ENPM809V
Linux Hijacking (Hooking)
What we will be covering?
- Hooking Basics
- Pointer Replacement
- Callback Registration
Hooking Basics
What is Hooking

What is Hooking
Methods and ways to change execution to yuor code instead of existing code
Reasons to Hook
- Suppress Notifications
- Input/Output Filtering
- Patching
- Replace Functionality
- Deny Access
- Circumvent Security
Static Linking
- .a files
- All required code is compiled into the executable
- Statically linked binaries can be large
- Changing ANYTHING requires recompilation
Dynamic Linking
- .so files
- Utilizing the Global Offset Table and Procedural Lookup Tables, we can determine the home of the functions
- The shared object must live somewhere on the machine
- Easy to reuse code at the consequence of some overhead
How Can we Hook in User Space?
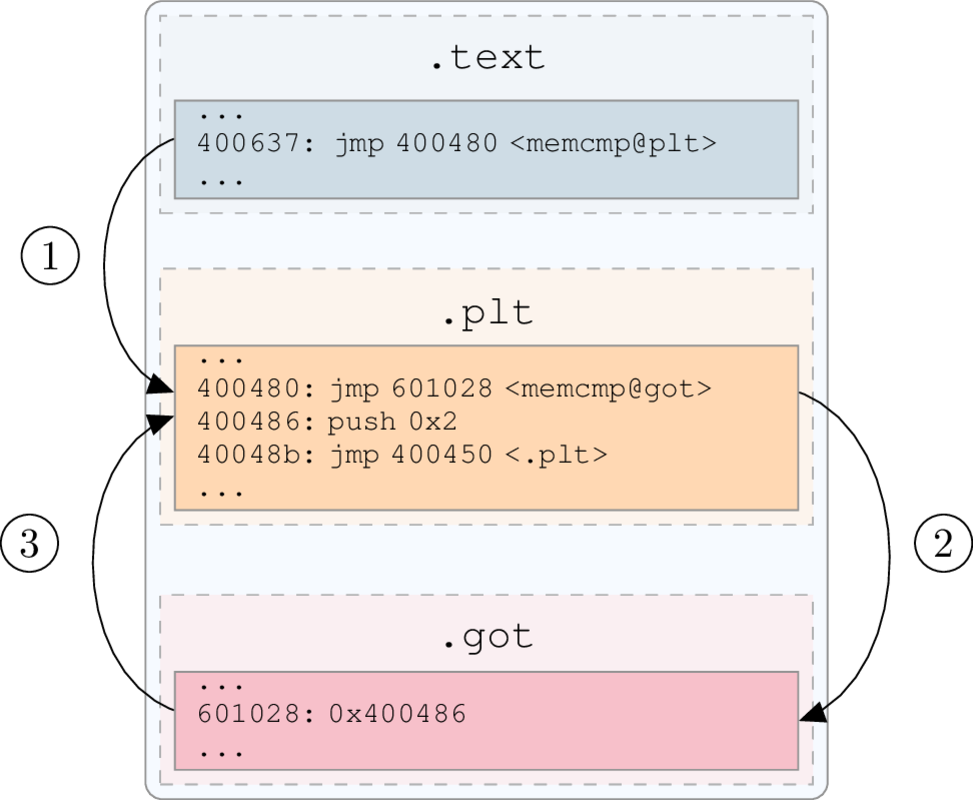
Remember the GOT and PLT?
- We can replace the address in the GOT to point to our own code.
