FESTIM: empowering tritium transport modelling for SPARC and ARC
Remi Delaporte-Mathurin



Outline
- Why FESTIM?
- What is FESTIM?
- FESTIM for SPARC
- FESTIM for ARC
- FESTIM & CFS
Why FESTIM
The tritium issue
- Radioactive substance
- Health risks
→ Limit inventories
→ Detritiation
→ Accurate assessment
Safety hazards
Risk of contamination
- Permeation to cooling systems
- Challenges for maintenance and safety
→ Permeation barriers
→ Clean-up
Tritium self-sufficiency
- Optimised fuel cycle is required for a fusion economy
→ Breeding blanket design
→ Sub-systems engineering
How to analyse this thermo-desorption spectrum?
What's the T inventory in the first wall of SPARC?
How much T will permeate to the coolant?
How long do we need to bake components for detritiation?
What is the extraction efficiency of the TES?
What is the T residence time of component X?
Hydrogen transport
Hydrogen transport

McNabb & Foster model
Mobile H concentration
Trapped H concentration
Temperature dependence
McNabb & Foster model
Time derivatives
McNabb & Foster model
Diffusive term
McNabb & Foster model
Trapping term
McNabb & Foster model
Detrapping term
Surface physics
Molecular dissociation and recombination
Sievert's law of solubility
Henry's law of solubility
Plasma + gas exposure
Application: ITER PFCs
We need a numerical tool
W
Cu
CuCrZr
Particle and heat fluxes
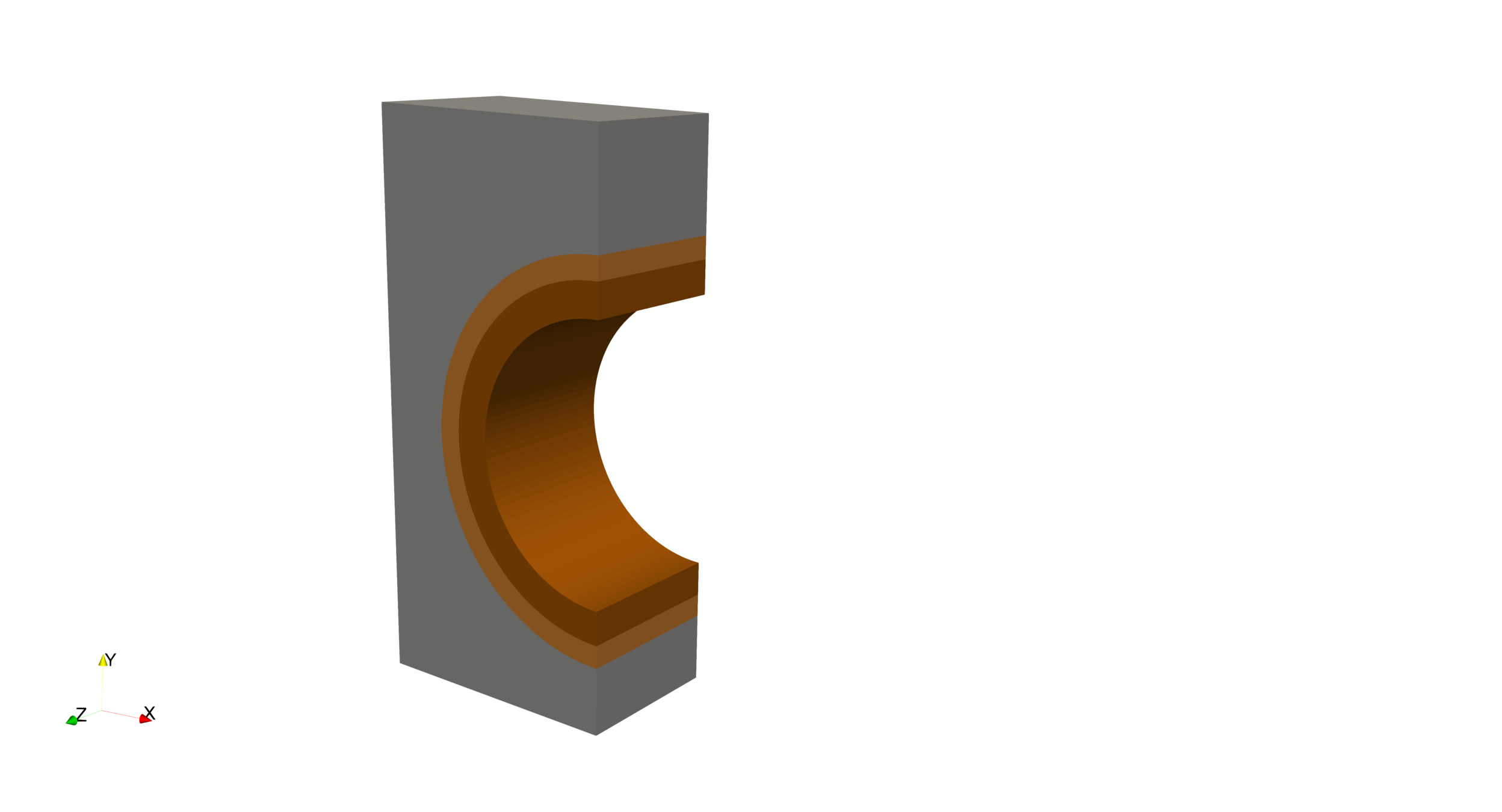

Convection
14 mm
Problem: predict T retention and permeation
- Multi-dimensional
- Multi-material
- non homogeneous temperature
What is FESTIM
User inputs
- Material properties
- Geometry
- Boundary conditions
- Initial conditions
Heat transfer model
Hydrogen transport model
FESTIM
Outputs
- Tritium concentration fields \(c(x,t)\)
- Temperature field \(T(x,t)\)
- surface fluxes
- inventories
- average concentration
- ...
2022
2019
Start of development
- 1D/2D/3D
- Finite elements
- Python
- multi-material
- Heat transfer
History of FESTIM
open-source
- development continuing at MIT
Oct 2023
v1.0 release
2024

FESTIM
An open-source python-based finite elements code for hydrogen transport
- Based on the FEniCS library
- Flexible
- Complex geometries
- Very well established library

FESTIM's philosophy
We want to make hydrogen transport simulations easy for everyone!
We also encourage contributions!
- Feedback (suggestions, bug reports...)
- Implement new features
- Bug fixing
- Documentation update (even small ones!)
- ...
Meet the development team
Jonathan Dufour
CEA, France
+ all contributors





FESTIM is open-source
✅ More transparency
✅ More collaborations
✅ More flexibility

The code is missing a feature?
Just add it!
Found a bug?
Report it and we'll fix it!

