redis
Fundamentals
Intros
Assess your Knowledge
Learning Objectives
- Know the characteristics of the different databases
- Understand where Redis fits in the Database world
- Recognize when and why to use Redis
- Explain the features and benefits of Redis
- Cite use cases for Redis
- Install and demo Redis
Types of Databases
A database, in the most general sense, is an organized collection of data.
Database Landscape
Relational Database
- A relational database is essentially a group of tables or, to use the technical name, entities.
- Each table is made up of rows (tuples) and columns (attributes).
Columns
Specific set of values in a table of the same type. It defines a specific attribute of the table or data.
Rows
Also called a record, represents a set of data about a spec ific item.
Row
Relational: Key Concepts cont...
The Problem
Some companies needed something more to accommodate their growing data
Non-relational DBMS
Intro to NoSQL
- NoSQL Database (1998)
- NoREL
- "Not only SQL"
- NoSQL (2009)
What exactly is NoSQL?
NoSQL is difficult to define but most NoSQL databases will share common characteristics:
- Non-relational
- Distributed
- Open-source
- Horizontally scalable
- Schema-less
An “Aggregate” is a collection of related objects that we wish to treat as a unit
What type of database do you think Redis is?
Primarily constructed of aggregates that have a Key or ID that’s used to access the data. The database cannot see structure within the aggregate

User follows user
User follows board
owns board

User follows user
User follows board
owns board
User follows implicity

- Like a Key-Value database, document databases primarily store and access data using aggregates
- In contrast to the Key-Value database, document data bases can see structure within the aggregate
- You are able to retrieve the whole aggregate or specific parts of it
Column Family
Column Family
Data can be structured in a couple of different ways:
- Row -oriented: each row is an aggregate with column families representing useful chunks of data within the aggregate
- Column-oriented: each column family defines a record type with rows for each of the records
Column Family
Graph Database
- Unique compared to most NOSQL types because it was not developed with the intention of scaling horizontally into a cluster
- Data is stored as “nodes” that are connected by edges
- Edges are directional in nature and must be specified
- Queries need a starting point and then will traverse the edges to gather the data requested
Companies using NoSQL
Redis
What is Redis?
- Redis is an open source, BSD licensed, advanced key-value store.
- It is often referred to as a data structure server.
- REmote DIctionary Server
What makes Redis advanced?
Keys can contain “advanced” structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets and sorted sets.
Redis Data Structures
Strings
Strings are the most basic kind of Redis value. Redis Strings are binary safe, this means that a Redis string can contain any kind of data, for instance a JPEG image or a serialized Ruby object.
Lists
Redis Lists are simply lists of strings, sorted by insertion order.
List
[A, B, C, D]
Sets
Redis Sets are an unordered collection of Strings.
Set
{A, B, C, D}
Sorted Sets
Redis Sorted Sets are, similarly to Redis Sets, non repeating collections of Strings. The difference is that every member of a Sorted Set is associated with score, that is used in order to take the sorted set ordered, from the smallest to the greatest score. While members are unique, scores may be repeated.
Sorted Set
{value:score}
{C:1, D:2, A:3, D:4}
Sorted Sets Example
Hashes
Redis Hashes are maps between string fields and string values, so they are the perfect data type to represent objects (eg: A User with a number of fields like name, surname, age, and so forth)
Hash
{key:value}
{field1: “A”, field2: “B”...}
In Memory
The entire dataset needs to be able to exist in memory on the server to take advantage of the potential speed benefits.
