Implementing Windows Anti-Debugging Techniques
Background

-
Implemented for CTF Challenges
- Give participants experience with reversing hardened Windows binaries
- Many CTFs focus heavily on Unix based Reverse Engineering
Focused on three anti-debugging techniques
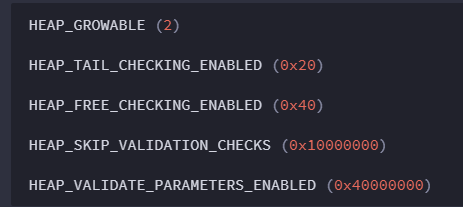
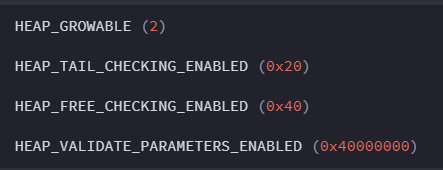
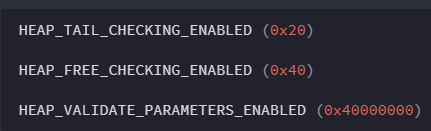
Heap Flag Checks
- Debuggers can modify flags in heap
- Flag that tracks state of heap (almost always growable)
- The Force Flags (which should be not set by a program alone).
- Check whether these flags have unexpected values
- Need to implement for both 32 and 64 bit
Windows NT, 2000 and XP 32 bit Heap Flags
Windows XP 64bit and Up
Force Flags
/* Gets the Heap Flag Offset */
int GetHeapFlagsOffset(bool x64)
{
int retVal = 0;
if (x64) {
if (IsVistaOrHigher()) {
retVal = 0x70;
}
else {
retVal = 0x14;
}
}
else {
if (IsVistaOrHigher()) {
retVal = 0x40;
}
else {
retVal = 0x0C;
}
}
return retVal;
}
/* Returns the Heap Force Flags offset */
int GetHeapForceFlagsOffset(bool x64)
{
int retVal = 0;
if (x64) {
if (IsVistaOrHigher()) {
retVal = 0x74;
}
else {
retVal = 0x18;
}
}
else {
if (IsVistaOrHigher()) {
retVal = 0x44;
}
else {
retVal = 0x10;
}
}
return retVal;
}
int CheckHeap()
{
/* Initializes variables and retrieves the process environment blocks */
PVOID pPeb = GetPEB();
PVOID pPeb64 = GetPEB64();
PVOID heap = 0;
DWORD offsetProcessHeap = 0;
PDWORD heapFlagsPtr = 0, heapForceFlagsPtr = 0;
BOOL x64 = FALSE;
#ifdef _WIN64
x64 = TRUE;
offsetProcessHeap = 0x30;
#else
offsetProcessHeap = 0x18;
#endif
/* Get the heap and the flags associated with it */
heap = (PVOID) * (PDWORD_PTR)((PBYTE)pPeb + offsetProcessHeap);
heapFlagsPtr = (PDWORD)((PBYTE)heap + GetHeapFlagsOffset(x64));
heapForceFlagsPtr = (PDWORD)((PBYTE)heap + GetHeapForceFlagsOffset(x64));
if (*heapFlagsPtr & ~HEAP_GROWABLE || *heapForceFlagsPtr != 0)
{
/* First instance of catching modified heap flags */
printf("That is not allowed!\n");
return -1;
}
/* For the case where we are using Process Environment Block 64 */
if (pPeb64)
{
/* Get the heap and the flags associated with it */
heap = (PVOID) * (PDWORD_PTR)((PBYTE)pPeb64 + 0x30);
