Graphs Algorithms
Specialisation Course for Competitive Programming

Exhaustive specialisation on Graph Algorithms for Competitive Programmers & Problem Solvers!

Welcome🎉!

Instructors
Prateek Narang & Apaar Kamal
Google Software Engineers, Competitive Programmers, Instructors


Hello!
I'm Prateek
I'm a software engineer
and course instructor,
creator of Coding Minutes
trained over 50,000 programmers!
Who is this course for?
If you can answer "Yes" to all of these -
-
Are you proficient in any one programming language?
-
Do you have some familiarity with data structures?
-
Do you want to master all graph algorithms?

Programming Language?
We will implement the codes in C++
-
Java, Python, JS programmers can still do this course, and implement the same algorithms.

Course Structured
Graph Essentials (Part-I)
Graph Advanced Algorithms (Part-II)
80+ Coding Questions for Practice

Graph Essentials
Representation
Breadth First Search
Depth First Search
Cycle Detection
Disjoint Set Union
Min Spanning Trees
Shortest Paths
(Dijkstra's, Bellman Ford, Floyd Warshall)
Graphs Advanced
Flood Fill
Multi Source BFS
DFS Trees & Backedge
Articulation Points & Bridges
SCC
Trees
Euler Tour
LCA
Network Flow


Takeaways 👀
- Build a solid understanding of graphs
- Learn to code complex graph algorithms
- Learn some advanced data structures like DSU
- Solve Graph problems with more confidence on platforms like Codeforces, HackerRank etc
- Develop quick thinking & come to speed for timed contests & hiring competitions
So Are you Ready?


Graph Data Structure

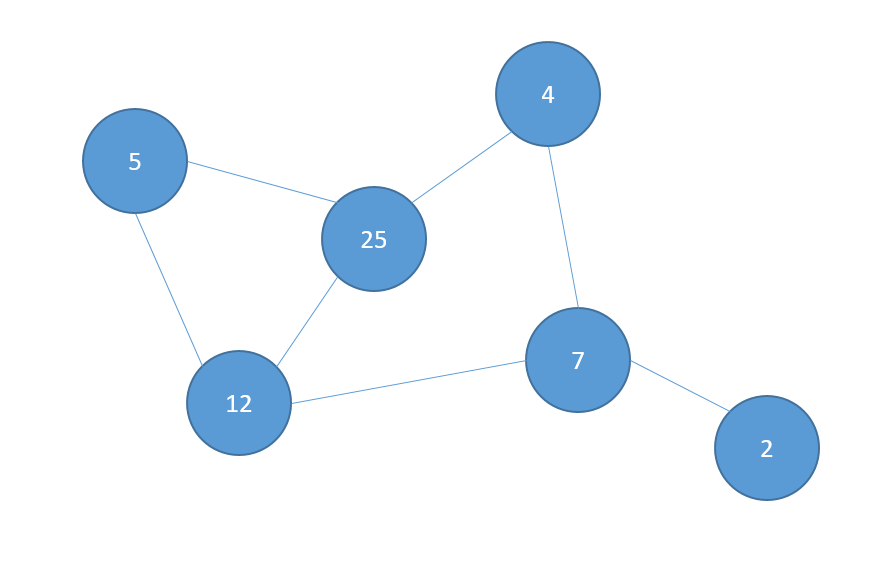
Storing a Graph
-
Adjacency List
-
Adjacency Matrix
-
Edge List
-
2D Matrix (Implicit Graph)
Adjaceny List
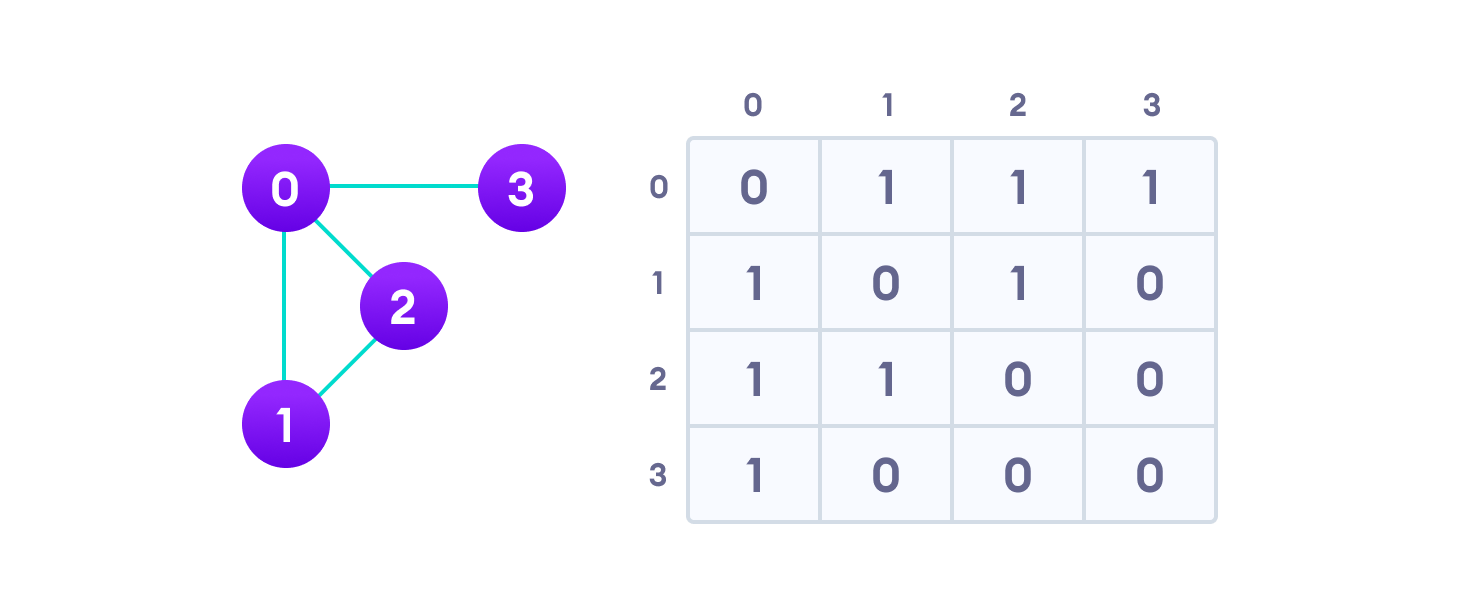
Adjacency Matrix

Edge List

Edges = { (0,1) , (0,3), (0,2) , (2,1) }

Implicit Graph
🚀 Topological Sorting
Topological sorting for Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a linear ordering of vertices such that for every directed edge u v, vertex u comes before v in the ordering. Topological Sorting for a graph is not possible if the graph is not a DAG.
🚀 Example
🚀 Applications
- Scheduling jobs from the given dependencies among jobs. computer science, applications of this type arise in
- Instruction scheduling,
- Ordering of formula cell evaluation when recomputing formula values in spreadsheets,
- Logic synthesis,
- Determining the order of compilation tasks to perform in make files, data serialization, and resolving symbol dependencies in linkers
🚀 Topological Sorting Algorithm
🚀 Travelling Salesman

- Finding Shortest round trip cost!
- Use in minimise cost of last mile delivery/supply chain/ Vehicle Routing Problem.
🚀 Travelling Salesman
TSP is classified as NP-hard because it has no “quick” solution and the complexity of calculating the best route will increase when you add more destinations to the problem.
Brute Force Approach
Calculates and compares all possible permutations of routes or paths to determine the shortest unique solution
Graphs Algorithms
By Prateek Narang
Graphs Algorithms
- 24



