Complete
SQL using MySQL

Prateek Narang

Module

-
Database
-
DBMS
-
Types of Databases
-
RDBMS
-
Installation & Setup



A database is a collection of data stored in a format that can be easily accessed, managed and updated.

Database

Most applications require a database to store and retrieve data.
A shopping website like Amazon will need a database to store data about customers, products, orders, suppliers etc.
Knowing how to monitor and optimize your database is essential for application performance.

Database


Database management systems are software systems used to manage and manipulate data in a database.

Database Management System

DBMS
Database

A DBMS serves as an interface between an end-user and a database, allowing users to create, read, update, and delete data in the database.

Database Management System


DBMS
Database

Text

Types of Databases
DBMS
Database
Relational Database
NoSQL Database



Text

Database Systems
DBMS
Database
RDBMS
NoSQL










Relational Database
- Its way of representing data in tables.
- Each row in the table is is a record with unique id called key.
- The columns of the table hold attributes of data.
- The relational data model provides a standard way of representing and querying data that could be used by any application
- Structured query language (SQL) is used to write and query data in a database



A relational database example
| ProductID | ProductName | CategoryId | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jean | 1 | 999 |
| 2 | Phillips Led | 2 | 220 |
| 3 | Trimmer | 2 | 1500 |
| 4 | T-Shirt | 1 | 499 |


| ProductID | ProductName | CategoryId | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jean | 1 | 999 |
| 2 | Phillips Led | 2 | 220 |
| 3 | Trimmer | 2 | 1500 |
| 4 | T-Shirt | 1 | 499 |
| CategoryId | CategoryName | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clothing | Clothes Mens & Girls |
| 2 | Electronics | Electronic items ... |
A relational database example

A relational database, or relational database management system (RDMS), stores information in tables. Often, these tables have shared information between them, causing a relationship to form between tables.
We use SQL to query these databases.

Relational (SQL) Database
Database


Example - One to Many Relationship
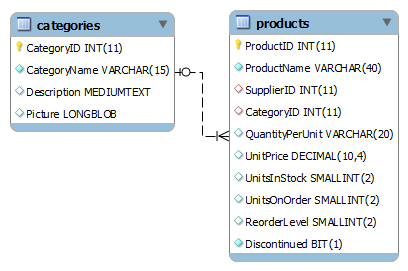


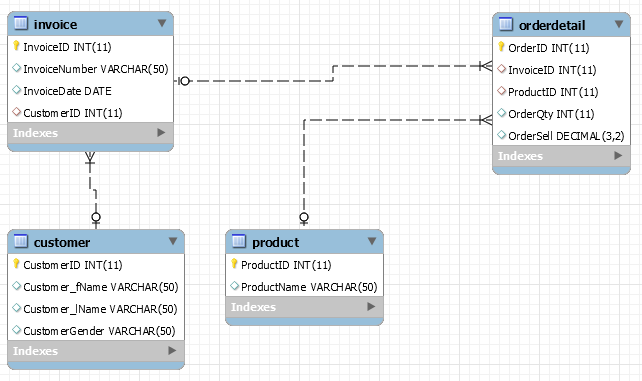
Database Schema

- SQL databases are relational, NoSQL databases are non-relational.
- SQL databases use structured query language and have a predefined schema. NoSQL databases have dynamic schemas for unstructured data, have their own query language.
- SQL databases are vertically scalable, while NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable.
- SQL databases are table-based, while NoSQL databases are document, key-value, graph, or wide-column stores. Non-relational databases use a storage model that is optimised for the specific requirements of the type of data being stored.

SQL vs NoSQL Databases

Relational databases are used in several applications
- track inventories,
- e-commerce transactions,
- sales,
- banking,
- finance,
- billing etc.

Use of RDBMS


1. MySQL
2. Oracle
3. Microsoft SQL Server
4. PostgreSQL

SQL Database Systems









- Free and open-source
- Huge community support
- Extensively tested
- High stability
- Available for all major platforms
- Replication and sharding are available
- Covers a wide range of use cases

MySQL


Go to mysql.com Downloads Page.
Download and Install the following using installation wizard.
- MySQL Community Server
- MySQL Workbench