Persistance
Toptionally, redis can and should write to disk to take advantage of its ability to survive reboots, make usable backups
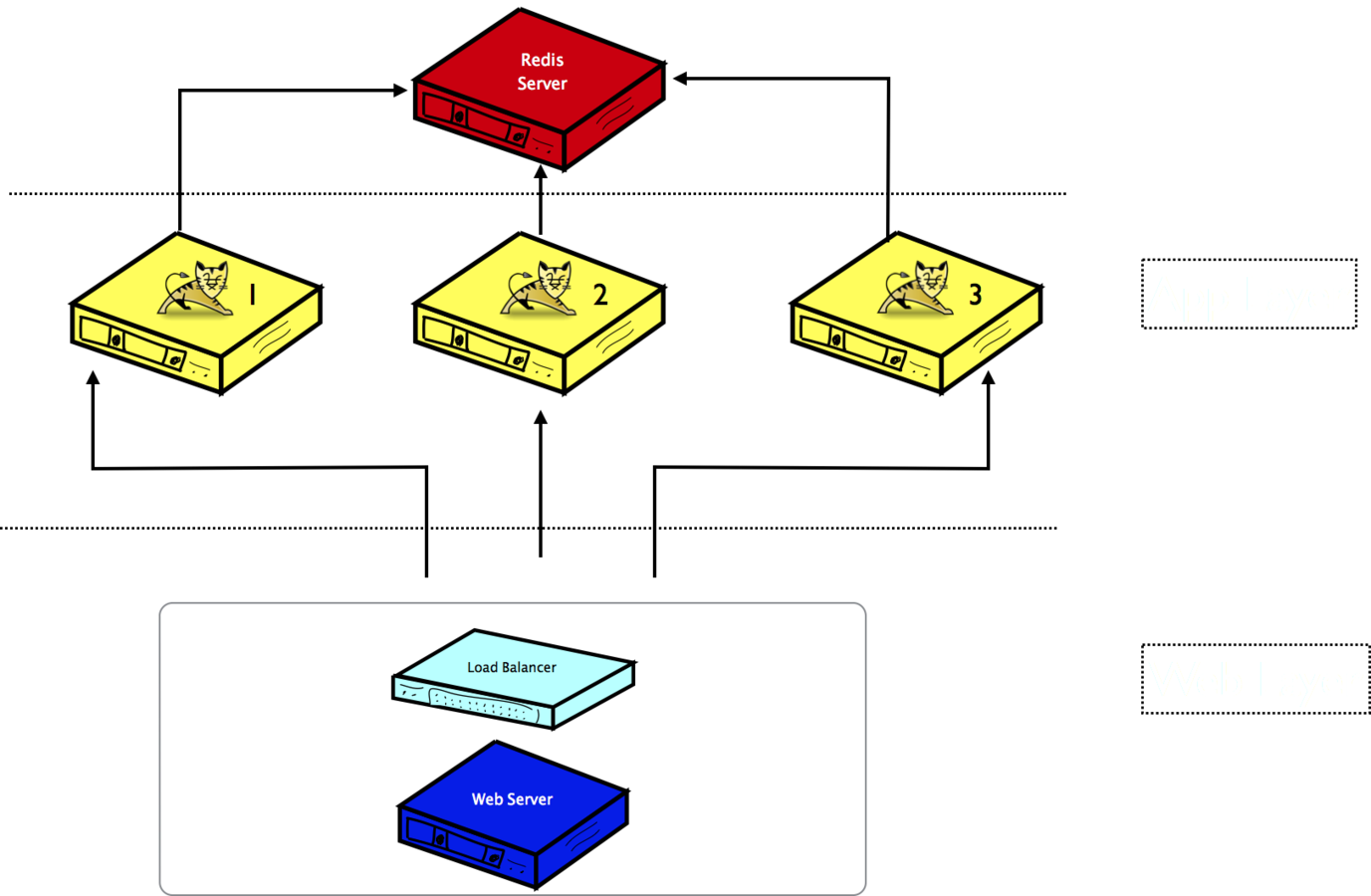
Client/Server Interaction
- The client sends a write command to the database (data is in client's memory).
- The database receives the write (data is in server's memory)
- The database calls the system call that writes the data on disk (data is in the kernel's buffer)
- The operating system transfers the write buffer to the disk controller (data is in the disk cache)
- The disk controller actually writes the data into a physical media (a magnetic disk, a Nand chip, ...)

Want to see data structures in action?
What is Redis used for?
Redis is used for...