FESTIM's development workflow
- Anyone can create their own copy (fork) of the FESTIM repository and make changes
- PRs are a place where FESTIM's maintainers review the proposed changes
- ~500 tests are automatically run
- The PR is only merged when all the tests pass ✅

fork
fork
pull request
FESTIM
Jane Doe
FESTIM
John Doe
FESTIM
festim-dev
pull request
How to use FESTIM


Documentation
and installation instructions
FESTIM is user-friendly

- Very easy to learn
- Plenty of libraries (numpy, scipy, matplotlib, HTM...)
- Inuitive interface
conda install -c conda-forge fenics
pip install festimTwo lines to install!
import festim as F
import numpy as np
my_model = F.Simulation()
my_model.mesh = F.MeshFromVertices(
vertices=np.linspace(0, 1e-6, num=1001)
)
my_model.materials = F.Material(id=1, D_0=1.9e-7, E_D=0.2)
my_model.T = 500 # K
my_model.boundary_conditions = [
F.DirichletBC(
surfaces=[1, 2],
value=1e15, # H/m3/s
field=0
)
]
my_model.settings = F.Settings(
absolute_tolerance=1e10,
relative_tolerance=1e-10,
final_time=100 # s
)
my_model.dt = F.Stepsize(0.1) # s
my_model.initialise()
my_model.run()FESTIM workshop
The FESTIM workshop is a series of tutorials
from basic problems to more advance cases
FESTIM is fully documented
Check out the complete documentation at
Installation instructions
User guide
- Development guide
- Tutorials
- Theory background
- API reference
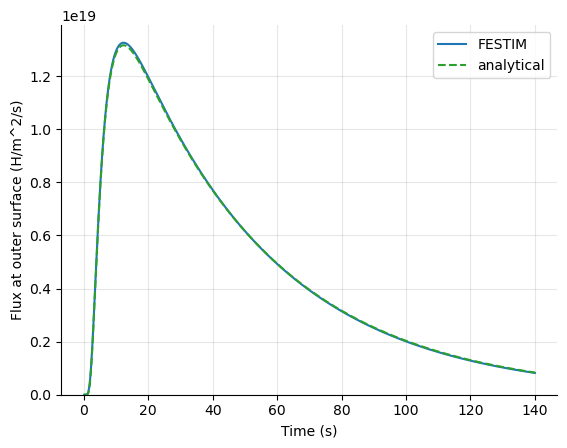
FESTIM is verified & validated
- Validated against TDS, permeation experiments...
- Verified against analytical solutions in many different problems
- New V&V online book
festim-vv-report.readthedocs.io
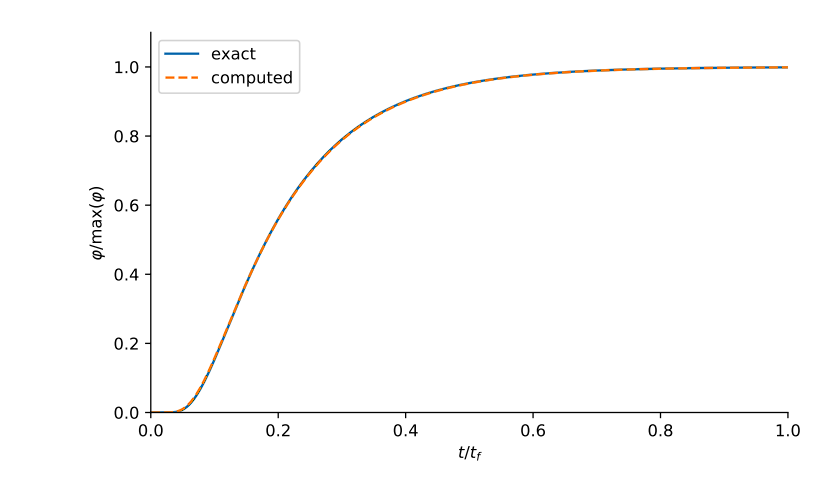
V&V
Effective-diffusion through a slab
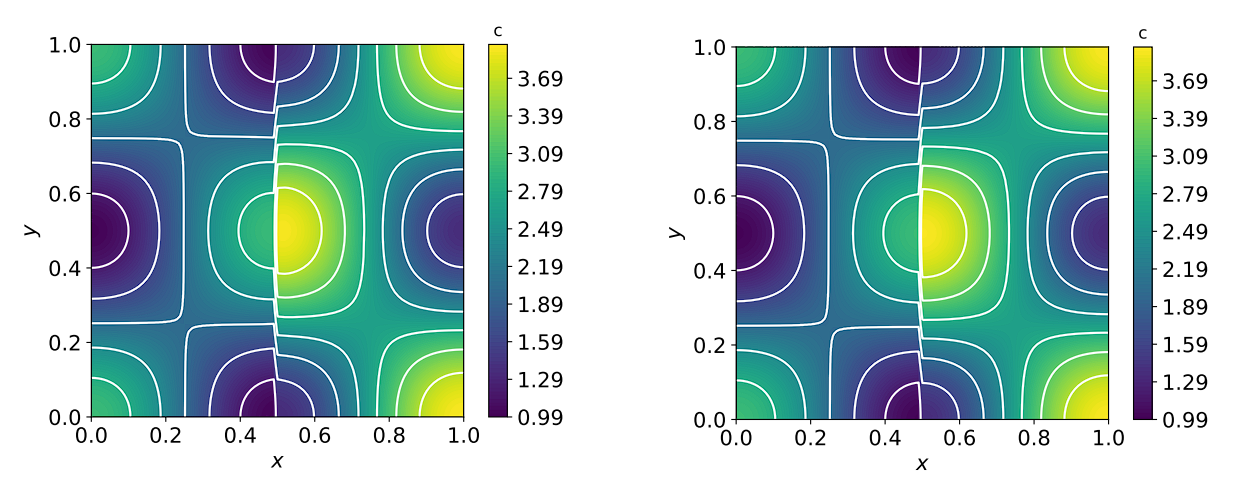
2D multi-material
Exact
Computed concentration
Method of Exact Solution
governing equations
exact solutions
parameters (sources, BCs, ICs)
FESTIM
computed solutions
solve
run
compare
⚠️sometimes very complex!
Method of Manufactured Solutions
governing equations
manufactured solutions
source terms, BCs and ICs
FESTIM
computed solutions
compare
FESTIM is used worldwide

8 private companies
10 universities
16 research organisations
📈5 years of development
📑13+ publications
🗣️110+ citations
🧑💻14+ contributors
🏛️24+ institutions using the code
🧑💻27+ Slack members
⭐75+ stars on GitHub
3 workshops
FESTIM in numbers

