CMS
Week 7
Drupal as a backend
Overview
- Week 7
- Content modelling
- Drupal as a backend
- Week 8 - Project
- Full Briefing Project
- Setting up
- Implementing a content model
- Week 9 - Project
- Adding an editable theme
- Implementing views
Overview
- Week 10 - Project
- Implementing views advanced
- Adding more structure
- Week 11 - Project
- Adding QOL
- User management
- Week 12 - Project
- Wrapping up - Go live
Drupal as a backend
Headless, Decoupled
Drupal as a backend?
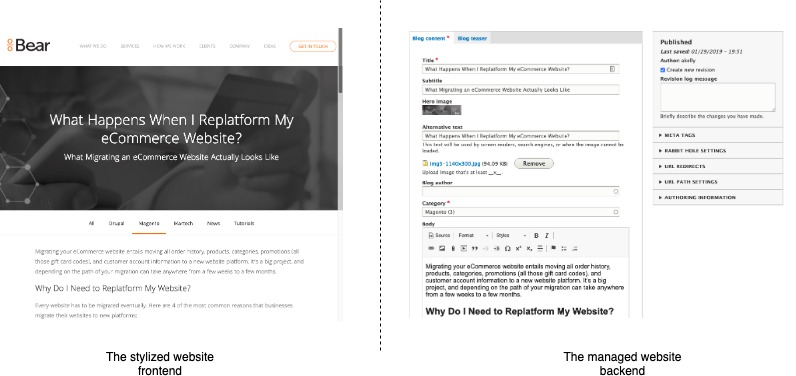
Drupal CMS provides an administrative back-end capable of making changes that display on the front-end of your website in HTML.
This is essentially what all CMS platforms do: provide an administrative suite to non-technical website managers.
Headless CMS?
The idea of a headless Drupal CMS is
you keep using the administrative back-end,
but the front-end and presentation can take many forms.
For example, a javascript framework like React might be used instead to present the front-end.
Content might be displayed on a desktop, smartphone, smartwatch, a tv set, ...
Frontend vs Backend

Headless vs Decoupled?
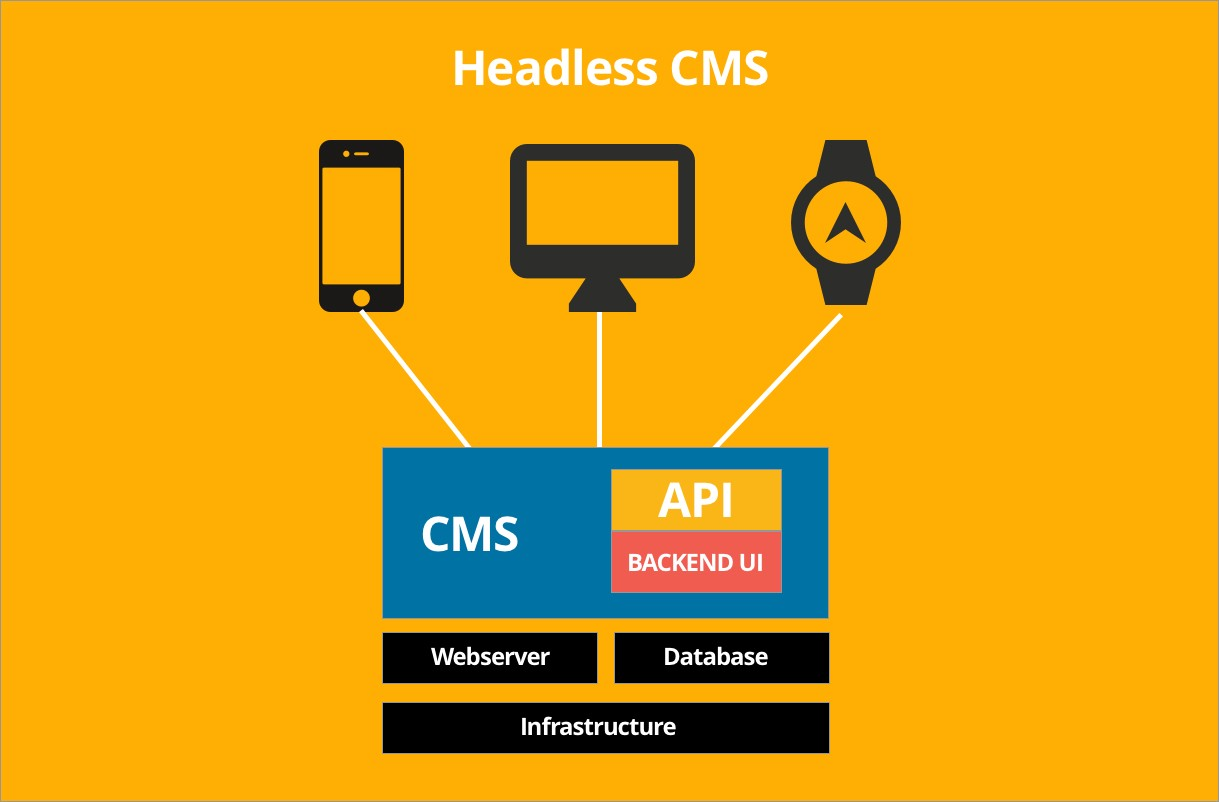
A Headless system only serves raw content through our API.
