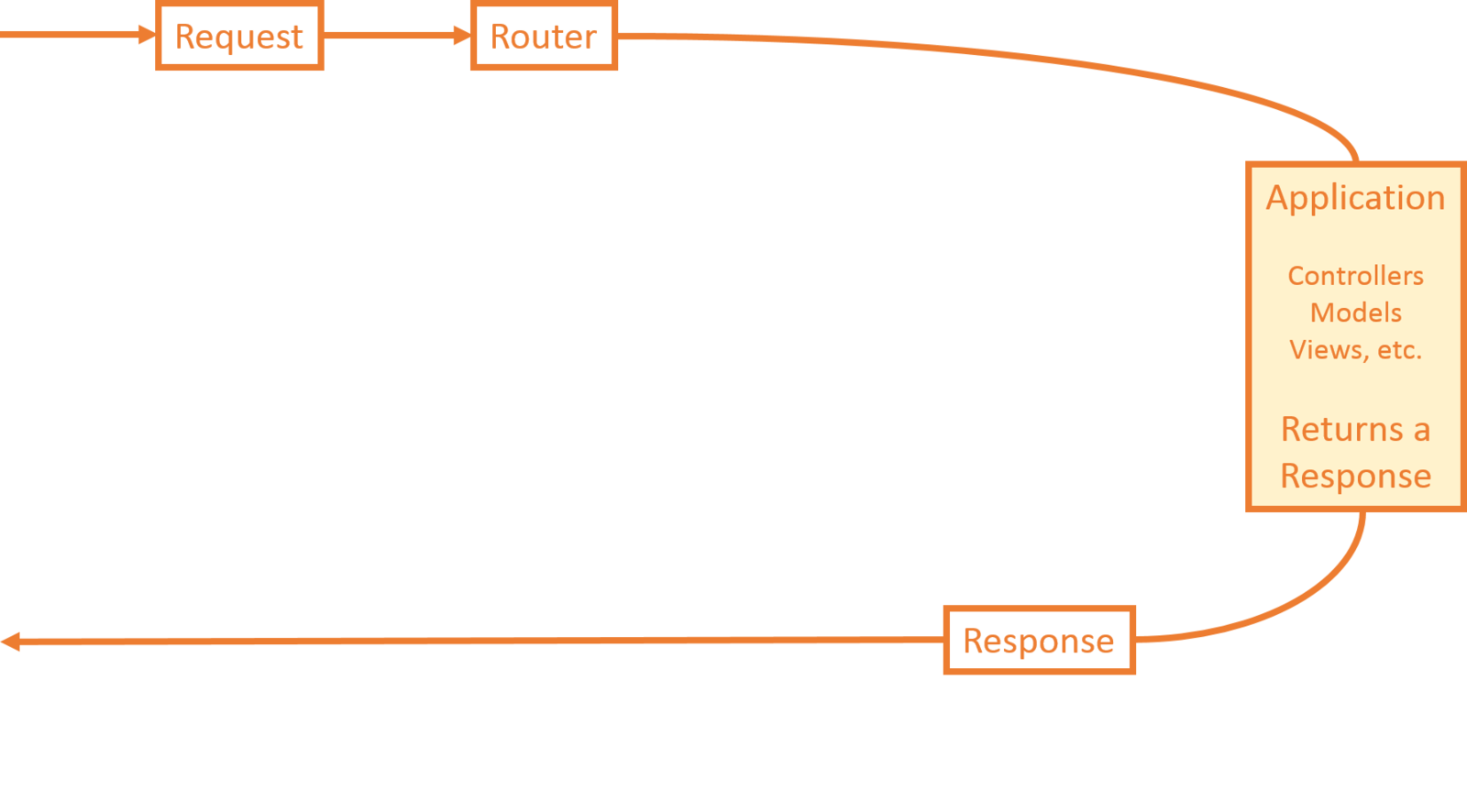
Laravel Lifecycle
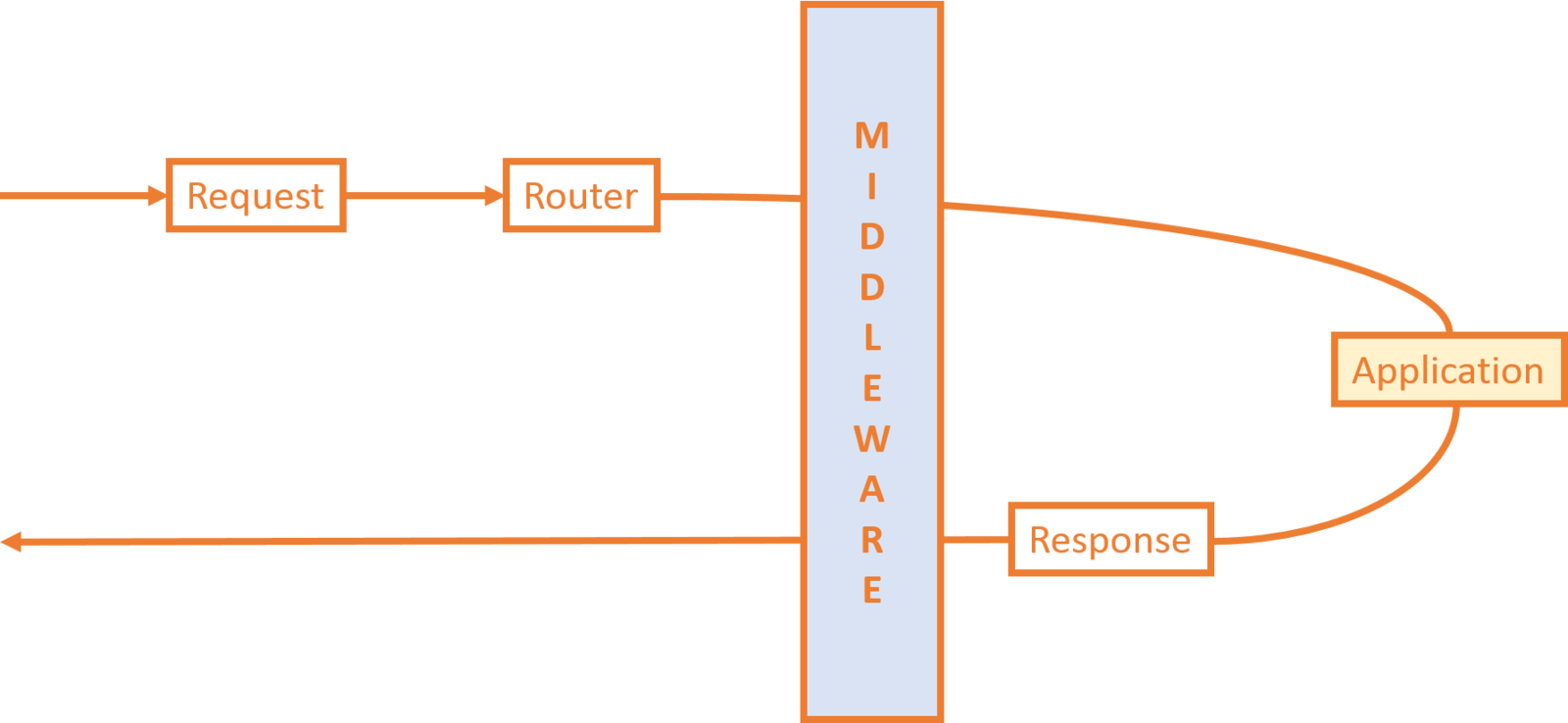
-
Request
- Router
- Middleware
- Application
- Controllers, Models, Views, etc.
- Middleware
- Response

Laravel Lifecycle

How It Works
public/index.php
<?php
// ...
/** @var Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Kernel $kernel */
$kernel = $app->make(Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class);
/** @var Illuminate\Http\Response $response */
$response = $kernel->handle(
$request = Illuminate\Http\Request::capture()
);
How It Works
Kernel.php
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Foundation\Http;
// ...
public function handle($request)
{
try {
$request->enableHttpMethodParameterOverride();
$response = $this->sendRequestThroughRouter($request);
} catch // a couple of catches & other stuff here...