Evolution of GitHub stars
Open source
SOFE workshop
New reference paper
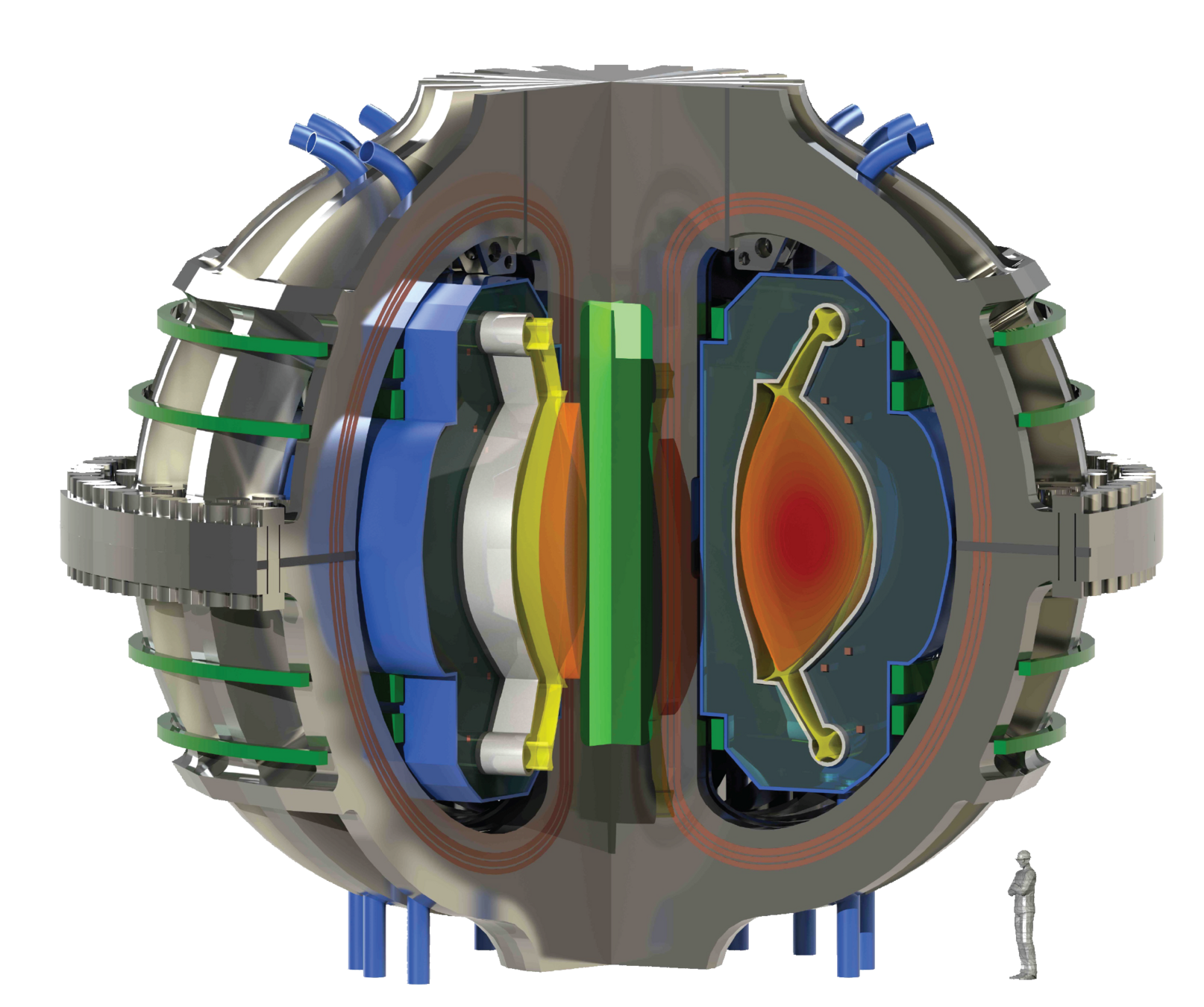
FESTIM for SPARC
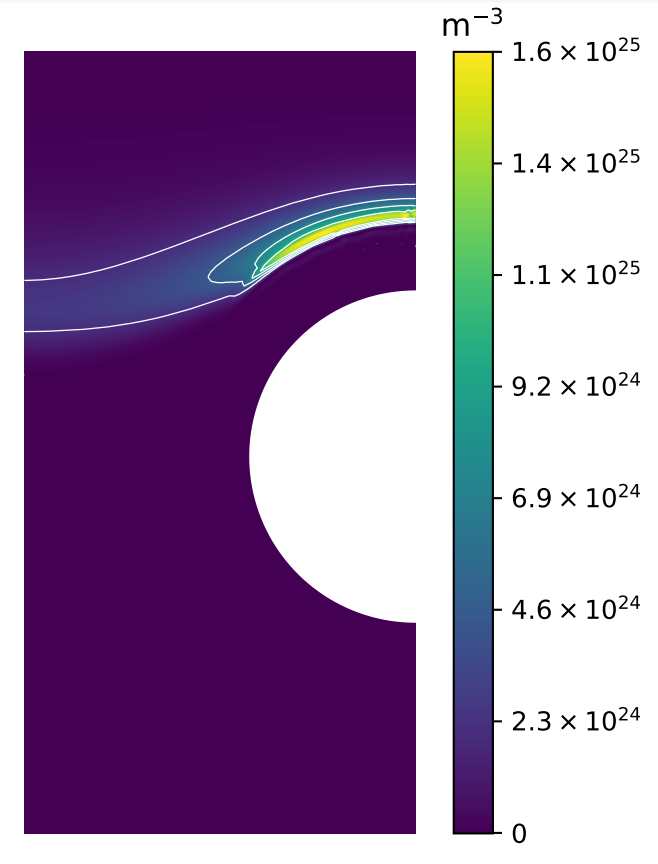
Retention studies

- Delaporte-Mathurin et al 2024 International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 63 786–802
- Delaporte-Mathurin et al 2024 Nucl. Fusion 64 026003

- ITER plasma facing components
- Transient estimation of tritium retention
T concentration
At
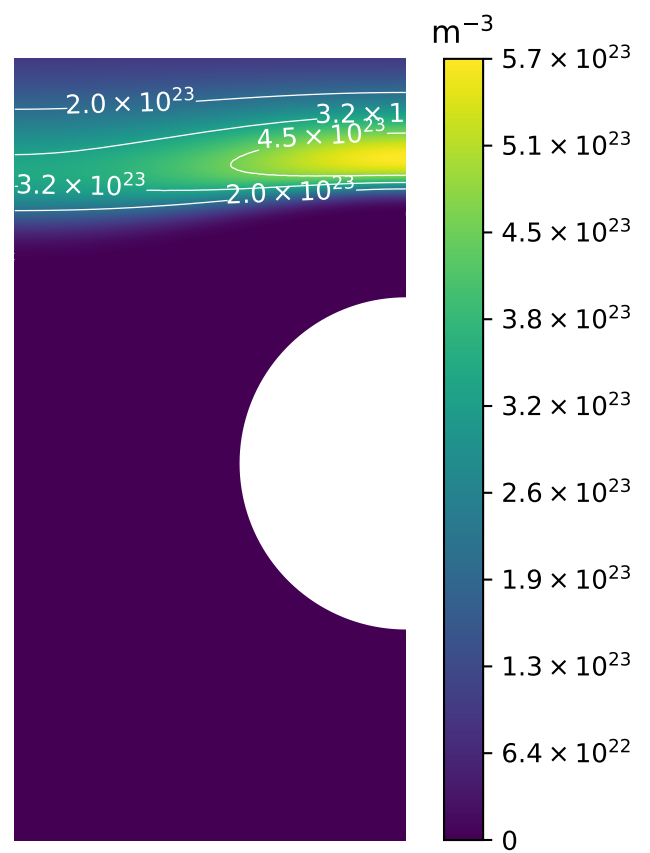
Parametric study