- Caching
- Session Store
- Pub/Sub
- Job Queue
- Leaderboards
- Order by user votes and time
- Compliments other databases
- Analytics
Caching
- Redis caching transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster
- Redis can be considered a superior replacement for memcached
Caching
Session Store
- Remembers all the data in your session, and forgets it as soon you close the browser you are working in
Using Redis for Session Storage
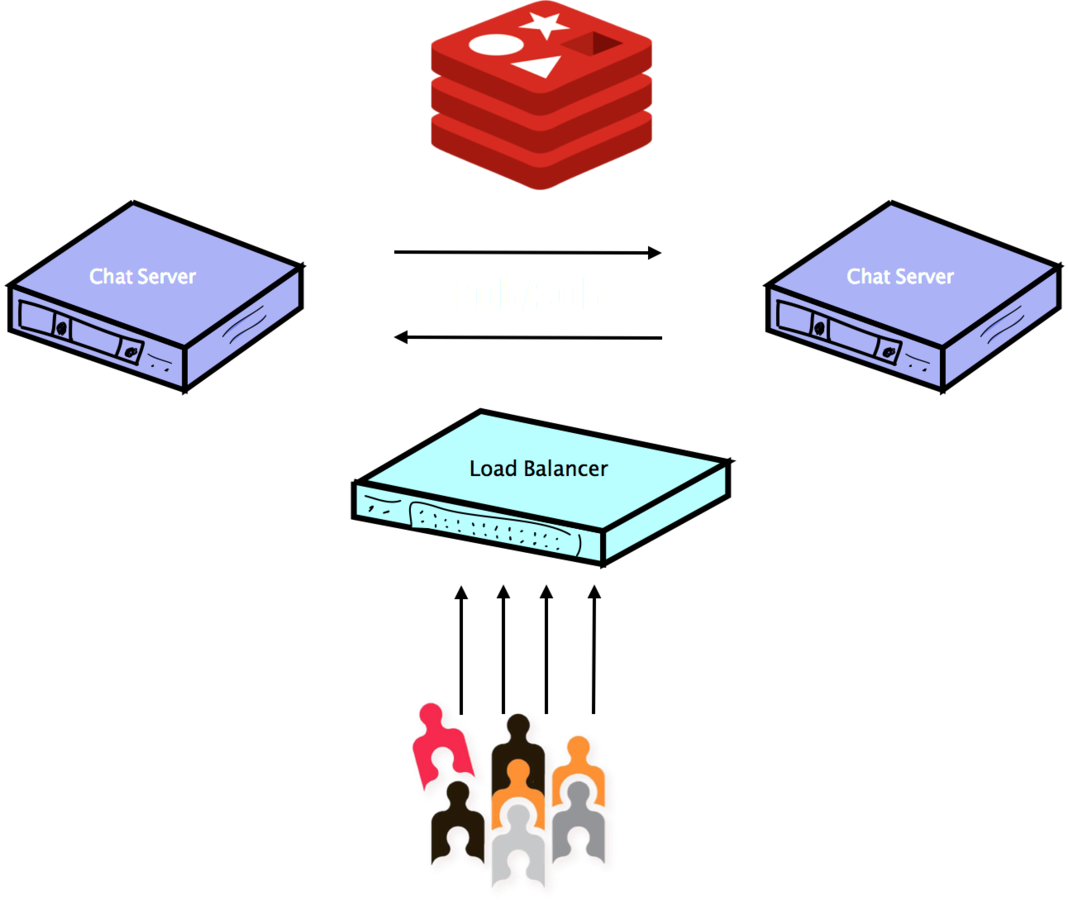
Pub/Sub
- SUBSCRIBE will listen to a channel
- PUBLISH allows you to push a message into a channel
- These two commands are all you need to build a messaging system with Redis.
Job Queue
- Redis is often used as a messaging server to implement processing of background jobs or other kinds of messaging tasks
Leaderboards
- Leaderboards are an effective way to show a user quickly where they currently stand within a gamified system
- Also, it can be a great social connection tool
- Generally there are two types of leaderboards: absolute leaderboard and relative leaderboards
Order by User Votes and Time
- This is a leaderboard like Reddit where the score's formula the changes over time.
Redis Compliments other Databases
- SQL, MySQL, Mongo etc.
Analytics
- Redis can conduct real time analysis of what is happening, for stats, anti spam, or whatever
When is Redis is a Good Fit?
Easy to run; but running it well can be difficult.
Performance & Throughput is Important
Reversible data structures solve a variety of problems.
