Consensus algorithms in distributed systems
Piotr Grzesik
What is consensus ?
Reaching an agreement between processes and proposed values.
Consensus is fundamental for solving problems like leader election, commiting a transaction to database or performing clock synchronisation.
Potential problems
- Network partitions
- Lost or duplicated messages
- Processes crashing
- Byzantine failures
- Storage failure
Properties of consensus protocols
- Agreement - final decision of all non-faulty processes must be the same
- Termination - each non-faulty process must eventually decide on a value
- Validity - final decision must be one of the values proposed by the processes (no default values)
Consensus protocols
- 2 phase commit
- 3 phase commit
- Paxos
- Raft
2 Phase commit
Simple approach to solving consensus problem. Constitutes of two distinct phases: Propose and Commit/abort
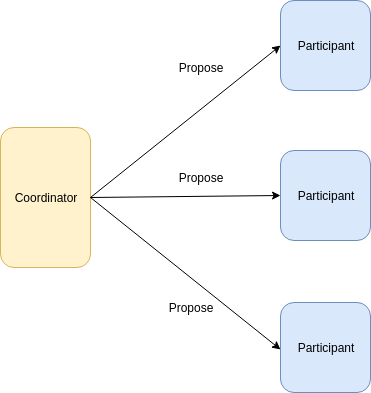
2 Phase commit - propose

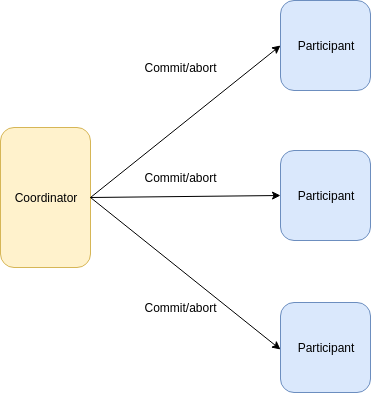
2 Phase commit - commit
Potential failures
- Coordinator fails before propose phase
- Coordinator fails during propose phase
- Participant fails during propose phase
- Participant fails during commit phase
- Coordinator fails during commit phase
3 Phase commit
- Improvement over 2PC at the cost of extra messages
- Splits commit phase into prepare-to-commit and commit phases
- Recovery node can take over in cases of coordinator crashing
- Can sustain failure of a participant that commited/aborted transaction (all other participants know the outcome)
- Prone to network partitioning
3 Phase commit
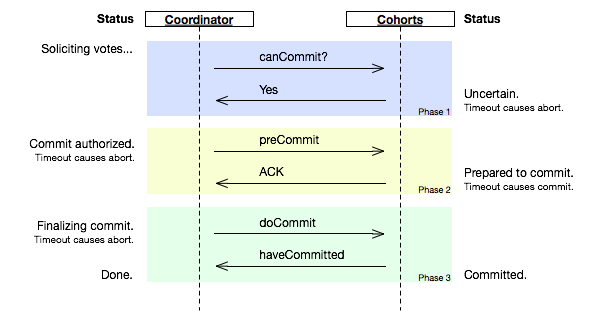
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three-phase_commit_protocol#/media/File:Three-phase_commit_diagram.png
Raft
- Proposed by Diego Ongaro in his paper "In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm"
- Built, as easier to understand alternative to (multi)Paxos
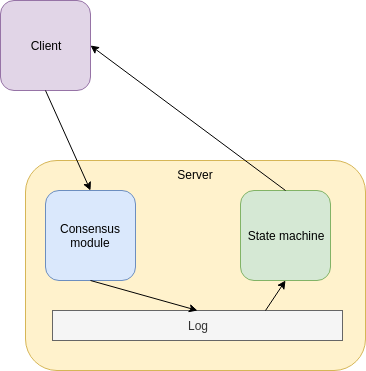
- Manages replicated log (replicated state machine)
- Separates leader election and log replication
- To operate needs at least n/2 +1 nodes (for 3 node cluster, can tolerate failure of 1 node)
- Time divided into terms (change of leader -> change of term)
Replicated state machine
Possible server states
- Leader - clients communicate with leader, responsible for log replication
- Follower - accept replicated logs from leader
- Candidate - candidate for a new leader during election
Used RPCs
- RequestVote - used by candidates during election
- AppendEntries - used by leaders to replicate log entries or serves as a heartbeat
- (optional) InstallSnapshot - used by a leader to sent log snapshot to follower
Leader election
- Increment term
- Switch to Candidate
- Vote for itself
- Send RequestVote RPC call to all other participants
- Become leader if received majority of votes
- Become follower if received AppendEntries from valid leader
- Start new election if no leader emerges (split vote)
Log
- Each participant stores log entries, which consist of log index, term and value (command)
- Logs are stored in a durable way
- Entry is commited if it was durably stored on majority of the participants
- No empty fields in log - if a given entry is commited all preceding entries are also commited
Log replication
- Client communicates with a leader(or follower and gets redirected to leader) and sends a command
- Leader appends the command to it's own log
- Leader sends AppendEntries RPC call to all followers
- On receiving responses from majority, leader passes command to it's state machine and returns result to the client
- Leader notifies followers of commited entries
- Followers pass command to their's state machines
Safety
- If log entry command has been applied to state machine, no other state machine can apply different command for that log entry
- Entries must be commited before applying to state machine
- Leader never overwrite entries in its log
- If entry is commited, it will be present in all future leader's logs
- Leader might order follower to overwrite its entries to 'fix' log
Usage
- Consul (https://www.consul.io/)
- etcd (https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd)
- rqlite (https://github.com/rqlite/rqlite)
- Apache Ratis (http://ratis.incubator.apache.org/)
Demo
Sources
- https://www.the-paper-trail.org/post/2008-11-27-consensus-protocols-two-phase-commit/
- In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm https://raft.github.io/raft.pdf
- https://www.the-paper-trail.org/post/2008-11-29-consensus-protocols-three-phase-commit/
- An Introduction to Raft (CoreOS Fest 2015) - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6bBggO6KN_k
- http://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft
deck
By progressive
deck
- 798