+
+
Parametric study
+
+

+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Parametric study

At
Gaussian Process Regression (GPR)
Parametric study

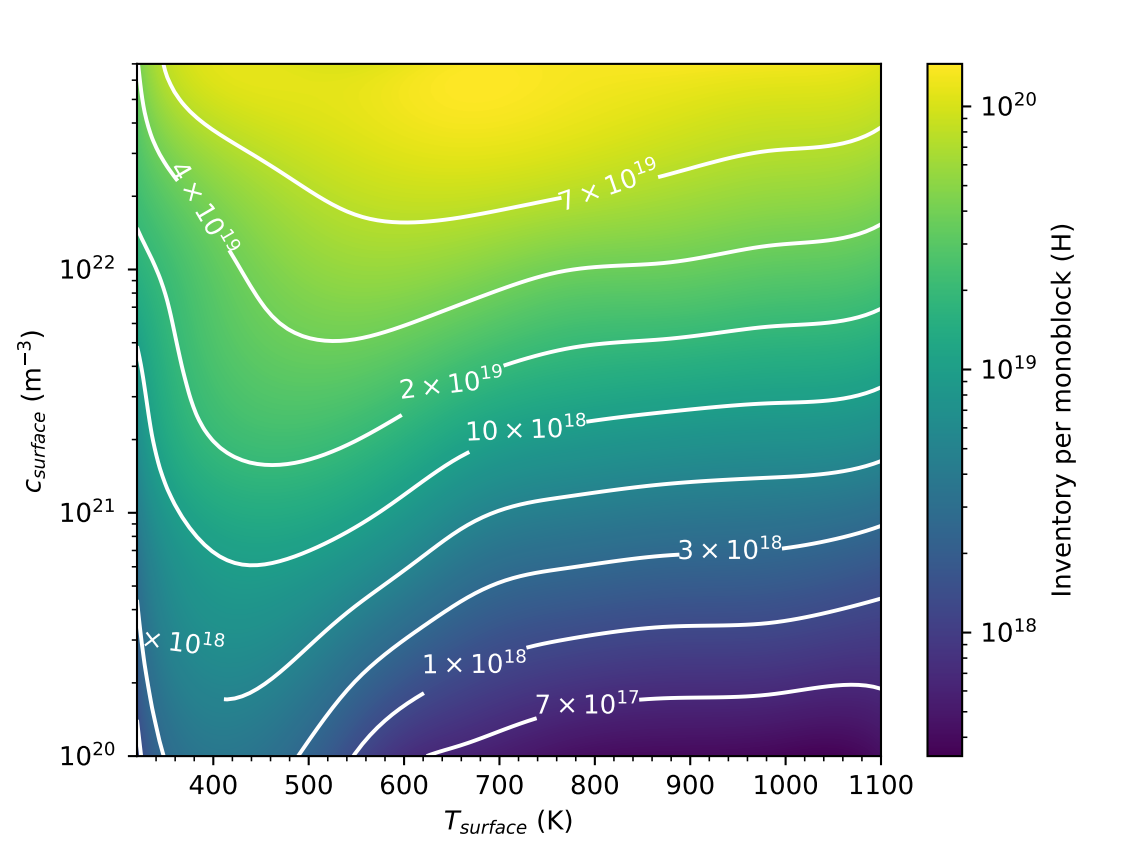
Monoblock behaviour law
At
Rapid assessment of monoblock inventories
Inner Vertical Target
Inner Strike Point
Outer Strike Point
Outer Vertical Target
Dome
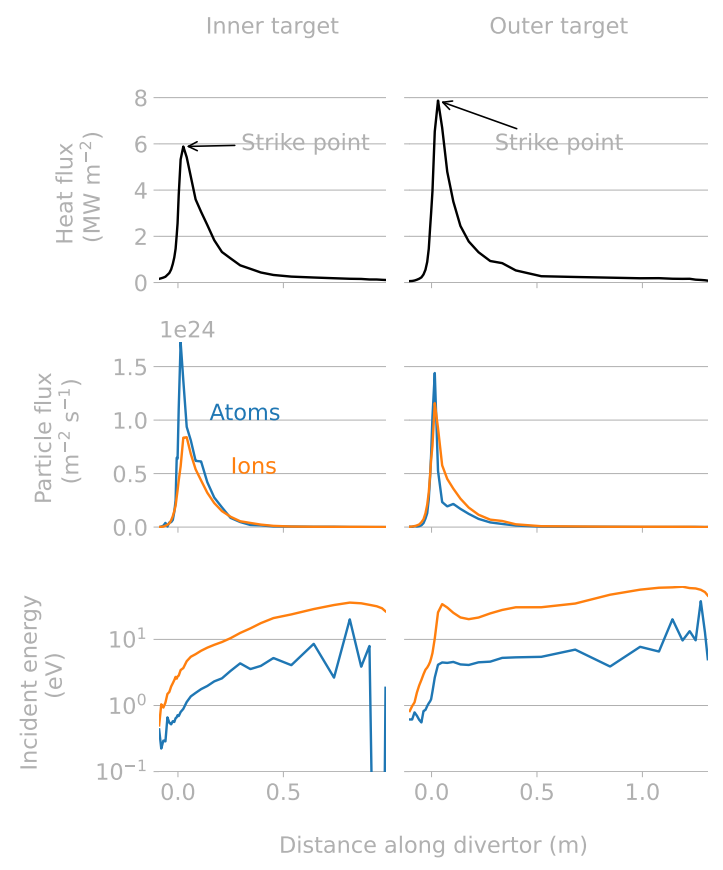
Converting SOLPS plasma inputs...
...to divertor inventory