Normal Behavior
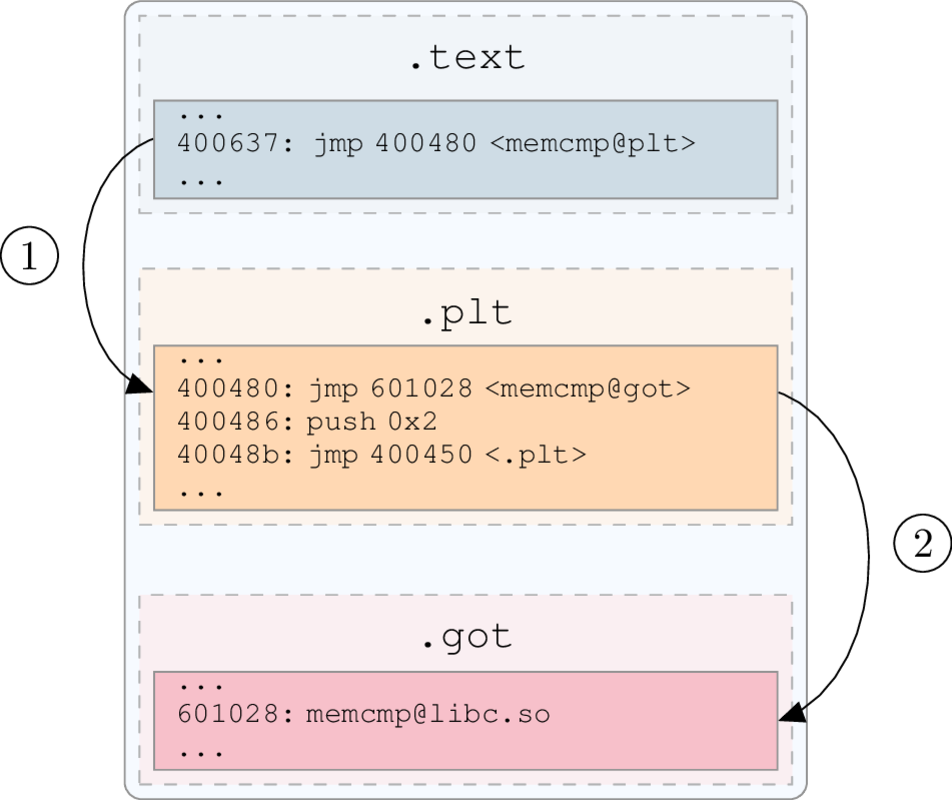
What We Are Doing

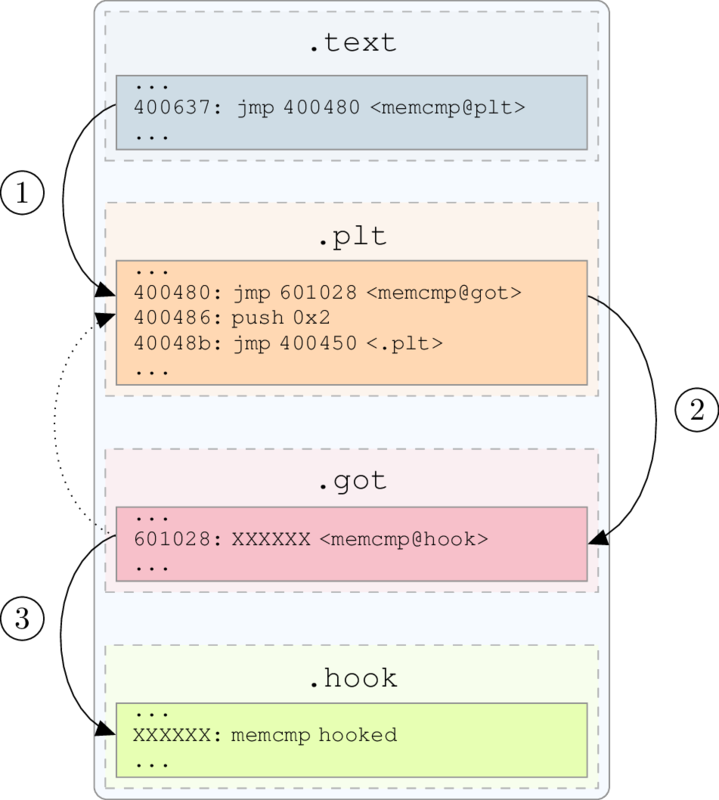
What hooking have we done so far?
LD_PRELOAD
- We are replacing what the GOT resolves with our own shared library.
- Think back on the waiter program - we created a hook to sleep such that it calls our sleep rather than calling LIBC's sleep.
