Getting Git

Intros
- Name
- Job/Role
- Length of time at Rackspace
- What you hope to get from this class
- Previous experience with version control tools
Learning Objectives
- Learn what version control is
- Recognize what Git and Github are and how they are used
- Practice day to day Git usage
- Collaborate online through GitHub
What is Version Control
- A time machine for files and projects
- Snapshots/checkpoints of the project as a timeline
- Also referred to as revision control
Why use Version Control?

What should we use Version Control for?
- Different kinds of files
- Text files
- Scripts, config files, software, etc.
- Binary files (with caveats)
- Images / logos (with caveats)
- Text files
- Files that are shared with others
- Anything that can be changed by multiple folks
- Managing the flow of changes
- Deploying known versions of files
What is Version Control
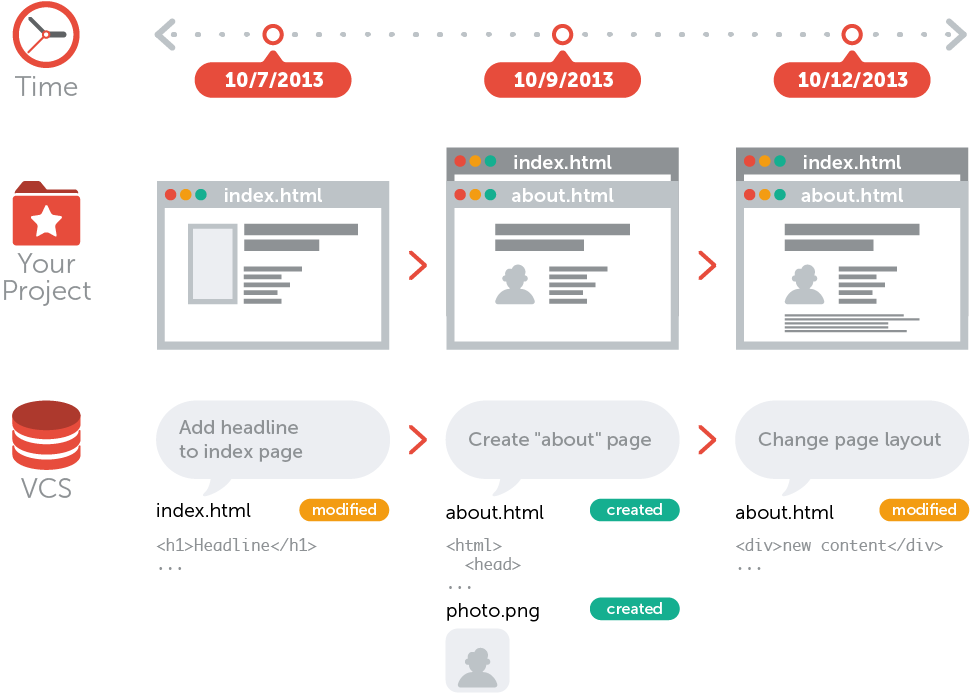
Nomenclature
- Version control
- Source control
- Revision control
Use Case 1:
- Multiple people (team members) working on the same stuff
Use Case 2:
- Keeping track of changes as you manage a system
Use Case 3:
- Tracking / managing common configs across multiple systems
War Stories
Work Flow
- Get / open a repository
- Pull down changes shared with you by others
- Create a branch for your work
- Do some work
- Check in (commit) changes periodically
- Push your branch to a server to share your work with others
- Merge branches to bring changes into the main "master" branch
- Lather, rinse, repeat
Work Flow
- Each step in that workflow maps to a Git command
- or a set of Git commands
- You can map your own workflow activities to Git
- It is really flexible
- We will work on labs that illustrate all these workflow steps
What is Git?
What is Git
- From the web: Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
- Git is a suite of tools for you to implement version control
- The core stuff is command line
- GUIs are available (more on that later)
Installing Git
- Git is available for all the major OSes
- Linux, Windows, OS X
- http://git-scm.com/downloads
- We will experience this in the upcoming lab
What is a repository?
- A repository is the place that stores all the data for your version controlled directory
- database for all the versions, metadata, file contents, etc.
- A repository can live on a local machine, cloud server, or other nebulous device
- Repositories can be cloned and shared
Git Commands - init
- Get / open / create a repository
git init .
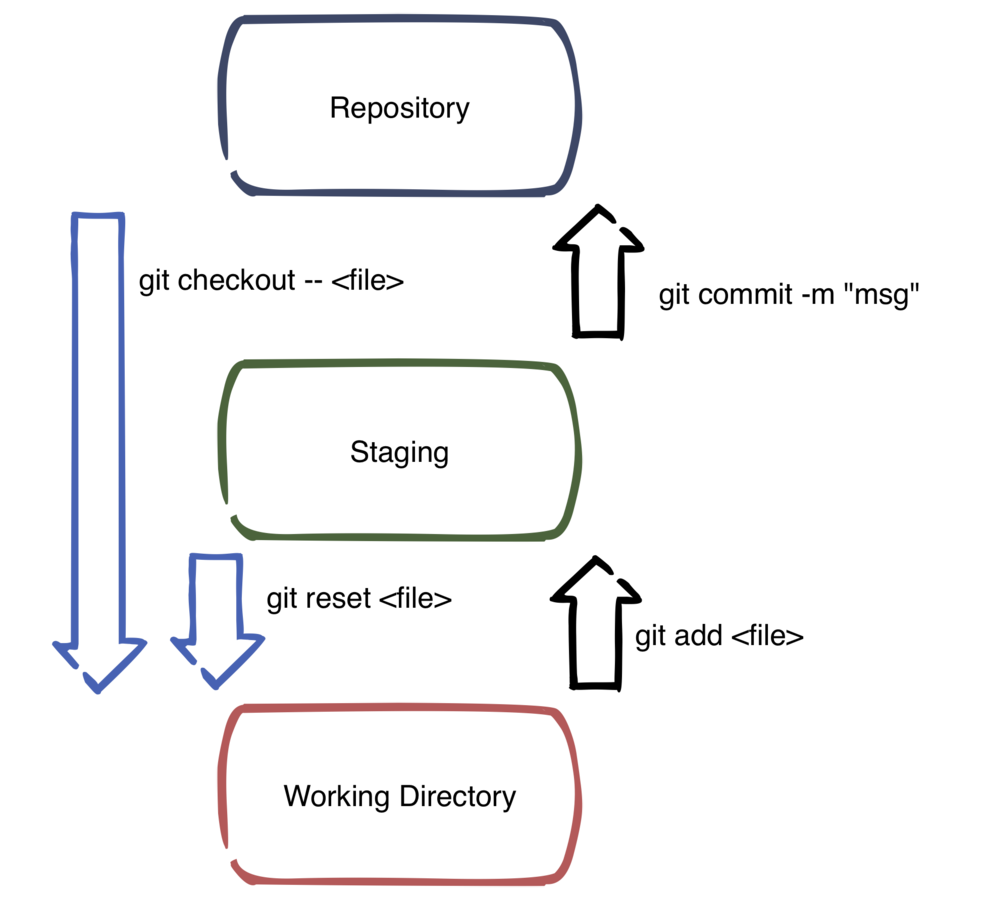
Git Commands - add
- Do some work
- Check in (commit) changes periodically
- To commit your changes first you have to stage them
- Tell Git which changes you will be committing
git commit -m "my cool comment"
git add my_file.txt image.jpg
Git Commands - rm
- Remove a file (or files) from the repo
git rm my_file.txt image.jpg