Monoblock inventory

+
Divertor inventory

SOLPS runs: Pitts et al NME (2020)
- The strike point is not the maximum H inventory
- The total divertor inventory can be computed
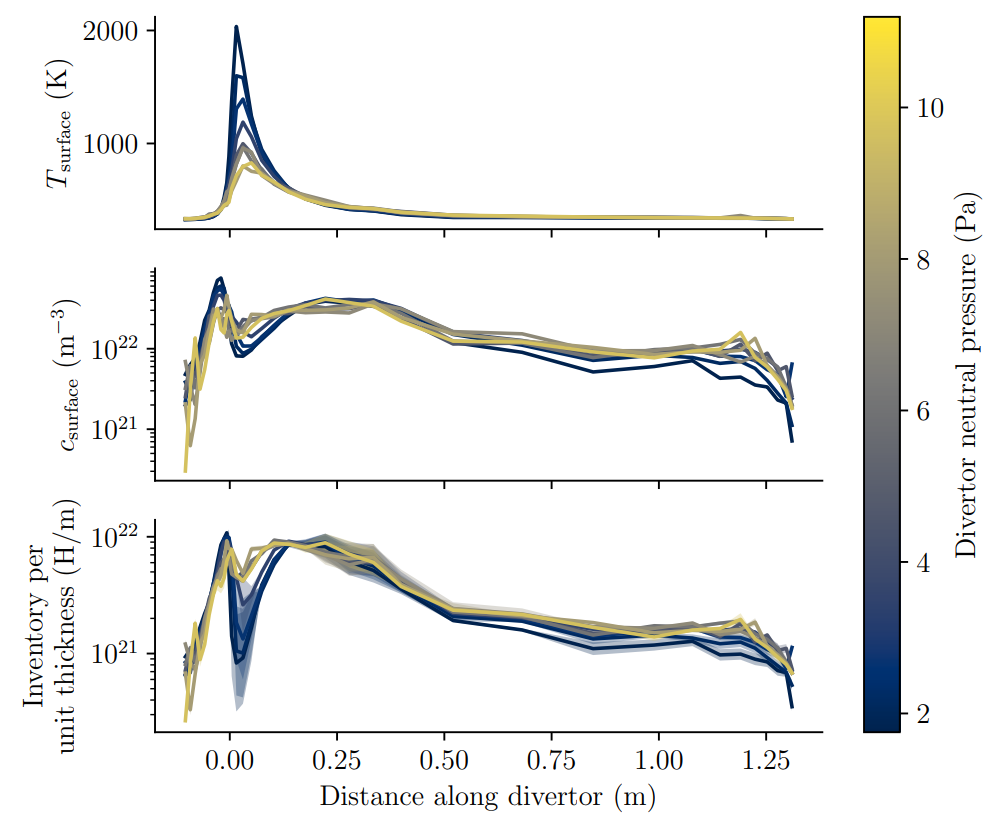
The inventory is estimated from the surrogate model
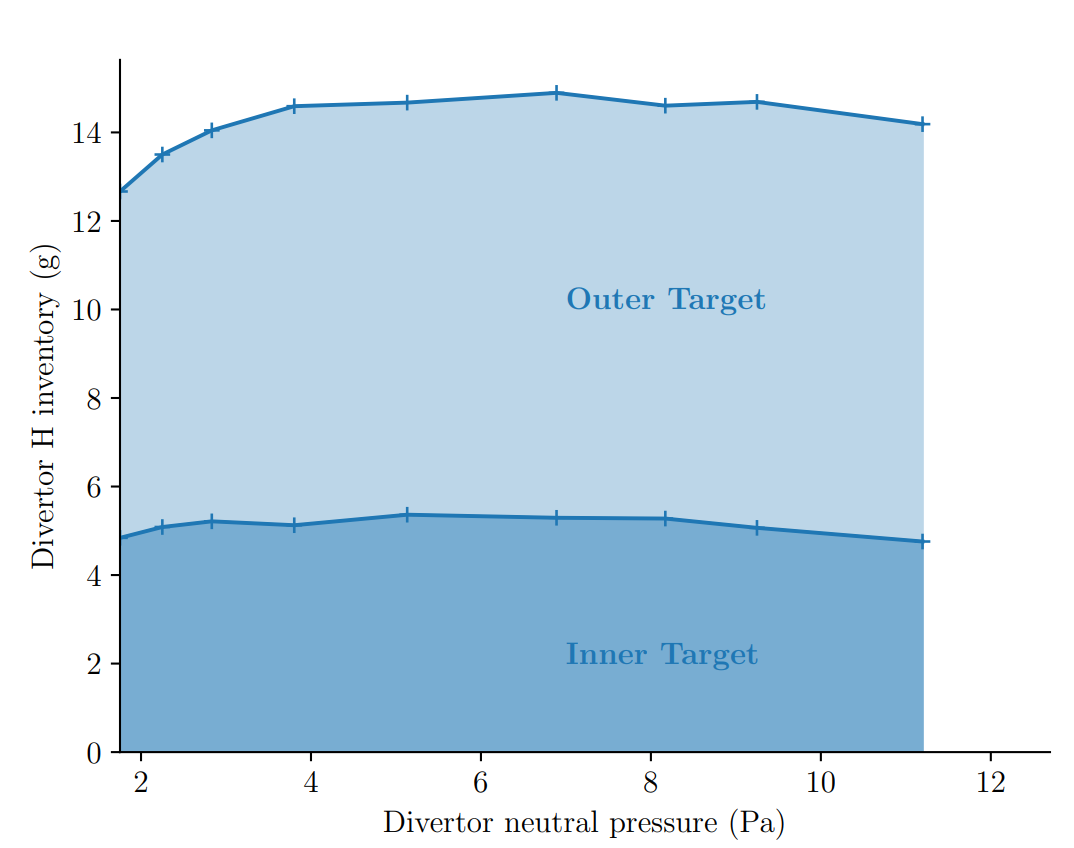
Divertor H inventory (g) at \( t = 10^7 \, \mathrm{s}\)
Safety limit \( = \) 700 g T
\( \max \approx \) 2 % limit ✅
ITER divertor inventory
Detritiation studies


Influence of ELMs on retention

- 1D model of a ITER monoblock
- Transient heat transfer simulation
- Varying surface heat flux
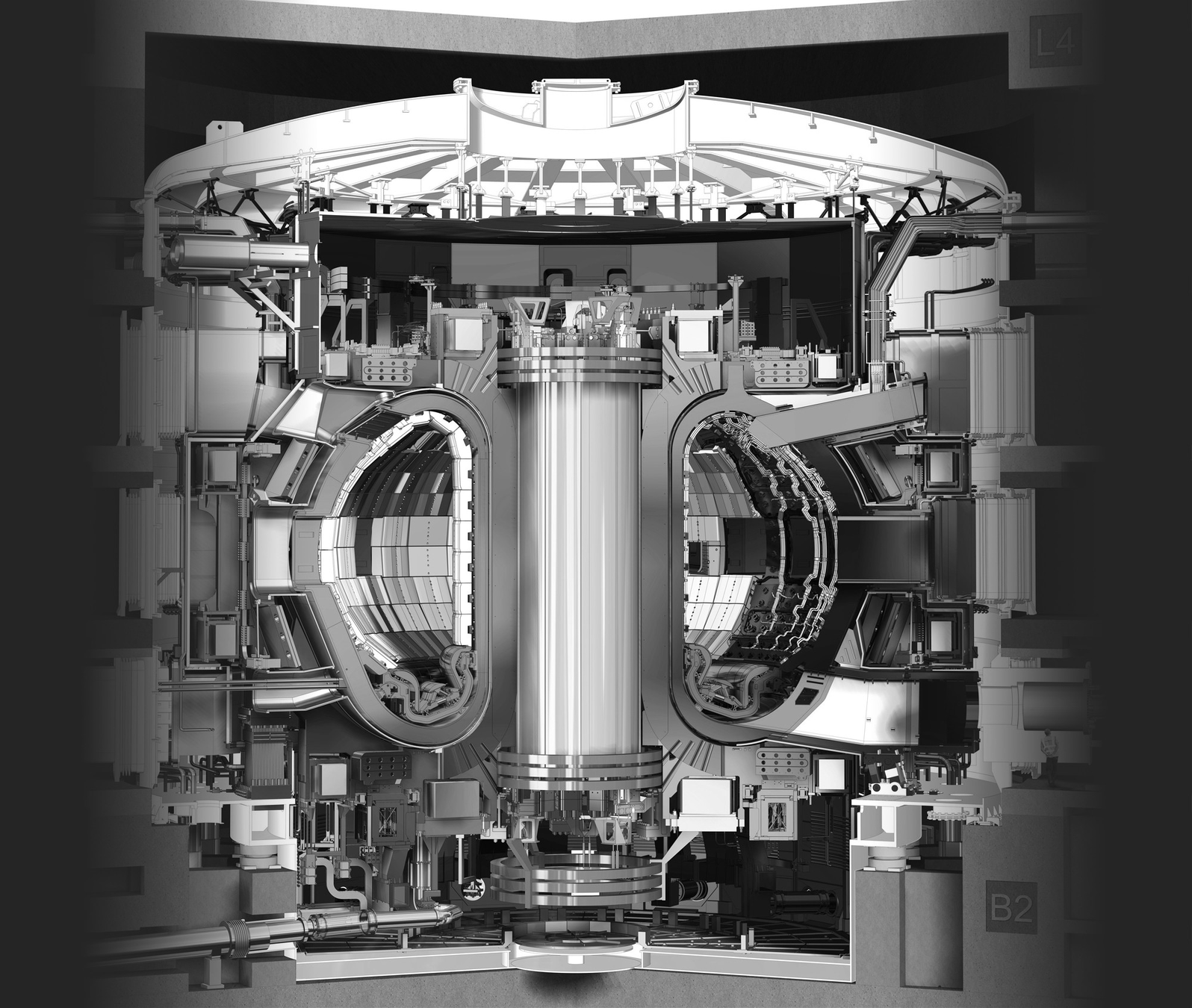
FESTIM for ARC
Breeding Blanket modelling