No markup is provided. CMS templates are not used.
Markup (html) will have to be added through the Front-end framework.
The CMS is only used for content management.
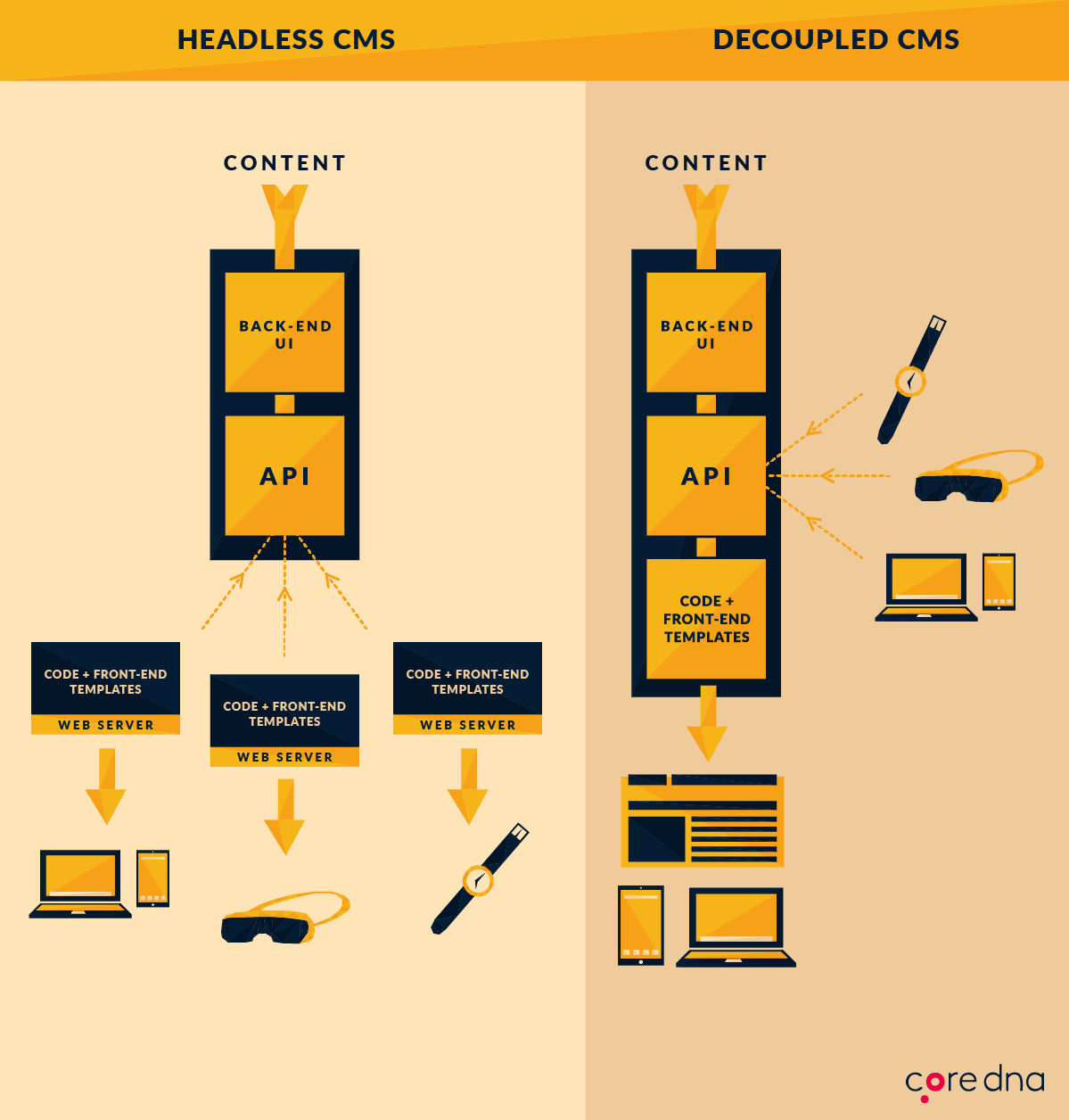
Headless vs Decoupled?