return $response;
}
How It Works
Kernel.php
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Foundation\Http;
protected function sendRequestThroughRouter($request)
{
$this->app->instance('request', $request);
Facade::clearResolvedInstance('request');
$this->bootstrap();
return (new Pipeline($this->app))
->send($request)
->through($this->app->shouldSkipMiddleware() ? [] : $this->middleware)
->then($this->dispatchToRouter());
}
How It Works
Pipeline.php
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Pipeline;
public function send($passable)
{
// this is the request
$this->passable = $passable;
return $this;
}
public function through($pipes)
{
// these are the middleware
$this->pipes = is_array($pipes) ? $pipes : func_get_args();
return $this;
}
How It Works
Pipeline.php
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Pipeline;
public function then(Closure $destination)
{
$firstSlice = $this->getInitialSlice($destination);
$pipes = array_reverse($this->pipes);
return call_user_func(
array_reduce($pipes, $this->getSlice(), $firstSlice), $this->passable
);
}
Registering
Middleware
Two Ways to Register
Middleware In Laravel
- Global Middleware
- Route Middleware
Global Middleware
Affects Every Single Request
Registered in
app/Http/Kernel.php
in the $middleware array
Global Middleware
app/Http/Kernel.php
<?php
// ...
protected $middleware = [
\Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\CheckForMaintenanceMode::class,
];
Route Middleware
A single middleware
that can be assigned to Routes
Registered in
app/Http/Kernel.php
in the
$routeMiddleware array.
Route Middleware
app/Http/Kernel.php
<?php
// ...
protected $routeMiddleware = [
'auth' => \App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
'auth.basic' => \Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\AuthenticateWithBasicAuth::class,
'can' => \Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\Authorize::class,
'guest' => \App\Http\Middleware\RedirectIfAuthenticated::class,
'throttle' => \Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\ThrottleRequests::class,
];
Laravel's Built-In Middleware
Global
- Maintenance mode
Route
- Cookies
- Session
- Verify CSRF Token
- Throttling
Middleware Groups
A group of middleware
that can be assigned to Routes
Registered in
app/Http/Kernel.php
in the
$middlewareGroups array.
For example, Laravel ships
with the 'web' and 'api' groups
Middleware Groups
app/Http/Kernel.php
<?php
// ...
protected $middlewareGroups = [
'web' => [
\App\Http\Middleware\EncryptCookies::class,