You need to offload workloads to optimize other datastores
When Redis isn't a Good Fit
Storing huge amounts of data in memory can get expensive
Data Security is a Concern
Complex Highly Available Redis is still … evolving
- Simple Failover - Sentinel
- Multi-Master Cluster - not yet
You need your data in a relational model
Running Redis on Windows
You need multi-master scaling and failover
Redis does not support master-master and you need ACID transactions
ACID transactions is a set of properties that you would like to apply when modifying a database.
- Atomicity
-
- Consistency
-
- Isolation
-
- Durability
- Atomicity refers to a database’s ability to either fully process or fully roll back a transaction
-
- Consistency database should ensure that all data written therein follows all rules and constraints specified in the database
-
- Isolation transactions must be processed securely and independently, without interfering with each other
-
- Durability the database must ensure that all committed transactions are saved permanently and cannot be accidentally erased, even in a database crash
ACID to base
- Atomic
-
- Consistent
-
- Isolated
-
- Durable
- Basically involved
-
- Soft state
-
- Eventually consistent
Real World Use Cases
Caching

- Local caching
- Site caching
- Global caching
- Redis is fast
Persistence Key Value
- Persistent Key Value to store route data
- Ramp up speed
User History
- Redis powers Hulu’s viewed history tracking system
- Stores 4 billion records
- Serves 7000 requests per second
- Replaced a complexed stack "memcached, python app, MySQL" with Redis
- Multi-zone replication, latency, scaling and performance were key
Likes and Followers
- Powers Pinterest’s follower graph
- 70M users have followed billions of things
- Every UI screen queries if board or user is followed
- Latency, concurrent users, scalability & failover
- Replaced MySQL with Redis
Analytics
- Monitoring of physical systems
- Thousands of data input sources
- Time series w/ability to accept out of order entries
- Pub/Sub used to extend the system
Video goes here
Group Activity...
More Use Cases...

Features and Benefits
Data Types
String
Can contain text or anything that can be represented in a binary safe value of 512MB or less. This means you can also store images, audio, or other large content within a string.
Strings
Strings cont...
Set
Unordered list of strings. You can remove and add anywhere in the set by value. You cannot have the same value twice.
Sets

Lists
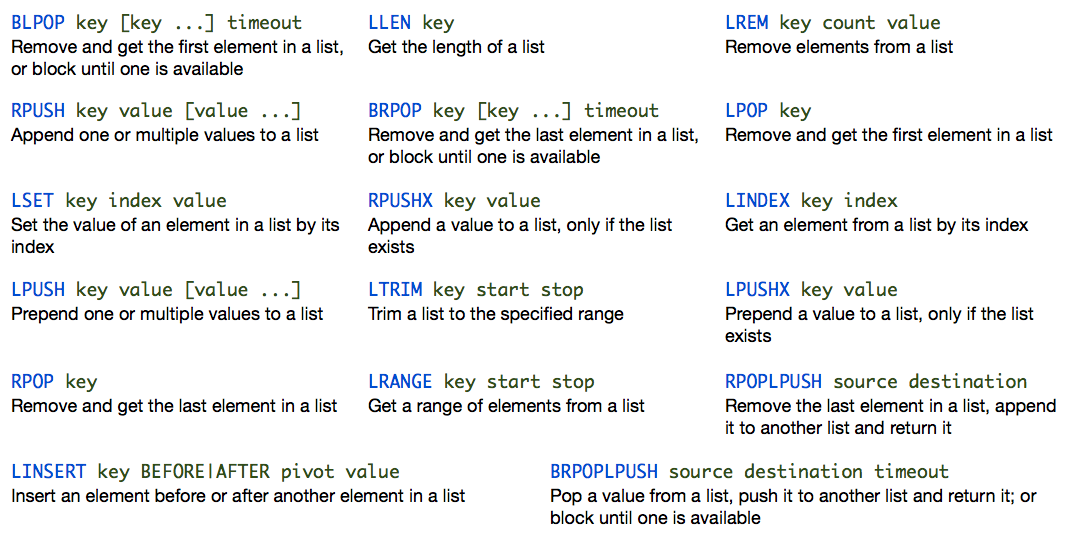
Lists
List of strings. You can only add and remove from the left or right “ends” of the list.