Installation and Setup


Testing our Setup & Creating our first Database for use


Module 1


SELECT STATEMENT


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *xp, int *yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
// A function to implement bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
// Last i elements are already in place
for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+1]);
}
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
cout<<"Sorted array: \n";
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Code Web Dev [CodePen]
// This slide uses Auto-Animate to animate between
// two different code blocks
const distanceBetween = ( p1, p2 ) => {
// TODO
}
distanceBetween([10,10], [50,50])
Code Transitions
Bubble Sort Algorithm # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; void swap ( int *xp, int *yp) { int temp = *xp; *xp = *yp; *yp = temp; } // A function to implement bubble sort void bubbleSort ( int arr[], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0 ; i < n -1 ; i++) // Last i elements are already in place for (j = 0 ; j < n-i -1 ; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1 ]) swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+ 1 ]); } /* Function to print an array */ void printArray ( int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0 ; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " " ; cout << endl ; } // Driver code int main () { int arr[] = { 64 , 34 , 25 , 12 , 22 , 11 , 90 }; int n = sizeof (arr)/ sizeof (arr[ 0 ]); bubbleSort(arr, n); cout << "Sorted array: \n" ; printArray(arr, n); return 0 ; } # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; void swap ( int *xp, int *yp) { int temp = *xp; *xp = *yp; *yp = temp; } // A function to implement bubble sort void bubbleSort ( int arr[], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0 ; i < n -1 ; i++) // Last i elements are already in place for (j = 0 ; j < n-i -1 ; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1 ]) swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+ 1 ]); } /* Function to print an array */ void printArray ( int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0 ; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " " ; cout << endl ; } // Driver code int main () { int arr[] = { 64 , 34 , 25 , 12 , 22 , 11 , 90 }; int n = sizeof (arr)/ sizeof (arr[ 0 ]); bubbleSort(arr, n); cout << "Sorted array: \n" ; printArray(arr, n); return 0 ; } # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; void swap ( int *xp, int *yp) { int temp = *xp; *xp = *yp; *yp = temp; } // A function to implement bubble sort void bubbleSort ( int arr[], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0 ; i < n -1 ; i++) // Last i elements are already in place for (j = 0 ; j < n-i -1 ; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1 ]) swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+ 1 ]); } /* Function to print an array */ void printArray ( int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0 ; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " " ; cout << endl ; } // Driver code int main () { int arr[] = { 64 , 34 , 25 , 12 , 22 , 11 , 90 }; int n = sizeof (arr)/ sizeof (arr[ 0 ]); bubbleSort(arr, n); cout << "Sorted array: \n" ; printArray(arr, n); return 0 ; } # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; void swap ( int *xp, int *yp) { int temp = *xp; *xp = *yp; *yp = temp; } // A function to implement bubble sort void bubbleSort ( int arr[], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0 ; i < n -1 ; i++) // Last i elements are already in place for (j = 0 ; j < n-i -1 ; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1 ]) swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+ 1 ]); } /* Function to print an array */ void printArray ( int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0 ; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " " ; cout << endl ; } // Driver code int main () { int arr[] = { 64 , 34 , 25 , 12 , 22 , 11 , 90 }; int n = sizeof (arr)/ sizeof (arr[ 0 ]); bubbleSort(arr, n); cout << "Sorted array: \n" ; printArray(arr, n); return 0 ; }
Bubble Sort Algorithm