\Illuminate\Cookie\Middleware\AddQueuedCookiesToResponse::class,
\Illuminate\Session\Middleware\StartSession::class,
\Illuminate\View\Middleware\ShareErrorsFromSession::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken::class,
],
'api' => [
'throttle:60,1',
],
];
Middleware Order
-
Global First, in order they are registered
- Route middleware, in the order they
are applied to the route - Middleware Groups, in the order they
are applied to the route, in the order
they are registered
Middleware Order
<?php // app/Http/Kernel.php
protected $middleware = [
\App\Http\Middleware\MyGlobalMiddleware::class,
];
protected $middlewareGroups = [
'my-group' => [
\App\Http\Middleware\MySecondMiddleware::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\MyThirdMiddleware::class,
],
];
protected $routeMiddleware = [
'my-fourth-middleware' => '\App\Http\Middleware\MyFourthMiddleware::class,
];
Middleware Order
<?php
// app/Http/routes.php
Route::get('my-route', [
'middleware' => ['my-group', 'my-fourth-middleware'],
'uses' => 'MyControllerd@hello'
]);
Using
Middleware
Using Middleware
On your route, you simply specify
the name of the middleware
Route::get('hello-world', ['middleware' => 'my-middleware', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}]);
Using Middleware
Or an array of middlewares
Route::get('hello-world', [
'middleware' => ['my-first-middleware', 'my-second-middleware'],
function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}
]);
Using Middleware
Or the name of a middleware group
Route::get('hello-world', ['middleware' => 'my-group', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}]);
& middleware groups
Types Of
Middleware
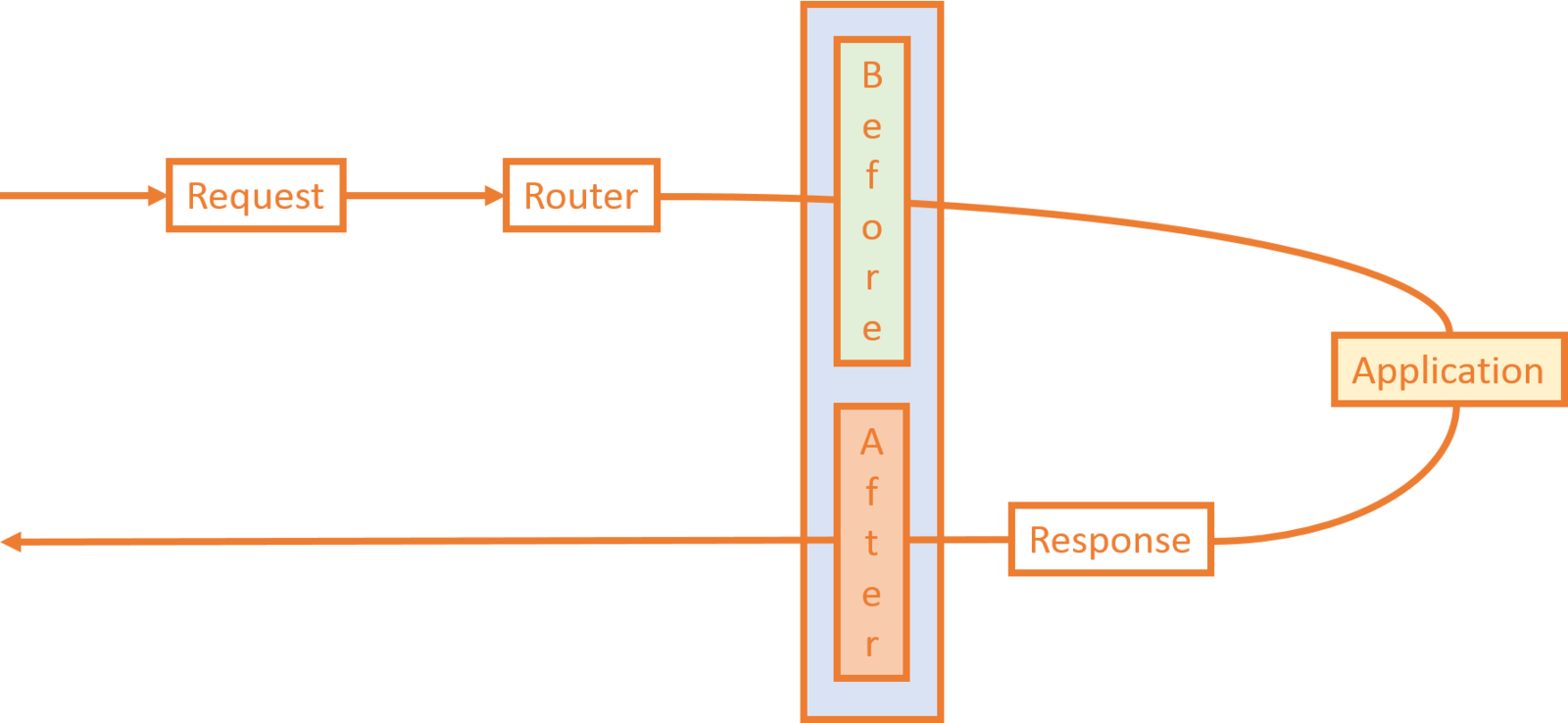
Two Types of
Middleware in Laravel
Before Middleware
After Middleware
Laravel Lifecycle
-
Request
- Router
- Before Middleware
- Application
- Controllers, Models, Views, etc.
- After Middleware
- Response

Two Types Of
Middleware In Laravel
Before Type
of Middleware
Examine/Modify the Request
Before Type
of Middleware
Examine/Modify the Request
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
// modify the $request here...
return $next($request);
}
After
Type
of Middleware
Examine/Modify the Response
After Type
of Middleware
Examine/Modify the Response
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
// modify the $response here...
return $response;
}
Before
and After
Are almost exactly the same,
except for where the call
to $next($request) happens
-
Same artisan command to generate
- Same location in app
- Same file boilerplate
Why Not Before
and After?