LPUSH mylist a # now the list is "a"
LPUSH mylist b # now the list is "b","a"
RPUSH mylist c # now the list is "b","a","c" (RPUSH was used this time)
Sorted Set
Like a set, however, each member has a “score” used to sort the values. Multiple members can have the same score, but not the same value.
Sorted Sets
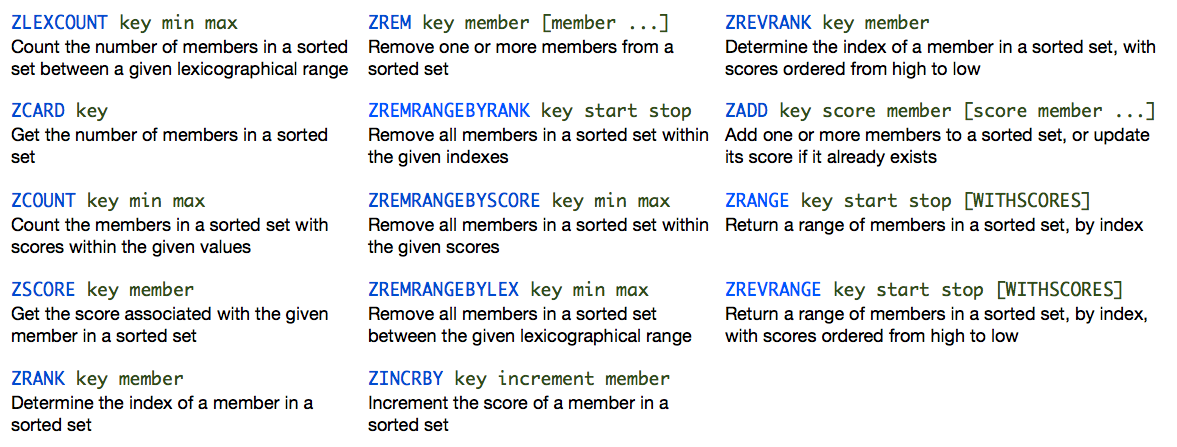
Sorted Sets cont...
Hashes
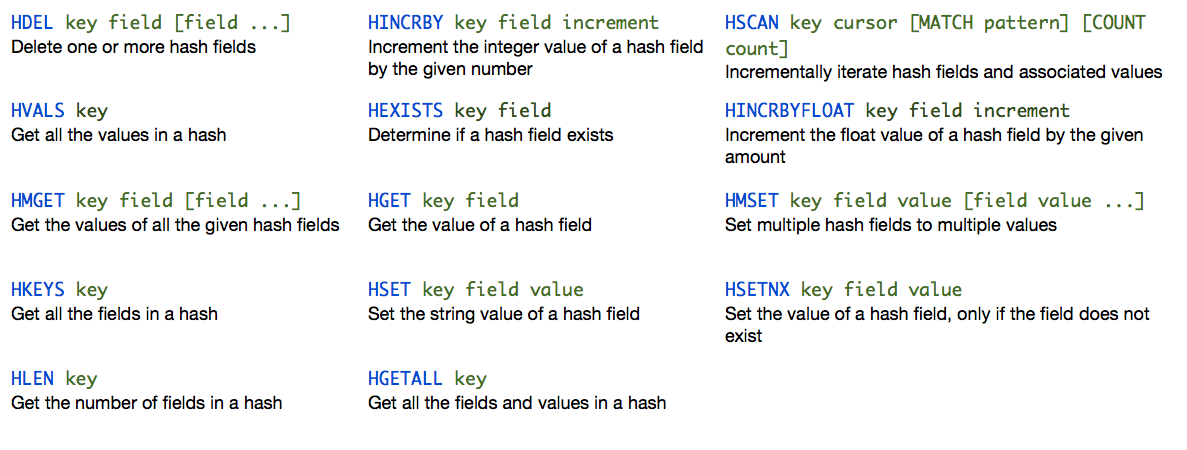
Hash
Maps between string keys and string values.
