SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT
By Ricardo A. Bermúdez Osorio
¿DO YOU KNOW YOUR STUFF?
SCM: Is the discipline of identifying the configuration of a system at distinct points in time for the purpose of systematically controlling changes to the configuration and maintaining the integrity and traceability of the configuration throughout the system life cycle.
* SCM Is closely related to the software quality assurance (SQA) activity. As defined in the Software Quality knowledge area (KA)
* SCM controls the evolution and integrity of a product by identifying its elements
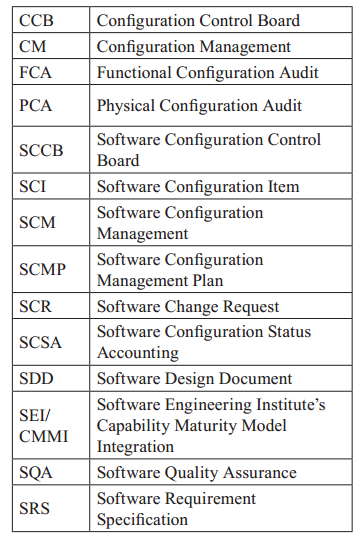
ACRONYMS
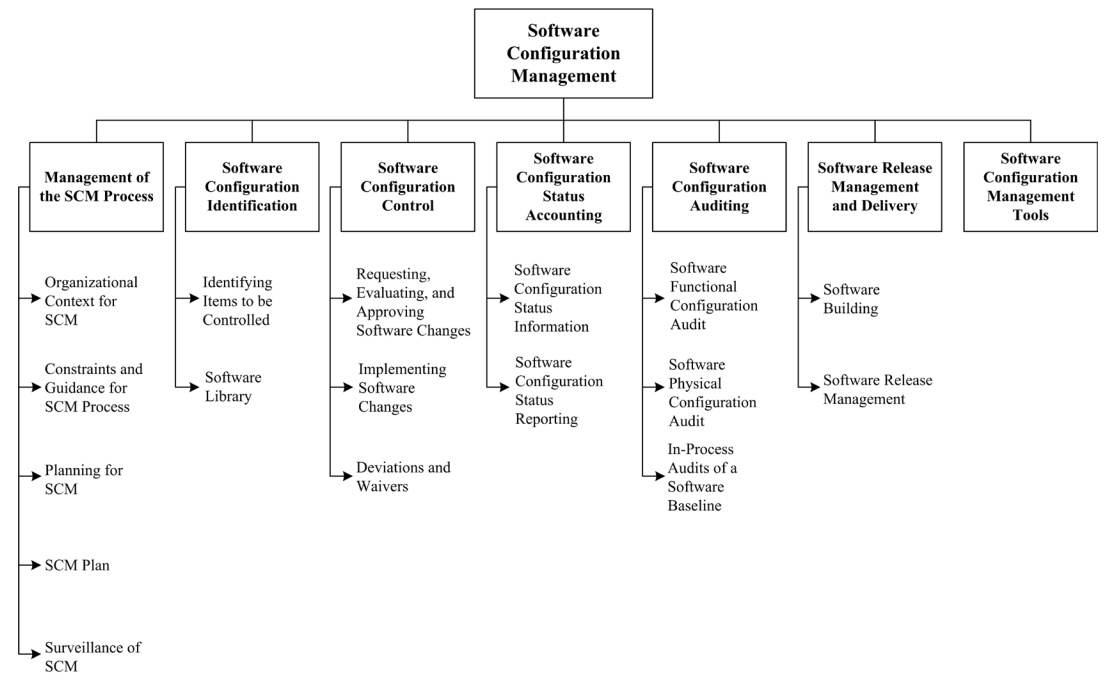
1. Management of the SCM Process: Organizational context
- Knowledge
- Relationships among organizational elements
1. Management of the SCM Process: Constraints and guidance
- Policies
- Procedures
- Acquirer-supplier relationship
- Particular software life cycle and formalism
1. Management of the SCM Process: Planning for SCM
- Organizational context
- Aplicable constraints
- Commonly accepted guidance
- Nature of the project (Size, safety criticality, security)
SC Identification
SC Control
SC Status accounting
SC Auditing
SC Release management
and delivery
1. Management of the SCM Process: Planning for SCM
In addition, issues such as organization and responsibilities, resources and schedules, tool selection and implementation, vendor and subcontractor control, and interface control are typically considered
Also... critical successful factors like
- Organization and responsabilities
- Resources and schedules
- Tool selection and implementation
- Vendor/subcontractor control
- Interface control
1. Management of the SCM Process: Planning for SCM