Don't Do That

Examples
How To Make
Middleware In Laravel
- Use Artisan to Create Middleware
-
Assign Route Middleware to routes
- Edit The Middleware
A Very Simple
Example Of
After
Middleware
Consider The
Following Route
Route::get('hello-world', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
});
Create Middleware
Use Artisan
$ php artisan make:middleware MyMiddleware
This creates a new Middleware file here:app/Http/Middleware/MyMiddleware.php
Register The Middleware
With The Application
Remember, There Are
2 Ways To Do This
- Global Middleware
- Route Middleware
Let's use Route Middleware
Register The Middleware
With The Application
app/Http/Kernel.php
<?php
// ...
protected $routeMiddleware = [
'auth' => \App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
'auth.basic' => \Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\AuthenticateWithBasicAuth::class,
'can' => \Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\Authorize::class,
'guest' => \App\Http\Middleware\RedirectIfAuthenticated::class,
'throttle' => \Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\ThrottleRequests::class,
// our new middleware here
'my-middleware' => \App\Http\Middleware\MyMiddleware::class,
];
Add The Middleware
To Our Route
Route::get('hello-world', ['middleware' => 'my-middleware', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}]);
Edit The Middleware
app/Http/Middleware/MyMiddleware.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
class MyMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
// modify the $response here...
return $next($request);
}
}
Edit The Middleware
app/Http/Middleware/MyMiddleware.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
class MyMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
$content = $response->getOriginalContent();
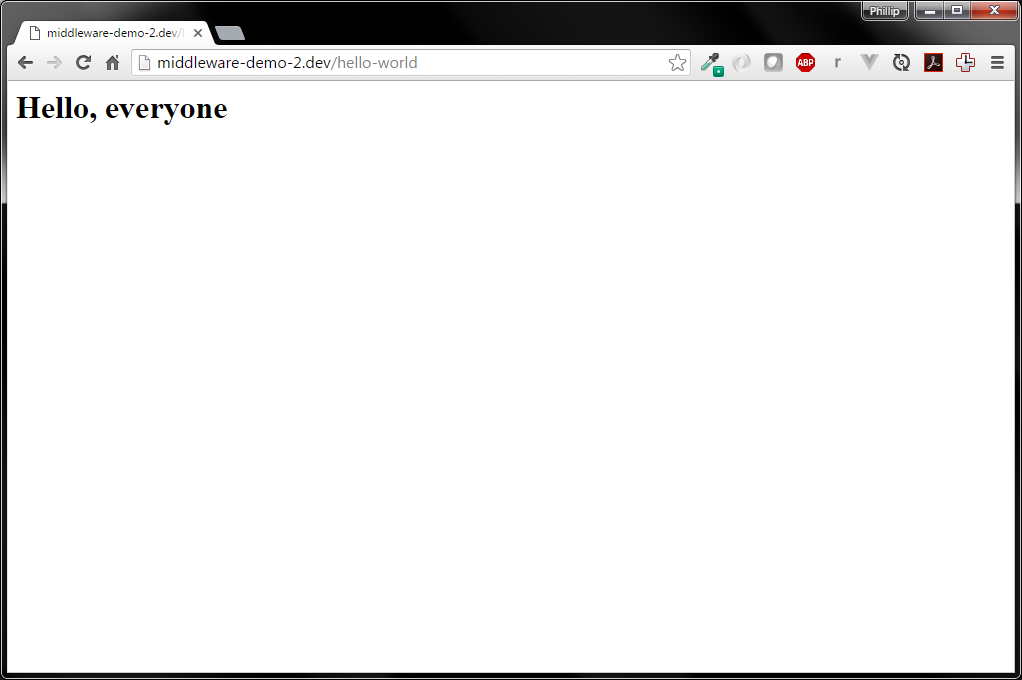
$response->setContent(str_replace('world', 'everyone', $content));
return $response;
}
}
An Example Of
Before
Middleware

A reading from Chapter 15 of
please wait while we try to insert your message ..... message
inserted. please wait while we try to insert your message ..
*** 60 second pause *** ...
deadlock, transaction aborted.