A Decoupled system serves formatted content (that already includes markup/html).
CMS templates are still used.
The CMS provides basic markup.
The CMS stores both the content
and parts of the presentation.
Decoupled is often considered Best of both worlds.
Headless vs Decoupled?
Drupal supports both.
Exposing data
RESTful webservices
REST?
Web Services make it possible for external applications to interact with our application (in this case our Drupal site).
The most common interactions are reading, creating, updating, and deleting resources. (= CRUD)
REST is one of the most popular ways of making Web Services work.
REST?
There are other formats such as SOAP or XML-RPC, but we are only going to focus on REST because it is the Drupal standard.
REST utilizes HTTP methods, such as GET, POST, and DELETE.
As an example, a popular usage of a REST interface is a mobile application that needs to read and write data from your site's database.
REST?
REpresentational State Transfer
Guiding Principles of REST
- Client–server
- Stateless
- Cacheable
- Uniform interface
- Layered system
- Code on demand (optional)
Modules?
Web Services have been implemented in Drupal 8 Core with the following modules:
RESTful Web Services (rest)
Exposes entities and other resources via a RESTful web API. It depends on the Serialization module for the serialization of data that is sent to and from the API.
Serialization (serialization)
Provides a service for serialization of data to and from formats such as JSON and XML.
Modules? (optional)
Hypertext Application Language (hal)
Extends the Serialization module to provide the HAL hypermedia format. This is what is used as the primary format in Drupal 8 Core. It only adds two reserved keywords, ‘_links’ for link relations (also used by Github's Pull Request API) and ‘_embedded’ for embedded resources. The HAL hypermedia format can be encoded in both JSON and XML. For more details see the initial HAL proposal.
Modules? (optional)
HTTP Basic Authentication (basic_auth)
This module implements basic user authentication using the HTTP Basic authentication provider. It facilitates the use of an username and password for authentication when making calls to the REST API. It is required for the examples shown in this blog post, and I would advise configuring SSL if you use it in production. For anyone looking for a more secure option, check out the contributed OAuth module which already has a Drupal 8 release.
Enable modules

Optionally enable
These are all CORE modules and are always included with Drupal.

Simple view export
Step by step
Goal
The Drupal framework supports many ways to expose data. Let's look at the most basic version.
First we will create a new content-type: portfolio.
Then we will use the Views module, to create a simple RESTful export of data in the JSON format.
We can then consume this JSON in an external application.
Step 1: Enable modules
Enable the following modules:
- RESTful Web Services (rest)
- Serialization
Step 2: Create data structure
Create a new content-type: Portfolio
Add fields:
- Title
- Abstract (Text, formatted long)
- Image (image)
- Website URL (link)
Create a few nodes (at least 3) using dummy content.