/* * . * . * * .
. * move your mouse to over the stars .
* . . change these values: . *
. * . . * . */
const STAR_COLOR = '#fff';
const STAR_SIZE = 3;
const STAR_MIN_SCALE = 0.2;
const OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD = 50;
const STAR_COUNT = ( window.innerWidth + window.innerHeight ) / 8;
const canvas = document.querySelector( 'canvas' ),
context = canvas.getContext( '2d' );
let scale = 1, // device pixel ratio
width,
height;
let stars = [];
let pointerX,
pointerY;
let velocity = { x: 0, y: 0, tx: 0, ty: 0, z: 0.0005 };
let touchInput = false;
generate();
resize();
step();
window.onresize = resize;
canvas.onmousemove = onMouseMove;
canvas.ontouchmove = onTouchMove;
canvas.ontouchend = onMouseLeave;
document.onmouseleave = onMouseLeave;
function generate() {
for( let i = 0; i < STAR_COUNT; i++ ) {
stars.push({
x: 0,
y: 0,
z: STAR_MIN_SCALE + Math.random() * ( 1 - STAR_MIN_SCALE )
});
}
}
function placeStar( star ) {
star.x = Math.random() * width;
star.y = Math.random() * height;
}
function recycleStar( star ) {
let direction = 'z';
let vx = Math.abs( velocity.x ),
vy = Math.abs( velocity.y );
if( vx > 1 || vy > 1 ) {
let axis;
if( vx > vy ) {
axis = Math.random() < vx / ( vx + vy ) ? 'h' : 'v';
}
else {
axis = Math.random() < vy / ( vx + vy ) ? 'v' : 'h';
}
if( axis === 'h' ) {
direction = velocity.x > 0 ? 'l' : 'r';
}
else {
direction = velocity.y > 0 ? 't' : 'b';
}
}
star.z = STAR_MIN_SCALE + Math.random() * ( 1 - STAR_MIN_SCALE );
if( direction === 'z' ) {
star.z = 0.1;
star.x = Math.random() * width;
star.y = Math.random() * height;
}
else if( direction === 'l' ) {
star.x = -OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD;
star.y = height * Math.random();
}
else if( direction === 'r' ) {
star.x = width + OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD;
star.y = height * Math.random();
}
else if( direction === 't' ) {
star.x = width * Math.random();
star.y = -OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD;
}
else if( direction === 'b' ) {
star.x = width * Math.random();
star.y = height + OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD;
}
}
function resize() {
scale = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
width = window.innerWidth * scale;
height = window.innerHeight * scale;
canvas.width = width;
canvas.height = height;
stars.forEach( placeStar );
}
function step() {
context.clearRect( 0, 0, width, height );
update();
render();
requestAnimationFrame( step );
}
function update() {
velocity.tx *= 0.96;
velocity.ty *= 0.96;
velocity.x += ( velocity.tx - velocity.x ) * 0.8;
velocity.y += ( velocity.ty - velocity.y ) * 0.8;
stars.forEach( ( star ) => {
star.x += velocity.x * star.z;
star.y += velocity.y * star.z;
star.x += ( star.x - width/2 ) * velocity.z * star.z;
star.y += ( star.y - height/2 ) * velocity.z * star.z;
star.z += velocity.z;
// recycle when out of bounds
if( star.x < -OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD || star.x > width + OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD || star.y < -OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD || star.y > height + OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD ) {
recycleStar( star );
}
} );
}
function render() {
stars.forEach( ( star ) => {
context.beginPath();
context.lineCap = 'round';
context.lineWidth = STAR_SIZE * star.z * scale;
context.globalAlpha = 0.5 + 0.5*Math.random();
context.strokeStyle = STAR_COLOR;
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo( star.x, star.y );
var tailX = velocity.x * 2,
tailY = velocity.y * 2;
// stroke() wont work on an invisible line
if( Math.abs( tailX ) < 0.1 ) tailX = 0.5;
if( Math.abs( tailY ) < 0.1 ) tailY = 0.5;
context.lineTo( star.x + tailX, star.y + tailY );
context.stroke();
} );
}
function movePointer( x, y ) {
if( typeof pointerX === 'number' && typeof pointerY === 'number' ) {
let ox = x - pointerX,
oy = y - pointerY;
velocity.tx = velocity.tx + ( ox / 8*scale ) * ( touchInput ? 1 : -1 );
velocity.ty = velocity.ty + ( oy / 8*scale ) * ( touchInput ? 1 : -1 );
}
pointerX = x;
pointerY = y;
}
function onMouseMove( event ) {
touchInput = false;
movePointer( event.clientX, event.clientY );
}
function onTouchMove( event ) {
touchInput = true;
movePointer( event.touches[0].clientX, event.touches[0].clientY, true );
event.preventDefault();
}
function onMouseLeave() {
pointerX = null;
pointerY = null;
}
Code Web Dev


// This slide uses Auto-Animate to animate between
// two different code blocks
const distanceBetween = ( p1, p2 ) => {
// TODO
}
distanceBetween([10,10], [50,50])Code Transitions


// Measure the distance between two points
const distanceBetween = ( p1, p2 ) => {
const dx = p1[0]-p2[0];
const dy = p1[1]-p2[1];
return Math.sqrt( dx*dx + dy*dy );
}
distanceBetween([10,10], [50,50])
Code Transitions


Problems!
Let's begin!



Problem Name
Given an array of size N, reverse the array.
Sample Input
N = 5
arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5}
Sample Output
5,4,3,2,1





Process
Build
During the ideation phase, expect to discuss the project in depth to clearly understand the goals and requirements.
1
2
3
Compile
During the ideation phase, expect to discuss the project in depth to clearly understand the goals and requirements.
Execute
During the ideation phase, expect to discuss the project in depth to clearly understand the goals and requirements.


With built-in \LaTeXLATEX typesetting, you can include math formulas like this:
f(x) = \int_{-\infty}^\infty \hat f(\xi)\,e^{2 \pi i \xi x} \,d\xi
f(x)=∫−∞∞^(ξ)e2πiξxdξ


Homework
Our design team has a collective 75 years of experience in crafting digital products.
Our diverse backgrounds offer a thorough mix of points of view.



Table
| C++ | Java | Python |
|---|---|---|


Discovery of requirements for a project.
1
Creating a Plan that sets the requirements for the design and build phases.
3
Review and Iterate on the designs with testing of ideas, client feedback and prototypes.
5
Review and Iterate on the designs with testing of ideas, client feedback and prototypes.
2
4
6
Research into the project space, competitors and the market.
Design a number of iterations that capture the plans and requirements.
Build the project to an MVP to test and evaluate. Iterate using these learnings.
SQL Course
By Prateek Narang
SQL Course
- 16