Git Commands - status
- Find out the status of the repo
git status
Git Commands - reset
- Unstage a change
- (after an add)
git reset new_file.txt

Git Commands - undo an edit
- Undo all edits to a file
- Great caution is advised here
git checkout -- changed_file.txt

Lab 1
Branching, Merging, and Conflicts
Workflow Continued
- Working linearly on a project doesn't scale well
- We need to be able to work on parallel sets of changes
- Thankfully, we have branching and merging
Branching and Merging Illustrated
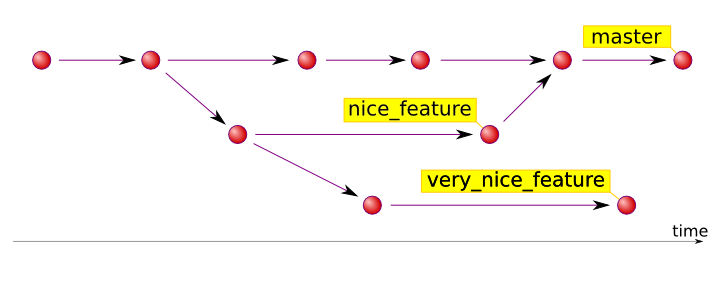
Branching
- Creating a branch called nice_feature
- Make that branch the active branch
git branch nice_feature
git checkout nice_feature
Branching
- Shortcut: Creating a branch called nice_feature and make it active
git checkout -b nice_feature
Merging Branches
- Merging branches asks Git to take the changes from one branch and put them in the other
- Merge changes from nice_feature into master
git checkout master git merge nice_feature

A note about the master branch
- The master branch is special
- It is considered the core branch that changes are merged into
- By convention, master is usually a known state of the files in the repository
- It is not the only branch you can merge changes into
- From Git's perspective it is just any old branch
Conflicts
- Merge conflicts happen when you try to merge changes that overlap from one branch to another
- Example: in your README file
-
Branch A: Hello world!
-
Branch B:Goodbye world!
-
- Git can't tell which one it should go with, so it tells you to pick
Lab 2
GitHub for Collaboration