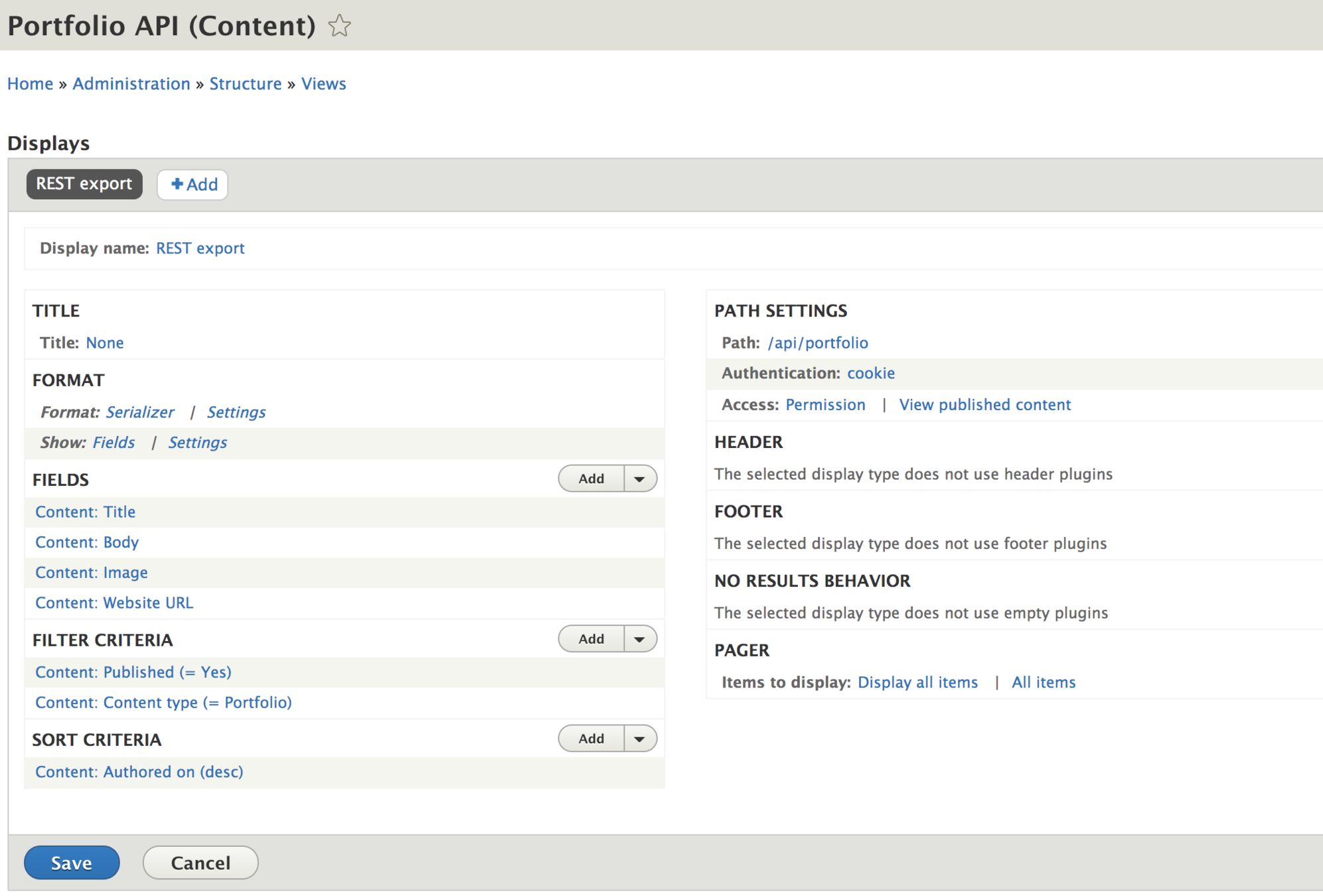
Step 3: Create view
Create a new view: Portfolio API
Choose "Provide REST export"
Set REST export path: "api/portfolio"
Make the following config:
- Format -> Settings -> JSON
- Display -> Fields
- Fields -> Title, Body, Image, Website URL
- Filter -> Content type = Portfolio
- Items to display -> All
Step 3: Create view
Make sure to check your result.
Visit: yoursitedomain:port/api/portfolio
f.e.: http://drupalimd.dd:8083/api/portfolio

Step 4: Disable CORS security
Drupal has a strict security policy. By default it does not allow for external services to communicate with itself.
For now we will disable the CORS security measures.
This is not best practice.
For a production site you should set up proper CORS & implement proper authentication.
Step 4: Disable CORS security
- Go to your site codebase
- Go to /sites/default
- or with Acquia DD: /sites/sitename.dd
-
Copy default.services.yml, save as services.yml
- same location
-
Scroll to the bottom and set cors.config to enabled
- Save the file, clear drupal caches
# Configure Cross-Site HTTP requests (CORS).
# Read https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Access_control_CORS
# for more information about the topic in general.
# Note: By default the configuration is disabled.
cors.config:
enabled: trueStep 5: Consume!
Your data is now ready for consumption.