Please hit Reload in five or ten minutes.ns_write "please wait while we try to insert your message ..."
ns_sleep 60
ns_write "... deadlock, transaction aborted. Please hit Reload
in five or ten minutes." 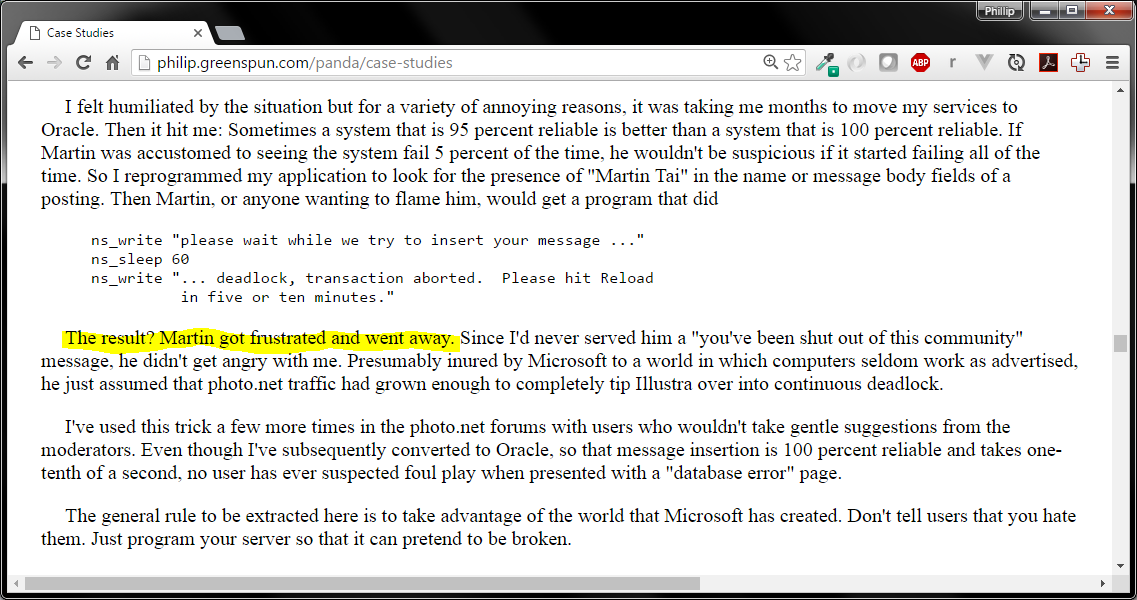
Consider The
Following Routes
Route::get('forum/create', ['uses' => 'MyController@forumCreate']);
Route::post('forum', [
'uses' => 'MyController@forumStore'
]);
The Controller
app/Http/Controllers/MyController.php
<?php
// ...
public function forumCreate()
{
// shows the forum post form
return view('forum.create');
}
public function forumStore(ForumPostRequest $request)
{
// inserts a post into the forum
Forum\Post::create( ... );
}
Create Middleware
Use Artisan
$ php artisan make:middleware JerkCheck
This creates a new Middleware file here:
app/Http/Middleware/JerkCheck.php
Register The Middleware
With The Application
app/Http/Kernel.php
<?php
// ...
protected $routeMiddleware = [
// ...
'my-middleware' => \App\Http\Middleware\MyMiddleware::class,
// our new jerk check middleware here
'jerk-check' => \App\Http\Middleware\JerkCheck::class,
];
Add The Middleware
To Our Route
Route::get('forum/create', ['uses' => 'MyController@forumCreate']);
Route::post('forum', [
'middleware' => 'jerk-check',
'uses' => 'MyController@forumStore'
]);
Edit The Middleware
app/Http/Middleware/JerkCheck.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Response;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
class JerkCheck
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
// code goes here
}
}
Edit The Middleware
app/Http/Middleware/JerkCheck.php
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
// get the user
$user = Auth::user();
// see if they're a jerk
if ($user->isAJerk()) {
// they're a jerk. serve them a pretend broken page
$view = view('forum.jerk');
return new Response($view->render());
}
// not a jerk; keep going
return $next($request);
}
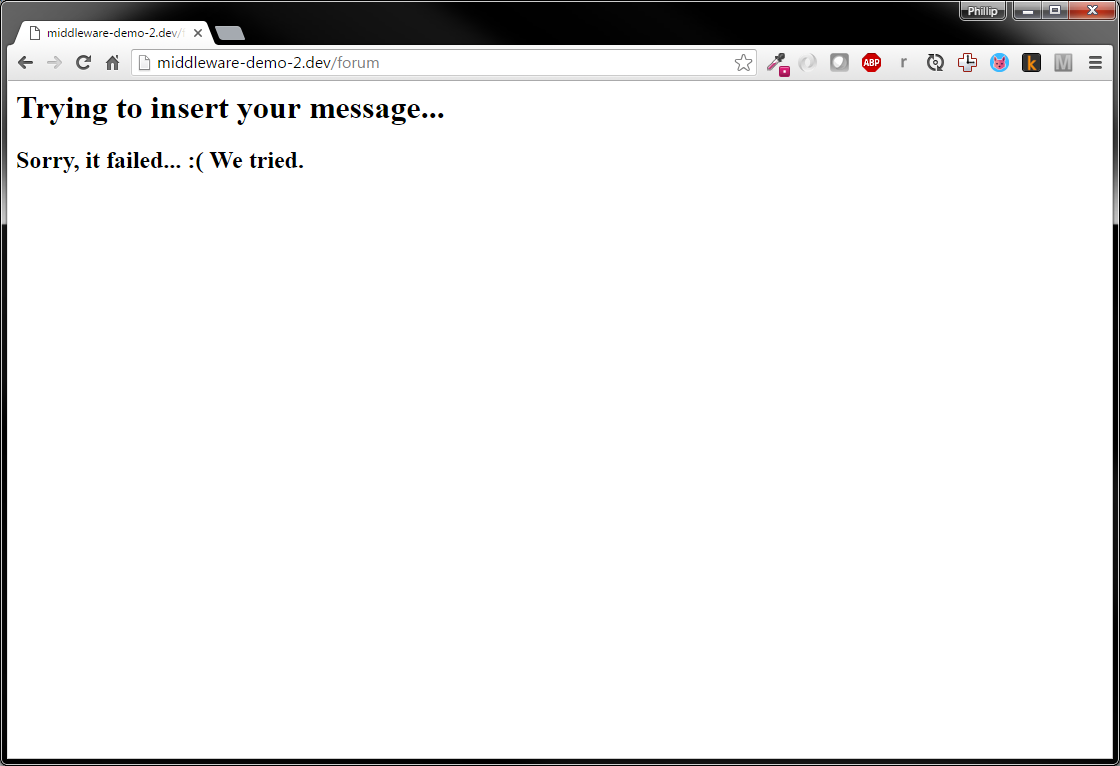
The View
resources/views/forum/jerk.blade.php
<h1>Trying to insert your message...</h1>
<img id="loading" src="/img/loading.gif">
<h2 id="sorry" style="display: none;">Sorry, it failed... :( We tried.</h2>
