Data Analysis
with Python
- Introduction
- Modules
- Numpy
- Pandas
- Matplotlib
Content
大量英文出沒,不是因為我英文很強,是因為英文字體比較好看。
– 魯迅,沒有說過
Introduction
What is Data Analysis?
-
資料收集:收集與主題相關資料。
-
資料清理:整理收集的資料,刪去 / 補闕漏數值等等。
-
資料探索:➊平均值、中位數和➋圖表等來探索資料。
-
資料轉換:對資料進行處理,如正規化、縮放、特徵工程等。
-
資料分析:運用統計學、機器學習或計算方法來進行深入分析。
-
解釋結果:根據分析結果得出結論。
Data Analysis
Modules
Introduce about numpy, pandas, matplotlib, plotly
-
numpy: 多維數組 & 數學運算 ( 進階 )
-
pandas: DataFrame & 資料讀取 / 清理 / 處理 / 匯出
-
matplotlib: 資料視覺化 ( 圖表 )
-
plotly: 資料視覺化 ( 互動式圖表 )
Modules
- VScode
-
Jupyter Notebook
-
Google Colab ( Recommend )
Environment
- Login your Google account
- Search "Google Colab"
- Open new notebook
Google Colab
Numpy
How to use numpy?
Import
import numpy as np
# numpy 通常簡寫成 nppip install numpy # For pip
# *Colab already has this.Array
import numpy as np
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4]
arr = np.array(lst)
print(arr, type(arr))
# [1 2 3 4] <class 'numpy.ndarray'>Create a ndarray:
name = np.array(object)
- object: array_like, like list, tuple...
- There's other parameters, like dtype...
numpy array 又稱 ndarray,是由相同型態及長度組成的多維陣列
Array Indexing
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([3, 1, 4, 2])
print(arr[0]) # 3
print(arr[2]+arr[3]) # 6For 1-D array:
arr[index] (starts from 0)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(arr[0]) #[1 2]
print(arr[0, 1]) # 2For 2↑-D array:
arr[index, index...] (starts from 0)
Array Slicing
import numpy as np
# 1-D
arr = np.array([3, 1, 4, 2])
print(arr[1:3:2]) # [1]
print(arr[:2]) # [3 1]
# 2-D
arr2 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(arr2[:1]) #[[1 2]]
print(arr2[1, 1:]) #[4]Same as Python list:
arr[start:end:step]
Array Copy & View
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
c = arr.copy()
arr[0] = 44
print(arr) # [44 2 3]
print(c) # [1 2 3]Copy an array:
c = arr.copy()
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
v = arr.view()
arr[0] = 44
print(arr) # [44 2 3]
print(v) # [44 2 3]View an array:
v = arr.view()
Array Shape
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([3, 1, 4])
arr2 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(arr.shape) # (3,)
print(arr2.shape) # (3, 2)Array's shape:
s = arr.shape
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([3, 1, 4], ndmin=3)
print(arr, arr.shape)
# [[[3 1 4]]] (1, 1, 3)* ndmin: 決定該陣列的最小維度數,根據需要會在陣列前面添加維度
Array Reshape
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
# 2-D, 4 elements
print("2-D:", arr.reshape(2, 4))
# 3-D, 2 elements
print("3-D:", arr.reshape(2, 2, 2))Reshape array:
r = arr.reshape(i1, i2...)
* i1, i2: i1 * i2 * ... * i(n) should be equal to the number of array's elements

Array Reshape: -1
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
print(arr.reshape(2, 2, -1))
# equal to (2, 2, 2)Unknown:
r = arr.reshape(i1, i2..., -1)
* -1: You can left one unknown dimension, numpy will calculate it

Flatten:
r = arr.reshape(-1)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(arr.reshape(-1))
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]Array Join
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)Join arrays:
c = np.concatenate((a1, a2...), axis=0)