For example: use a bit of jquery to see if we can retrieve and show data.
(function($) {
'use strict';
$( document ).ready(function() {
$.ajax('http://drupalimd.dd:8083/api/portfolio', // request url
{
dataType: 'json', // type of response data
// success callback Function
success: function (data, status, xhr) {
console.log(data);
},
}
);
});
})(jQuery);Step 5: Consume!
Another example: Test via console
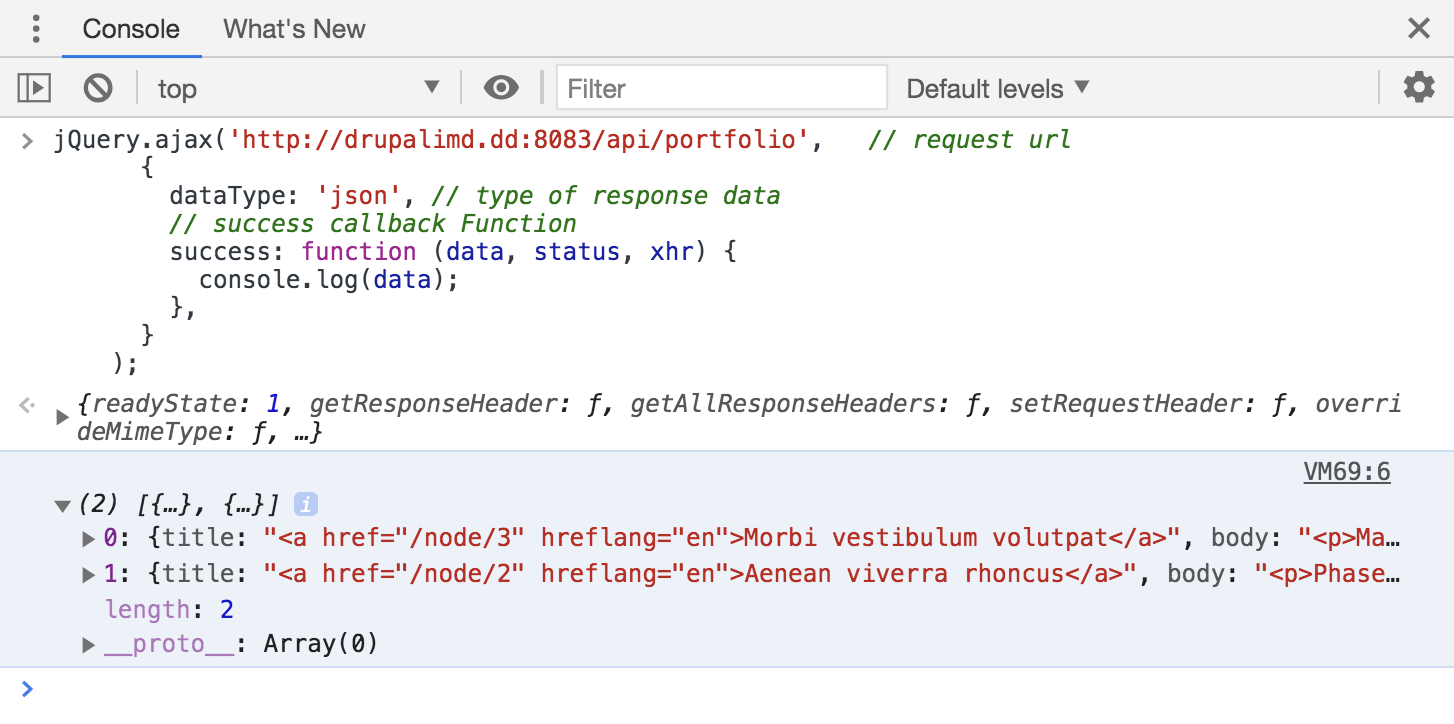
jQuery.ajax('http://drupalimd.dd:8083/api/portfolio', // request url
{
dataType: 'json', // type of response data
// success callback Function
success: function (data, status, xhr) {
console.log(data);
},
}
);Docs & Tuts
Exercise
Recreate the api/portfolio
Follow Step by step guide, see previous slides
By next week
In the next class Mobile Development,
you will be required to use this API.
CMS W7 - Drupal as a backend
By Pieter Mathys
CMS W7 - Drupal as a backend
Drupal as a backend
- 571