heapFlagsPtr = (PDWORD)((PBYTE)heap + GetHeapFlagsOffset(true));
heapForceFlagsPtr = (PDWORD)((PBYTE)heap + GetHeapForceFlagsOffset(true));
if (*heapFlagsPtr & ~HEAP_GROWABLE || *heapForceFlagsPtr != 0)
{
/* Second instance of catching modified heap flags */
printf("That is not allowed!\n");
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}Heap Flag Check Bypass
- Override their value when being debugged
- PowerShell
- Plugins like ScyllaHide
- Set the HEAP_GROWABLE flag for the Heap Flags
- Set the Force Flags to 0
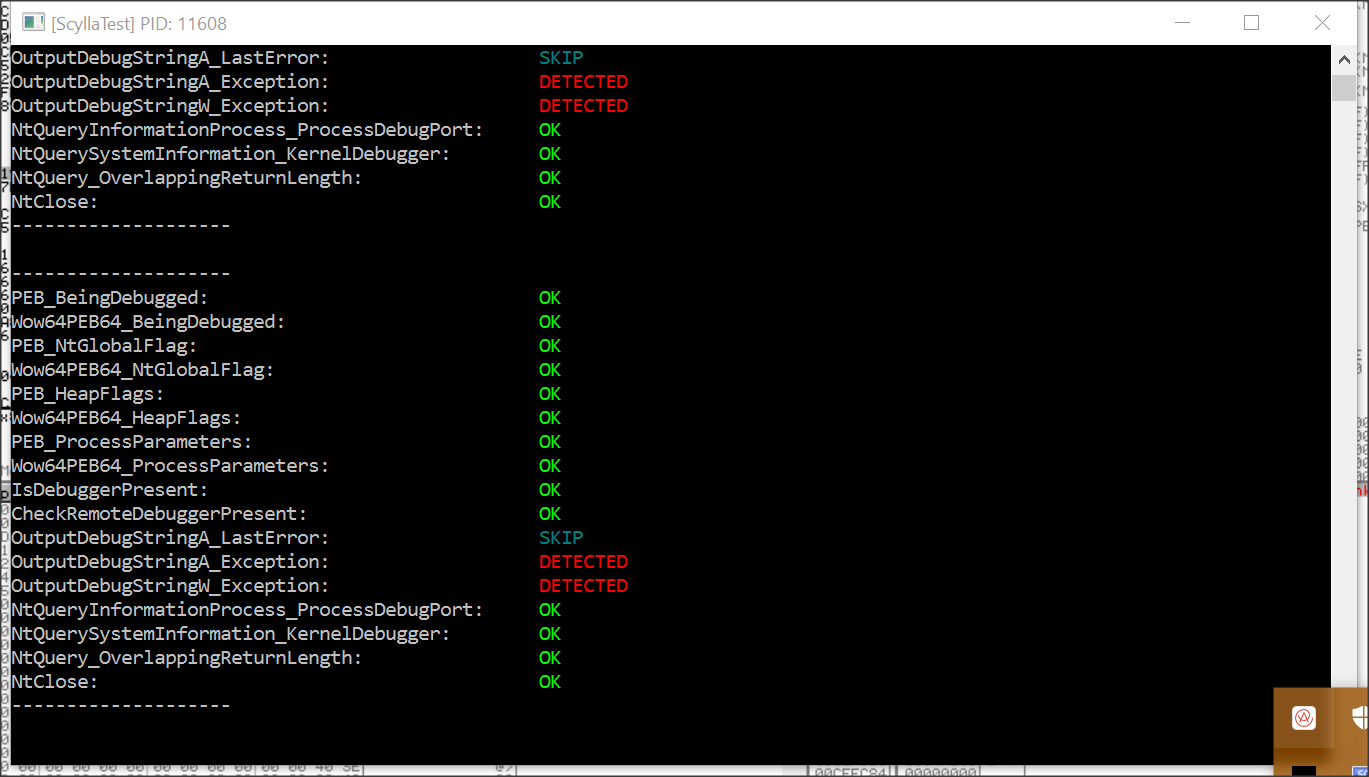
It is possible by using a different debugger, you can bypass this.
Checksum to Detect Software Breakpoints
- Performs checksum of functions.
- Checks for injected instructions (like int 3)
- Need to calculate checksum beforehand
- If checksums don't match, then it is likely a debugger is being used.
DWORD g_origCrc = value; //Initialize with Crc value
DWORD CalcFuncCrc(PUCHAR funcBegin, PUCHAR funcEnd)
{
DWORD crc = 0;
for (; funcBegin < funcEnd; ++funcBegin)
{
crc += *funcBegin;
}
return crc;
}
VOID BeginSimulation(){
//Code Goes here
}
VOID EndSimulation() {
//Can be empty or do nothing
}
int main(){
DWORD crc = CalcFuncCrc((PUCHAR)BeginSimulation, (PUCHAR)EndSimulation);
if (g_origCrc != crc)
{
printf("Stop debugging program!");
exit(-1);
}
}
DWORD g_origCrc = value; //Initialize with Crc value
DWORD CalcFuncCrc(PUCHAR funcBegin, PUCHAR funcEnd)
{
DWORD crc = 0;
for (; funcBegin < funcEnd; ++funcBegin)
{
crc += *funcBegin;
}
return crc;
}
VOID BeginSimulation(){
//Code Goes here
}
VOID EndSimulation() {
//Can be empty or do nothing
}
int main(){
DWORD crc = CalcFuncCrc((PUCHAR)BeginSimulation, (PUCHAR)EndSimulation);
if (g_origCrc != crc)
{
printf("Stop debugging program!");
exit(-1);
}
}
The address to Begin Simulation and End Simulation are used to calculate funcBegin and FuncEnd
Checksum Bypass
- No universal way of bypassing
- Implementation dependent
- Override the value being checked with the value of the original checksum
- Change the output of calculating checksum with a constant
Hardware Breakpoint Check
- Uses Windows API CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS to determine whether debug registers are set.