- DEMO WCLL
- Complex 3D geometry
- Coupled to fluid dynamics
- Tritium generation in the LiPb volume (computed from OpenMC)
James Dark et al 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 116076
Tritium extraction system

courtesy of K. Dunnell (MIT)
- Permeation Against Vacuum
- Complex 3D geometry
- Coupled with fluid dynamics
- Tritium extraction from permeable membranes

Tritium extraction system
courtesy of K. Dunnell (MIT)

① neutrons are generated
② tritium is created from nuclear reactions
③ tritium is transported in the salt
④ tritium is released into the gas phase
⑤ tritium is collected and counted
BABY breeding experiment
BABY breeding experiment

Velocity
Temperature
Tritium concentration
BABY breeding experiment
courtesy of C. Weaver (MIT)


0D model
FESTIM model
Metal Foil Pumps for DIR

- H is implanted in the first \( 10 \ \mathrm{nm} \)
- Super-permeation regime is attained at high recombination energy (upstream surface)
- Source code

Benedikt & Day, (2017) Fusion Engineering and Design
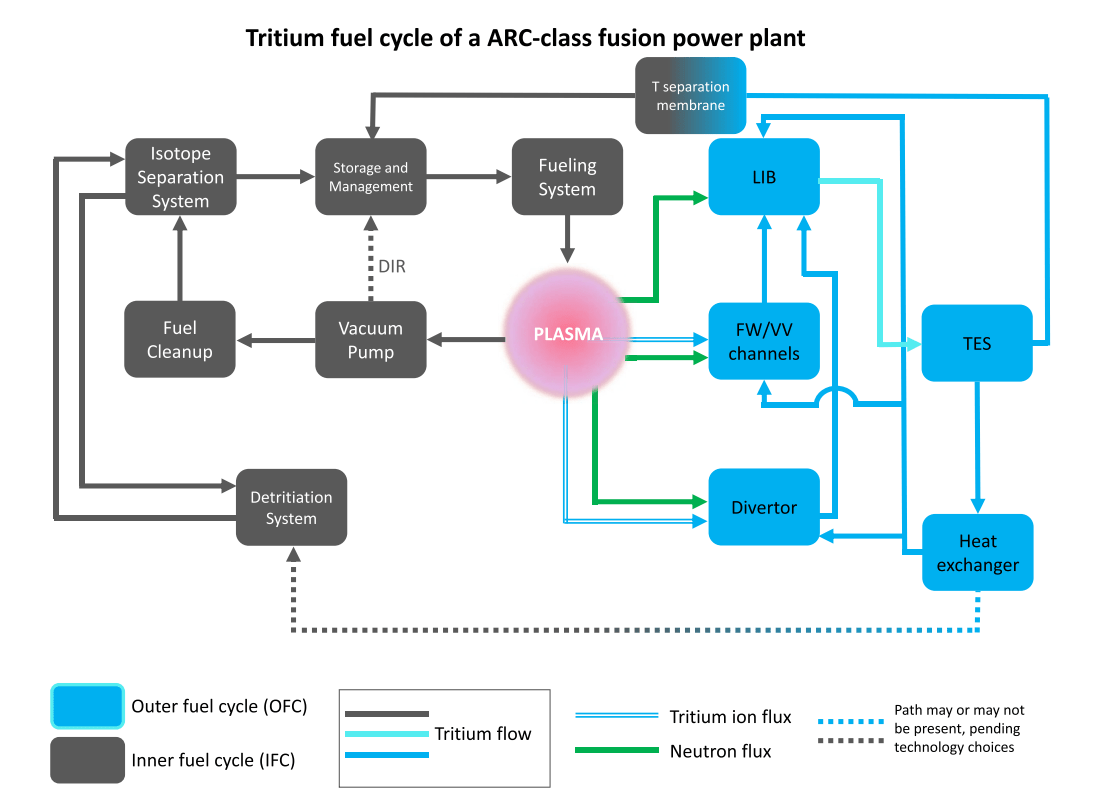
FESTIM can inform fuel cycle models
Text
Permeation barriers
Towards the future: FESTIM 2
Chemical reactions
- More suitable for molten salts
- Even more flexibility
Multi-species transport
- Isotopic exchange
- Multi-level trapping
- Transport of impurities, He, interstitials...
- Validation on WEST PFCs
Finite element engine upgrade
- Better performances (including in parallel)
- Bigger models
- Mixed topology meshes
Graphical user interface
Follow the development roadmap
New examples
Isotope swapping


same underlying equations!
Can be represented by festim.Reaction
Isotope swapping
my_model.species = [
mobile_H,
mobile_D,
trapped_H,
trapped_D,
]
my_model.reactions = [
F.Reaction(
k_0=k_0,
E_k=0.39,
p_0=1e13,
E_p=1.2,
reactant1=mobile_H,
reactant2=empty_trap,
product=trapped_H,
volume=my_subdomain,
),
F.Reaction(
k_0=k_0,
E_k=0.39,
p_0=1e13,
E_p=1.2,
reactant1=mobile_D,
reactant2=empty_trap,
product=trapped_D,
volume=my_subdomain,
),
F.Reaction(
k_0=k_0,
E_k=0.1,
p_0=k_0,
E_p=0.1,
reactant1=mobile_H,
reactant2=trapped_D,
product=[mobile_D, trapped_H],
volume=my_subdomain,
),
]Usual trapping reactions
Swapping reaction
4 species are defined
Multi-isotope, multi-level trapping

- 7 different species
- 6 reactions
- \( c_H = 10^{20} \ \mathrm{m^{-3}} \) on the left
- \( c_D = 10^{19} \ \mathrm{m^{-3}} \) on the right
- Source code available here
1 trap, 2 levels, 2 isotopes
\( \mathrm{H} \) = mobile H
\( \mathrm{D} \) = mobile D
\( [\mathrm{H}_x\mathrm{D}_y] \) = \(x\) H and \(y\) D in trap
Spherical cavity trapping

see Zibrov and Schmid, NME, 2024
for complete description
- Implementation in FESTIM of the spherical cavity trapping model developed by Zibrov and Schmid
- Custom trapping equations
- Smooth implementation in FESTIM
Anisotropy
- Anisotropic materials can be simulated with very few modifications