-
(a1, a2): Sequence of array_like
- All the input arrays must have same number of dimensions
-
axis: The axis along which you will concatenate the array.
- The number of axis should smaller than dimension.
- Default is 0.
-
If axis=
None, arrays are flattened.
Array Join: axis
- axis: The axis along which you will concatenate the array.
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=1)
print(arr)
# [[1 2 5 6]
# [3 4 7 8]]arr1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
arr2
axis=1
axis=0
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
1
2
5
6
3
4
7
8
Array Split
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
newarr = np.array_split(arr, 3)
print(newarr)
# [array([1, 2]), array([3]), array([4])]Split array:
s = np.array_split(arr, i, axis=0)
- arr: Array_like.
- i: How many section you want to split.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
newarr = np.array_split(arr, 3)
print(newarr[0]) # [1 2]
print(newarr[1]) # [3]Access them from the result just like any array element.
Array Split: 2↑-D
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
newarr = np.array_split(arr, 2)
print(newarr)
# [array([[1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6]])]Use axis to split the 2-D array into two 2-D arrays along rows.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
newarr = np.array_split(arr, 2, axis=1)
print(newarr)
# [array([[1, 2],
# [4, 5]]), array([[3],
# [6]])]Array Broadcast
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
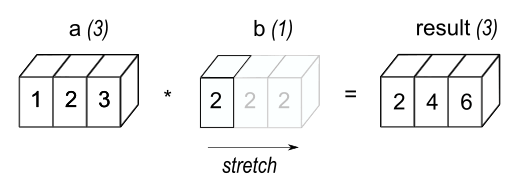
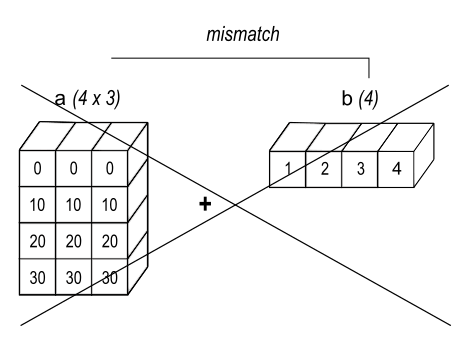
print(arr*2) # [2 4 6]Broadcast: 廣播,意思是將「比較小的陣列內容,廣播到比較大的陣列中」,產生互相兼容的尺寸形狀
* Two dimensions are compatible when ➊ they are equal ➋ one of them is 1.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[0, 0, 0],
[10, 10, 10],
[20, 20, 20],
[30, 30, 30]])
b = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(a+b) # Correct
b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(a+b) # ValueError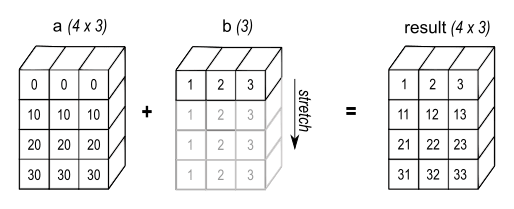
Array Search
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(np.where(arr < 3)) # (array([0, 1]),): index
print(np.where(arr < 3, arr, arr*10)) #[1 2 30 40 50]Search array:
w = np.where(condition, x, y)
-
condition: Array_like, bool.
- Where True, yield x, otherwise yield y.
-
x, y: Array_like.
- Values from which to choose.
- Need to be broadcastable to some shape.
- Either both or neither of x and y should be given.
Array Sort
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2], [5, 3], [4, 1]])
print(np.sort(arr)) # 2-D, so it is equal to axis=1.
print(np.sort(arr, axis=0))
print(np.sort(arr, axis=None)) # [1 1 2 3 4 5]Search array:
s = np.sort(arr, axis=-1)
- arr: Array_like.
-
axis: Axis along which to sort.
- The default is -1, which sorts along the last axis.
- If None, the array is flattened before sorting


Array Sort: axis
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2], [5, 3], [4, 1]])
print(np.sort(arr)) # 2-D, so it is equal to axis=1.
print(np.sort(arr, axis=0))
print(np.sort(arr, axis=None)) # [1 1 2 3 4 5]axis=±1
axis=0
sort
sort
4
1
1
2
5
3
1
4
1
2
3
5
4
1
1
2
5
3
5
3
1
1
4
2
Pandas
How to use pandas?
Import
import numpy as np
import pandas as pdpip install pandas # For pip
# *Colab already has this.Data Structure
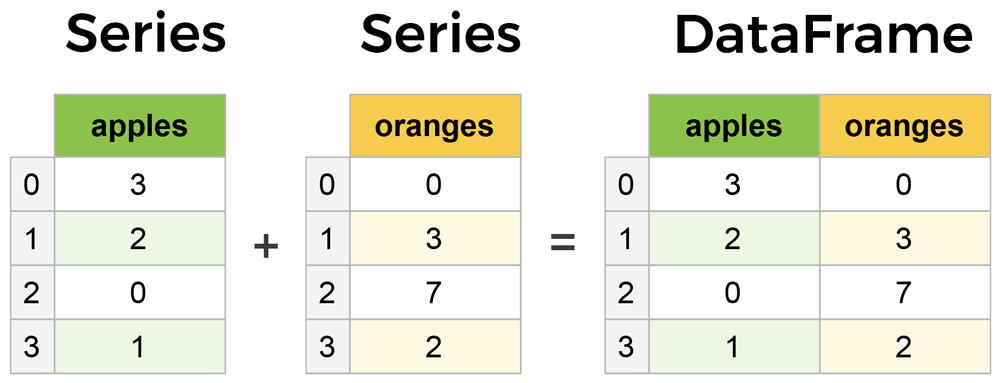
- Series: 單維度 / 單一欄位
- DataFrame: 二維度
Series
import pandas as pd
lst = ["Apple", "Banana", "Kiwi"]
series = pd.Series(lst)
print(series)Create a Series:
name = pd.Series(data, index=index)
- data: dict / list / ndarray / a scalar value (like 5)...
- index: a list of axis labels
* The length of index should be the same as that of data (for ndarray & list)

import pandas as pd
lst = ["Apple", "Banana", "Kiwi"]
index = ['a', 'b', 'c']
series = pd.Series(lst, index=index)
print(series)
Data Analysis
By pomer0
Data Analysis
- 147