- Dr0 - Dr3 are for hardware breakpoints (Dr4-Dr7 are used for other purposes).
int main()
{
CONTEXT ctx = {};
ctx.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS;
if (GetThreadContext(GetCurrentThread(), &ctx))
{
if (ctx.Dr0 != 0 || ctx.Dr1 != 0 || ctx.Dr2 != 0 || ctx.Dr3 != 0)
{
printf("Stop debugging program!");
exit(-1);
}
}
}Hardware Breakpoint Check Bypass
- Based on the Windows API We know that GetThreadContext calls NtGetContextThread
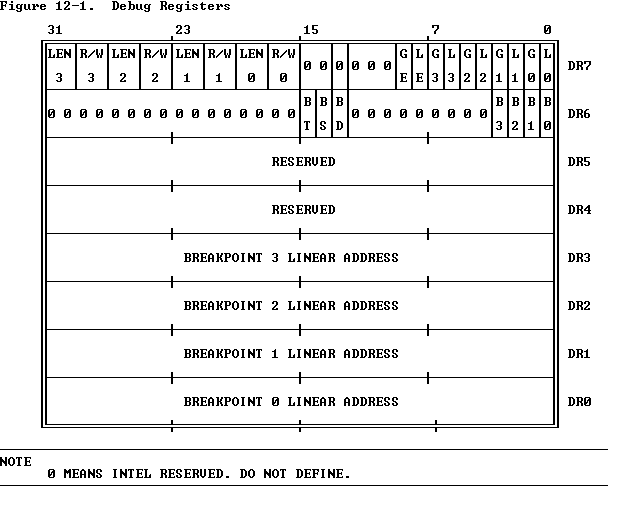
- After Retrieving thread, reset the CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS
- Sets Dr0 - Dr7 to all be 0
- Can be implemented through NtSetContextThread
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
/* From https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/367-anti-reverse-engineering-protection-techniques-to-use-before-releasing-software */
typedef NTSTATUS(NTAPI *pfnNtGetContextThread)(
_In_ HANDLE ThreadHandle,
_Out_ PCONTEXT pContext
);
typedef NTSTATUS(NTAPI *pfnNtSetContextThread)(
_In_ HANDLE ThreadHandle,
_In_ PCONTEXT pContext
);
pfnNtGetContextThread g_origNtGetContextThread = NULL;
pfnNtSetContextThread g_origNtSetContextThread = NULL;
NTSTATUS NTAPI HookNtGetContextThread(
_In_ HANDLE ThreadHandle,
_Out_ PCONTEXT pContext)
{
DWORD backupContextFlags = pContext->ContextFlags;
pContext->ContextFlags &= ~CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS;
NTSTATUS status = g_origNtGetContextThread(ThreadHandle, pContext);
pContext->ContextFlags = backupContextFlags;
return status;
}
NTSTATUS NTAPI HookNtSetContextThread(
_In_ HANDLE ThreadHandle,
_In_ PCONTEXT pContext)
{
DWORD backupContextFlags = pContext->ContextFlags;
pContext->ContextFlags &= ~CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS;
NTSTATUS status = g_origNtSetContextThread(ThreadHandle, pContext);
pContext->ContextFlags = backupContextFlags;
return status;
}
void HookThreadContext()
{
HMODULE hNtDll = LoadLibrary(TEXT("ntdll.dll"));
g_origNtGetContextThread = (pfnNtGetContextThread)GetProcAddress(hNtDll, "NtGetContextThread");
g_origNtSetContextThread = (pfnNtSetContextThread)GetProcAddress(hNtDll, "NtSetContextThread");
Mhook_SetHook((PVOID*)&g_origNtGetContextThread, HookNtGetContextThread);
}Other Considerations
- Handle Tracing
- Checking the handle error code when calling Close Handle
- Debug messages
- Windows 10 - Raise Exception prints directly to a debugger (if fails then no debugger detected).
EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION ExceptionRoutine(
PEXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord,
PVOID EstablisherFrame,
PCONTEXT ContextRecord,
PVOID DispatcherContext)
{
if (EXCEPTION_INVALID_HANDLE == ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode)
{
std::cout << "Stop debugging program!" << std::endl;
exit(-1);
}
return ExceptionContinueExecution;
}
int main()
{
__asm
{
// set SEH handler
push ExceptionRoutine
push dword ptr fs : [0]
mov dword ptr fs : [0], esp
}
CloseHandle((HANDLE)0xBAAD);
__asm
{
// return original SEH handler
mov eax, [esp]
mov dword ptr fs : [0], eax
add esp, 8
}
return 0
}#define DBG_PRINTEXCEPTION_WIDE_C 0x4001000A
WCHAR * outputString = L"Any text";
ULONG_PTR args[4] = {0};
args[0] = (ULONG_PTR)wcslen(outputString) + 1;
args[1] = (ULONG_PTR)outputString;
__try
{
RaiseException(DBG_PRINTEXCEPTION_WIDE_C, 0, 4, args);
printf("Debugger detected");
}
__except (EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER)
{
printf("Debugger NOT detected");
}Learn More
-
Anton Kukoba's Blog
- www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/367-anti-reverse-engineering-protection-techniques-to-use-before-releasing-software
-
Cody Cutler and Anton Burtsev's PowerPoint Slide
- www.cs.utah.edu/~aburtsev/malw-sem/slides/02-anti-debugging.pdf
-
Peter Ferrie's Anti-Debugging Reference
- www.anti-reversing.com/Downloads/Anti-Reversing/The_Ultimate_Anti-Reversing_Reference.pdf
- Slides: https://slides.com/ragnarsecurity/windows-anti-debugging/edit
Thank You
Windows Anti-Debugging Techniques
By Ragnar Security
Windows Anti-Debugging Techniques
- 684