FESTIM & CFS
Your next tritium systems are likely to rely on tritium transport modelling.
Why not get involved in FESTIM to make sure it suits your needs?
Other application cases
Thermo-desorption
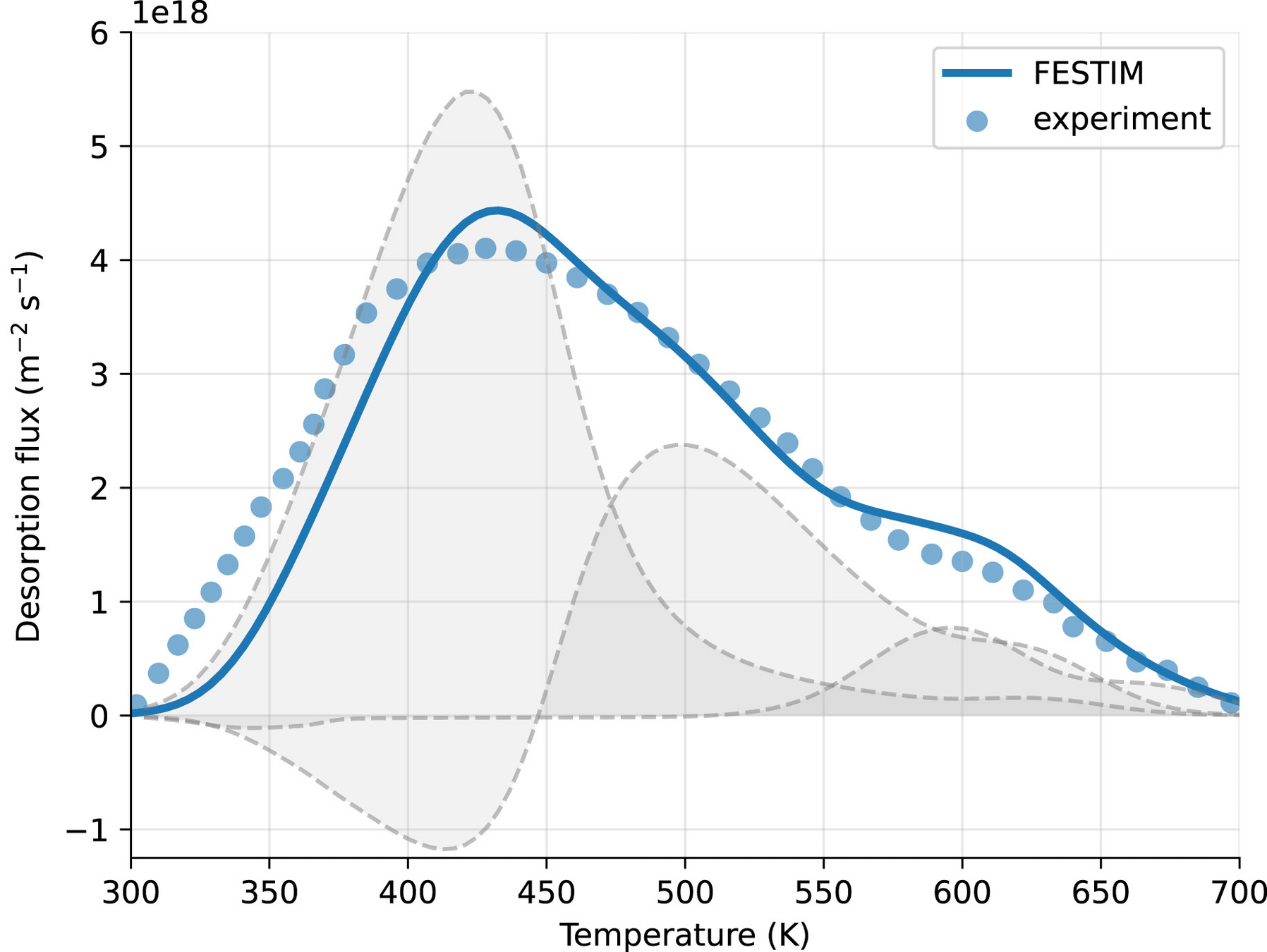
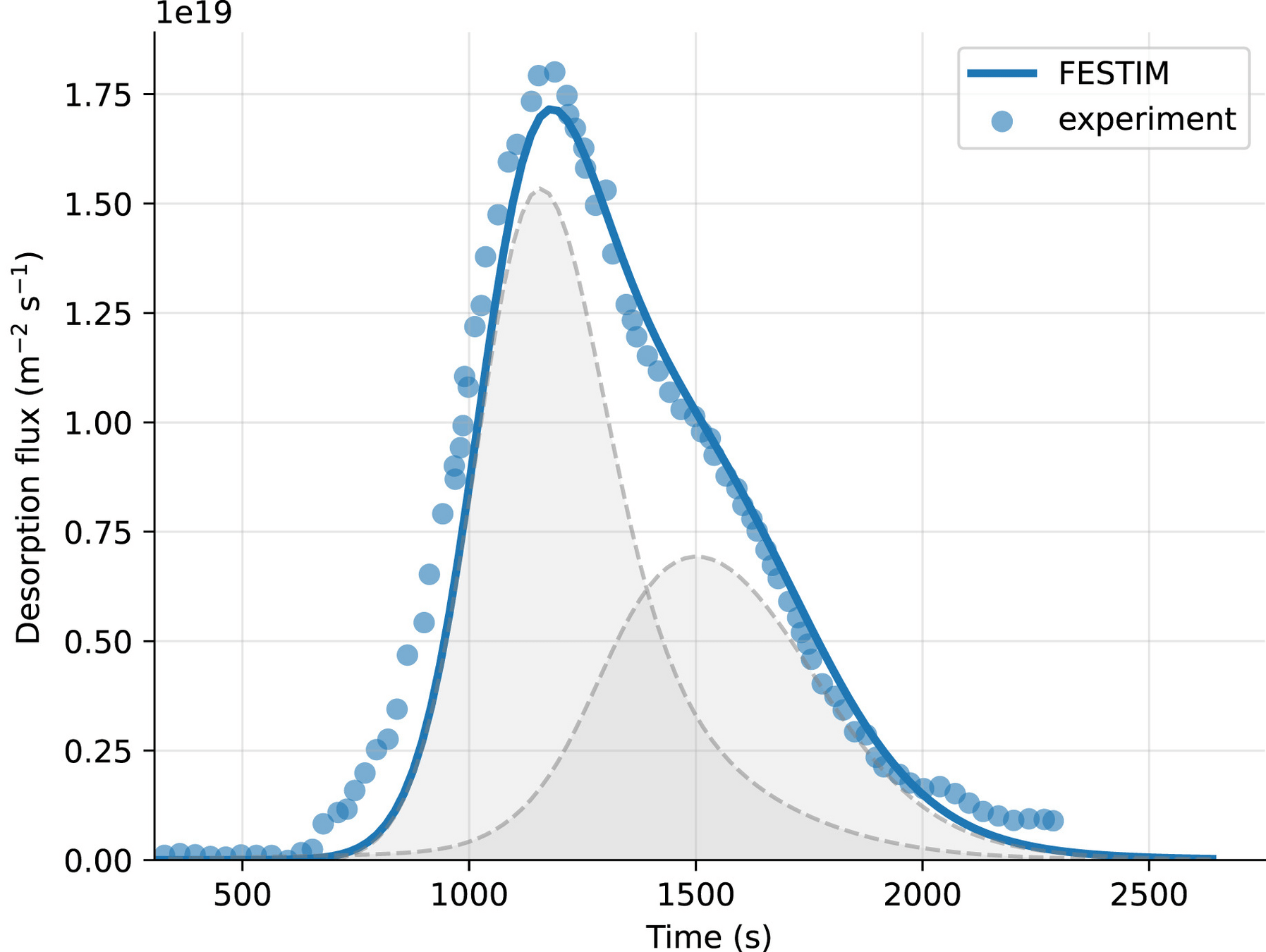
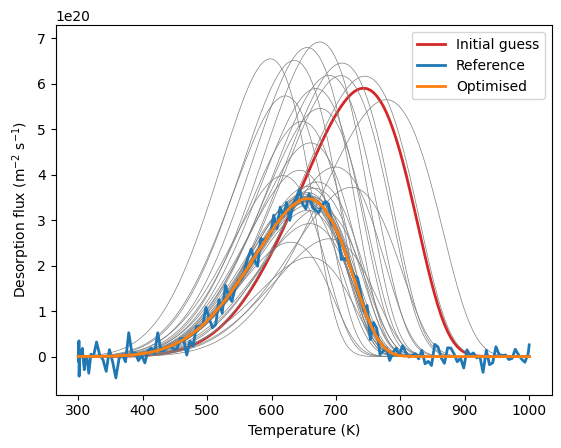
- TDS analysis
- Automated fitting routines
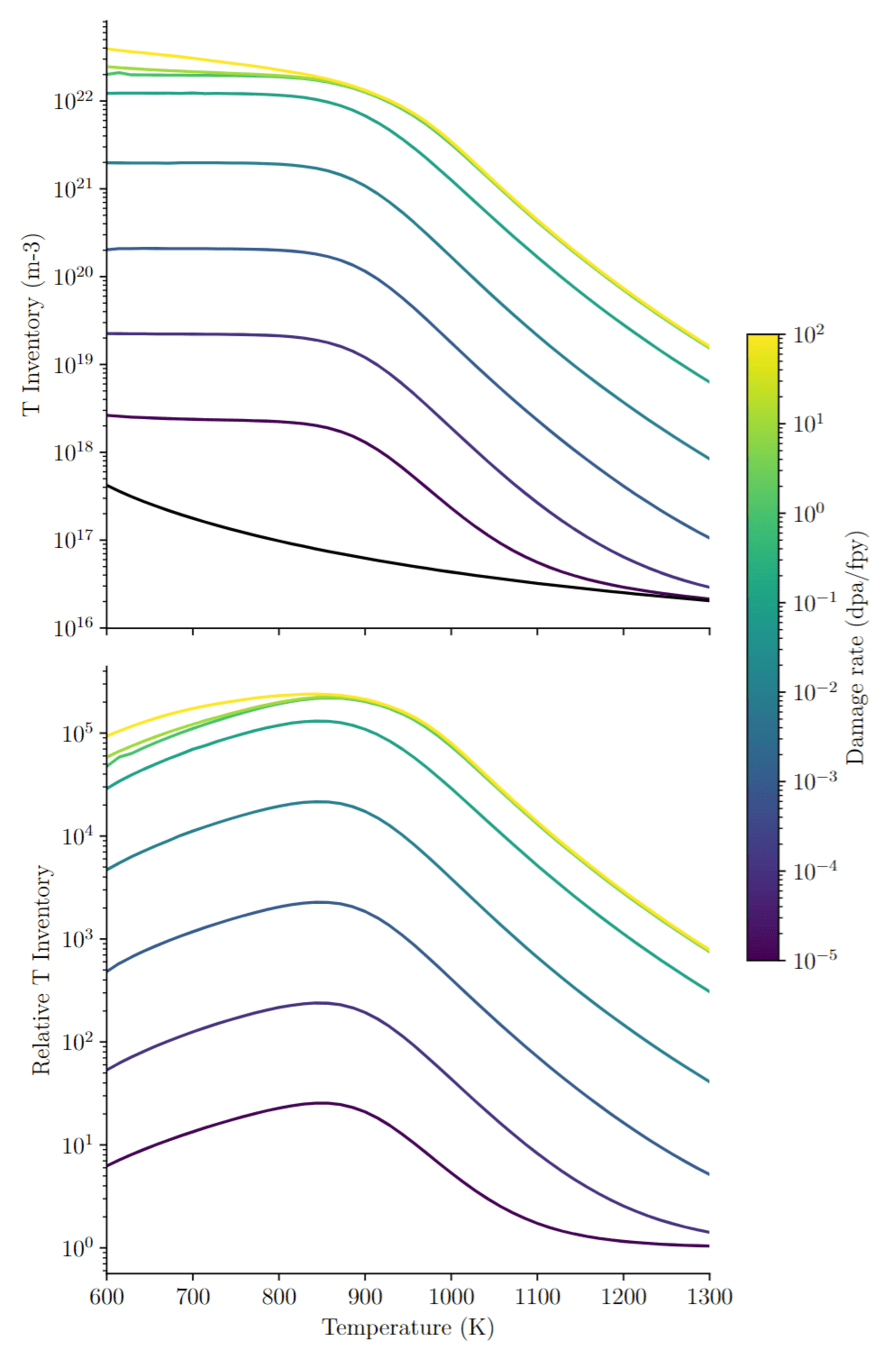
Neutron-induced trap model