GitHub
- GitHub is a web-based Git repository hosting service
- Centralized repository
- Social coding features
- pull requests
- documentation (markdown)
- wikis
- issue tracking
- small websites
- history browsing
- code reviews
- Example: https://github.com/jeremyprice/GettingGit
Lab 3
Other Topics
GUI Clients
- (Mac) Tower - http://www.git-tower.com
- (Mac) GitHub - http://mac.github.com
- (Win) GitHub - http://windows.github.com
- (Mac, Win) SourceTree - https://www.sourcetreeapp.com/
- (Linux) gitg - https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gitg/
Good list of GUI apps:
Demo of Git GUI
SourceTree
Further reading
- Git Pro book - http://git-scm.com/
- Git Immersion tutorial - http://gitimmersion.com/
- Try Git - https://try.github.io/
- Learn Git branching - http://pcottle.github.io/learnGitBranching/
- Git Tower - http://www.git-tower.com/learn/git/ebook/
- Getting started with GitHub - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TAObtTxBUzk
- Good advice about Git Style - https://github.com/agis-/git-style-guide
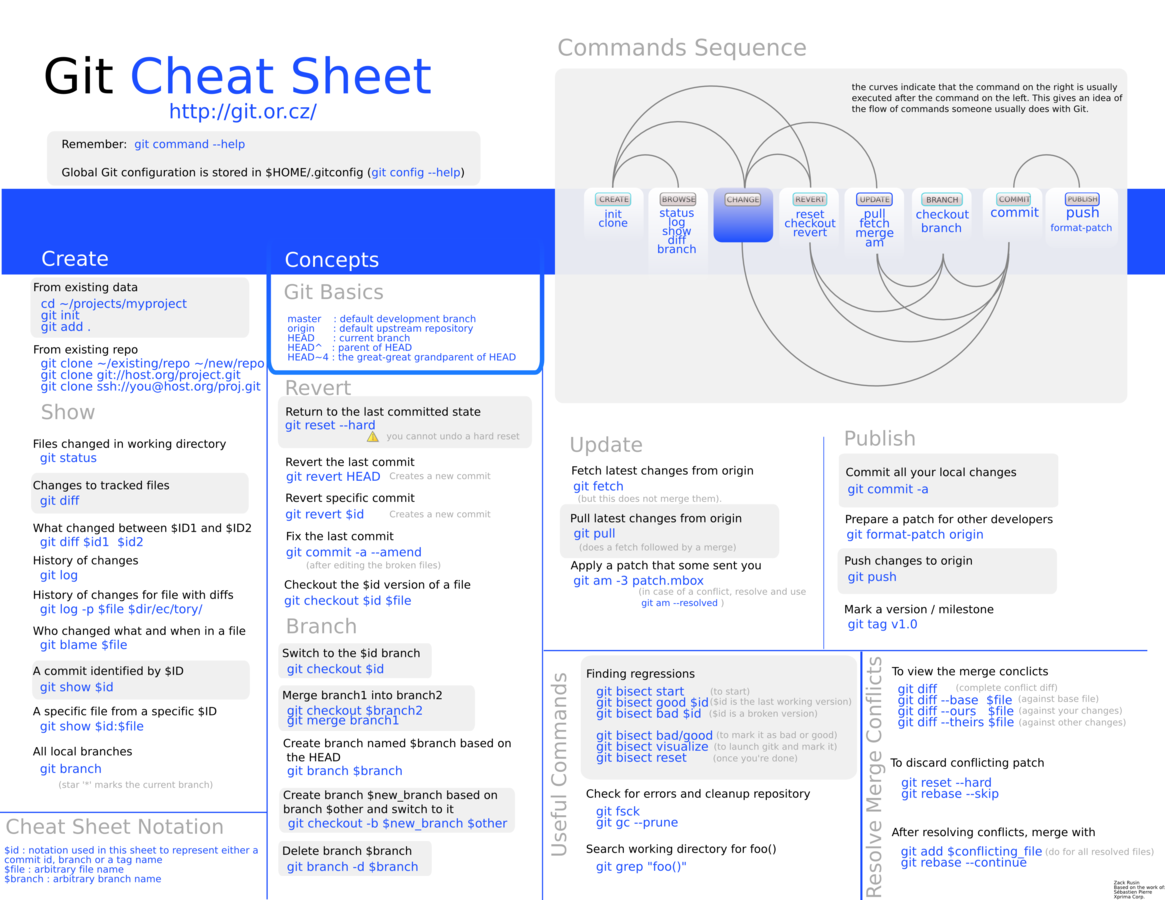
Desk Reference
Cheat Sheet
Your feedback is important to us
- Please take a moment to fill out a brief evaluation for this class:
- Go to mylearn.rackspace.com
- Scroll down to My Tasks on your myLearn welcome page
- Click on the evaluation link for this class
- Fill out the evaluation then submit
We appreciate your feedback!
Getting Git
By Rackspace University
Getting Git
Learning Git and GitHub
- 2,114