But there's another way
GOT Hooking
- At run time, we find address of the GOT, and then replace it.
- We have to parse through the ELF to find the location of the GOT
- Find the image header address
- Use /proc/self/maps
- Parse through the program headers to that are based on dynamically linking
- Find in particular DT_PLTGOT and return that address
- Loop through the GOT until you find the function you are looking for
- Do a pointer replacement to your desired function.
- Find the image header address
What are some ideas that we might get the code to the other side?
Pointer Replacement
How Can We Replace Pointers?
- Compiled code calls external functions by using a table of function pointers
- In contrast to relative offsets
- Hook by changing the value of the function pointer
- Save the original pointer to the callback function
Didn't we already do this with GOT replacement?
Sort of.... yes
- Replacing the GOT Entry you can usually hook the function just for the module
- Won't hook explicit imports
- Won't work if import address is stored somewhere else
vsyscalls
- vsyscall is the precursor to vDSO
- Created because system calls have overhead with kernel context switching
- vsyscall can reduce this by mapping information required from the kernel
- Also implement a "quick version" of the syscall in user-memory
vsyscalls
- Still has problems...
- vsyscall page can only hold four entries
- vsyscall page had to be staticaly mapped ot the same location in memory for all processes
- Mitigations
- Remove useful instructions from vsyscall page
- Move variables into other pages iwth execute permissions turned off
- Replace remaining code with trap instructions
vDSO
- vDSO = virtual dynamic shared object
- It's vsyscall without the limitations
- Mapped into every user-mode process
- Still exposes kernel functionality in userspace
- but memory is allocated dynamically
- room for more than four entries
- Depending on kernel config, vDSO is either RX or RO
- Can use mprotect to overwrite these protections
Callback Registration
When we need to register a hook through via another mechanism
Examples
- Signal handlers
- Thread-Local storage
- Constructors and destructors
- atexit
- not called if program calls exec()
- not called if process terminates abnormally (delivery of a signal)
- Limited to the information and filtering proivded by the API
Code Patching
What is it?
- Overwriting instructions to modify behavior of a program.
- Great power comes great responsibility!
- Most powerful but most complicated
- Usually consists of a method for "diverting" execution to another function or shellcode
- Example: Jump to register...
Simple Patching - Basic Diversion
- Example: Jump to register...
mov rax, 0x7ffffffff
jmp rax- Typically, you would want to put something like this at the beginning of a function
- Placing it in the middle can cause problems, need to tailor it to the function
- 5-byte relative jump is normal, best if you need to jump to an address. < 2GB away.
Alternative Patches
- Disable Function
- Return something like a success
- Repalce full blocks of code...
- Entry Stub Trampoline
Entry Stub Trampoline
- A way to patch code without losing the original behavior of the function
- Patched code gets saved off
- Execute patched code
- Afterward, jump back to the original code.
- Resume normal behavior
Entry Stub Trampoline
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 0x10
mov rdi, -0x8[rbp]
mov -0x4[rbp], 0
etc.....
0x401234
Entry Stub Trampoline
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 0x10
mov rdi, -0x8[rbp]
mov -0x4[rbp], 0
etc.....
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 0x10
mov rdi, -0x8[rbp]
mov rax, 0x401234
jmp rax
Trampoline
Original
0x401234
Entry Stub Trampoline
mov rax, 0x7ffff7ff1234
jmp rax
mov -0x4[rbp], 0
etc.....
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 0x10
mov rdi, -0x8[rbp]
mov rax, 0x401234
jmp rax
Trampoline
Original Entry/In
0x401234
0x7ffff7ff1234
filter input
Filter Output
Call Trampoline
Entry Stub Tampoline Gotchas
- Can't overwrite entire function
- Might need a disassembler to know:
- Where to jump to at the end of the trampoline
- How many bytes to put in the trampoline
- Simple disassemblers are fine, but can use a full one
- Simple Disassemblers: objdump, capstone
- Full Disassemblers: Ghidra, Binary Ninja, radare2, IDA
ENPM809V - Linux Hijacking
By Ragnar Security
ENPM809V - Linux Hijacking
- 322