@cli
HMSET user:1000 username antirez password P1pp0 age 34
HGETALL user:1000
HSET user:1000 password 12345
HGETALL user:1000
Common Operations ( Demo )
Common Operations Demo
- SET key value | Sets your key-value pair
- GET key | Gets a value based off “key”text goes here
- RPUSH/LPUSH key value [value] [value] | Appends one or more values to a list “key” on the right or left end.
- RPOP/LPOP key | Retrieves and removes the right-most or left-most value in a list “key”
- SADD key member [member] [member] | Adds one or more members to a set
- SREM key member [member] [member] | Removes one or more members from a set
Programming Models
Message Queues
- RPOP and LPUSH can be used to turn a List into a message queue
- Each message is a String of data
RPOPLPUSH
Example
redis> RPUSH mylist "one"
(integer) 1
redis> RPUSH mylist "two"
(integer) 2
redis> RPUSH mylist "three"
(integer) 3
redis> RPOPLPUSH mylist myotherlist
"three"
redis> LRANGE mylist 0 -1
1) "one"
2) "two"
redis> LRANGE myotherlist 0 -1
1) "three"
redis>
Publish/Subscribe Messaging
- Subscribers subscribe to channels
- Publishers send messages to channels
- Channels forward messages to subscribers
Pub/Sub Commands
- SUBSCRIBE channel [channel ...] - Subscribes the client to the specified channelst
- UNSUBSCRIBE [channel [channel ...]] - Unsubscribes the client from the given channels, or from all of them if none is given
- UPUBLISH channel message - Posts a message to the given channel
PUB/SUB
Performance
Redis Server Performance
- Single threaded
- Typically network-bound (bandwidth and latency)
- 80k+ operations per second w/ individual requests
- Millions of operations per second using pipelining
Additional Reading: How Fast is Redis
Persistence and Replication
Persistence
- Saves state of Redis to disk
- Can be disabled for maximum performance
- AOF - Append Only File stores all write operations
- RDB - Redis Database stores a concise snapshot of data
Demo and Installation
Demo
- Install Redis
- Verify Redis is running
- Get Data in/out of Redis
Choose your own Adventure
Real Installation and Naviagtion
Try Redis Online
Lab: Real Installation and Navigation
- Install Redis
- Verify Redis is running
- Get Data in/out of Redis
Retrieve the code from here:
http://redistogo.com/documentation/introduction_to_redis?language
LAB: Try Redis Online
- http://try.redis.io
- Practice | Practice | Practice
challenge
Time
Redis fundamentals challenges
-
Create a key and assign it your name. Display its output to confirm.
-
Create a second key and assign it your team lead's name. Display its output to confirm.
-
Create a key to be used as a hash to store your car's year, make & model. Display…
-
Create a set of all the Rackers sitting on your row. Display...
-
Create a sorted set that includes names of your friends in order of most liked. Display…
- Can you display this in reverse order?
-
Create a list of courses you took in school in the order taken. Display…
- Retrieve the newest course (the one you attended last in school) from the list and place it into a new list by itself.
- Add another entry to the original list for the Redis Fundamentals course, as the newest course.
- Display the original list, again, to ensure the removal of the initial course and addition of this one.
Redis fundamentals challenges
-
Create a key and assign it your name. Display its output to confirm. set | get
-
Create a second key and assign it your team lead's name. Display its output to confirm. set | get
-
Create a key to be used as a hash to store your car's year, make & model. Display… hmset | hmget | hget | hgetall
-
Create a set of all the Rackers sitting on your row. Display... sadd | smembers
-
Create a sorted set that includes names of your friends in order of most liked. Display… zadd | zrange
- Can you display this in reverse order? zrevrange
-
Create a list of courses you took in school in the order taken. Display… lpush | rpush | lrange
- Move the newest course (the one you attended last) from here into a new list by itself. rpoplpush
- Add another entry to the original list for the Redis Fundamentals course, as the newest course. lpush | rpush
- Display the original list, again, to ensure the removal of the initial course and addition of this one. lrange
Assess your Knowledge
A massive thanks to the content dev team...
Bill Anderson
Chris Caillouet
Chris Old
Daniel Morris
Daniel Salinas
Joe Engel
Juan Montemayor
Mark Lessel
David Grier
redis
http://redis.io
Redis Fundamentals
By Rackspace University
Redis Fundamentals
- 3,270