- Custom trapping model
- Dynamic evolution of trap densities including annealing
- Parametrised on TDS data from T Schwartz Selinger

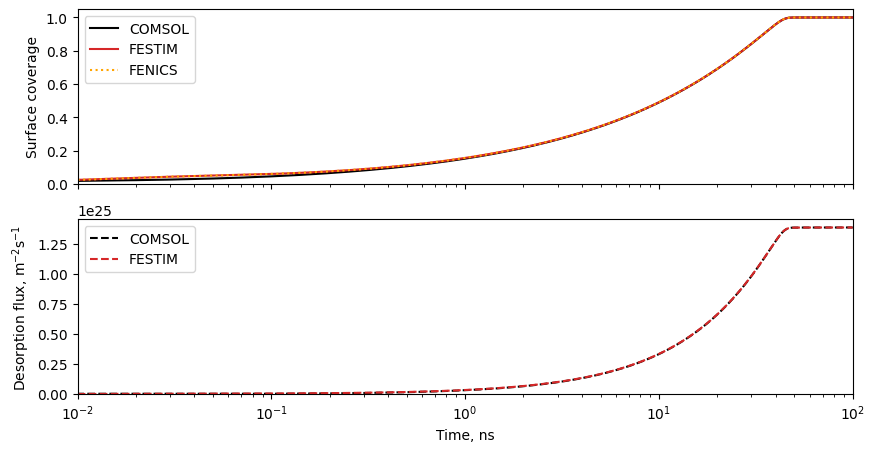
Permeation experiment

No barrier
with barrier
Permeation barrier
Substrate
High H pressure
Low H pressure
Conservation of chemical potential
Permeation flux
Kinetic surface model
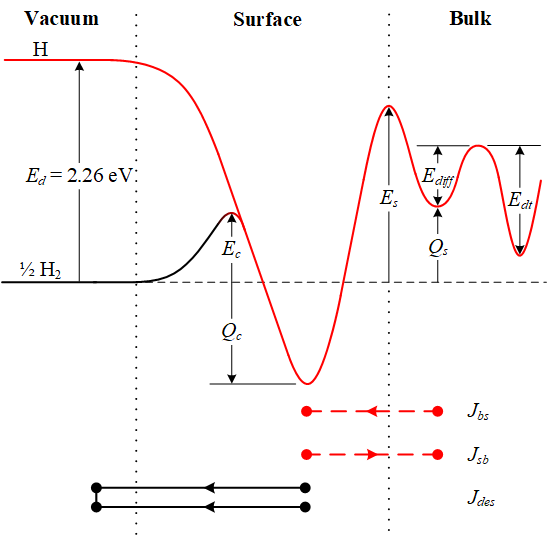
courtesy of V. Kulagin (MePhi)
Depleting enclosure
\(P(t)\)
permeation flux
Enclosure
FESTIM @ CFS
By Remi Delaporte-Mathurin
FESTIM @ CFS
- 619