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout(function(){
var loading = document.getElementById('loading');
var sorry = document.getElementById('sorry');
loading.style.display = 'none';
sorry.style.display = 'block';
}, 3000);
</script>
Testing
Middleware
Testing Middleware
- Middleware is enabled
on routes you test
-
You can disable it
Consider The
Following Route
Route::get('hello-world', ['middleware' => 'my-middleware', function()
{
return '<h1>Hello, world</h1>';
}]);
It Has This Middleware
app/Http/Middleware/MyMiddleware.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
class MyMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
$content = $response->getOriginalContent();
$response->setContent(str_replace('world', 'everyone', $content));
return $response;
}
}
Testing Middleware
tests/ExampleTest.php
<?php
use Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\DatabaseMigrations;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\DatabaseTransactions;
class ExampleTest extends TestCase
{
public function testHello()
{
// this will pass, because the middleware changes "world" to "everyone"
$this->visit('hello-world')
->see('Hello, everyone');
}
}
Testing With
Middleware Disabled
tests/ExampleTest.php
<?php
// ... other use statements
use Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\WithoutMiddleware;
class ExampleTest extends TestCase {
use WithoutMiddleware;
public function testHello()
{
// this will fail, because with the middleware disabled,
// "world" is not changed to "everyone"
$this->visit('hello-world')
->see('Hello, everyone');
}
}
What Else You Can Do
With
Middleware In Laravel
- Authentication/Permission
- Users
- Groups
- Modifying Response Headers
- Cache-Busting
- API/HAL Headers
- ETags
- Modifying The Response
- Minification
- Many others!
Q&A
Thank You!
Laravel 5 Middleware
By Phillip Harrington
Laravel 5 Middleware
Middleware is a powerful feature of Laravel 5. In this talk, you'll learn what middleware is and how to create it. Then we'll look at several real-world use cases that demonstrate where middleware is appropriate, and where not to use it.
- 2,419