1. Management of the SCM Process: Planning for SCM
The results of the planning activity are
recorded in an SCM Plan (SCMP), which is typically subject to SQA review and audit
1. Management of the SCM Process: SCM Plan
SCMP is a "Living Document"
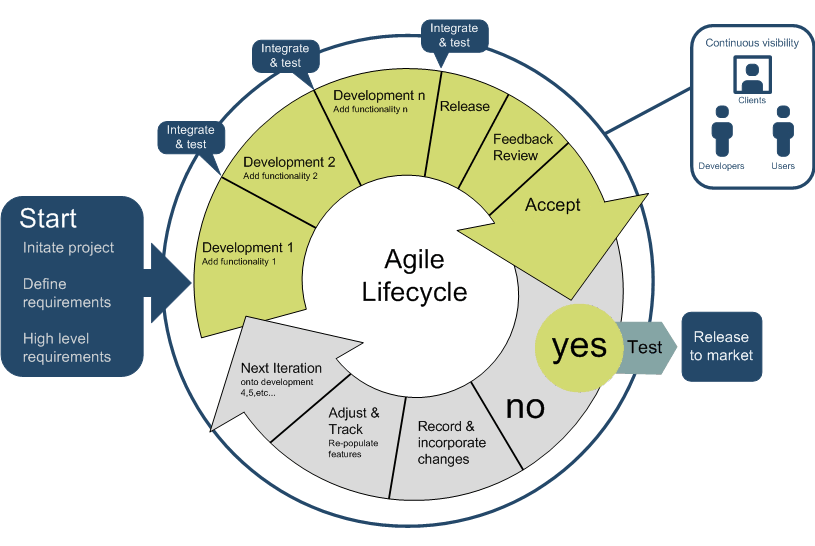
* which branching strategies will be used and how frequently builds occur and automated tests of all kinds are run
1. Management of the SCM Process: Surveillance of SCM
* which branching strategies will be used and how frequently builds occur and automated tests of all kinds are run
- Measures and measurement
- In-process audits
2. Software Configuration Identification: Identifying Items to Be Controlled
- Software Configuration
- Sofware Configuration Item
- Software Configuration Item Relationship
- Software Version
- Baseline
- Acquiring Software Configuration Items
2. Software Configuration Identification: Software library

- Collections
- Software
- Documentation
2. Software Configuration Identification: Software library
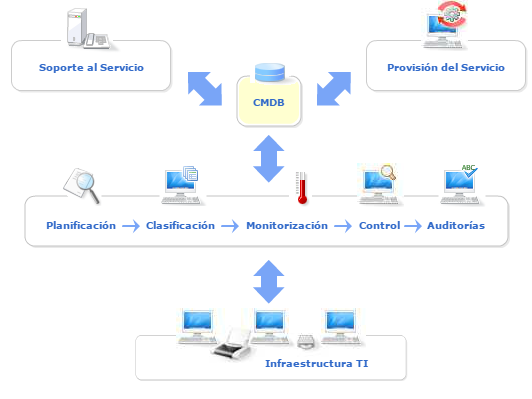
CMDB
2. Software Configuration Identification: Software library
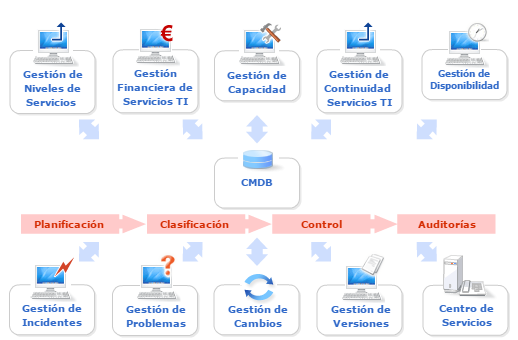
CMDB
3. Software Configuration Control: Requesting, Evaluating, and Approving Software Changes
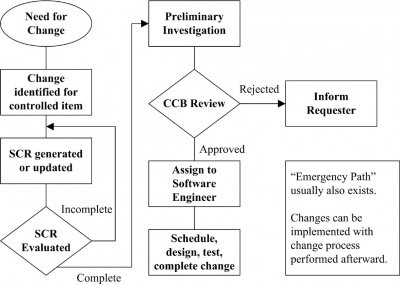
3. Software Configuration Control: Requesting, Evaluating, and Approving Software Changes
- Software Configuration Control Board
- software Change Request Process
3. Software Configuration Control: Implementing Software Changes
Changes may be supported by source code version control tools. These tools allow a team of software engineers, or a single software engineer, to track and document changes to the source code.


3. Software Configuration Control: Deviations and Waivers
The constraints imposed on a software engineering effort or the specifications produced during the development activities might contain provisions that cannot be satisfed at the designated point in the life cycle.
4. Software Configuration Status Accounting: Software Configuration Status Information
- Software configuration status information (Identify. collect, mantain)
- Software configuration staus reporting
- Can be used by stakeholders
- Predesigned reports
- Can serve as a basis of various measurements. (Example: Number of change request per SCI and average time needed to implement a change request)
5. Software Configuration Auditing
Is an indepent examination of a work product or set of work products to assess compliance with specifications, standards, contractual agreements, or other criteria.
Ensure the CMDB information is according to real Software functional and physical configuration
5. Software Configuration Auditing: Software Functional Configuration Audit
5. Software Configuration Auditing: Software Physical Configuration Audit

The purpose of the PCA is to ensure that the design and reference documentation is consistent with the product
5. Software Configuration Auditing: In-Process Audits of a software baseline
Audits can be carried out during the development process to investigate the current status of specific elements of the configuration. In this case, an audit could be applied to sampled baseline items to ensure that performance is consistent with specifications or to ensure that evolving documentation continues to be consistent with the developing baseline item.
6. Software Release Management and Delivery
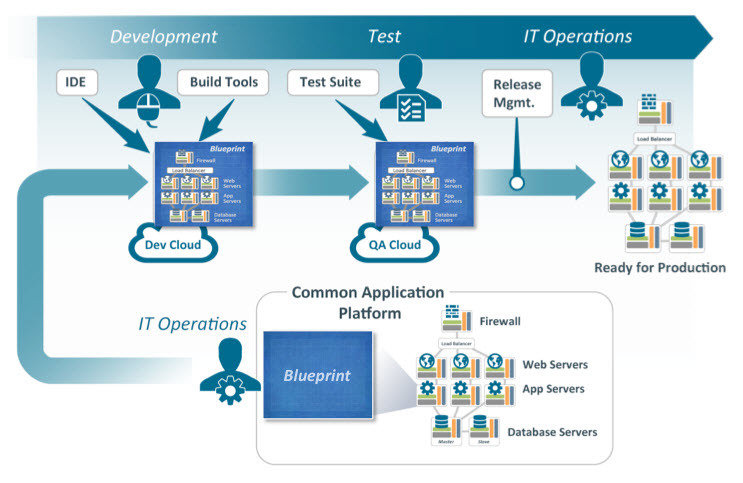
7. Software Configuration Management tools

deck
By Ricardo Bermudez Osorio
deck
- 116



